0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
68 viewsN420 N421 TG2-03A TG2-03B Practical1 Practical2: Osteology
N420 N421 TG2-03A TG2-03B Practical1 Practical2: Osteology
Uploaded by
Naina Karamina SakinaThe document provides a detailed description of bone structures in the shoulder and arm regions, including the scapula, humerus, ulna, and radius. It describes key features such as the scapular notch, acromion process, greater and lesser tubercles, and epicondyles. The summary also outlines several important muscles that act on the shoulder and arm, including the deltoid, rotator cuff muscles (supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, subscapularis), biceps brachii, brachialis, and coracobrachialis. It notes their origins, insertions, actions, and innervation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
N420 N421 TG2-03A TG2-03B Practical1 Practical2: Osteology
N420 N421 TG2-03A TG2-03B Practical1 Practical2: Osteology
Uploaded by
Naina Karamina Sakina0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
68 views7 pagesThe document provides a detailed description of bone structures in the shoulder and arm regions, including the scapula, humerus, ulna, and radius. It describes key features such as the scapular notch, acromion process, greater and lesser tubercles, and epicondyles. The summary also outlines several important muscles that act on the shoulder and arm, including the deltoid, rotator cuff muscles (supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, subscapularis), biceps brachii, brachialis, and coracobrachialis. It notes their origins, insertions, actions, and innervation.
Original Description:
ul
Original Title
Upper Limb 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
The document provides a detailed description of bone structures in the shoulder and arm regions, including the scapula, humerus, ulna, and radius. It describes key features such as the scapular notch, acromion process, greater and lesser tubercles, and epicondyles. The summary also outlines several important muscles that act on the shoulder and arm, including the deltoid, rotator cuff muscles (supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, subscapularis), biceps brachii, brachialis, and coracobrachialis. It notes their origins, insertions, actions, and innervation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
68 views7 pagesN420 N421 TG2-03A TG2-03B Practical1 Practical2: Osteology
N420 N421 TG2-03A TG2-03B Practical1 Practical2: Osteology
Uploaded by
Naina Karamina SakinaThe document provides a detailed description of bone structures in the shoulder and arm regions, including the scapula, humerus, ulna, and radius. It describes key features such as the scapular notch, acromion process, greater and lesser tubercles, and epicondyles. The summary also outlines several important muscles that act on the shoulder and arm, including the deltoid, rotator cuff muscles (supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, subscapularis), biceps brachii, brachialis, and coracobrachialis. It notes their origins, insertions, actions, and innervation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 7
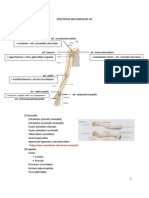
Osteology
Bone Structure Description Notes
scapula
(N420, N421,
TG2-03A,
TG2-03B,
Practical1,
Practical2)
the bone of the shoulder the scapula floats in a sea of muscles, so it is difficult to fracture; it articulates with the axial skeleton through only one bone - the clavicle at the
coracoclavicular and acromioclavicular joints
scapular notch a notch on the superior border
of the scapula located medial to
the attachment of the coracoid
process
it is bridged by the superior transverse scapular ligament; the suprascapular a. passes superior to the superior transverse scapular ligament and the
suprascapular n. passes inferior to it (Army goes over the bridge, Navy goes under the bridge)
acromion(Practical) a broad, flat process located at
the lateral end of the scapular
spine
it articulates with the clavicle through a synovial joint (acromioclavicular joint) (Latin, akron = tip + omos = shoulder, therefore the tip of the shoulder)
supraspinous fossa a broad depression located
superior to the spine of the
scapula
it is the site of origin of the supraspinatus m.
infraspinous fossa a broad depression located
inferior to the spine of the
scapula
it is the site of origin of the infraspinatus m.
humerus
(N420,N421,
TG2-03A,
TG2-03B,
Practical)
the bone of the arm (brachium) the humerus articulates proximally with the scapula at the glenoid fossa; it articulates distally with the radius and ulna at the elbow joint
head(Practical) the smooth, rounded proximal
end of the humerus
it articulates with the glenoid cavity of the scapula to form the shoulder joint
anatomical neck the constricted region located
inferolateral to the head
it is located at the circumference of the smooth articular surface of the head
surgical neck the proximal part of the shaft of
the humerus
it is located inferior to the greater and lesser tubercles; it is a site of frequent fracture; fractures of the surgical neck of the humerus endanger the
axillary n. and the posterior circumflex humeral a.
greater tubercle the large projection located
lateral to the head of the
humerus
it is the attachment site of the supraspinatus, infraspinatus & teres minor mm.
lesser tubercle the projection located lateral to
the head of the humerus on the
anterior surface
it is the insertion site of the subscapularis m.
intertubercular groove the groove on the anterior
surface of the humerus that is
located between the crest of
the greater tubercle and the
crest of the lesser tubercle
it is occupied by the tendon of the long head of the biceps brachii m.; the transverse humeral ligament spans the intertubercular groove and holds the
biceps tendon in place; it is the attachment site for the tendon of the pectoralis major (lateral lip), teres major (medial lip), and latissimus dorsi (floor)
crest of the greater
tubercle
the ridge of bone on the
anterior surface of the humerus
extending inferiorly from the
greater tubercle
it forms the lateral lip of the intertubercular groove; it is the attachment site for the transverse humeral ligament and the pectoralis major m.
crest of the lesser
tubercle
the ridge of bone on the
anterior surface of the humerus
extending inferiorly from the
lesser tubercle
it forms the medial lip of the intertubercular groove; it is the attachment site for the transverse humeral ligament and the teres major m.
deltoid tuberosity the roughened process on the
lateral surface of the mid-shaft
of the humerus
it is the insertion site of the deltoid m.
lateral epicondyle a knob-like projection on the
lateral side of the humerus
proximal to the capitulum
it is the site of attachment of the common extensor tendon which is the origin of several forearm extensor muscles (extensor carpi radialis brevis m.,
extensor digitorum m., extensor digiti minimi m., extensor carpi ulnaris m. and supinator m.); inflammation of the attachment of the common extensor
tendon is called lateral epicondylitis which is also known as "tennis elbow" (Greek, kondylos = the knob formed by the knuckle of any joint)
medial epicondyle a knob-like projection on the
medial side of the humerus
proximal to the trochlea
it is the attachment site of the common flexor tendon which is the origin for the superficial group of forearm flexor muscles (pronator teres m., flexor
carpi radialis m., palmaris longus m., flexor carpi ulnaris m. and flexor digitorum superficialis m.); inflammation of the attachment of the common flexor
tendon is called medial epicondylitis which is also known as "tennis elbow"; the ulnar nerve is in contact with bone as it courses posterior to the medial
epicondyle where it is susceptible to injury from blunt trauma or fracture Greek, kondylos = the knob formed by the knuckle of any joint)
radial groove (Practical) the groove that spirals around
the posterior surface of the
shaft of the humerus
it is a depression for the radial n. and the deep brachial vessels; fracture of the humerus at mid-shaft can injure the radial nerve and deep brachial
vessels because they are in contact with bone at this location
ulna
(N436,N439,
TG2-04AB,
Practical)
the bone on the medial side of
the forearm (antebrachium)
the ulna articulates proximally with the trochlea of the humerus and the head of the radius; it articulates distally with the ulnar notch of the radius (Latin,
ulna = elbow or arm)
olecranon the proximal end of the ulna it is the insertion site of the tendon of the triceps brachii m.; when the elbow is extended, the olecranon of the ulna engages the olecranon fossa of the
humerus (Greek, olecranon = the head or point of the elbow)
coronoid process the anterior projection of bone
located distal to the trochlear
notch
(Greek, coronoid = resembles a crow)
styloid process a small projection from the
distal surface of the head of the
ulna
it is the site of attachment of the articular disk of the distal radioulnar joint
radius
(N436,N439,
TG2-04AB,
Practical)
the bone on the lateral side of
the forearm (antebrachium)
the radius pivots on its long axis and crosses the ulna during pronation
head the rounded proximal end of
the radius
it has a smooth, rounded surface for articulation with the ulna; the head of the radius is encircled by the annular ligament (4/5 of a circle) and the radial
notch of the ulna (1/5 of a circle)
neck the constricted area of the
radius located distal to the
head
the annular ligament of the radius surrounds the head of the radius, not the neck of the radius
radial tuberosity a roughened area on the
anteromedial surface of the
radius located just distal to the
neck
it is the insertion site of the tendon of the biceps brachii m.
styloid process the distal-most projection from
the lateral side of the radius
the radial styloid process projects lateral to the proximal row of carpal bones
Muscles
Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Notes Image
deltoid
(N424, TG2-07,
Practical)
lateral one-third of clavicle, acromion, lower lip of
the crest of the spine of the scapula
deltoid tuberosity of the
humerus
abducts arm; anterior
fibers flex & medially rotate
arm; posterior fibers
extend & laterally rotate
arm
axillary nerve (C5,6)
from posterior cord of
brachial plexus
deltoid is the principle abductor of the arm but due to
poor mechanical advantage it cannot initiate this action;
assisted by supraspinatus
teres major
(N424, TG2-07, TG2-
08)
dorsum of the inferior angle of scapula crest of lesser tubercle
of humerus
adducts arm, medially
rotates arm, assists in arm
extension
lower subscapular
nerve (C5,6) from the
posterior cord of the
brachial plexus
teres major inserts beside the tendon of latissimus dorsi,
and assists latissimus in its actions (Latin, teres =
round)
rotator cuff
supraspinatus
(N425, N426, TG2-08,
TG2-16A, TG2-16B,
TG2-16C, Practical)
supraspinatus fossa greater tubercle of
humerus (highest facet)
abduct arm (initiate
abduction)
suprascapular nerve
(C5,6) from superior
trunk of brachial plexus
supraspinatus initiates abduction of the arm, then the
deltoid muscle completes the action
infraspinatus
(N425, N426, TG2-08,
TG2-16A, TG2-16B,
TG2-16C, Practical1,
Practical2, Practical3)
infraspinatus fossa greater tubercle of
humerus (middle facet)
laterally rotate arm suprascapular nerve infraspinatus, supraspinatus, teres minor and
subscapularis are the rotator cuff muscles
teres minor
(N425, N426, TG2-08,
TG2-16A, TG2-16B,
TG2-16C, Practical)
upper 2/3 of the lateral border of the scapula greater tubercle of
humerus (lowest facet)
laterally rotates arm axillary fixes head of humerus in glenoid fossa during abduction
& flexion of arm
subscapularis
(N425, N426, TG2-08,
TG2-16A, TG2-16B,
TG2-16C)
medial two-thirds of costal surface of scapula
(subscapular fossa)
lesser tubercle of
humerus
medially rotates arm;
assists extension of arm
upper and lower
subscapular nerves
(C5,6)
subscapularis, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and teres
minor are the rotator cuff muscles
biceps brachii
(N431, TG2-17)
short head: tip of coracoid process; long head:
supraglenoid tubercle of scapula
tuberosity of radius flexes forearm, flexes arm
(long head), supinates
musculocutaneous
nerve (C5,6)
a powerful supinator only if the elbow is flexed
brachialis
(N431, TG2-17)
anterior surface of lower one-half of humerus and
intermuscular septa
ulnar tuberosity of ulna flexes forearm musculocutaneous
nerve (C5,6)
powerful flexor
coracobrachialis
(N431, TG2-17,
Practical)
coracoid process of scapula medial humerus at mid-
shaft
flexes and adducts arm musculocutaneous
nerve (C5,6)
musculocutaneous nerve passes through the
coracobrachialis muscle to reach the other arm flexors
(biceps brachii and brachialis)
serratus anterior
(N191, TG4-07,
Practical1, Practical2)
ribs 1-8 or 9 medial border of the
scapula on its costal
(deep) surface
it draws the scapula
forward; the inferior fibers
rotate the scapula
superiorly
long thoracic nerve
(from ventral rami C5-
C7)
a lesion of long thoracic nerve will cause winging of the
scapula (i.e., the medial border of the scapula falls away
from the posterior chest wall and looks like an angel's
wing) (Latin, serratus = to saw)
triceps brachii
(N432, TG2-18A, TG2-
18B, Practical)
long head: infraglenoid tubercle of scapula; lateral
head: posterolateral humerus & lateral
intermuscular septum; medial head:
posteromedial surface of inferior 1/2 of humerus
olecranon process of
the ulna
extends forearm; long
head extends and adducts
arm
radial nerve long head of triceps separates the triangular and
quadrangular spaces (teres major, teres minor and the
humerus are the other boundaries)
anconeus
(N432,N444, TG2-18)
lateral epicondyle lateral side of olecranon
and upper one-fourth of
ulna
extends forearm nerve to anconeus from
radial nerve
(Greek, ankon = elbow or a bend)
Nerves
Nerve Source Branches Motor Sensory Notes
brachial plexus
(N429,N430, TG2-14,
TG2-13, Practical1,
Practical2, Practical3,
Practical4)
ventral
primary
rami of C5-
8 & T1
dorsal scapular, long thoracic, n. to
subclavius, suprascapular, lateral & medial
pectoral, medial brachial & antebrachial
cutaneous, upper, middle & lower
subscapular, musculocutaneous, ulnar,
median, axillary, radial
muscles of upper limb, excluding trapezius skin of upper
limb
axons from spinal cord levels C5-T1 are mixed (braided) in the
brachial plexus and repackaged into terminal branches so that each
branch contains axons from several spinal cord levels (Latin, plexus
= a braid. A network of nerves, blood vessels, or lymphatic vessels)
dorsal scapular
(N429, TG2-14,
Practical1, Practical2)
brachial
plexus (C5)
rhomboid major & minor; levator scapulae passes through scalenus medius
long thoracic
(N429,N190, TG2-13,
TG2-14)
brachial
plexus (C5-
C7)
serratus anterior located on superficial surface of serratus anterior; lesion causes
scapular winging, hence the saying "C5, 6, & 7 keep the wings from
heaven"
lateral cord
(N429, N474, TG2-13,
TG2-14)
union of
anterior
divisions of
upper &
middle
trunks
lateral pectoral, lateral root of median n.,
musculocutaneous
anterior arm; contributes to anterior forearm &
thenar compartment
lateral forearm;
contributes to
palmar hand
medial cord
(N430, TG2-14)
anterior
division of
lower trunk
medial pectoral, medial brachial cutaneous,
medial antebrachial cutaneous, medial root
of median n., ulnar
fl. carpi ulnaris & medial half of fl. dig. profundus,
contributes to other anterior forearm muscles; hand
muscles
medial forearm &
hand
posterior cord
(N430, TG2-13, TG2-
14)
posterior
divisions of
upper,
middle, &
lower
trunks
upper, middle, & lower subscapular, axillary,
radial
deltoid, teres major & minor, subscapularis,
posterior arm & forearm
posterior arm &
forearm,
posterolateral
hand
suprascapular
(N429, N426, TG2-08,
TG2-14, Practical)
superior
trunk of the
brachial
plexus (C5-
C6)
no named branches supraspinatus, infraspinatus no cutaneous
branches
passes through the suprascapular notch inferior to the superior
transverse scapular ligament
lateral pectoral
(N429, TG2-13, TG2-
14, Practical)
lateral cord
of brachial
plexus
pectoralis major communicates with medial pectoral n. anterior to axillary a.; pierces
clavipectoral fascia
musculocutaneous
(N474, TG2-13, TG2-
14, Practical)
lateral cord
of brachial
plexus
(C5,6)
lateral antebrachial cutaneous coracobrachialis, biceps brachii, brachialis skin of lateral
side of forearm
pierces coracobrachialis
medial pectoral
(N429, TG2-13,
Practical1, Practical2)
medial cord
of the
brachial
plexus
pectoralis minor & major communicates with lateral pectoral n. anterior to axillary a.; pierces
pectoralis minor
medial brachial
cutaneous
(N433,N479, TG2-13,
medial cord
of brachial
plexus
skin of the
medial side of
the arm
communicates with intercostobrachial n. (Latin, cutis = skin)
TG2-14)
medial antebrachial
cutaneous
(N433,N479, TG2-13,
TG2-14)
medial cord
of brachial
plexus
skin of medial
side of forearm
travels with basilic vein for part of course (Latin, cutis = skin)
ulnar
(N433,N476, TG2-13,
TG2-14, Practical1,
Practical2, Practical3)
medial cord
of the
brachial
plexus
palmar cutaneous br., dorsal br., superficial
& deep br.
flexor carpi ulnaris, flexor digitorum profundus
(ulnar half), abductor digiti minimi, flexor digiti
minimi brevis, opponens digiti minimi, ulnar 2
lumbricals, palmar & dorsal interossei, adductor
pollicis
skin of medial
side of wrist &
hand & ulnar 1
1/2 digits on
palmar side and
2 1/2 digits
dorsally
motor to most of the muscles of the hand (Latin, ulna = elbow or
arm)
upper subscapular
(N429, TG2-13, TG2-
14)
posterior
cord of
brachial
plexus
subscapularis (superomedial part)
thoracodorsal (middle
subscapular)N426,
TG2-13, TG2-14)
posterior
cord of
brachial
plexus
latissimus dorsi
lower subscapular
(N426, TG2-13, TG2-
14)
posterior
cord of
brachial
plexus
subscapularis (lateral part), teres major
radial
(N477,N478, TG2-13,
TG2-14, Practical1,
Practical2)
posterior
cord of
brachial
plexus
posterior brachial cutaneous, inferior lateral
brachial cutaneous, posterior antebrachial
cutaneous, superficial & deep br.
triceps brachii, anconeus, brachioradialis, extensor
carpi ulnaris, extensor carpi radialis longus &
brevis, extensor digitorum, extensor digiti minimi,
supinator, abductor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis
longus & brevis, extensor indicis
skin of posterior
arm, forearm &
hand
motor to the extensor muscles of the arm and forearm
axillary
(N426, TG2-13, TG2-
14. Practical1,
Practical2)
posterior
cord of
brachial
plexus
superior lateral brachial cutaneous nerve deltoid, teres minor skin of upper
lateral arm
endangered by surgical neck fractures
median
(N473,N475, TG2-13,
TG2-14, Practical1,
Practical2)
lateral &
medial
cords of
brachial
plexus
anterior interosseous, palmar br., recurrent
(motor) br., common palmar digital ns. (1st-
3rd)
pronator teres, flexor carpi radialis, palmaris
longus, flexor digitorum superficialis, flexor
digitorum profundus (radial half), flexor pollicis
longus, pronator quadratus, abductor pollicis brevis,
flexor pollicis brevis, opponens pollicis, radial 2
lumbricals
skin of radial half
of palm & palmar
side of radial 3
1/2 digits (and
nail bed for these
digits)
motor to the flexor muscles of the forearm (except flexor carpi
ulnaris and the medial 1/2 of the flexor digitorum profundus),the
muscles of the thenar compartment and the lateral 2 lumbricals
intercostobrachial
(N429,N473,N479)
lateral cut.
branch of
2nd
intercostal
floor of axilla,
medial and
posterior
surfaces of arm
communicates with the medial brachial cutaneous n.
Arteries
Artery Source Branches Supply Notes
suprascapular
(N426, TG2-08,
thyrocervical trunk muscular supraspinatus & infraspinatus,
shoulder joint
anastomoses with the circumflex scapular a. and the dorsal scapular a. to
form the scapular anastomosis
N427TG2-15,
Practical)
axillary
(N184,N189, TG2-
15A, TG2-15B,
Practical)
subclavian (continuation of
the subclavian lateral to the
1st rib)
1st part: superior thoracic; 2nd part: thoracoacromial, lateral
thoracic; 3rd part: ant. & post. humeral circumflex,
subscapular
shoulder & upper limb pectoralis minor crosses the axillary artery anteriorly and is used to
delineate the 3 parts mentioned at left (Latin, axillary = armpit)
superior thoracic axillary, 1st part muscular intercostal spaces 1 & 2 laterally
thoracoacromial
(N427, TG2-15,
Practical1,
Practical2)
axillary, 2nd part pectoral br., clavicular br., acromial br., deltoid br. pectoralis major & minor,
subclavius, deltoid, shoulder joint
lateral thoracic
(N191,N427, TG2-
15A, TG2-15B)
axillary, 2nd part muscular serratus anterior & adjacent
muscles, skin & fascia
a rare artery in that it enters the serratus anterior from its superficial
surface
subscapular
(N427, TG2-15A,
TG2-15B)
axillary, 3rd part circumflex scapular, thoracodorsal subscapularis, teres major, teres
minor, infraspinatus, latissimus
dorsi
anastomoses with suprascapular, dorsal scapular & deep br. of transverse
cervical
circumflex scapular
(N427, TG2-09A,
TG2-15)
subscapular muscular teres major & minor,
infraspinatus
anastomoses with suprascapular & dorsal scapular branches (Latin,
circum- = around + -flex = to bend)
thoracodorsal
(N427, TG2-15A,
TG2-15B)
subscapular muscular latissimus dorsi
anterior circumflex
humeral
(N427, TG2-09A,
TG2-15, Practical)
axillary, 3rd part muscular arm muscles near surgical neck
of humerus
(Latin, circum- = around + -flex = to bend)
posterior circumflex
humeral
(N427, TG2-09A,
TG2-15)
axillary, 3rd part muscular arm muscles near surgical neck
of humerus
passes through quadrangular space with axillary nerve
brachial
(N434,N429, TG2-
17, TG2-19,
Practical)
axillary (continuation distal to
teres major m.)
deep brachial, sup. ulnar collateral, nutrient, inf. ulnar
collateral; terminal branches are the radial & ulnar
arm, forearm & hand normally terminates at the level of the elbow, but high branching may
occur
deep brachial
(N434, TG2-18,
TG2-19)
brachial ascending br., terminal branches are the middle collateral &
radial collateral
post. arm
Lymphatics of the Axillary Region
Structure Location Afferents from
Efferents
to
Regions drained Notes
axillary
nodes
(N184,
TG2-11)
axilla efferents
form
subclavian
trunk
upper limb, most of
breast, some
anterolateral chest wall
axillary nodes are grouped as: 1) pectoral/anterior nodes, along lower border of pectoralis major; 2) lateral nodes, distal along
axillary v.; 3) central nodes, centrally located along axillary v.; 4) subscapular/posterior nodes, along subscapular v. & tributaries; 5)
apical nodes, at apex of axilla, receiving lymph from all other groups
pectoral lateral border of most of breast, central anterolateral thoracic wall also known as anterior axillary or level I nodes; an important group of nodes to examine during breast exam
nodes
(N184,
TG2-11)
pectoralis major anterolateral
chest wall &
muscles
axillary
nodes
and muscles, including
most of the mammary
gland
lateral
axillary
(N184,
TG2-11)
along distal axillary
v.
small nodes in
cubital fossa
central
axillary
nodes
upper limb
posterior
axillary
(N184,
TG2-11)
anterior to
subscapularis m.
central
axillary
nodes
posterior shoulder a.k.a. subscapular nodes
central
axillary
(N184,
TG2-11)
along axillary v.
posterior to
pectoralis minor m.
lateral, anterior
& posterior
axillary nodes
apical
axillary
nodes
upper limb, breast,
posterior shoulder, lateral
chest wall
a.k.a. level II nodes
apical
axillary
(N184,
TG2-11)
along axillary v.
medial to pectoralis
minor m. at apex of
axilla
central axillary
nodes
subclavian
lumph trunk
upper limb, breast,
posterior shoulder, lateral
chest wall
a.k.a. level III nodes
You might also like
- Table of Upper Limb MusclesDocument7 pagesTable of Upper Limb MusclesLjubica Nikolic90% (10)
- FIRST AID Is An Immediate Care Given To A Person Who Has Been Injured or Suddenly Taken IllDocument6 pagesFIRST AID Is An Immediate Care Given To A Person Who Has Been Injured or Suddenly Taken IllLeigh Yah88% (8)
- REVISED Physics14 PROJECT, WorkedDocument23 pagesREVISED Physics14 PROJECT, WorkedDiovinyl KartilNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The Upper LimbDocument17 pagesMuscles of The Upper LimbJhanelle S. Dixon-LairdNo ratings yet
- Oskar DavičoDocument5 pagesOskar DavičoSofija ŽivkovićNo ratings yet
- Case Studies On Industrial Accidents - 2Document84 pagesCase Studies On Industrial Accidents - 2Parth N Bhatt100% (2)
- Bones of The Upper LimbDocument14 pagesBones of The Upper Limbyachiru121No ratings yet
- Upperlimbbones 181202102428Document32 pagesUpperlimbbones 181202102428qaziafifa404No ratings yet
- Upper Limb SummaryDocument19 pagesUpper Limb SummaryPremangshu GhoshalNo ratings yet
- General Anatomy of The Human BodyDocument18 pagesGeneral Anatomy of The Human BodyVarenLagartoNo ratings yet
- UPPER LIMB ANATOMY UPDATEDDocument40 pagesUPPER LIMB ANATOMY UPDATEDmohmmed alzbaidiNo ratings yet
- Upper LimbDocument17 pagesUpper LimbPapadoveNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Anatomy SummaryDocument4 pagesShoulder Anatomy Summaryapi-246259817No ratings yet
- Upper Limb Anatomy 1Document6 pagesUpper Limb Anatomy 1shahab shamsiNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb BonesDocument16 pagesUpper Limb Bonesharis13.hsNo ratings yet
- Muscle of Upper LimbsDocument5 pagesMuscle of Upper LimbsFong Yu-heng100% (1)
- Bones of The The RegionDocument51 pagesBones of The The RegionjazzyNo ratings yet
- Muscle Origin Insertion Action Abdominal WallDocument2 pagesMuscle Origin Insertion Action Abdominal WallAnthea Manguera AllamNo ratings yet
- Shoulder JointDocument42 pagesShoulder Jointcaystone99No ratings yet
- Cat Muscles OiaDocument4 pagesCat Muscles Oianathan3602No ratings yet
- Humerus AnatomyDocument1 pageHumerus AnatomyNicoleta PSNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The Human BodyDocument150 pagesMuscles of The Human BodyJoseph EpsteinNo ratings yet
- OIA Upper ArmsDocument3 pagesOIA Upper ArmsMarianne Michelle Quiambao de la RosaNo ratings yet
- FLASH Download MergedDocument15 pagesFLASH Download MergedChristine PaulineNo ratings yet
- Osteology of The Upper Limb 2Document71 pagesOsteology of The Upper Limb 2obehi4rNo ratings yet
- 1 ANT Anatomy of The Upper Limp TGDocument129 pages1 ANT Anatomy of The Upper Limp TGReath Gatkuoth DuothNo ratings yet
- Origins and InsertionsDocument12 pagesOrigins and Insertionsking54591No ratings yet
- 0608 Arm-1Document48 pages0608 Arm-1Jaeho LeeNo ratings yet
- Summary Topographic Anatomy, Extras and Muscles To 1 Proof!!Document10 pagesSummary Topographic Anatomy, Extras and Muscles To 1 Proof!!Geovanna FernandesNo ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy CheatsheetDocument302 pagesGross Anatomy CheatsheetNobody2015100% (1)
- Cat Muscular System: Muscles of The Abdominal WallDocument6 pagesCat Muscular System: Muscles of The Abdominal WallGiaFelicianoNo ratings yet
- Blue Boxes Upper ArmDocument3 pagesBlue Boxes Upper ArmLardel CarayNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The Back Region - Listed Alphabetically Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Artery NotesDocument32 pagesMuscles of The Back Region - Listed Alphabetically Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Artery NotesMaria Celina Lomboy SerapioNo ratings yet
- The OneDocument436 pagesThe OneSheena ChenNo ratings yet
- Appendicular SkeletonDocument61 pagesAppendicular SkeletonNizam ullahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The ShoulderDocument61 pagesAnatomy of The ShoulderChaman Lal KarotiaNo ratings yet
- As UpperlimbDocument3 pagesAs UpperlimbUma MounaNo ratings yet
- Dissection 11 - Extensor Compartment of The Forearm, Deep Hand, Wrist and Hand JointsDocument29 pagesDissection 11 - Extensor Compartment of The Forearm, Deep Hand, Wrist and Hand JointsLeonard EllerbeNo ratings yet
- Osteology of Upper LimbDocument13 pagesOsteology of Upper Limbdie1only100% (1)
- Appendicular Skeleton - UL - TranscriptDocument2 pagesAppendicular Skeleton - UL - Transcriptestellasr00No ratings yet
- The Humerus - Proximal - Shaft - Distal - TeachMeAnatomyDocument5 pagesThe Humerus - Proximal - Shaft - Distal - TeachMeAnatomymuhammad HaseebNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Joint Complex and Arm RegionDocument61 pagesShoulder Joint Complex and Arm Regionfrancisco raphaelNo ratings yet
- Orthobullet HandDocument506 pagesOrthobullet HandRicky Wibowo67% (3)
- Upper LimbDocument14 pagesUpper LimbAmbg GhalyNo ratings yet
- HUMAN BIOmuscles Origin Insertion ActionDocument3 pagesHUMAN BIOmuscles Origin Insertion ActionandrealohrNo ratings yet
- Petunjuk Praktikum Anatomi Extremitas SuperiorDocument9 pagesPetunjuk Praktikum Anatomi Extremitas SuperiorMuti Arizka RaniNo ratings yet
- Animal Osteopathy, 3 A Comprehensive Guide To The Osteopathic Treatment-121-221Document101 pagesAnimal Osteopathy, 3 A Comprehensive Guide To The Osteopathic Treatment-121-221valentinaNo ratings yet
- Origins and InsertionsDocument12 pagesOrigins and InsertionsFrancesca vitaleNo ratings yet
- Upper LimbDocument31 pagesUpper LimbNandhana Kattuparambil SunojNo ratings yet
- Muscles in The Posterior Scapula Muscle Proximal Attachment Distal Attachment Nervous Supply FunctionDocument37 pagesMuscles in The Posterior Scapula Muscle Proximal Attachment Distal Attachment Nervous Supply FunctionMicky TsuiNo ratings yet
- The Upper LimbsDocument9 pagesThe Upper Limbsfortuneabla8195No ratings yet
- Upper Limb ProperDocument15 pagesUpper Limb Properamoswaiswa9No ratings yet
- Mped Ii Sem 202 2.1Document19 pagesMped Ii Sem 202 2.1jadu45934No ratings yet
- Group 2 TleDocument40 pagesGroup 2 Tleralph divinaNo ratings yet
- Cat Muscles and O.I.A.: Body Region Muscle Origin Insertion ActionDocument5 pagesCat Muscles and O.I.A.: Body Region Muscle Origin Insertion ActioneumarasiganNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Units 9-12 ObjectivesDocument18 pagesAnatomy Units 9-12 ObjectivespoNo ratings yet
- Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper ExtremityDocument12 pagesMuscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper ExtremityKaren ManlapazNo ratings yet
- Clavicle BoneDocument4 pagesClavicle Bonepari59084No ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument9 pagesAnatomyfarahjurdi8No ratings yet
- Anatomy Chart2Document16 pagesAnatomy Chart2Jeff WuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Upper Limb: 1) ClavicleDocument4 pagesAnatomy - Upper Limb: 1) ClavicleJasmine TeoNo ratings yet
- Kończyna GórnaDocument5 pagesKończyna Górnaxpathetic.aestheticNo ratings yet
- Oina MusclesDocument73 pagesOina MusclesShen AndradeNo ratings yet
- Critical Thinking: Moral ReasoningDocument2 pagesCritical Thinking: Moral ReasoningNaina Karamina SakinaNo ratings yet
- Global Health Article - Naina Karamina SakinaDocument1 pageGlobal Health Article - Naina Karamina SakinaNaina Karamina SakinaNo ratings yet
- Acne Vulgaris Hidradenitis Dermatitis: Stages of Acne. (A) Normal Follicle SUPPURATIVA (C) Closed Comedo (Whitehead)Document8 pagesAcne Vulgaris Hidradenitis Dermatitis: Stages of Acne. (A) Normal Follicle SUPPURATIVA (C) Closed Comedo (Whitehead)Naina Karamina SakinaNo ratings yet
- Proteomic ReportDocument37 pagesProteomic ReportNaina Karamina SakinaNo ratings yet
- Meperidine: Use in Drug and Alcohol AddictionDocument3 pagesMeperidine: Use in Drug and Alcohol AddictionNaina Karamina SakinaNo ratings yet
- Muscles of The Upper Limb - Listed AlphabeticallyDocument5 pagesMuscles of The Upper Limb - Listed AlphabeticallyNaina Karamina SakinaNo ratings yet
- Cleft PalateDocument5 pagesCleft PalateNaina Karamina SakinaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Physiological StressDocument2 pagesEffect of Physiological StressNaina Karamina SakinaNo ratings yet
- Wo Repro Week 2Document25 pagesWo Repro Week 2Naina Karamina SakinaNo ratings yet
- Case 1Document1 pageCase 1Naina Karamina SakinaNo ratings yet
- Print Week 3 GitDocument3 pagesPrint Week 3 GitNaina Karamina SakinaNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Cerebellum or The Posterior Columns of The Spinal Cord May Involve The Limbs, Head, or TrunkDocument5 pagesDisorders of The Cerebellum or The Posterior Columns of The Spinal Cord May Involve The Limbs, Head, or TrunkNaina Karamina Sakina100% (1)
- Unit V. Method of Transport of Injured Person/Casualties Transportation of The InjuredDocument4 pagesUnit V. Method of Transport of Injured Person/Casualties Transportation of The InjuredcriminologyallianceNo ratings yet
- .Tii'r I : EkstremitasDocument6 pages.Tii'r I : EkstremitasRetno Noor FebbyNo ratings yet
- Intracranial AneurysmDocument5 pagesIntracranial AneurysmSarah Eddiah0% (1)
- Motoman gp50 PDFDocument109 pagesMotoman gp50 PDFCésar AtachauNo ratings yet
- Blast Resistant StructuresDocument62 pagesBlast Resistant StructuresTezin100% (2)
- Bhel EsvDocument4 pagesBhel EsvKarthi Keyan100% (1)
- AIIMS Prof Anat 2Document11 pagesAIIMS Prof Anat 2Utkarsh ChhallaniNo ratings yet
- Chap6 Muscular Anaphy NotesDocument13 pagesChap6 Muscular Anaphy NotesAxel Neil VidalNo ratings yet
- Simple PresentDocument4 pagesSimple PresentSundara LingamNo ratings yet
- Anterior & Medial Compartment of ThighDocument25 pagesAnterior & Medial Compartment of ThighnasibdinNo ratings yet
- Balutan - Chapter 1. LectureDocument8 pagesBalutan - Chapter 1. LecturePrinces Jecyvhel De LeonNo ratings yet
- Techniques in Cognitive Neuroscience: Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)Document33 pagesTechniques in Cognitive Neuroscience: Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)ANTolaniNo ratings yet
- Yscp WaiverDocument1 pageYscp WaiverMark Alvin JimenezNo ratings yet
- Top 10 NPTE Musculoskeletal CheatsheetsDocument40 pagesTop 10 NPTE Musculoskeletal Cheatsheetshajarebhagyashree12No ratings yet
- Dorsal Blocking SplintDocument2 pagesDorsal Blocking Splintapi-234072677No ratings yet
- Tensile TestDocument4 pagesTensile TestZhao YunNo ratings yet
- Project Report: Personal Protective EquipmentDocument89 pagesProject Report: Personal Protective EquipmentVivace SystmNo ratings yet
- 12 Basic Exercises Molly GalbraithDocument22 pages12 Basic Exercises Molly GalbraithCanh LuongtienNo ratings yet
- Walking MechanismDocument15 pagesWalking MechanismKamran AmeerNo ratings yet
- Trigger Point InjectionDocument10 pagesTrigger Point Injectionv_vijayakanth7656No ratings yet
- L5 CerebellumDocument17 pagesL5 CerebellumAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- Silver Sol Revolutionary Silver For The BodyDocument9 pagesSilver Sol Revolutionary Silver For The BodyALKESWWNo ratings yet
- Technologies - Milling Machine - No 60Document4 pagesTechnologies - Milling Machine - No 60Malayalam musical CollectionNo ratings yet
- Emergency MedicineDocument11 pagesEmergency MedicineJai Singh100% (1)
- Explanation of HINRI LabsDocument21 pagesExplanation of HINRI Labsjgoode73No ratings yet
- PFO UpdateDocument33 pagesPFO UpdateMitesh PatelNo ratings yet