Engineering MEchanics Part - B
Engineering MEchanics Part - B
Uploaded by
Preethi SharmiCopyright:
Available Formats
Engineering MEchanics Part - B
Engineering MEchanics Part - B
Uploaded by
Preethi SharmiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Engineering MEchanics Part - B
Engineering MEchanics Part - B
Uploaded by
Preethi SharmiCopyright:
Available Formats
E217
1. The magnitude of the resulatant of two concurrent forces including an angle of 90
between them is root of 13 kN. When the included angle between the forces is 60, the
magnitude of their resultant is root of 19kN. Find the magnitude of the two forces.
2. The lines of action of three forces are concurrent at the origin O passing through
points A,B and C having coordinates A[-1,2,4] and B[3,0,-3] and C[2,-2,4]. The
magnitude of forces are F
A
=40 N, F
b
=10N and F
C
=30N. Find the magnitude and
direction of their resultant.
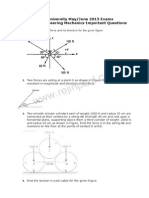
3. A table 600x600 mm is mounted on 3 legs shown in fig. there are 4 loads acting on
the table. Determine the reaction at the supports.
4. Find the reaction ar the supports A and B for the beam as shown in fig
5. Determine the moment of inertia of the area shown below with respect to centroidal
axes respectively parallel and perpendicular to the side AB
6. Determine the centroid of the plane area shown in fig
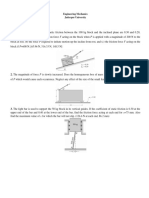
7. Two stopping points of an electric tram car are 450mm apart. The maximum speed of
the car is 20Km/hr and it covers the distance between the stops in 100 sec. If both
acceleration and retardation are uniform and the later is twice as great as former. Fine
the value of each of them and also how for the car runs at maximum speed.
8. A 40 N mass is dragged alon the surface of the table by means of a cord which passes
over a frtiction less pulley ar the edge of the table and is attached to a 12N mass. If the
coefficient of friction between 40N mass and the table is 0.15, determine the
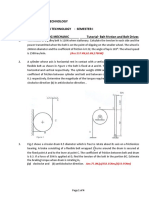
acceleration of the system and the tension in the cord.
9. Two weights each of 100 N are suspernded from a compound pulley as shown in fig.
Find i) angular acceleration of the pulley ii) linear acceleration of the blocks A and B
iii) Tension in the string. Take weight of the pulley as 300 N and its radius of gyration
0.25m
10. A force of 300N is required just to move a block up a plane inclined at 20 to the
horizontal, the force being applied parallel to the plane. IF the inclination of the plane
is increased to 25, the force required just to move the block up is 340 N, the force
acting parallel to the plane. Determine the weight of the block and the coefficient of
friction
L1108
11. Determine the tension in the cables AB, AC and AD if the crate shown in fig is
weighing 9.07kg
12. Determine the reactions at supports A,B,C and D for the beam shown in fig
13. Determine the resultant of the coplanar non-concurrent force system shown in fig.
calculate its magnitude and direction and locate its position with respect to the sides
AB and AD.
14. Find I
xx
, I
yy
through centroid of the fig with uniform thickness of 3cm throughout
15. Derive an equation for the mass moment of inertia of cone
16. A stone is projected with a speed of 30m/s at an angle of elevation of 50. Find its
velocity
i) After two seconds
ii) At the highest point of its path
iii) At a height of 6m
Find also the time interval between the two points at which the stone attains a speed of 23m/s
17. In the oblique central impact shown in fig, the coefficient of restitution is 0.8. The flat
disks shown , slide on a smooth horizontal surface. Determine the final velocity of
each disk directly after impact.
18. Determine whether the block shown in fig having a mass of 40kg is in equilibrium
and find the magnitude and direction of the friction force. Take
s
= 0.40 and
k
=0.30
19. Determine the least value of P required to cause the motion impend the system shown
in fig. Assume coefficient of friction on all contact surface as 0.2
C110
20. A 30kg block is suspended by two springs having stiffness as shown. Determine the
unstretched length of each spring after the block is removed.
21. Determine the tension in cable AC and BC in the following system
22. A 60kN force passes from point A(0,0.9,1.2) to point B(3.6,0,2.4). Determine the
moment of this force about point C(3.6,1.8,1.2)
23. A table 600x600 mm is mounted on three legs as shown. There are four loads applied
as shown. Determine the reaction at the supports.
24. A 200kN vertical force is applied to the end of lever which is attached to a shaft at B
as shown in the fig. Determine
i) Magnitude of horizontal force applied at A which creates same moment about B
ii) The smallest force applied at A which creates the same moment about B
iii) How far from the end B, a 400kN vertical force must act to create the same
moment about B.
iv) Replace the given system of force at B
25. Determine the magnitude and direction of single force P as shown which keeps the
system in equilibrium
26. Determine the moment of inertia of the section shown in the fig XX and YY axes
27. Prove that the mass moment of inertia of a cube of mass m about a centroidal axis
parallel to a side is ma
2
/6, where a is the length of the side,
28. Determine the principal moment of inertia of the following section about point A
29. Two men of mass 60kg and 90kg dive off from the end of a boat of mass 400kg so
that their relative velocity with respect to the boat is 8m/s. If the boat is initially at rest
determine its final velocity for the following conditions
i) If two men dive simultaneously
ii) The 60kg man dives first followed by 90kg man
iii) The 90kg man dives first followed by 60kg man
30. Car A is accelerating in the direction of motion at the rate of 1.2m/s
2.
Car B is
rounding a curve at a constant speed of 54kmph at 150m radius. Determine the
velocity and acceleration that car B appears to have to an observer in the car A has
reaches a speed of 72kmph for the positions represented.
31. A reciprocating engine mechanism is shown in fig. The crank OA is of length 150mm
and rotating at 600 rpm. The connecting rod AB is 700mm long. Determine
i) Angular velocity of the connecting rod
ii) Velocity of piston B
iii) Velocity of point C on the connecting rod at a distance of 200mm from A when
is 45
0
32. A uniform rod shown in the figure is acted upon by 30 N force which always acts
perpendicular to the bar. If the bar has an initial clockwise angular velocity
o
=10rad/sec when = 0
0
, determine the angular velocity at the instant = 90
0
33. In the following figure , the blocks A and B have masses 45 kg and 60kg respectively.
The drum has a moment of inertia of 16kgm
2
about its axis of rotation. Radius of
inner pulley is 300mm whereas for outer pulley is 900mm. Determine the distance
through which the blocks A falls, before it reaches a speed of 2m/s.
Q2256
34. Find the magnitude and direction of the force A so that the resultant of the system of
force shown in fig is horizontal and has a magnitude of 14.4kN.
35. Find the magnitude and the points of meeting of the line of action of th resultant with
the side kL for the system of forces shown in fig
36. A uniform rod of length 2m is supported on a knife edge at its centre. A container is
suspended from the rod at 0.5m from one end and a block of weight 4kN is suspended
at 1.6m from the same end. Find the weight of the container so that the rod remains
horizontal.
37. A beam is loaded as shown in fig. Find the equivalent single force for the system of
forces and the equivalent force-couple at P and at S. Use vector approach.
38. A frustum of a solid cone of height 250mm has a base diameter of 300mm and top
diameter of 150mm. It has an axial hole of diameter 60mm. Determine the position of
the centre of gravity of the solid.
39. Find the product of inertia of the section shown in fig. With respect to the x and y
axes. All dimensions are in mm. Also find the principal axes and the principal
moments of inertia of the section.
40. A stone is projected form a point P on a 30 inclive at an angle of 65 with the plane
with velocity of 10m/s. The stone hits the inclined at Q below P. Find the time of
flight, difference in height between P and Q and also the range along the incline.
41. A car P is running towards east at a uniform speed of 40kmph. When the car P just
crosses the intersection shown in fig, another car Q starts from rest in the north 50m
from the intersectin and travels towards south with a uniform acceleration of 1.5m/s
2
.
Find the position, velocity and acceleration of Q relative to P, three seconds after P
crosses the intersection.
42. A force of 300N is required just to move a block up a plane inclined at 20 to the
horizontal, the force being applied parallel to the plane. IF the inclination of the plane
is increased to 25, the force required just to move the block up is 340N, the force
acting parallel to the plane. Determine the weight of the block and the coefficient of
friction
43. A small pulley of radius 100mm is connected to the shaft on an electric motor. A belt
connects this pulley with a bigger pulley of radius 300arm. Contact angle between the
bigger pulley and the belt is 230. The maximum tension punishable in the belt is
2000N. The coefficient of friction
s
between the belt and both the pulleys is 0.25.
Find the torque exerted by the belt on the bigger pulley. Also check that
s
utilised in
the lax of bigger pulley at the time of slipping in the smaller pulley is less than 0.25
S4043
44. Calculate the moment of inertia about XX axis. (XX axis is the centroidal axis) for the
plane figure shown in fig. Assume AB as the reference axis to locate XX.
45. Locate the centroid for the following sections as shown in fig
46. Determine the resultant of the force system acting in plane shown. Locate the distance
from A where the resultant cuts the x axis.
47. A container weighing 450kN is suspended at P by using two cables PB and PA
anchored as shown in fig. A horizontal force F keeps the Q container in the current
position. Find the magnitude of force F and forces in cable PA and PB.
48. Two identical rollers each of weight 5kN rest in between an inclined wall and a
vertical wall as shown in fig. Determine the reactions at the points of contact P, Q and
R. Assume the wall surface to be smooth.
49. A shaft is subjected to forces in x,y and z direction as shown in fig. Replace these
forces by a resultant R at origin O and a couple
50. A rod CD of 8kg length 0.8m is welded to a uniform dics of mass 5kg and radius
0.16m. A spring of constant k=100N/mm is attached to a disc as shown in fig. when
the rod CD is horizontal the spring is unstretched. Assembly is released from rest
from the position shown. What is angular velocity of the disc and rod if it has rotated
through /2 angle ( use work energy principle)
51. Two bodies of weights w
1
and w
2
respectively are connected by an inextensible string
passing over a frictionless pulley. The coefficient of friction between w
1
and plane is
0.2 what is the velocity of the weights before w
1
reaches the top edge of plane.
Calculate the velocity of weights after 2 secs if w
1
= 100N; w
2
= 80N ; = 30
0
refer
fig ( use impulse momentum principle)
52. A pulley assembly shown in fig weighs 50kg with a radius of gyration of 0.5m. The
blocks A and B are connected through strings wrapped around the pulleys. Determine
the acceleration of each block and tension in each string.
53. Blocks A and B connected through a cord rest on inclined planes are shown in fig,
What is the tension in the cord is the friction at block A reaches the maximum valus?
State whelther the system is at rest or motion
S4821
54. A spherical ball of weight 500N is suspended vertically by a string 500mm long. Find
the magnitude and direction of the least force that can hold the ball 100mm above the
lowest point. Find also the tension in the string. Ignore the size of the ball.
55. Two forces P and Q are acting at the origin. The force P whose magnitude is 70 N is
directed towards (3,-6,2). The force Q is inclined at 45
0
, 60
0
and 60
0
respectively to x,
Y and Z axes. Determine the magnitude of Q so that the resultant of P and Q will be
in XZ plane. Also determine the magnitude and direction cosines of the resultant.
56. A system of three forces 10N , 10N and 5N act at A, B and C respectively in the
direction of AB, BC and CA. If A,B and C form an equilateral triangle, find an
equivalent force system consisting of three forces acting at the points A,B and C and
parallel to the opposite sides
57. Find the magnitude and nature of forces in each member of he trusses given in fig
58. A ladder 3m long and weighing 200N is resting on the horizontal floor and leaning
against a verticall wall, making 30
0
with the wall. The friction coefficient at the
ground and wall contact surfaces are 0.35 and 0.25 respectively. It has to support a
weight of 100N at the top. To prevent slipping, a string is tied to the foot of the ladder
and attached to the wall in the horizontal position. Determine the minimum tension
required in the string for this condition. Find also the minimum angle with the floor at
which the above ladder with the weight at the top could be placed without slipping in
the absence of the string
59. In fig calculate so that the motion of lower block can just occur down the plane.
The weight A and B are 30 N and 90 N respectively. The coefficient of friction for all
contact surfaces is 1/3.
60. Find the moments of inertia of the section given in the fig about the horizontal and
vertical centroidal axes. Also find the polar moment of inertial and minimum raidus of
gyration ( all dimension are in mm)
61. Derive the expression for mass moment of inertia of circular plate about any axis
passing through centre and i) lying on the plate ii) perpendicular to plate and hence
fine mass moment of inertia of a steel plate of radius 100mm and thickness 1mm
about each of the above axes. Take specific gravity of steel as 7.8.
62. A stone falls past a window 2 m high in 0.5 s. Find the height above the window from
where the stone is dropped.
63. A shot is fired with a velocity of 30m/s from a point 15m in front of a vertical wall
6m high. Find the angle of projection with the horizontal to enable the shot to just
clear the wall. Explain the double answer.
64. Two identical balls of radius 150mm are moving with velocities of 5m/s and 8m/s
along parallel lines 200mm apart. If the coefficient of restitution is 0.6, determine the
magnitude and direction of their velocities after they collide.
C123
65. Determine the magnitude T of the tension in the supporting cable and the magnitude
of the force on the pin at A for the jib crane shown in fig. The beam AB is standar 0.5
m I beam with a mass of 95 kg per meter of length.
66. A string ABCD hangs from fixed points A and D carrying a mass of 50kg at B and a
mass of m kg at C. AB is inclined at 60
0
to the horizontal. BC is horizontal and CD is
inclined at 45
0
to the horizontal. Determine the tension in AB,BC,CD and the mass m
67. Locate the centroid of the cross section of an angle 150 by 100 by 12mm shown in fig
68. Determine the moment of inertia of the area shown in fig i) about the vertical gravity
axis YY ii) about a horizontal axis a-a 50mm below the base
69. A body having a mass of 46 kg rests on a horizontal plane shown in fig for which =
0.4. a force P acts on the body an angle of 20
0
with the horizontal. Find its magnitude
for impending motion.
70. A flexible cable which supports the 100kg load is passed over a fixed circular drum
shown in fig and subjected to a force P to maintain equilibrium. The coefficient of
static friction between the cable and the fixed drum is 0.3. i) for = 0, determine the
maximum and minimum values which P may have in order not to raise or lower the
load ii) For P 500 n, determine the minimum value which the angle may have
before the load begins to slip.
71. Two automobiles A and B traveling in the same direction in adjacent lanes are
stopped at a traffic signal. As the signal turns green , automobile A accelerates at a
constant rate of 2m/s
2
. Two seconds later automobile B starts and accelerates at a
constant rate of 3.6 m/s
2
Determine i) when and where B will overtake A ii) The
speed of each automobile at that time
72. The two blocks shown in fig are originally at rest. Neglecting the masses of the
pulleys and the effect of friction in the pulleys and between the blocks and the incline
deternine i) the acceleration of each block ii) the tension in the cable
73. A driver of a light truck applies the brakes when travelling 40km/hr , it skids 3m
before stopping. How far will the truck skid if it is travelling 88km/hr when the brakes
are applied?
74. Block A has a mass of 3 kg and is sliding on a rough horizontal surface with a
velocity 2m/s when it makes a direct collision with block B which has a mass of 2kg
and is originally at rest. If the collision is perfectly elastic, determine the velocity of
each block just after collision and the distance between the blocks when they stop
sliding. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the blocks and the plane is 0.3
11516
75. Determine the resultant of the concurrent force system shown in figure
76. Fig shows a 10kg lamp supported by two cables AB and AC find the tension in each
cable
77. Forces 32kN,24kN and 120kN are concurrent at origin and are respectively directed
through the points whose coordinates are A(2,1,6), B(4,-2,5),C(-3,-2,1) and D(5,1,-2).
Determine the magnitude of the resultant and the angles it makes with coordinate
axes.
78. Distinguish between Moment of a force about a point and Moment of a force about an
axis
79. Find the resultant force and its location of the force system shown in figure. The (x,z)
coordinates of the points of application of the forces are given in metres.
80. Two identical rollers, each of weight 500N are supported by an inclined plane making
an angle of 30
0
to the horizontal and vertical wall as shown in the figure. Sketch the
free body diagram of the two rollers. Assuming smooth surfaces, find the reactions at
the support points.
81. Derive the expressions for the location of the centroid of a triangular area shown in
figure by direct integration.
82. Locate the centroid of the plane area shown in the figure below
83. An area in the form of L section is shown in figure. Find the moments of inertia I
xx
,
I
yy
, I
xy
about its centroidal axes. Also determine the principal moments of inertia.
84. A bullet is fired making an angle 30
0
to the horizontal from a hill which strikes the
target which is 80 m lower than the horizontal passing through the firing point. The
initial bullet velocity is 100m/s. find the maximum height above horizontal to which
the bullet will rise, the velocity of bullet when it strikes the target, and the total time
required for the bullet when it strikes the target.
85. Block P of weight 100 N and block Q of weight 50 N are connected by a rope that
passes over a smooth pulley as shown in figure. Find the acceleration of the blocks
and the tension in the rope, when the system is released from the rest. Neglect the
mass of the pulley.
86. A 2000kg automobile is driven down a 5
0
inclined plane at a speed of 100km/h when
the brakes are applied causing a constant total breaking force (applied by the road on
the tires) of 7kN. Determine the distances travelled by the automobile as it comes to a
stop)
87. A ladder of weight 1000 N and length 4 m rests as shown in figure, if a 750 N weight
is applied at a distance of 3m from the top of ladder, it is at the point of sliding.
Determine the coefficient of friction between ladder and the floor.
88. A rope is wrapped three times around a rod as shown in figure. Determine the force T
required on the free end of the rope, to support a load of W = 20kN. Take =0.30
89. Figure shows a stepped pulley. The smaller radius is 150mm and the bigger radius is
200mm. Two loads P and Q are connected by inextensible taut cords. Load P moves
with an initial velocity of 0.2m/s and has a constant acceleration of 0.25m/s
2
both
downwards. Determine the number of revolutions turned by the pulley in 4 seconds
and velocity and the distance travelled by load Q after 4 seconds. Acceleration of
point B located on the rim of the pulley at t=0. Give both magnitude and direction.
C1369
90. A spherical ball of weight 500N is suspended vertically by a string 500mm long. Find
the magnitude and direction of the least force that can hold the ball 100mm above the
lowest point. Find also the tension in the string. Ignore the size of the ball.
91. A mass AB is supported by a hinge at A(0,0,0) and two guy wires BC and BD. The
mast is subjected to a load of 100kN at B(4,3,5). IF the coordinates of C and D are
(4,0,5) and (0,3,5) respectively, determine the forces in BA, BC and BD. The load
acts in the negative z direction.
92. A system of three forces 10N, 10N and 5N act at A,B and C respectively in the
direction of Ab, BC and CA. IF A,B and C form an equilateral triangle. Find an
equivalent force system consisting of three forces acting at the points A,B and C and
parallel to the opposite forces.
93. For the system of forces shown in fig a, find P and Q such that the resultant of the
system passes through A and B
94. Find the moments of inertia of the section given in the fig about the horizontal and
vertical centroidal axes. Also find the polar moment of inertia and minimum radius of
gyration( all dimensions are in mm).
95. Derive the expression for mass moment of inertia of a cylinder of massM, length L
and radius R about the centroidal axis perpendicular to the axis and also about the
axis.
96. An effort of 150N is required to just move a body up a rough plane inclined at 12
0
with the horizontal, the force required was 172N. Find the weight of the body and the
coefficient of friction.
97. A weight of 10N resting on a n inclined plane that makes an angle of 30 with
horizontal is connected by a string passing over a frcitonless pulley at the upper end
of the plane. On the free end of the string a weight of 20N is connected. If the
coefficient of friction between the plane and 10N weight 0.2, calculate the time taken
by the hanging weight to descend by 1m.
98. What is meant by Translation in rigid body motion? Explain its two types.
99. A wheel is attached to the shaft of an electric motor of rated speed of 2000rpm. When
the power is switched on the unit attains the rated speed in 10 seconds and when the
power is switches off, the unit comes to rest in 100 seconds, assuming uniformly
accelerated motion determine the number of revolutions the unit turns (1) to attain the
rated speed (2) to come to rest.
100. A cycle is traveling along a straight road with a velcotiy of 10m/s. Determine
the velocity of point situated at the middle of one of the spokes at angle of 30
0
with
horizontal in the front whell ( with respect to the centre of the wheel ). The radius of
the cycle wheel is 400mm.
101. Distinguish with sketches between constrained motion of a rigid body with a
point and that with a line.
Q2720
102. Determine the tension in the cables AB, AC and AD if the crate shown in fig
is weighing 10kg.
103. A 100kg crate is hung by means of two cables AB and AC which are attached
to the top of a vertical wall. A horizontal force of magnitude 185N perpendicular to
the wall holds the cylinder in the position as shown in fig. Determine the tension in
each cable.
104. Determine the moment created by the force acting at point B of the rod shown
in fig about point A.
105. The 8m pipe AB shown in fig has a fixed end at A. A steel cable is stretched
from B to a point C on the vertical wall. If the tension in the cable is 1200 N,
Determine the moment about A of the forces exerted by the cable at B.
106. Determine the smallest force P required to lift the 15kN load shown in fig. The
coefficient of static frciton between A and C and between B and D is 0.3 and that
between A and B is 0.4.
107. Assuming the coefficient of rolling resistance to be 3.0mm, determine the
horizontal force required to move a 2700kg automobile along a horizontal road at a
constant speed. The diameter of each tyre is 1150mm. Neglect all forms of friction
except rolling resistance.
108. A wheel 250mm in diameter carries a load of 10kN, If a horizontal force of
100 N is necessary to move it over a level surface, determine the coefficient of rolling
resistance.
109. For the section shown in fig determine the principal moments of inertia and
locate the principal planes.
110. Find the moments of inertia about the centroidal axes for the section shown in
fig.
111. The 50kg block shownin fig rests on a horizontal plane for which the
coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.3. If the block is pulled by a 350N force as shown
determine the velocity of the block after it has moved 65m starting from the rest. Use
principal of work and energy.
112. A stone is thrown vertically upward from the top of a 30 m high building with
a velocity of 15m/s. Taking the acceleration of stone as 9.81m/s
2
and taking that as
constant, determine the velocity v and elevation SY of the stone above the ground at
any time t, the maximum altitude reached by the stone and the time when the stone
strikes the ground.
ETGE181
113. The three concurrent forces in space F1, F2 and F3 acting at A shown in fig an
unknown force F, attached to the system makes the particle A in equilibrium. Find the
magnitude and direction of the unknown force F
114. Two cables which have known tensions are attached to the top of the tower
AB. A third cable AC is used as a guy wire as shown in figure. Determine the tension
in AC if the resultant of the forces exerted at A by the three cables acts vertically
downward.
115. Find the resultant of the system shown in fig. Find the point of intersection of
its line of action with AC and CD. The 27nm couple applied at the C is removed and
replaced by a couple of unknown magnitude M. Determine the value of M if the
resultant forces is pass through C.
116. A truss of 8m span is loaded as shown in fig. Find the support reactions
117. Locate the centroid of the area shown below
118. Find the moment of inertia of an unsymmetrical I section of top flange 60 x 20
mm, bottom flange 100 x 20mm and web 20 x 60mm about its centroidal axes
119. The equation of motion of a particle is given acceleration a in terms of time t
as below a = 3t
2
+2t+4 in which acceleration is in m/s
2
and time t is in seconds. It is
observed that the velocity of the particle is 12m/s after 4 seconds and the
displacement of the particle is 8m after 4 seconds. Determine the velocity after 8
seconds and displacement after 2 seconds
120. The figure shows a body of weight 300N on a smooth horizontal plane is
attached by a string to a 30N weight which hangs vertically. Find the acceleration of
the system and the tension in the string.
121. Find the force P inclined at an angle of 32
0
to the inclined plane making an
angle of 25
0
with the horizontal plane to slide a block weighing 125kN. Up the
inclined plane and down the inclined plane when =0.5
122. In the engine system shown in figure the crank AB has a constant clockwise
angular velocity of 300rpm. For the crank position indicated find the angular velocity
of the connecting rod and velocity of the piston.
V4594
123. State and prove Varignons theorem.
124. The resultant of two forces f
1
and F
2
acting at a point is R. If F
2
is doubled R is
also doubled and if the direction of F
2
is changed R is again doubled. Prove that
F
1
:F
2
:R=2:3:2
125. Forces 32kN, 24kN, 24kN and 120kN are concurrent at origin and are
respectively directed through the points whose coordinates are A(2,1,6), B(4,-2,-5),
C(-3,-2,1) and D(5,1,-2). Determine the resultant.
126. Find the resultant of the force system shown in fig and its position from A. (
force in kN and distance in m)
127. For the force system shown in fig determine the direction and magnitude of
the resultant from 0
128. Find the reaction at supports for the beam shown in fig.
129. The weight of the plate is 350N and is supported by three wires as shown in
fig, Determine the tension in the wires
130. Reduce the force system shown in fig into force couple system at 0
131. Calculate the moment of inertia of the section shown in fig about its centroidal
xx and yy axis.
132. State and prove perpendicular axis theorem
133. Find the mass moment of inertia of a thin circular disc ( I
xx
,I
yy
,I
zz
)
134. A block of wt 1290N rests on a horizontal surface and supports another block
of weight 570 N on top of it as shown in fig. Find the force P applied to the lower
block that will be necessary to cause slipping to impend. Coefficient of friction
between block 1 and 2 is 0.25 and coefficient of friction between block 1 and surface
is 0.40
135. A mass 12 kg travelling to the right with a speed of 8m/s collides with another
mass 20kg to the left travelling with a speed of 25m/s. IF the coefficient of restitution
is 0.60 find the velocities of the particles after collision and loss of kinetic energy.
What is the impulse acting on either particle during impact?
136. A truck moving with a velocity of 10m/s experiences a suddenly applied
brake. It was observed that the truck shown in fig skidded to rest in 7.5m. If the mass
of the truck is 300kg, determine the magnitude of normal reaction and frictional foce
on each wheel when the truck skidded to rest.
137. The link Bc shown in fig is rotating clockwise with an angular velocity of
0.25rad/s. determine the velocity of the block c and the angular velocity of the link
AB at that instant.
C3374
138. Five forces act on a particle as shown in fig. determine the resultant force in
magnitude and direction
139. A force of magnitude 10kN starts from a point A(2,1,-3) and passes thorugh
the point B (6,3,1). Represent the force in terms of unit vectors i,j,k. Also find the
components of the force along the three directions and the angle made by the force
with these directions.
140. Two cylinders of diameter 50mm and 25mm weighing 150N and 50N
respectively are placed as shown in fig. Assuming all contact surfaces to be smooth
and find the reactions at A, B, C and D.
141. For a hanging weight of 300N at A as shown in fig. find the forces in the
members AB, AC and AD of the wall bracket.
142. For the plane section shown in fig determine the moment of inertia about its
horizontal and vertical centroidal axes.
143. From first principles derive the expressions for the mass moment of inertia of
a thin circular plate about its polar axis and a sphere.
144. A body of weight 100 N is placed on a 30
0
inclined plane. Determine the
minimum force to be applied on the block and parallel to the plane to just move the
body up the plane and just prevent the body from sliding down the inclined plane.
Take the coefficient of friction as 0.2.
145. A body of mass 5kg moving with an unknown speed hits centrally a stationary
body B of mass 10kg. The speed of the body B after impact is 8m/s, if the coefficient
of restitution is 0.6, find the velocity of A before and after impact. Also find the
kinetic energy lost during impact.
146. The end A of the rod AB 1.8m long shown in fig moves with a velocity of
6m/s towards left. When =25
0
, determine the angular velocity of the rod and the
velocity of the end B.
147. What is the angular acceleration of the pulley shown in fig if its mass moment
of inertia is 20kgm
2
?
H252
148. Determine the magnitude direction and position of a single force P which
keeps in equilibrium the system of forces acting ath the corners of a rectangular block
as shown in the fig. The position of force P may be stated by reference to axes with
origin O and coinciding with the edges of the block
149. Two smooth circular cylinders each of weight 1000N and radius 15cm are
connected at their centres by a suing AR of length 40cm and rest upon a horizontal
plane. A third cylinder of weight 2000N and of same radius is above the these two
cylinders as shown in the fig. Determine the force in the string AR and the pressure
produced on the floor at the points of contact D and E
150. Determine the moment of inertia of the shaded area shown in the following fig
151. Prove that the mass moment of inertia of a right circular cone of base radius
R, height H and mass M about its axis is 3/10 MR
2
.
152. A ladder 5m long and 250N weighs is placed against a vertical wall in a
position where its inclination to the vertical is 30
0
. A man weighing 800 N climbs the
ladder. At what position will he induce slipping? The coefficient of friction between
the wall and floor with the ladder is 0.2.
153. A leather belt is required to transmit 9kW from a pulley 120cm in diameter
running at 200rpm. The angle embraced is 165
0
and the coefficient of friction between
the leather belt and pulley is 0.3. The safe working stress for the leather belt is
140N/cm
2
thickness of the belt is 10mm and the density of the leather is 1gm/cm
3
.
Determine the width of the belt taking the centrifugal tension into account.
154. The angle of rotation of a body is given by the equation = 2r
3
-5t
2
+8t+6. Here
is expressed in radians and t in seconds. Determine angular velocity and angular
acceleration when t is 0 and 4 seconds.
155. A train of weight 1960 kN starts from rest and attains a speed of 120km/hr in 5
minutes. If the friction resistance of the track is 10N per kN of the trains weight,
determine the average pull required. Take gas 9.8m/s
2
.
156. Three locations A, B and C at a distance of 100m each are located along a
straight road. A car starting from rest and with uniform acceleration passes the
location A and takes 10 seconds to reach B and further 8 seconds to reach location C.
Calculate magnitude of acceleration of car, velocity of car at A, velocity of car at B
and distance of location A from the starting point.
157. A body of weight 196.2 N slides up a 30
0
inclined plane under the action of an
applied force 300N acting parallel to the inclined plane. The coefficient of friction is
0.2. If the body moves from rest, determine acceleration of the body ,the distance
travelled by the body in 4 seconds, velocity of the body after 4 seconds, kinetic
energy of the body after 4 seconds, work done in the body in 4 seconds, momentum of
the body after 4 seconds and impulse applied in 4 seconds.
158. Two bodies of mass m
1
and m
2
and of initial velocities u
1
and u
2
are having a
direct impact. Prove that the loss of kinetic energy due to impact in terms of masses of
two bodies and their velocities before impact is
)
[1-e
2
].
H313
159. The resultant of force system shown in fig is 520N alon the negative direction
of y axis. Determine P and.
160. Three concurrent forces in space F
1
, F
2
,F
3
are acting at A as shown in fig. An
unknown force F attached to the system makes the particle A in equilibrium. Find the
magnitude and direction of the unknown force F
.
161. A system of parallel forces are acting on a rigid bar as shown in fig. reduce the
system to a single force, a single force and couple at A and a single force and couple
at B.
162. The coordinates of points A and B in meters are A[1,2,3] and B[4,3,2]. A
force of magnitude 10kN passes through these points and is directed from A towards
B. Find the moment of these force about origin, about c[1,1,1], about x axis and about
an axis passing through points D[2.5,1.5,4] and E[4,3,5].
163. Find the centroid of the plane area shown in the fig.
164. Find the product of inertia and principal moment of inertia of the section
shown below.
165. A ball of mass 0.5kg moving with a velocity of 1m/s impinges on a ball of
mass 1kg, moving with a velocity of 0.75m/s. At the time of impact, the velocities of
the balls are parallel and inclined at 60
0
to the line joining centres. Determine the
velocities and directions of the balls after impact. Take e = 0.6.
166. Two cars are travelling towards each other on a lane road at 16m/s and 12m/s
respectively when 120m apart, both drivers realize to apply brakes. They succeed in
stopping simultaneously and just short of collision. Assuming constant deceleration of
each car determine time required for the cars to stop, deceleration of each car and
distance travelled by each car.
167. A ladder 4m long leans against a smooth vertical wall at an angle 60
0
with the
horizontal. The weight of the ladder is 700N. When a person weighing 600 N stands
on a rung 1.2m from the bottom of the ladder, the ladder is just about to slide.
Calculate the coefficient of friction between the ladder and the floor.
168. A 5kg uniform disc is attached upon a couple with constant magnitude of
10Nm. Find the work done when the disc has completed 2 revolutions starting from
rest. Find the angular velocity of disc. Take the radius of the disc as 0.4m.
You might also like
- The World Below Ashcan (Final Download)Document56 pagesThe World Below Ashcan (Final Download)Máté H.100% (2)
- Architecture Now 6Document31 pagesArchitecture Now 6Antoine Amphx50% (2)
- Assignment-3 Last Date To Submit-12/05/2023Document9 pagesAssignment-3 Last Date To Submit-12/05/2023Parth PawarNo ratings yet
- Anna University May/June 2013 Exams ME2151 Engineering Mechanics Important QuestionsDocument12 pagesAnna University May/June 2013 Exams ME2151 Engineering Mechanics Important QuestionsPrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- Engineering MechanicsDocument8 pagesEngineering MechanicsNanna ShivuNo ratings yet
- Part B Question BankDocument9 pagesPart B Question BankSriram SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Assignment Questions For All UnitsDocument10 pagesAssignment Questions For All UnitsPiyush BhandariNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Engg. MechanicsDocument18 pagesQuestion Bank Engg. MechanicsSakendra Kumar0% (2)
- 07a1ec09 Engineering MechanicsDocument4 pages07a1ec09 Engineering Mechanicsأشرف عليNo ratings yet
- Btes103 203 em QBDocument10 pagesBtes103 203 em QBSurajNo ratings yet
- Qns For End TermDocument8 pagesQns For End TermNilesh Tanna TannaNo ratings yet
- EM Coaching QBDocument10 pagesEM Coaching QBsaravananNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Predicted 3Document5 pagesMechanics Predicted 3rashmit.gharat0908No ratings yet
- Assignment I: Statics of Particles and Rigid BodiesDocument8 pagesAssignment I: Statics of Particles and Rigid BodiesmNo ratings yet
- PHYF105 Tutorial Questions S3y0809edDocument17 pagesPHYF105 Tutorial Questions S3y0809edfillyana01No ratings yet
- 12 MarksDocument23 pages12 Markslakshmigsr6610No ratings yet
- 1Document5 pages1reddiNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 1 of Engineering MechanicsDocument4 pagesAssignment No. 1 of Engineering Mechanicsfire912522No ratings yet
- Mechanics DADocument5 pagesMechanics DAMihir AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium Lamis Theorem and CylindersDocument10 pagesEquilibrium Lamis Theorem and Cylinders241154No ratings yet
- Em QPDocument3 pagesEm QPkb210538No ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 FrictionDocument5 pagesTutorial 5 FrictionAjwad HaziqNo ratings yet
- r05010302 Engineering Mechanics Feb 2008Document12 pagesr05010302 Engineering Mechanics Feb 2008prabhuram2005No ratings yet
- Kom 208Document2 pagesKom 208Muzaffar AlamNo ratings yet
- Engineering MechanicsDocument37 pagesEngineering Mechanicser_paramjeetgillNo ratings yet
- Pokhara University Applied Mechanics - I Question PapersDocument4 pagesPokhara University Applied Mechanics - I Question PapersBuddhisagar BastolaNo ratings yet
- Est 100 QP June 2022Document21 pagesEst 100 QP June 2022Arjun B KNo ratings yet
- EMech Prob Set IV FrictionDocument3 pagesEMech Prob Set IV FrictionSamrat SadhukhanNo ratings yet
- EM - Model Questions - 2023Document8 pagesEM - Model Questions - 2023Aadi AhwanitNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems Meng 223Document5 pagesPractice Problems Meng 223tambadavidpessimaNo ratings yet
- Practice Numericals On MOSDocument14 pagesPractice Numericals On MOSBinil Varghese AbrahamNo ratings yet
- HowDocument43 pagesHowAudrey Ruth V. SirunoNo ratings yet
- Ge8292 Rejinpaul Iq April May 2019 PDFDocument8 pagesGe8292 Rejinpaul Iq April May 2019 PDFThamizh gomathiNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument9 pagesQuestion Bankpragash100% (1)
- Belt Friction-Tute - 2021 PDFDocument4 pagesBelt Friction-Tute - 2021 PDF凵又个已刀了七乙个入厂大No ratings yet
- EM QB_Mid TermDocument6 pagesEM QB_Mid Termjayeshjoshi240No ratings yet
- DOM Unsolved ProblemDocument2 pagesDOM Unsolved ProblemAnkush LaybarNo ratings yet
- Corona Leave Assignment - EmechDocument14 pagesCorona Leave Assignment - EmechraghulNo ratings yet
- Statics of Rigid BodiesDocument11 pagesStatics of Rigid BodiesVan Christian QuerubinNo ratings yet
- Tutorial MEP 2023Document5 pagesTutorial MEP 2023Joshua Ng'ang'aNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics Part B Part C QuestionsDocument38 pagesEngineering Mechanics Part B Part C QuestionskganesanNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science MECE 3210U - Mechanical VibrationsDocument4 pagesFaculty of Engineering and Applied Science MECE 3210U - Mechanical VibrationsBilly JhunNo ratings yet
- QB18 PDFDocument10 pagesQB18 PDFRaNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT 1 Essentials of Mechanical EngineeringDocument2 pagesASSIGNMENT 1 Essentials of Mechanical EngineeringHari OmNo ratings yet
- Engineering MechanicsDocument18 pagesEngineering MechanicsSiva ChidambaramNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document3 pagesTutorial 2Muhammed IfkazNo ratings yet
- Correl 2 Until MidtermsDocument23 pagesCorrel 2 Until MidtermsKimberly TacaisanNo ratings yet
- Parallel ForceDocument3 pagesParallel ForceArif NecNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 4 2324Document3 pagesAssignment No 4 2324Pranav DhariwalNo ratings yet
- Pisiks 71 Prob SetsDocument8 pagesPisiks 71 Prob SetsAndroNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- A New System of Alternating Current Motors and TransformersFrom EverandA New System of Alternating Current Motors and TransformersRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- GearDocument14 pagesGearPreethi SharmiNo ratings yet
- Engineering MEchanics Part - ADocument7 pagesEngineering MEchanics Part - APreethi SharmiNo ratings yet
- Mark DataDocument8 pagesMark DataPreethi SharmiNo ratings yet
- UnitDocument6 pagesUnitPreethi SharmiNo ratings yet
- Edited AssignmentDocument1 pageEdited AssignmentPreethi SharmiNo ratings yet
- AmmeterDocument1 pageAmmeterPreethi SharmiNo ratings yet
- Eg AssignmentDocument2 pagesEg AssignmentPreethi Sharmi100% (1)
- Physics: Unit - Iii Fibre Optics and Its Applications PART - A (2 Marks)Document3 pagesPhysics: Unit - Iii Fibre Optics and Its Applications PART - A (2 Marks)Preethi SharmiNo ratings yet
- Physics: Unit - Iii Fibre Optics and Its Applications PART - A (2 Marks)Document3 pagesPhysics: Unit - Iii Fibre Optics and Its Applications PART - A (2 Marks)Preethi SharmiNo ratings yet
- Unit Wise 16 Mark QuestionsDocument29 pagesUnit Wise 16 Mark QuestionsPreethi SharmiNo ratings yet
- BooksDocument1 pageBooksPreethi SharmiNo ratings yet
- UnitDocument6 pagesUnitPreethi SharmiNo ratings yet
- Program AwardsDocument4 pagesProgram AwardsCantonCompassNo ratings yet
- Titan Case StudyDocument9 pagesTitan Case Studycoolmanvns2No ratings yet
- Villaflores V LimosDocument13 pagesVillaflores V LimosJenicaNo ratings yet
- Kirk KinnellDocument1 pageKirk Kinnelljody.eth.gonzalesNo ratings yet
- BIO091 Lab Course Info 20162017Document1 pageBIO091 Lab Course Info 20162017Imran AriffNo ratings yet
- No Words & Meaning Sentences: Written By:Nigah Hussain M.SC Physics:0349-7987024Document6 pagesNo Words & Meaning Sentences: Written By:Nigah Hussain M.SC Physics:0349-7987024Zawar HussainNo ratings yet
- U4.4.1 - Grammar - Presentation and ExercisesDocument32 pagesU4.4.1 - Grammar - Presentation and ExercisesASTRID NAOMI MALDONADO HUERTANo ratings yet
- 5 - Historical Foundation of Philippine Education - Pre-Spanish and Spanish EraDocument13 pages5 - Historical Foundation of Philippine Education - Pre-Spanish and Spanish EraPeter ReidNo ratings yet
- Astrology, Medicine and HealthDocument56 pagesAstrology, Medicine and HealthSoror Onyx100% (2)
- Ec 3 Lab Viva QuestionsDocument4 pagesEc 3 Lab Viva QuestionsDeepti Chandrasekharan0% (1)
- Crude Oil Research TaskDocument2 pagesCrude Oil Research TaskThomas BartelsNo ratings yet
- Project Topics RetailDocument2 pagesProject Topics RetailroyalbeastNo ratings yet
- Final Paper Migration and Diaspora - Presences in Wide Sargasso SeaDocument9 pagesFinal Paper Migration and Diaspora - Presences in Wide Sargasso SeaYa BoiNo ratings yet
- Nagkakaisang Maralita V Military ShrineDocument13 pagesNagkakaisang Maralita V Military ShrineJennefer AngolluanNo ratings yet
- Laxmi Handicrafts CatalogueDocument11 pagesLaxmi Handicrafts Catalogueideasthat worthNo ratings yet
- Physical, Mechanical, and Durability Properties of Gypsum-Portland Cement-Natural Pozzolan BlendsDocument8 pagesPhysical, Mechanical, and Durability Properties of Gypsum-Portland Cement-Natural Pozzolan BlendsIS AANo ratings yet
- CME Group Report On The Flash CrashDocument6 pagesCME Group Report On The Flash CrashDealBook100% (1)
- University of Malta Faculty of Economics, Manangement and Accountancy Department of AccountancyDocument12 pagesUniversity of Malta Faculty of Economics, Manangement and Accountancy Department of AccountancyAgenttZeeroOutsiderNo ratings yet
- 57 Best Keanu Reeves Quotes On Love, Loss, Movies & More - ParadeDocument1 page57 Best Keanu Reeves Quotes On Love, Loss, Movies & More - Paradefpvftp4v5vNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Forecasting: Nassim Nicholas Taleb, Yaneer Bar-Yam, Pasquale CirilloDocument10 pagesInternational Journal of Forecasting: Nassim Nicholas Taleb, Yaneer Bar-Yam, Pasquale CirilloStewart HendersonNo ratings yet
- EDUC 202: An Output Prepared byDocument13 pagesEDUC 202: An Output Prepared byAlcely TamegaNo ratings yet
- Eng Ek 127 Worksheet 2ADocument8 pagesEng Ek 127 Worksheet 2AkhicomNo ratings yet
- (M3-MAIN) Mediums and Styles in ArtDocument70 pages(M3-MAIN) Mediums and Styles in ArtKhristian SorianoNo ratings yet
- Gerhard Richter & HeideggerDocument3 pagesGerhard Richter & HeideggerKayra ÖzNo ratings yet
- Petitioners, vs. The Honorable Court of Appeals, San Miguel Corp., and Fgu InsuranceDocument194 pagesPetitioners, vs. The Honorable Court of Appeals, San Miguel Corp., and Fgu InsuranceRacel AbulaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Trains Australia 1st Edition E Mag OptimiseDocument34 pagesAnatomy Trains Australia 1st Edition E Mag OptimiseMartin Fabián100% (1)
- Liver Anatomy and Physiology: FunctionDocument4 pagesLiver Anatomy and Physiology: FunctionTheresa BergonioNo ratings yet
- I.21.109 Sayan Samanta Presentation On PET CTDocument20 pagesI.21.109 Sayan Samanta Presentation On PET CTSayan SamantaNo ratings yet