Cat Body Language
Cat Body Language
Uploaded by
NathanCopyright:
Available Formats
Cat Body Language
Cat Body Language
Uploaded by
NathanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Cat Body Language
Cat Body Language
Uploaded by
NathanCopyright:
Available Formats
UNDERSTANDING FELINE BODY LANGUAGE
The giving and interpreting of sign language is innate in cats. The house cat has an exceptionally vast supply of
many forms of expression.
Domestic cats have advanced far beyond their wild ancestors in the capacity to develop new forms of social
organization and communication. They use their bodies and facial expressions to communicate their intentions to
all around them. By studying the various signals that make up the cat’s language, you will find that you will
better understand the messages your cat is trying to convey. A basic understanding of this language will aid in
deepening the bonds of friendship with your feline companion.
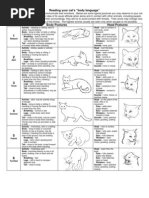
Body Gestures
Happy, Friendly Content Threatened, Defensive
Gestures are body positions and movements that convey a message. The cat’s ability to erect the hairs on certain
parts of her body must also be included.
Body
A stretched body can indicate that the cat is sure of herself or prepared to attack. A contracted body indicates
fear. The arched back conveys the idea that the cat is in readiness for defense. Aggression is expressed with
erect ears, constricted pupils and tail swings in low arcs close to the body. A defensive cat crouches in a cringing
position with her eyes averted and ears flat and thumps the top of her tail on the ground. A happy cat relaxes her
whiskers, perks up her ears and holds her head and tail high in the air.
Head
A head stretched forward is ready for contact. Facial expressions and other gestures indicate whether the
encounter is antagonistic or friendly. A cat feeling dominant raises her head, and inferior feelings cause the head
to lower. If the head is lowered in a jerky manner and the chin is pulled in or the head turned sideways, the cat
is displaying a lack of interest. The cat uses this gesture if she desires not to provoke or be provoked when
encountering another cat. When meeting another cat that is being very persistent, the cat that wants to avoid
contact will raise her head high and pull it far back.
AHS: Understanding Feline Body Language
Rev. January 9, 2007
Legs
Stretching legs to their full length is a sign of self-confidence. Depending on the facial expression, this gesture
could also mean a readiness to attack. A cat bends her hind legs to convey her uncertainty or timidity.
By bending the forelegs, the cat is expressing her desire to avoid conflict, while stating she will defend herself if
necessary. Complete defensiveness is communicated by bending both fore and hind legs. A slightly raised paw
indicates readiness to defend herself.
Playful Angry Back-Off! Submissive
Tail
The tail is one of the best barometers of feline mood. A still, raised tail means a friendly greeting. A sudden whip
of the tail shows a threat of impending attack. The highly excited cat waves her tail from side to side in jerky,
rapid motions. The top of a tail moving means slight dissatisfaction or impatience. A relaxed cat allows the tail to
hang straight down. A tail held straight out behind indicates caution. The top ships back and forth in moments of
great excitement.
Hair
When the cat is afraid, the hair on her body stands erect, fairly evenly all over the body. A cat who is ready to
attack or trying to threaten will raise its hair in a narrow strip all along the spine and the tail. In this mood the
hair will incline slightly toward the middle of both sides, forming a sharp ridge.
Facial Expressions
Happy Angry Frightened Playful Content
Cheek Ruff
The cheek muscles pull the cheek ruff downward and toward the throat during excitement or expectation mixed
with fear. A pulsing rhythm is sometimes present. This is easy to see in cats with prominent cheek ruffs, such as
those with Persian ancestry.
Ears
Ears pointed forward can convey friendly interest and different degrees of attentiveness or suspense. Ears that
are pricked up and turned slightly backward indicate a warning that an attack is contemplated. Ears that are
raised and twisted back combined with hissing mean that a cat is ready to attack. Ears fully erect but furled back
indicate anger.
AHS: Understanding Feline Body Language
Rev. January 9, 2007
A frightened cat lays the ears down flat. Ears that are bent back and drawn down sideways can signal a
defensive attitude, fear or readiness to take flight. A cat playing or hunting will hold the ears open, erect and
slightly forward.
Lips
Movements of the lips are usually combined with some type of sound. The grimace is a response to certain smalls.
The mouth is slightly open, with the nose and upper lip drawn upward expressing displeasure or disgust. The
mouth is open very slightly and the nose is barely wrinkled. Another lip gesture is embarrassment. The mouth
may stay open or closed, with the lips drawn back and not too far upward. The nose is not wrinkled. At the same
time the head will swing slowly from side to side. This gesture expresses friendly rejection to another cat
approaching with friendly intentions, and translated means “please be kind and leave me alone.”
Pupils
Narrowed pupils may indicate aggressive threat, tension or a heightened interest. Surprise, fear and a defensive
attitude are expressed by dilated pupils. Mood shifts can be magnified by changes in light, since the size of the
pupils depends on light. A cat’s eyes can speak volumes about how they are feeling:
• If your cat’s eyes are wide open and looking at you, she is saying, "I'm listening."
• If her eyes are half closed it means, "I'm sleepy."
• If her eye pupils look like slits she is telling you that she is feeling alert and confident.
• A “bug-eyed” looks means, "I'm frightened"...so be careful!
• If she is blinking and winking at you, she is very content.
• If your kitty’s eyes are clouded, she is likely very relaxed but may be ill, so keep an eye on her!
• A kitty whose eyes are staring straight at you is saying, "Stay away." A stare is a challenge.
Whiskers
The position of the whiskers says a great deal. When a cat is excited, tense and ready to act, the whiskers will be
pointed forward and fanned out. On a calm or comfortable cat, the whiskers point outward and are less spread
apart. This position can also mean a friendly disposition or indifference. A cat that is hunting prey will thrust her
whiskers forward. The shy, timid or reserved cat will bunch the whiskers together and flatten them out to the
side of the face. Whiskers flat against the face signify the cat is frightened.
Vocalizations
Cats have a different vocal apparatus from humans. They can vocalize when exhaling as well as inhaling. The
variations in the phonetic quality of sounds are achieved mainly by changing the tension of the throat and oral
muscles and by changes in the speed of air moving over the vocal cords. The position of the tongue is not as
important as it is in human speech. There are three general sound categories in cat vocalization. Murmuring
comprises the soft sounds used for acknowledgment, approval, attention, calling and greeting; purring is included
in this group. The majority of these sounds are formed with the mouth closed.
The vowel sounds are another category of sound. Cats use these particular sounds, which consist of the meows, in
very specific context. Most cats have an impressive vocabulary of these sounds to express needs such as hunger,
gratitude, in or out, “no,” “come here,” “move over,” to name a few. Cats seem to train their humans more
readily to this part of their language than any other. The last group is made up of high-intensity, strained sounds.
These are usually reserved for cat-to-cat communications and consist of the hiss, spit, growl, wail and snarl. Such
sounds generally indicate anger, pain or frustration. When directed at humans these sounds mean, “Leave me
alone, NOW.”
Purring
It is thought that this sound originated as a vocalization of kittens to tell a mother they are content. When they
produce this sound while nursing, it does not interfere with suckling, and sound contact can be maintained with
the mother cat. A mother cat purrs when approaching her kittens in order to reassure them of her presence.
Older kittens purr when they are trying to get an older cat to play with them.
AHS: Understanding Feline Body Language
Rev. January 9, 2007
Adult cats purr when all is well with their world. A dominant cat will purr when approaching another cat with
playful or peaceful intentions. A sick cat will purr in order to try to soothe a potential aggressor. It is not known
how cats purr. One theory maintains that it is the vibration of the false vocal cords. Another theory suggests that
it is the result of turbulence in the bloodstream of the vena cava (the main vein returning to the heart).
Gurgling
A high-pitched gurgle means a friendly greeting. This sound is sometimes combined with gentle meows to become
a chatting sound that will vary in quality in cats. It is a social contact sound. The cat has a tremendous capacity
for variation on this sound. It seems to play an important role in vocal exchanges, but it has not yet been studied
in depth.
Meowing
The vowel sounds a cat makes are the meowing sounds and are used in specific context. These sounds form
distinct words in that the cat closes her mouth after making each sound. These sounds are used in communicating
with humans, and the manner in which a cat pronounces them gives the individual a specific voice. Cats have a
broad range of several types of meows. The best known of the meow sounds is that of an unhappy kitten. A short,
high meow in adults expresses discontent or unhappiness. A hungry cat shows displeasure with loud, almost
screaming meows. A cat seeking attention or wanting to be petted will meow softly.
Caterwauling
This is a song of threat and war, sometimes called wailing. It is the sound that rival tomcats emit as they
approach each other. It is often mistaken by humans to be a love song between a tom and a queen.
Growling
This sound is usually accompanied by a facial expression. Growling indicates offense rather than defense. When
growling, the corners of the mouth are drawn up more than the upper lip. Repeated growling will eventually turn
into snarling.
Hissing
This is a common sound. When hissing, the cat will open her mouth about halfway, drawing back the upper lips
and arching the tongue. The breath is expelled with force. This is why a cat will shy away if you blow in her face.
The expression of hissing without sound will succeed in repulsing a cat.
Screeching
This sound seems to have evolved from a meowing sound and is usually used to mean distress.
Spitting
This is a warning or threatening sound. It is a sudden and violent non-vocal sound, accompanied by a forepaw
hitting the ground. Cats use this sound as a bluff when approached by an attacker.
For more information, please visit
www.azhumane.org
Adapted from material originally developed by applied animal behaviorists at the Dumb Friends League, Denver, Colorado
©1999 Dumb Friends League All rights reserved.
AHS: Understanding Feline Body Language
Rev. January 9, 2007
You might also like
- Nate Schoemers Dog Training Manual Third Edition Animal Planets Dog Trainer Shares His Dog Training Secrets 9781692362256Document138 pagesNate Schoemers Dog Training Manual Third Edition Animal Planets Dog Trainer Shares His Dog Training Secrets 9781692362256EpiCuriousMindNo ratings yet
- Susan Garrett 25 Challenges For Your DogDocument1 pageSusan Garrett 25 Challenges For Your DogDi DiNo ratings yet
- Advertisement in The Philippines: History, Evolution, and The Filipino ConsumerDocument12 pagesAdvertisement in The Philippines: History, Evolution, and The Filipino ConsumerZeus LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Susan Garrett Treat DivingDocument4 pagesSusan Garrett Treat DivinggodwinjaminNo ratings yet
- CatsDocument49 pagesCatsNev Erquit100% (6)
- Cat Nutrition - EbookDocument7 pagesCat Nutrition - Ebookdilekzade100% (1)
- As 1860.2-2006 Particleboard Flooring InstallationDocument7 pagesAs 1860.2-2006 Particleboard Flooring InstallationSAI Global - APAC0% (1)
- Develops Your Dog's "Hidden Intelligence" To Eliminate Bad Behavior and Create The Obedient, Well-Behaved Pet of Your DreamsDocument15 pagesDevelops Your Dog's "Hidden Intelligence" To Eliminate Bad Behavior and Create The Obedient, Well-Behaved Pet of Your DreamsWhizcashkidNo ratings yet
- Cats Behaving Badly Why Cats Do The Naughty Things They DoDocument13 pagesCats Behaving Badly Why Cats Do The Naughty Things They DoMacmillan Publishers25% (8)
- Everything About DogsDocument326 pagesEverything About Dogstobiasaxo5653100% (3)
- IllustratedstandardDocument29 pagesIllustratedstandardapi-255712054100% (1)
- Puppy ManualDocument21 pagesPuppy Manualaly100% (1)
- Dog Training TipsDocument24 pagesDog Training TipsShubhamYadav83% (6)
- The Dog Encyclopedia (VetBooks - Ir)Document362 pagesThe Dog Encyclopedia (VetBooks - Ir)miki122296% (25)
- ABCs of Living With DogsDocument237 pagesABCs of Living With Dogsamy100% (2)
- Curing Dog Separation Anxiety - How To End Bad Dog Habits ForeverDocument88 pagesCuring Dog Separation Anxiety - How To End Bad Dog Habits ForeverJoegi Ruky Ungef0% (1)
- 101 Ways To Improve Your Dogs BehaviorDocument27 pages101 Ways To Improve Your Dogs Behaviorjmason_5100% (1)
- Speaking III Cat's BehaviourDocument17 pagesSpeaking III Cat's BehaviourYanuarika Alyun Timur SaputriNo ratings yet
- Reading Cat Body LanguageDocument2 pagesReading Cat Body LanguageRamil Carcamo100% (2)
- Canine Body LanguageDocument4 pagesCanine Body LanguageAB0% (1)
- Fear in DogsDocument8 pagesFear in DogsNevaeh Valli DeevaNo ratings yet
- UnderstandingCanineBodyLanguage1 PDFDocument5 pagesUnderstandingCanineBodyLanguage1 PDFChristine Mae De Guzman Alamar100% (1)
- Cat LanguageDocument50 pagesCat Languagebba2k2100% (3)
- Guide To Cat Behavior and Body LanguageDocument10 pagesGuide To Cat Behavior and Body LanguageJunna May ARADO100% (1)
- Socializing Very Shy or Fearful Cats: by Terri Gonzales and Sherry WoodardDocument51 pagesSocializing Very Shy or Fearful Cats: by Terri Gonzales and Sherry WoodardJohnM89100% (3)
- Cat Breeds: Dr.D.Anil Pavan Kumar M.V.SC.,PH.DDocument55 pagesCat Breeds: Dr.D.Anil Pavan Kumar M.V.SC.,PH.DNaveen BasudeNo ratings yet
- DitchTheRoutine v02Document16 pagesDitchTheRoutine v02Ella Carlsen-O'Connor100% (1)
- The Cat Care GuideDocument36 pagesThe Cat Care Guidewolf-hearted100% (5)
- 101 Essential Tips Cat CareDocument74 pages101 Essential Tips Cat Carevortex6951575% (4)
- Cat Behaviour GuideDocument20 pagesCat Behaviour Guideredlandadam100% (3)
- Feline Vocalization - Excessive: Why Is My Cat Persistently Crying?Document4 pagesFeline Vocalization - Excessive: Why Is My Cat Persistently Crying?Brook Farm Veterinary CenterNo ratings yet
- Dog Training EquipmentDocument7 pagesDog Training EquipmentNicholay AtanassovNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Behavior MythsDocument3 pagesVeterinary Behavior MythsNerea Pradana TapiaNo ratings yet
- Flat-Coated Retriever Training: The Beginner’s Guide to Training Your Flat-Coated Retriever Puppy: Includes Potty Training, Sit, Stay, Fetch, Drop, Leash Training and Socialization TrainingFrom EverandFlat-Coated Retriever Training: The Beginner’s Guide to Training Your Flat-Coated Retriever Puppy: Includes Potty Training, Sit, Stay, Fetch, Drop, Leash Training and Socialization TrainingNo ratings yet
- Complete Cat Care PDFDocument98 pagesComplete Cat Care PDFMagda Rafael100% (18)
- Grooming StudentsDocument22 pagesGrooming StudentsPG FlorenceNo ratings yet
- Fearful Dogs 101: Give Them Space But Not Too Much!Document2 pagesFearful Dogs 101: Give Them Space But Not Too Much!JamieNo ratings yet
- Howto Cure Separation AnxietyDocument27 pagesHowto Cure Separation AnxietyAli Khader Abbas100% (2)
- How To Take Care of A DogDocument4 pagesHow To Take Care of A DogGerrick BalberanNo ratings yet
- The Rescue DogDocument5 pagesThe Rescue DogJaqi BunnNo ratings yet
- Dog TrainingDocument2 pagesDog Trainingjed8r9dzsc100% (1)
- So, You Want To Become An Animal Behaviorist?: Family Dog Project Dog Cognition LabDocument7 pagesSo, You Want To Become An Animal Behaviorist?: Family Dog Project Dog Cognition Labsandu_danut_1100% (3)
- Top 10 Tips: For Taking Care of Your PetsDocument27 pagesTop 10 Tips: For Taking Care of Your PetsclarenceNo ratings yet
- Animalogy: Cats and Other FelinesDocument11 pagesAnimalogy: Cats and Other FelinesShubham Bobby BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- 12 Amazing Australian Dog Breeds - The Complete Guide To Australian DogsDocument17 pages12 Amazing Australian Dog Breeds - The Complete Guide To Australian DogsAdelaNo ratings yet
- DitchTheBowl v7Document12 pagesDitchTheBowl v7Ella Carlsen-O'Connor100% (1)
- AKC Doberman DescriptionDocument3 pagesAKC Doberman Descriptionsumeet_nigamNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Border ColliesDocument34 pagesPresentation On Border ColliesSofía BerrotaránNo ratings yet
- 16 Cat MannersDocument2 pages16 Cat MannersmysticpaganNo ratings yet
- WellCat Veterinary HandbookDocument36 pagesWellCat Veterinary HandbookKatSiebrecht100% (7)
- DOG TRAINING - The Complete Guide For Beginners To Raise Your Dog and Train A Perfect Pet. Step by Step Behaviour Lessons & Tips.Document43 pagesDOG TRAINING - The Complete Guide For Beginners To Raise Your Dog and Train A Perfect Pet. Step by Step Behaviour Lessons & Tips.TonijetoNo ratings yet
- How To Be The Alpha Dog and Stop Your Dog's Behavior ProblemsDocument27 pagesHow To Be The Alpha Dog and Stop Your Dog's Behavior ProblemsJohnny Tanner50% (2)
- A Layman's Walk Through Basic Canine Genetics and Genetic DiseasesDocument58 pagesA Layman's Walk Through Basic Canine Genetics and Genetic DiseasesmarcloubonNo ratings yet
- Canine Aggression - TerritorialDocument4 pagesCanine Aggression - TerritorialBrook Farm Veterinary CenterNo ratings yet
- Bark No More PlaybookDocument21 pagesBark No More Playbookgloves.car0t100% (2)
- The Complete Dog Book (1921) PDFDocument418 pagesThe Complete Dog Book (1921) PDFAshish Misra0% (1)
- Dog Obedience Training Tips For Dog Club MembersDocument3 pagesDog Obedience Training Tips For Dog Club MembersShoshannah ForbesNo ratings yet
- Healthy Pooch CookbookDocument58 pagesHealthy Pooch Cookbooklokikg100% (1)
- HaircutsDocument39 pagesHaircutsLega DeviNo ratings yet
- Behind The Meow: Why Cats Act The Way They Do, Think Like Cats And Start Training ThemFrom EverandBehind The Meow: Why Cats Act The Way They Do, Think Like Cats And Start Training ThemNo ratings yet
- A.112 B.118 C.121 D.124: Airtel Placement Paper QuestionsDocument8 pagesA.112 B.118 C.121 D.124: Airtel Placement Paper QuestionsAvdhut Gopewad100% (1)
- Cross Walk Sec-93Document12 pagesCross Walk Sec-93a.dea.a.day3No ratings yet
- HSC English Second PaperDocument4 pagesHSC English Second PaperAsad Ullah100% (2)
- IRC Bangladesh Annual Report 2023Document42 pagesIRC Bangladesh Annual Report 2023TasbirNo ratings yet
- Agri Manual Bhavina Revised FINALDocument64 pagesAgri Manual Bhavina Revised FINALKrupal ContractorNo ratings yet
- 9 IELTS SpeakingDocument21 pages9 IELTS SpeakingVictor Alfonso Mateos MeloNo ratings yet
- Copia de Boxer Bm150 SPC PDFDocument73 pagesCopia de Boxer Bm150 SPC PDFRusbel LaitonNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 FSQCDocument28 pagesUnit 4 FSQCvaralakshmi KNo ratings yet
- Team 3 - Means of EgressDocument25 pagesTeam 3 - Means of EgressRhey LuceroNo ratings yet
- Hawaiian Dance Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesHawaiian Dance Lesson Planapi-311981237No ratings yet
- Running Head: Literature Course Reflection 1Document4 pagesRunning Head: Literature Course Reflection 1Paul WahomeNo ratings yet
- 45350news 12062022120344Document2 pages45350news 12062022120344PranjalNo ratings yet
- Last Train To LondonDocument2 pagesLast Train To LondonPepe MirandaNo ratings yet
- Airport SignsDocument26 pagesAirport SignsJay Franco100% (1)
- 12th EM Notes 2019 PDFDocument225 pages12th EM Notes 2019 PDFAman Adatia100% (1)
- Infosys Test IDocument16 pagesInfosys Test Irajesh199155No ratings yet
- Ron Brookmeyer, Donna F. Stroup-Monitoring The Health of Populations - Statistical Principles and Methods For Public Health Surveillance (2003)Document389 pagesRon Brookmeyer, Donna F. Stroup-Monitoring The Health of Populations - Statistical Principles and Methods For Public Health Surveillance (2003)Medical_Doctor100% (1)
- The Lemon in China and ElsewhereDocument18 pagesThe Lemon in China and ElsewhereChen LvNo ratings yet
- ID NoneDocument11 pagesID Noneherlina yuriskaNo ratings yet
- Leon Gto EnglishDocument9 pagesLeon Gto EnglishMaximiliano Muñoz AmezquitaNo ratings yet
- Critique Paper BA211 12 NN HRM - DacumosDocument2 pagesCritique Paper BA211 12 NN HRM - DacumosCherBear A. DacumosNo ratings yet
- AC Milan 2013-14 Home KitDocument1 pageAC Milan 2013-14 Home KitzeroualihaikihNo ratings yet
- Acetaminophen Toxicity: Michira I Getange Umb/15-A/054Document31 pagesAcetaminophen Toxicity: Michira I Getange Umb/15-A/054Ahmed Ben BellaNo ratings yet
- Yle Flyers WorksheetsDocument13 pagesYle Flyers WorksheetsCarmen TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- NASA Postdoctoral Program Opportunities: Earth Science: Climate and Radiation ProcessesDocument2 pagesNASA Postdoctoral Program Opportunities: Earth Science: Climate and Radiation ProcessesAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- Receiving IDOCs From SAP by Using BizTalk ServerDocument13 pagesReceiving IDOCs From SAP by Using BizTalk ServerKishore ReddyNo ratings yet
- CGS AG Schoen+Sandt 5050 - En-1 PDFDocument2 pagesCGS AG Schoen+Sandt 5050 - En-1 PDFOscarBarretoNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire Vol.2 Questionaire Survey On Collection and Waste Segregation ProblemDocument4 pagesQuestionnaire Vol.2 Questionaire Survey On Collection and Waste Segregation ProblemGynolderNo ratings yet