G703 Interface Adapter IB40 201 7
G703 Interface Adapter IB40 201 7
Uploaded by
renjithas20050 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
89 views9 pagesG703 Interface Adapter IB40 201 7
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentG703 Interface Adapter IB40 201 7
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
89 views9 pagesG703 Interface Adapter IB40 201 7
G703 Interface Adapter IB40 201 7
Uploaded by
renjithas2005G703 Interface Adapter IB40 201 7
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 9
G.
703 Interface Adapter
Instruction Leaflet
40-201.7
All possible contingencies which may arise during installation, operation or maintenance, and all details and
variations of this equipment do not purport to be covered by these instructions. If further information is desired
by purchaser regarding this particular installation, operation or maintenance of this equipment, the local ABB
Power T&D Company Inc. representative should be contacted.
ABB Power T&D Company Inc.
Relay Division
Coral Springs, FL 33065
NEW INFORMATION
Effective: March 1994
1. INTRODUCTION
The G.703 Interface Adapter interfaces CCITT G.703
compliant Data Communication System to 64 kbs
Fiber Optic or RS 422 port operating at 64 k baud.
2. FEATURES
The G.703 interface complies with CCITT G.703 co-
directional, 64 kbps specifications. There is a five ter-
minal, screw terminal block with two terminals for the
transmit line, two for the receive line and one for earth
ground.
The fiber optic and RS 422 ports operate at 64 kbps.
Data rate clock signals are not needed or provided by
the adapter.
NOTE: Only the transmit and receive data signals
are available. Therefore a self clocking
code like NRZI must be used.
The fiber optic port has a separate transmitter and
detector connectors (separate transmit and receive
fibers are required). Wavelength is 850 nm and ST
type connectors are used. The transmitter is HFBR-
14XX series and the receiver is HFBR-24XX series.
The RS 422 interface has transmit and receive differ-
ential pairs that comply with RS 422 electrical specifi-
cations. The connector and pins (chassis and signal
grounds, transmit and receive pairs) comply
with RS 530 specifications.
3. SPECIFICATIONS
3.1. Power Requirements
Input Voltage: 48 Vdc nominal (42 to 60 V range)
or
125 Vdc nominal (100 to 200 V range)
Power Consumption: 5W
3.2. Temperature Range
Operating: 0C to 65C
Storage: -20C to 80C
3.3. Physical Data
Height: 5.30 (134.6 mm)
Width: 3.43 (87.1 mm)
Depth: 4.25 (108 mm)
Weight: 2.0 lbs (0.9 kg)
3.4. Communication Ports
3.4.1. G.703 Port
CCITT G.703 co-directional 64 kbs compliant, trans-
former coupled.
3.4.2. Fiber Optic, 64 kbs Port
Transmit and receive lines 850 nm, ST connector,
multi-mode cable, 10 dB optical power budget.
3.4.3. RS 422, 64 kbs Port
Transmit and receive lines are RS 422 (electrical)
and RS 530 (mechanical, connector and pin num-
bers) compliant.
G.703
Adapter
X R
R X
CCITT
G.703
64 kbs
256 k baud
RS 422
or
Fiber
Optic
64 kbs
64 k baud
Figure 1. G.703 Block Diagram
I.L. 40-201.7
2
The female (receptacle) DB25 connector is used in
adherence to Data Communication Equipment
(DCE) definition.
4. INDICATORS
The four LEDs indicate:
Transmitted signal activity (transitions)
Received signal activity (transitions)
Presence of G.703 received signal carrier and
sync.
power
5. INSTALLATION
5.1. Power
Connect 48 Vdc or 125 Vdc nominal to DC Power
Input terminals.
5.2. G.703 Port
Connect transmit and receive ports to G.703 TX
OUT and G.703 RX IN terminals respectively. Use
of shielded twisted pairs is strongly recommended.
Connect earth ground to terminal Chassis GND.
5.3. 64 kbs Port
5.3.1. RS 422 / RS 530 Option
The G.703 Interface Adapter is equipped with DB25
female (Receptacle) connector. Therefore the inter-
connecting cable must use DB25 male connector.
Connect transmit pair (data from Interface Adapter)
to pins 3 and 16. (Pin 3 positive and pin 14 negative).
Connect receive pair to pins 2 (positive) and 14 (neg-
ative).
Connect pin 7 (signal common) to corresponding sig-
nal common pin at the other end of the cable.
5.3.2. Fiber Optic Option
Connect transmit data cable to XMT fiber optic
transmitter.
Connect receive data cable to RCV fiber optic
receiver.
NOTE: ST connectors and multi-mode fiber optic
cables are required.
6. DETAILED DESCRIPTION
6.1. G.703 Fundamentals
The following describes 64 kbit/s G.703 co-direc-
tional interface in which the information and its asso-
ciated timing signal are transmitted in the same
direction.
Code conversion rules
Step 1 A 64-kbit/s bit period is divided into four
unit intervals.
Step 2 A binary one is coded as a block of the
following four bits:
1 1 0 0
Step 3 A binary zero is coded as a block of the
following four bits:
1 0 1 0
Step 4 The binary signal is converted into a
three-level signal by alternating the
polarity of consecutive blocks.
Step 5 The alternation in polarity of the blocks is
violated every 8th block. The violation
block marks the last bit in an Octet.
These conversion rules are illustrated in Figure 2.
6.2. Circuit Description
Both G.703 line pairs (refer to Internal Schematic
Dwg. 1617C21) are coupled to U1 via transformers
T1 and T2.
U1 converts the received analog signal at secondary
of T1, to digital form and monitors received signal
level. U1 also has level interface devices and output
transistors that drive the transmit line pair via the pri-
mary of T2.
Co-directional Digital Data Processor U2 decodes
the received G.703, 256 k baud signal and extracts
the 64 kbps received data. It also converts 64 kbps
data into a 256 k baud G.03 transit signal and moni-
tors the received signal for correct sync.
U2 does not output and input 64 kbps data directly. It
communicates in bursts of 8 bits at a time, at a 2.048
MHz clock rate, 8,000 times per second. This is
because this particular IC is designed for equipment
that processes T-1, CEPT or ISDN signals.
I.L. 40-201.7
3
EPLD U3 contains shift registers, counters, clock
dividers and other logic that interfaces binary, syn-
chronous, 64 kbps data to the bursts of data used by
U2. The EPLD also detects transmit and receive data
transitions and will pulse the data activity LEDs.
The EPLD divides clock from crystal oscillator U5, or
2.048 MHz and 256 kHz for U2. It also switches from
fiber optic port to the RS 530 port as determined by
position of Jumper J1. The EPLD monitors carrier
detector and sync signals from U1 and U2 and if
these are all good, it will light the received signal OK
LED.
When the fiber port is enabled, then transmitter LE1
and receiver LE2 are active. Q1 is an emitter follower
which when conducting (EPLD drives its base low),
will turn off the LED transmitter by absorbing all the
R5 current. when Q1 is turned off by the EPLD driv-
ing its base high, then all current goes to LED trans-
mitter LE1.
When the RS 422 port is enabled, than the signal
path between U4 and the EPLD is active. U4 con-
verts standard CMOS / TTL logic level to the differen-
tial RS 422 levels used for the data transmit and
receive paths.
The only internal voltage is +5 Vdc (Power Supply
Module schematic #1617C22). This is supplied by an
internal Vicor power supply PS1. A different Vicor
supply and input filter capacitor is required for 48 V,
or 125 Vdc input voltage. DC input is applied to P5.1
and P5.22. this is fused by F1 and F2 before being
applied to bridge rectifier BR1 and then to the Vicor
dc input. BR1 always directs the right polarity to the
power supply regardless of supply voltage polarity.
7. ORDERING INFORMATION
7.1. Catalog Number
Typical Catalog Number
G.703 1 R
Input Voltage
1 - 48 Vdc
2 - 125 Vdc
Interface Type
R - RS 422/RS 530
H - Fiber Optic
850 nm
ST Connector
7
1
Bit number
64 kbit/s data
Steps 1 - 3
Step 4
Step 5
Octet Timing
8
0
1
0
2
1
3
0
4
0
5
1
6
1
7
1
8
0
1
1
Violation Violation
Figure 2. Code Conversions
I
.
L
.
4
0
-
2
0
1
.
7
4
Figure 3. Internal Schematic (Main Module)
1617C21
Sub 1
I.L. 40-201.7
5
Figure 4. Internal Schematic (Power Supply)
1617C22
Sub 1
I.L. 40-201.7
6
Figure 5. Assembly Drawing (Main Module)
1617C20
Sub 1
I.L. 40-201.7
7
Figure 6. Assembly Drawing (Power Supply)
1617C23
Sub 1
I
.
L
.
4
0
-
2
0
1
.
7
8
Figure 7. Outline Drawing
1617C34
Sub 1
I
.
L
.
4
0
-
2
0
1
.
7
9
Figure 8. General Assembly
1617C33
Sub 1
You might also like
- Fundamentals of Power System Protection and CoordinationDocument54 pagesFundamentals of Power System Protection and Coordinationrenjithas2005100% (1)
- YS-C20L ManualDocument3 pagesYS-C20L ManualminhaaaNo ratings yet
- RTU560 InterfaceDocument15 pagesRTU560 Interfacehare ramNo ratings yet
- Dvor 900 PDFDocument17 pagesDvor 900 PDFAgnelo Mapande100% (1)
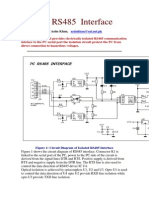
- Interface Rs485Document13 pagesInterface Rs485jol1386100% (1)
- 10Gbps 20km LC BIDI SFP+ TransceiverDocument11 pages10Gbps 20km LC BIDI SFP+ TransceiverrauolNo ratings yet
- 51d27f2ae34e24d8140004b9 PDFDocument22 pages51d27f2ae34e24d8140004b9 PDFkripterNo ratings yet
- JZ862 User ManualDocument6 pagesJZ862 User ManualEhab IsmailNo ratings yet
- Abb Ag: Remote Terminal Unit Onnections and Settings DIN Rail RTU 560CIG10Document16 pagesAbb Ag: Remote Terminal Unit Onnections and Settings DIN Rail RTU 560CIG10Cosmic Garash 2No ratings yet
- PCF8582C-2: 1. DescriptionDocument21 pagesPCF8582C-2: 1. DescriptionroozbehxoxNo ratings yet
- Door Bell System Using Arduino and RF ModuleDocument6 pagesDoor Bell System Using Arduino and RF ModuleDeepak PorwalNo ratings yet
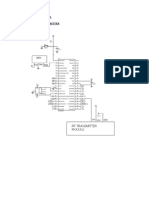
- Pce Mini Project Report: "RF Transmitter and Receiver"Document9 pagesPce Mini Project Report: "RF Transmitter and Receiver"sumit sanchetiNo ratings yet
- Circuit Diagram Wireless TransmitterDocument17 pagesCircuit Diagram Wireless Transmitterumaiya1990100% (2)
- YS-C20K ManualDocument3 pagesYS-C20K ManualQasimNo ratings yet
- Wireless Robot Control Through RFDocument9 pagesWireless Robot Control Through RFarun1cmNo ratings yet
- Ys 1100uDocument3 pagesYs 1100ukurocans100% (2)
- 1.25Gbps SFP Optical Transceiver, 10km Reach: FeaturesDocument9 pages1.25Gbps SFP Optical Transceiver, 10km Reach: FeaturesJorge Luizaga GabrielNo ratings yet
- Mini Project EEE PDFDocument7 pagesMini Project EEE PDFAmit Kr SinghNo ratings yet
- RF Id Attendence MemoryDocument128 pagesRF Id Attendence Memoryakhilesh thapliyalNo ratings yet
- Framed/Non-Framed Ethernet To E1 Protocol Converter Model No. BXT-E10Document16 pagesFramed/Non-Framed Ethernet To E1 Protocol Converter Model No. BXT-E10Amanuel Tadele100% (1)
- WarField Land Rover That Alerts On Sensing Panted Land MinesDocument32 pagesWarField Land Rover That Alerts On Sensing Panted Land MinesPavan KPNo ratings yet
- Digital Transmission Receiver Fiber Optic Trainer: MODEL-FOT102Document5 pagesDigital Transmission Receiver Fiber Optic Trainer: MODEL-FOT102CauVong JustinNo ratings yet
- 2nd Review DocumentDocument6 pages2nd Review DocumentBrightworld ProjectsNo ratings yet
- XGXP 1396 10dDocument7 pagesXGXP 1396 10dPeter AdelNo ratings yet
- Operating Manual: Power / Phase Angle / Power Factor TransducerDocument44 pagesOperating Manual: Power / Phase Angle / Power Factor TransducerpadmawarNo ratings yet
- RS-232, 422 or 485 Signals Up To 2.5 Miles With Fiber Optic ModemDocument6 pagesRS-232, 422 or 485 Signals Up To 2.5 Miles With Fiber Optic ModemVictor QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Presentation PDFDocument17 pagesPresentation PDFvinodNo ratings yet
- Print OutDocument13 pagesPrint Outnazece08No ratings yet
- Power Electronics - Kits PDFDocument31 pagesPower Electronics - Kits PDFGaganVishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Cip 8Document4 pagesCip 8hthusithNo ratings yet
- File 1406270302Document25 pagesFile 1406270302rupeshNo ratings yet
- Data Conditioning & Carrier Modulation Transmitter & Data Reconditioning & Carrier Demodulation ReceiverDocument49 pagesData Conditioning & Carrier Modulation Transmitter & Data Reconditioning & Carrier Demodulation ReceiverCauVong JustinNo ratings yet
- RF-Based Multiple Device Control Using MicrocontrollerDocument7 pagesRF-Based Multiple Device Control Using Microcontrollermv mvNo ratings yet
- Advanced Communication Design For Mobile Disabling at Restricted Areas Microcontroller:-FeaturesDocument8 pagesAdvanced Communication Design For Mobile Disabling at Restricted Areas Microcontroller:-FeaturesIndhumathi MohanNo ratings yet
- 2-Com115 FSK PDFDocument9 pages2-Com115 FSK PDFChauthanh94No ratings yet
- Gateway e 2m G SHDSL 2 3 4 6 Mbps nx64 ModemDocument2 pagesGateway e 2m G SHDSL 2 3 4 6 Mbps nx64 ModemfatimarconnectNo ratings yet
- Packet Drop Caused by The Ethernet Port Working Mode MismatchDocument5 pagesPacket Drop Caused by The Ethernet Port Working Mode Mismatchouamakone7No ratings yet
- PN532C1Document25 pagesPN532C1Subashini de SilvaNo ratings yet
- H25X Optical Absolute EncoderDocument2 pagesH25X Optical Absolute EncoderDanielAliNo ratings yet
- RF ModuleDocument20 pagesRF ModuleDipankar ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Description of Components 3.1 MPU 6050Document13 pagesDescription of Components 3.1 MPU 6050nishtha bansalNo ratings yet
- 520AOD01 CS enDocument13 pages520AOD01 CS enBhageerathi SahuNo ratings yet
- Wireless Equipment Timeout ControlDocument5 pagesWireless Equipment Timeout ControlAnand BhaskarNo ratings yet
- DownloadDocument14 pagesDownloadAbomsa TsebayNo ratings yet
- RF Based Station Name DisplayDocument58 pagesRF Based Station Name Displayarunkn4480100% (2)
- NecDocument6 pagesNecOscar Javier GomezNo ratings yet
- STC 60020Document9 pagesSTC 60020darrylcarvalhoNo ratings yet
- RS-232 To RS-485: User ManualDocument6 pagesRS-232 To RS-485: User ManualEdward MainaNo ratings yet
- 2PD315 English V01Document10 pages2PD315 English V01Narendra BholeNo ratings yet
- By Batch 09 CH - Nitish J.srinivas Narendra Chary Chandra ShekarDocument39 pagesBy Batch 09 CH - Nitish J.srinivas Narendra Chary Chandra ShekarS Sri ReddyNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Speed Control System Using RF CommunicationDocument20 pagesVehicle Speed Control System Using RF CommunicationRaina John100% (2)
- Simple Radio Frequency (RF) Based Code LockDocument5 pagesSimple Radio Frequency (RF) Based Code LockkaleemullaNo ratings yet
- War Field Spying Robot With Night Vision Wireless Camera: Submitted byDocument26 pagesWar Field Spying Robot With Night Vision Wireless Camera: Submitted byankita dhengaleNo ratings yet
- MD44Document8 pagesMD44Zachary ScottNo ratings yet
- RF Transmiter and ReceiverDocument2 pagesRF Transmiter and ReceiverarmarceloNo ratings yet
- SU66AA FTLF1323P1xTR SpecRevADocument11 pagesSU66AA FTLF1323P1xTR SpecRevAKCVNo ratings yet
- "Power Line Communication": 1.dhiraj S. Bhojane 2.saurabh R. Chaudhari 3. Prakash D. More 4.eshant G. RajgureDocument7 pages"Power Line Communication": 1.dhiraj S. Bhojane 2.saurabh R. Chaudhari 3. Prakash D. More 4.eshant G. RajgureChanna SenavirathnaNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Analog Dialogue, Volume 48, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #13From EverandAnalog Dialogue, Volume 48, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #13Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Control Systems EngineerDocument1 pageControl Systems Engineerrenjithas2005No ratings yet
- Commercial Electricians NeededDocument1 pageCommercial Electricians Neededrenjithas2005No ratings yet
- Education:: Date Posted Location Country Degree Required Job Type Min Experience Position Id Job DescriptionDocument2 pagesEducation:: Date Posted Location Country Degree Required Job Type Min Experience Position Id Job Descriptionrenjithas2005No ratings yet
- Central Maintenance SupervisorDocument2 pagesCentral Maintenance Supervisorrenjithas2005No ratings yet
- Saskatchewan: Toddler/Preschool Social ResumeDocument3 pagesSaskatchewan: Toddler/Preschool Social Resumerenjithas2005No ratings yet
- Apprentice Electrician - Required Immediately!: Job Order #: 5159923Document1 pageApprentice Electrician - Required Immediately!: Job Order #: 5159923renjithas2005No ratings yet
- FAT For 132 KV Accesories MTSBDocument7 pagesFAT For 132 KV Accesories MTSBrenjithas2005No ratings yet
- Factory Test Procedure For AccessoriesDocument7 pagesFactory Test Procedure For Accessoriesrenjithas2005No ratings yet
- 3039 Type Test 66 KV 500sqmm Rev1 20060913Document8 pages3039 Type Test 66 KV 500sqmm Rev1 20060913renjithas2005No ratings yet
- CONSORTIUM - GTC/5/2004: Sie-Gtc5/Dts/ Document Transmittal SheetDocument1 pageCONSORTIUM - GTC/5/2004: Sie-Gtc5/Dts/ Document Transmittal Sheetrenjithas2005No ratings yet
- Short CT Calc Cu Tube 500 and 1000sqmmDocument2 pagesShort CT Calc Cu Tube 500 and 1000sqmmrenjithas2005No ratings yet
- CII3D4 SisTerPar 04 Interprocess Communication v2Document26 pagesCII3D4 SisTerPar 04 Interprocess Communication v2MUHAMMAD ABU RIJAL KUSNAEDINo ratings yet
- 1.5 Vsphere-Esxi-Vcenter-Server-701-Security-GuideDocument366 pages1.5 Vsphere-Esxi-Vcenter-Server-701-Security-GuideranjithramachNo ratings yet
- EI2401-Industrial Data NetworksDocument11 pagesEI2401-Industrial Data NetworksarumugamNo ratings yet
- Modbus in ML200Document30 pagesModbus in ML200cunconfunnyNo ratings yet
- Texas Ranger TR-936 Owners ManualDocument8 pagesTexas Ranger TR-936 Owners ManualbellscbNo ratings yet
- Signaling in The Core Network - Mobile Softswitch Solution: DescriptionDocument3 pagesSignaling in The Core Network - Mobile Softswitch Solution: DescriptionKhắc Tiệp BùiNo ratings yet
- Recitation 457Document38 pagesRecitation 457cv31415No ratings yet
- PLDT Written ReportDocument9 pagesPLDT Written ReportAnthony AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Active Filters Resource Persons: Amna Arif Ayesha Ali Class: FA18 BEE A, B, CDocument72 pagesActive Filters Resource Persons: Amna Arif Ayesha Ali Class: FA18 BEE A, B, Csuleman ikhtiarNo ratings yet
- Mobile Number Portability: K - Tirumaleswara ReddyDocument16 pagesMobile Number Portability: K - Tirumaleswara ReddySai Kiran KurichetiNo ratings yet
- Overview of TETRA FunctionalityDocument15 pagesOverview of TETRA FunctionalityhrfmoxNo ratings yet
- Alcatel-Lucent 1650 SMC: Synchronous Multiplexer Compact - Release 4.7Document4 pagesAlcatel-Lucent 1650 SMC: Synchronous Multiplexer Compact - Release 4.7Robison Meirelles junior100% (1)
- 3GPP TS 23.018 V14.0.0 - Basic Call HandlingDocument300 pages3GPP TS 23.018 V14.0.0 - Basic Call Handlingoscar609No ratings yet
- Router Research PaperDocument6 pagesRouter Research Paperh00sprt3100% (1)
- Juniper Secure Connect Administrator GuideDocument113 pagesJuniper Secure Connect Administrator GuidePhuong TranNo ratings yet
- Distance To FaultDocument20 pagesDistance To FaultRv SalazarNo ratings yet
- BLU VIVO X6-6.1" HD+ Display, 64GB+3GB RAM - Gradient BlueDocument1 pageBLU VIVO X6-6.1" HD+ Display, 64GB+3GB RAM - Gradient Blueed drayceNo ratings yet
- DT 300Document41 pagesDT 300Marlon LòpezNo ratings yet
- Pexip Infinity Version 29 Specifications and RequirementsDocument8 pagesPexip Infinity Version 29 Specifications and RequirementsInc hrgNo ratings yet
- Mitec Redundant C Band 213265-001MA - Rev - 0 - (WRK-340420RX-485-ES-00) 1 - 1 Down Redundant System)Document51 pagesMitec Redundant C Band 213265-001MA - Rev - 0 - (WRK-340420RX-485-ES-00) 1 - 1 Down Redundant System)Danny NjomanNo ratings yet
- I 2 CDocument32 pagesI 2 Ckamarajme2006No ratings yet
- Installation Manual: JY997D26401ADocument2 pagesInstallation Manual: JY997D26401AcarlcoxNo ratings yet
- Dynamic TDD Transmissions in Homogeneous Small Cell NetworksDocument6 pagesDynamic TDD Transmissions in Homogeneous Small Cell NetworksCharles JenNo ratings yet
- 2 SQLatk EcampusDocument2 pages2 SQLatk EcampusAllister Darren NavarovNo ratings yet
- Getting Started With Vmware HCX PDFDocument45 pagesGetting Started With Vmware HCX PDFgautamatulNo ratings yet
- Active Directory DocumentationDocument3 pagesActive Directory Documentationit.rjcastronuevoNo ratings yet
- File Name: EAAS034113EN - Docx Rev. 13 Data: 15/11/2018 ID Document: EAAS0341 Product: Serial Port Communication, Modbus/RTU Protocol and SMSDocument57 pagesFile Name: EAAS034113EN - Docx Rev. 13 Data: 15/11/2018 ID Document: EAAS0341 Product: Serial Port Communication, Modbus/RTU Protocol and SMSWaqas EjazNo ratings yet
- Aeroflex IFR Marconi 2948B DatasheetDocument13 pagesAeroflex IFR Marconi 2948B DatasheetRostand NoukimiNo ratings yet
- Buried Cable Intrusion Detection System: Key FeaturesDocument4 pagesBuried Cable Intrusion Detection System: Key FeaturesMohammed ElsayedNo ratings yet