Patient Assignment
Patient Assignment
Uploaded by
Rj MagalingCopyright:
Available Formats
Patient Assignment
Patient Assignment
Uploaded by
Rj MagalingCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Patient Assignment
Patient Assignment
Uploaded by
Rj MagalingCopyright:
Available Formats
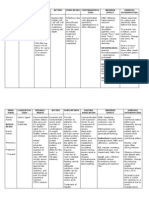
Drug Generic Name: lactulose Brand Name: Duphalac Drug Classification: Ammonia reduction drug Laxative
Dose 30 ml ODHS hold for bowel movement 2x/day
Mechanism of Action The drug passes unchanged into the colon where bacteria break it down to organic acids that increase the osmotic pressure in the colon and slightly acidify the colonic contents, resulting in an icrease in stoll water content, stool softening, laxative action. This alsi results in migration of blood ammonia into the colon contents with sbsequent trapping and expulsion in the feces.
Indications and Contraindications Indication: - Treatment of constipation Contraindication: - Allergy to lactulose, loq-galactose diet
Side Effects and Adverse Effects Side Effects: -Abdominal fullness - Flatulence - Belching Adverse Effects: - Distention - Intestinal cramps - Diarrhea - Nausea
Nursing Responsibilities - Do not freeze laxative form. Extremely dark or cloudy syrup may be unsafe; do not use. - Give laxative syrup orally with fruit juice, water, or milk to increase palatability. - Administer retention enema using a rectal balloon catheter. - DO not administer other laxatives while using lactulose. - Monitor serum ammonia levels. - Monitor with long-term therapy for potential electrolyte and acid-base imbalances. - Carefully monitor blood glucose levels in diabetec patients. - Make sure patient has access to bathroom; bowel movements will be increased to two or three per day.
Drug Generic name: Aspirin Brand name: Aspilet Drug classification: Antiplatelet
Dose 80mg/tab PO OD
Mechanism of action Prevent blood coagulation due to hypertension (narrow blood vessels may cause blood to aggregate.
Indication and contraindication Indication: CVA Contraindication: Hypersensitivity to salicylates
Side effects and adverse effect GI: dyspepsia, heartburn, anorexia, nausea, epigastric discomfort, potentiation of peptic ulcer Allergic: bronchospasm, skinrashes, urticarial. Hematologic: prolongation of bleeding time, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia.
Nursing responsibilities - Monitor renal function. - Determine history of peptic ulcer disease or bleeding tendencies. - Give drug with food and full glass of water.
Drug, Dosage and Route Generic Name Ranitidine Hydrochloride Brand Name Zantac Classification Histamine-2 antagonist Dosage & Route 75 mg bid PO
Mechanism of Action Competitively inhibits the action o histamine at the H2 receptors of the parietal cells of the stomach, inhibiting basal gastric acid secretion and gastric acid secretion that is stimulated by the food, insulin, histamine, cholinergic agonists, gastrin and pentagatrin.
Indications Short term treatment of active duodenal ulcer Maintenance therapy for duodenal ulcer at reduced dosage Short-term treatment and maintenance therapy of active, benign gastric ulcer Short-term treatment of GERD Treatment of erosive esophagitis Treatment of heartburn, acid indigestion, sour stomach
Contraindications Contraindicate d with allergy to ranitidine, lactation Use cautiously with impaired renal or hepatic function pregnancy.
Side Effects CNS: Headache, malaise, dizziness CV: Tachycardia, Bradycardia, PVCs Dermatologic: Rash GI: Contipation, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain Local: Pain at IM site, local burning or itching at IV site.
Nursing Considerations Assessment: History: Allergy to ranitidine, impaired renal function, lactation, pregnancy Interventions: Administer oral drug with meal and at bed time. Decrease doses in renal and liver failure Provide concurrent antacid therapy to relieve pain. Administer IM dose undiluted, deep into large muscle group. You may experience constipation or diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, enlargement of breasts, impotence, libido, headache
Drug, Dosage and Route Generic Name Rosuvastatin calcium Brand Name Crestor Classification Antilipemic HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor Dosage 10 mg/day Route PO
Mechanism of Action Selectively and competitively inhibits HMGCoA reductase, which catalyzes its conversion to the cholesterol precursor mevalonate and thus limits cholesterol synthesis. This action increases high-density lipoprotein level and decreases low-density lipoprotein level.
Indications Hypertriglyceridemia
Contraindications -Breast feeding or pregnancy -Hypersensitivity to drug and its component
Side Effects CNS: headache, dizziness, anxiety, depression, insomnia, hypertonia CV: palpitations, tachycardia, hypertension, angina pectoris EENT: rhinitis, sinusitis, pharyngitis GI: nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain GU: UTI, acute renal failure Metabolic: hypoglycemia Musculoskeletal: Rhabdomyolysis Skin: rash, pruritus
Nursing Considerations Check liver function tests before therapy starts. Give with or without food. Monitor CK, creatinine, and urine protein levels closely. Watch for signs of rhabdomyolysis with acute renal failure. Tell patient he may take with or without food. If hes using antacids, instruct him to take these 2 hours after rosuvastatin. Encourage to limit caffeine intake and avoid ephedra. Advise against heavy intake of alcohol.
Drug, Dosage and Route Generic Name Enoxaparin Brand Name Lovenox Classification Anticoagulant Antithrombotic Dosage 1mg/kg q12h until stabilized with aspirin 100-325mg daily x >2days Route SQ
Mechanism of Action Binds to antithrombin III inactivating factors Xa/IIa resulting in higher ratio of antifactor Xa to IIa
Indications Prevention of ischemic complications in unstable angina/non-Q-wave MI
Contraindications Hypersensitivity to this drug, benzyl alcohol, heparin or pork; active major bleeding hemophilia, leukemia with bleeding, peptic ulcer disease, thrombocytopenic purpura, heparininduced thrombocytopenia
Side Effects Fever, confusion, nausea, hemorrhage, hypochromic anemia, thrombocytopeni a, bleeding -
Nursing Considerations Assess blood studies Administer only after screening patient for bleeding disorders Administer SQ only; do not give IM Do not mix with other drugs or infusion fluids Administer at the same time each day to maintain steady blood levels Teach patient to use softbristle toothbrush to avoid bleeding gums Instruct patient to report any signs of bleeding; gums, under skin, urine stools
You might also like
- Electrical Safety ProcedureDocument25 pagesElectrical Safety ProcedureAsso100% (1)
- Clinical Medication ListDocument181 pagesClinical Medication Listsophia onu100% (2)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Top 75 KPIs For Human Resources DepartmentDocument9 pagesTop 75 KPIs For Human Resources DepartmentAlexxyaNo ratings yet
- FINAL Drug StudyDocument9 pagesFINAL Drug StudyKristen Leigh MarianoNo ratings yet
- Icu Drug StudyDocument7 pagesIcu Drug StudyHazel Palomares100% (1)
- Common MedicationsDocument12 pagesCommon MedicationsJasmeen KaurNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyFranco ObedozaNo ratings yet
- Drugs StudyDocument35 pagesDrugs StudyMark CapillanesNo ratings yet
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNo ratings yet
- Medication: Captopril (Capoten) Is An ACE Inhibitor and A Common Antihypertensive. Captopril Generic Name Contents (Hide)Document43 pagesMedication: Captopril (Capoten) Is An ACE Inhibitor and A Common Antihypertensive. Captopril Generic Name Contents (Hide)Kath Rubio0% (1)
- Case Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDocument12 pagesCase Pres PREECLAMPSIA Drugs NCPDanica May Galvez100% (1)
- Osmotic LaxativesDocument2 pagesOsmotic LaxativesACanNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Dose, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Drug Indications Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument15 pagesDrug Name Dose, Route, Frequency Mechanism of Drug Indications Adverse Effects Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitiesitsmechachaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyHelen ReonalNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument19 pagesDrug StudyLovely EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudySharwen_R_Rome_5572No ratings yet
- Spironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationDocument5 pagesSpironolactone: Generic Name Brand Name ClassificationShermalyn SalahuddinNo ratings yet
- Nrn101 and Nrn102 Drug Card: 500mg BID 10-16yrs 850mg QD 2000mg Max 2550mg Max Daily DoseDocument1 pageNrn101 and Nrn102 Drug Card: 500mg BID 10-16yrs 850mg QD 2000mg Max 2550mg Max Daily DoseJanet SheldonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - LeptospirosisDocument19 pagesDrug Study - LeptospirosisCamille PinedaNo ratings yet
- Availability: Verapamil HydrochlorideDocument21 pagesAvailability: Verapamil Hydrochloridesteffy sojanNo ratings yet
- DADocument8 pagesDAErditha MirandaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyAl-nazer Azer AlNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Liver DiseaseDocument17 pagesDrugs Used in Liver Diseaseblast2111No ratings yet
- DrugsDocument2 pagesDrugsKC IgnacioNo ratings yet
- DRUG StudyDocument2 pagesDRUG StudyKC IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Action Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument8 pagesDrug Name Action Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesMcDo DonatoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Capitol)Document8 pagesDrug Study (Capitol)Joy CalmerinNo ratings yet
- ACE Inhibitors PrintDocument5 pagesACE Inhibitors PrintBernard TangNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyCamilley De Vera100% (1)
- Backup NclexDocument61 pagesBackup NclexSarah PlunkettNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug Studyjanelle123 toribioNo ratings yet
- Medication Brand Name and Generic NameDocument12 pagesMedication Brand Name and Generic Namexaliokoli127No ratings yet
- Drug Study DMDocument8 pagesDrug Study DMJana Ross Serranilla100% (2)
- Labs Drug Study 1Document17 pagesLabs Drug Study 1Drei LanuzoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Agent Central-Acting, Antihypertensive Autonomic Nervous System Agent Alpha-Adrenergic Agonist (Sympathomimetic)Document13 pagesCardiovascular Agent Central-Acting, Antihypertensive Autonomic Nervous System Agent Alpha-Adrenergic Agonist (Sympathomimetic)Maica EspañolaNo ratings yet
- NCP DrugDocument13 pagesNCP DrugMhar CamposanoNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Constipation & DiarrhoeaDocument64 pagesDrugs Used in Constipation & DiarrhoeaYatharth SinghNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument7 pagesDrugsEloisa Abarintos RacalNo ratings yet
- Ranitidine Hydrochloride: Generic Name Therapeutic Actions Indications Side Effects Nursing ActionsDocument5 pagesRanitidine Hydrochloride: Generic Name Therapeutic Actions Indications Side Effects Nursing ActionsAyanne ArcenaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyOdarp PradzNo ratings yet
- ATORVASTATINDocument4 pagesATORVASTATINeshikaNo ratings yet
- Vi. Drug Study: Drug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reactions Nursing ConsiderationsDocument4 pagesVi. Drug Study: Drug Classification Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reactions Nursing ConsiderationsMilton CruzNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyAdelaine LorestoNo ratings yet
- ATORVASTATINDocument2 pagesATORVASTATINAubrey Unique EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of The Gastrointestinal Drugs (Ii) Choleretics, Cholagogues and Other Biliary Secretion ModifiersDocument14 pagesPharmacology of The Gastrointestinal Drugs (Ii) Choleretics, Cholagogues and Other Biliary Secretion ModifiersanaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyDick Morgan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug StudyJoan RabeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (MS)Document9 pagesDrug Study (MS)Kristine GallardoNo ratings yet
- Ify Drug StudiesDocument15 pagesIfy Drug StudiesifyNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Captopril Brand NamesDocument18 pagesGeneric Name Captopril Brand NamesAiko Villacortes100% (1)
- Allopurinol Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDocument9 pagesAllopurinol Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComifyNo ratings yet
- Parenteral NutritionDocument5 pagesParenteral NutritionReanne PaulineNo ratings yet
- Brand Names: Generic NameDocument3 pagesBrand Names: Generic NameEzraManzanoNo ratings yet
- Nephrolithiasis - Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNephrolithiasis - Drug StudyAia JavierNo ratings yet
- DRUG StudyDocument18 pagesDRUG StudyMargaux Moir0% (1)
- Dugs CVADocument10 pagesDugs CVAMarie AntoinetteNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Diseases - E.G. From Ischemia Due To Stroke, Where Citicoline Accelerates The Recovery of Consciousness and Overcoming Motor DeficitDocument5 pagesCerebrovascular Diseases - E.G. From Ischemia Due To Stroke, Where Citicoline Accelerates The Recovery of Consciousness and Overcoming Motor DeficitRae Marie AquinoNo ratings yet
- Adult: PO HTN Initial: 12.5 Mg/day, May Increase To 25-50 MG Once Daily, Either Alone or WDocument3 pagesAdult: PO HTN Initial: 12.5 Mg/day, May Increase To 25-50 MG Once Daily, Either Alone or WrLythaaaNo ratings yet
- Top 100 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2023 Edition)From EverandTop 100 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2023 Edition)No ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Jahhhhh! Curriculum VitaeDocument10 pagesJahhhhh! Curriculum VitaeRj MagalingNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MannitolDocument2 pagesDrug Study Mannitoljasielle80% (5)
- Diagnosis & DetectionDocument1 pageDiagnosis & DetectionRj MagalingNo ratings yet
- Room #/ Name Diagnosis Treatment/ Diagnostic Procedure Diet IVF Vital Signs 8 Am 12Nn I & ODocument2 pagesRoom #/ Name Diagnosis Treatment/ Diagnostic Procedure Diet IVF Vital Signs 8 Am 12Nn I & ORj MagalingNo ratings yet
- Course in The WardDocument1 pageCourse in The WardRj MagalingNo ratings yet
- Crystal River PEMEDocument10 pagesCrystal River PEMESea BlackNo ratings yet
- NIAGARA Cranial Flap (v2) 5Document1 pageNIAGARA Cranial Flap (v2) 5marceloNo ratings yet
- The Cambridge Companion To Modernist Women Writers CambridgeDocument17 pagesThe Cambridge Companion To Modernist Women Writers CambridgeMaria EsterNo ratings yet
- Perdosri MukernasDocument26 pagesPerdosri MukernasMad MadNo ratings yet
- Dopamine DetoxDocument4 pagesDopamine DetoxGinoNo ratings yet
- PubMed7 PDFDocument15 pagesPubMed7 PDFKoas PatoNo ratings yet
- Ethical Paper Senior SemDocument6 pagesEthical Paper Senior Semapi-643481686No ratings yet
- Rainsure Company, Instrument and Assays Introduction CLVDocument61 pagesRainsure Company, Instrument and Assays Introduction CLVMohammed H. KeshtaNo ratings yet
- Sri Lanka NMRA GazetteDocument9 pagesSri Lanka NMRA GazetteSanjeev JayaratnaNo ratings yet
- Course DivisionDocument3 pagesCourse DivisionJithinNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pharmacokinetics Pharmacy Handbook CCPH 2nd Edition Rev 2.0 - 0 PDFDocument280 pagesClinical Pharmacokinetics Pharmacy Handbook CCPH 2nd Edition Rev 2.0 - 0 PDFNur Shahira Binti HananNo ratings yet
- Noise Pollution (Regulation and Control) Rules, 2000Document7 pagesNoise Pollution (Regulation and Control) Rules, 2000Latest Laws Team100% (1)
- Motivation Letter For Scholarship PHD and MastersDocument4 pagesMotivation Letter For Scholarship PHD and MastersGooftilaaAniJiraachuunkooYesusiinNo ratings yet
- RejectedDocument2 pagesRejectedAileen Mae CariagaNo ratings yet
- Impact of Government Expenditure On Human Capital Development (1990-2022)Document55 pagesImpact of Government Expenditure On Human Capital Development (1990-2022)malijessica907No ratings yet
- Coliform Analysis in Wastewater 2012Document24 pagesColiform Analysis in Wastewater 2012engrbvgNo ratings yet
- The Daniel FastDocument3 pagesThe Daniel FastPfanelo Crayola MakungoNo ratings yet
- Nursing SchoolDocument2 pagesNursing SchoolTangerine DianeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 24 LegionellaDocument17 pagesLecture 24 LegionellaKhalifa Sifaw GhengheshNo ratings yet
- Surgitron CatalogueDocument25 pagesSurgitron CatalogueVISHNU RAVINDRANATHNo ratings yet
- Final: Patient Name: Dummy 0002UG999999Document1 pageFinal: Patient Name: Dummy 0002UG999999mirtunjay kumarNo ratings yet
- Palisades AmenitiesDocument1 pagePalisades AmenitiesCarringtonNo ratings yet
- 17 Plasma Cell Neoplasms - Libre Pathology PDFDocument5 pages17 Plasma Cell Neoplasms - Libre Pathology PDFfadoNo ratings yet
- Cleaning The Delivery Room - EquipmentsDocument7 pagesCleaning The Delivery Room - EquipmentsAnne BasilesNo ratings yet
- Storage and Display of Swimming Pool Chemicals: PermitsDocument3 pagesStorage and Display of Swimming Pool Chemicals: PermitsMina MagdyNo ratings yet
- Sealing Ability of Zinc Oxide Eugenol and Non-Eugenol-Based Temporary FillingDocument6 pagesSealing Ability of Zinc Oxide Eugenol and Non-Eugenol-Based Temporary FillingTahir TahirNo ratings yet
- Designated Hotel List v3 - enDocument4 pagesDesignated Hotel List v3 - enMohammedNo ratings yet
- Res. LdrrmoDocument5 pagesRes. LdrrmoJimmy C. AndangNo ratings yet