Practical: 3 Aim: GSM:: To Study and Compare Working Principle of GSM and CDMA
Practical: 3 Aim: GSM:: To Study and Compare Working Principle of GSM and CDMA
Uploaded by
trivedi_urvi9087Copyright:
Available Formats
Practical: 3 Aim: GSM:: To Study and Compare Working Principle of GSM and CDMA
Practical: 3 Aim: GSM:: To Study and Compare Working Principle of GSM and CDMA
Uploaded by
trivedi_urvi9087Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Practical: 3 Aim: GSM:: To Study and Compare Working Principle of GSM and CDMA
Practical: 3 Aim: GSM:: To Study and Compare Working Principle of GSM and CDMA
Uploaded by
trivedi_urvi9087Copyright:
Available Formats
Mobile Comm.
Lab Manual
Date:
PRACTICAL: 3
AIM: To study and compare working principle of GSM and CDMA.
GSM:
GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications, originally Groupe Spcial
Mobile), is a standard set developed by the European Telecommunications Standards
Institute (ETSI) to describe protocols for second generation (2G) digital cellular
networks used by mobile phones. It became the de facto global standard for mobile
communications used in all countries but a few.
The GSM standard was developed as a replacement for first generation (1G)
analog cellular networks, and originally described a digital, circuit switched network
optimized for full duplex voice telephony. This was expanded over time to include
data communications, first by circuit switched transport, then packet data transport via
GPRS (General Packet Radio Services) and EDGE (Enhanced Data rates for GSM
Evolution or EGPRS).
Further improvements were made when the 3GPP developed third generation
(3G) UMTS standards followed by fourth generation (4G) LTE Advanced standards.
Future of the Mobile Telephone:
In the future, your mobile phone could tell your computer to prepare the next
days schedule remind you about your evenings appointment, order your air conditions
to cool your house, heat the water in and turn on for the evening news, etc.
This is possible due to many news up working technologies. Technologies that
connect you any time, any where with many persons. All these technologies are uses
internet as a medium. In the future coverage is going to be the main factor.
GPRS (GENERAL PACKET RADIO SYSTEM):
GPRS which is the next generation technology has addressed most of the
problems associated with WAP. General packet radio system, which works more or
less on basic on which e-mail works, sends text and high and graphics data as packet
at very high speed. GPRS comes under 2.5 generation. Slow speed circuit switching
of GSM is replaced by high speed packet switching in GPRS.
The first generation mobile phones add only voice call facility, which was
replaced. By the second generation digital phones which added tax, data and message
services. The idea behind 3G to have c/g network std. instead of different types
adopted in America, Europe and Japan.
BLUETOOTH:
In the ultimate communication, Bluetooth is best technology, which allows
intelligent gadgets to the communication. With each other this how technology will
more science fiction a reality.
For example, it will make your refrigerator to place order for vegetables when
the stock is low. In the future, everyday devices such as cordless phone and palm
devices will operate on a single internet protocol and anything that is not on a web
enabled will fall.
DECE GP, Dahod
Mobile Comm. Lab Manual
Date:
3G:
3G is watching chips from your train with favourite soup. 3G is sending
images from the field to headquarters for analysis. The 3G is sharing your morocen
variation with your friend from morroco. 3G is video conferencing in a taxi. 3G is
future of everyday communication. You may have seen terms in like GPRS, EDGE,
HSPA and UMTS. All of these are concepts related to development of mobile
communication n/ws to 3G.
CDMA:
Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) is a spread spectrum technology that
spreads multiple conversations across a wide segment of the spectrum as opposed to
splitting a channel into time slots, it comes under 3G. With CDMA, unique digital
codes are used to differentiate subscribers that are simultaneously using the same
spectrum.
GSM and CDMA:
Although both refer to cellular phone networks, GSM and CDMA differ in the
technology that they use. CDMA uses a system in which all signals are sent at the
same time, but each is spread across multiple frequencies. Servers assign an
individual code to each transmission so that the signals don't interfere with each other
and can be matched up between the sender and receiver.
Originally, the two protocols differed in signal quality, consistency, and voice
distortion, among other features. Both methods have been improved, however, and
there are few significant differences between the two in terms of call quality. GSM
phones are slightly more likely to drop calls as a user moves between cell towers, but
they have better coverage in places with a lot of mountains. This technology also
allows for voice and data transmission at the same time, which most CDMA phones
cannot do.
CDMA ADVANTEGES:
1. Increases Voice Capacity
2. Higher Throughput
3. Frequency Band Flexibility
4. Multicast Services
5. Service Multiple Market
6. Supports Multiple Service Platforms.
7. Full Backward Compatibility
8. Increased Battery Life
9. Synchronization
10. Power Control
11. Soft Handoff
12. Transmit Diversity
13. Traffic Channel
14. Supplemental Channel
15. Turbo Coding
DECE GP, Dahod
Mobile Comm. Lab Manual
Date:
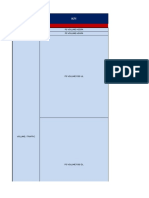
COMPARISION OF GSM AND CDMA:
GSM
CDMA
Uses time division multiple access.
Uses code division multiple access.
Information transmitted over small period Information transmitted over wide
of time called burst.
bandwidth with unique code known to
intended transmitter & receiver only.
Frequency reuse concept is used.
All cells have frequency band.
Hard handoff requires.
Soft hand off is employed.
Capacity is compare to CDMA.
Capacity is high compare to GSM.
GSM has a fixed maximum cell site CDMA can use higher range by increase
range of 35km, which is imposed by power spectrum density but it increase to
technical limitation.
other system.
Data transfer speed is lower compare to Data transfer speed is higher compare to
CDMA.
GSM.
For higher speed & value added service The migrate path of CDMA is from ISGSM adds the concept of GPRS and 95A to CDMA2000 to CDMA2000 3*
EDGE technology from 2G to 3G & MC for higher speed & value added
migrate toward WCDMA.
service.
GPRS uses GMSK modulation while CDMA uses Direct sequence or
EDGE uses 8PSK modulation.
frequency hoping modulation.
Most popular around the globe word wide Growing at faster rate.
roaming in more than 200 countries.
Capacity is limited by allocated Capacity is limited by available codes.
bandwidth.
Data transmission is discontinuous hence CDMA extends battery life by using
increase battery life.
effective power control.
Security is less compare to CDMA.
CDMA systems are more secure.
CONCLUSION:
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
DECE GP, Dahod
You might also like
- Session 21: Telecom TechnologiesDocument11 pagesSession 21: Telecom TechnologiesPrateek DagarNo ratings yet
- C C C C C CC C C C C CDocument50 pagesC C C C C CC C C C C Cankitahuja25No ratings yet
- State of The Art of Modulation Techniques Being Used in Various Communication TechnologiesDocument5 pagesState of The Art of Modulation Techniques Being Used in Various Communication TechnologiesSabbir AhmedNo ratings yet
- 3g Technology Background4901Document2 pages3g Technology Background4901Ridwanul HaqNo ratings yet
- EDGE: Enhanced Data Rates For GSM EvolutionDocument38 pagesEDGE: Enhanced Data Rates For GSM EvolutionShebin.A.Khalam100% (1)
- 2g HistoryDocument8 pages2g HistoryVivek DubeyNo ratings yet
- 4G and Its EvolutionDocument11 pages4G and Its EvolutionVamsee KrishnaNo ratings yet
- History of Mobile GenerationsDocument7 pagesHistory of Mobile GenerationsBasel wesamNo ratings yet
- CDMA InterviewDocument6 pagesCDMA InterviewronyiutNo ratings yet
- Different Communication Methods: Short Message Service (SMS) Is A Service Available On Most DigitalDocument6 pagesDifferent Communication Methods: Short Message Service (SMS) Is A Service Available On Most Digitalapi-26681123No ratings yet
- What Is 1G?: System For Mobile CommunicationsDocument6 pagesWhat Is 1G?: System For Mobile CommunicationsRajiv BhardwajNo ratings yet
- A New Approach To Minimise Network Blocking in 4g For Better AccessibilityDocument5 pagesA New Approach To Minimise Network Blocking in 4g For Better AccessibilityericNo ratings yet
- 4G TechnologyDocument28 pages4G Technologyarpit109100% (3)
- EE-480 Wireless Communications Week 9: Dr. Sajjad Shami Eed SST UMT LahoreDocument25 pagesEE-480 Wireless Communications Week 9: Dr. Sajjad Shami Eed SST UMT LahoreM Usman RiazNo ratings yet
- GSM Vs CDMA Vs TDMADocument3 pagesGSM Vs CDMA Vs TDMAMohak BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of GSM, CDMA, 2G, 3G and 4 G Methods What Is GSM?Document14 pagesComparative Study of GSM, CDMA, 2G, 3G and 4 G Methods What Is GSM?Clean 91No ratings yet
- What Is 2G?Document19 pagesWhat Is 2G?Haya MalikNo ratings yet
- Edge TechDocument18 pagesEdge TechshashiNo ratings yet
- Need For A Wireless WAN SolutionDocument27 pagesNeed For A Wireless WAN Solutionపుష్ప ఎం ఎస్ డిNo ratings yet
- 2G ScamDocument27 pages2G ScamDurgesh SawantNo ratings yet
- General Packet Radio ServicDocument38 pagesGeneral Packet Radio ServicAmitesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Telecom PresentationDocument33 pagesTelecom PresentationGamme T MijanNo ratings yet
- General Packet Radio ServiceDocument30 pagesGeneral Packet Radio ServicesamhithaupadhyaNo ratings yet
- Presented To: Presented byDocument23 pagesPresented To: Presented byfazlurrahman86No ratings yet
- Cellular Network ArchitectureDocument7 pagesCellular Network ArchitectureArul DeepaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Mobile Phone Service (AMPS) - Can Support 5 To 10 Times More Users in TheDocument2 pagesAdvanced Mobile Phone Service (AMPS) - Can Support 5 To 10 Times More Users in Thehoiyen92No ratings yet
- Wireless Telephone Technology GSM Finland Radiolinja Elisa OyjDocument4 pagesWireless Telephone Technology GSM Finland Radiolinja Elisa OyjHemalatha BalusamyNo ratings yet
- 3G 4GDocument24 pages3G 4Gsyed_engrNo ratings yet
- EDGE ReportDocument22 pagesEDGE ReportSowmya SowmyaNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks Assignment-2: Topic-Working of Physical Layer in 1G, 2G, 3G and 4G NetworksDocument12 pagesComputer Networks Assignment-2: Topic-Working of Physical Layer in 1G, 2G, 3G and 4G NetworksPunit KyalNo ratings yet
- 3G Is An One of A Most Recent Radio Transmission Technologies (RTTS)Document19 pages3G Is An One of A Most Recent Radio Transmission Technologies (RTTS)th_vaibhavsinghNo ratings yet
- Access Methods For Mobile Networks - ShavaneDocument2 pagesAccess Methods For Mobile Networks - ShavaneDrumz Staff50% (2)
- GPRS 143Document10 pagesGPRS 143Engr. Naveed MazharNo ratings yet
- Mobile Evolution v1.5Document7 pagesMobile Evolution v1.5Sandeep Guha NiyogiNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Joemarie C. Tiyang John Lyod Limen Gilbas Josue U. Ruenata Jr. Reyniel John FranciscoDocument24 pagesGroup 4 Joemarie C. Tiyang John Lyod Limen Gilbas Josue U. Ruenata Jr. Reyniel John FranciscotiyangjoemNo ratings yet
- (3G and Wcdma) : Project ReportDocument42 pages(3G and Wcdma) : Project ReportMukesh ManwaniNo ratings yet
- GPRS, GSM, CdmaDocument3 pagesGPRS, GSM, CdmaDulce DeNo ratings yet
- Devasenapathi. A, Mohamed Siraj. B Theni Kammavar Sangam College of TechnologyDocument7 pagesDevasenapathi. A, Mohamed Siraj. B Theni Kammavar Sangam College of TechnologyJose DahlsonNo ratings yet
- Technical DetailsDocument6 pagesTechnical DetailsShamim AhmedNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication TechnologiesDocument10 pagesWireless Communication TechnologiesDino LigutanNo ratings yet
- GPRS - User CountDocument6 pagesGPRS - User CountAlthaf HussainNo ratings yet
- 2 G Network: 2G (Or 2-G) Is Short For Second-Generation Wireless Telephone Technology. Second GenerationDocument26 pages2 G Network: 2G (Or 2-G) Is Short For Second-Generation Wireless Telephone Technology. Second GenerationVikas NagareNo ratings yet
- Mobile Technology: Evolution From 1G To 4G: CommunicationsDocument5 pagesMobile Technology: Evolution From 1G To 4G: CommunicationsHammna AshrafNo ratings yet
- Difference in 1G, 2G, 3G, 4GDocument5 pagesDifference in 1G, 2G, 3G, 4GAamir MalikNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Mobile CommunicationDocument6 pagesEvolution of Mobile CommunicationIroshan Priyantha100% (2)
- 1G, 2G and 3G Spectrum: 1G (Or 1-G) Refers To The First-Generation ofDocument6 pages1G, 2G and 3G Spectrum: 1G (Or 1-G) Refers To The First-Generation ofEkta RaiNo ratings yet
- Mobile and Wireless Communication Complete Lecture Notes #2Document28 pagesMobile and Wireless Communication Complete Lecture Notes #2Student Lecture NotesNo ratings yet
- Mobile Multimedia CommunicationDocument24 pagesMobile Multimedia CommunicationVikas KadamNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On Cdma TechnologyDocument102 pagesA Project Report On Cdma Technologyanujag007100% (2)
- Past Applications of Multi-Carrier - COMDocument3 pagesPast Applications of Multi-Carrier - COMNipuna Nuwan NanayakkaraNo ratings yet
- How 2G Technology WorksDocument4 pagesHow 2G Technology WorksAltin Tini100% (1)
- Evolution: Zero Generation (0G - 0.5G)Document22 pagesEvolution: Zero Generation (0G - 0.5G)Saurabh G100% (5)
- Chapter 2Document12 pagesChapter 2Badri Vishal PandeyNo ratings yet
- WP Trillium 3G WirelessDocument10 pagesWP Trillium 3G WirelessrajeshgautNo ratings yet
- 3G ArchitectureDocument11 pages3G ArchitecturelqcckagopzkluvrayxNo ratings yet
- GSM Structure 2G and 3GDocument2 pagesGSM Structure 2G and 3GChris Ng'weno OmotoNo ratings yet
- Why People Choose 3G-Radio Access SystemDocument4 pagesWhy People Choose 3G-Radio Access SystemNur E'zzati RidzuanNo ratings yet
- Essential 4G Guide: Learn 4G Wireless In One DayFrom EverandEssential 4G Guide: Learn 4G Wireless In One DayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (12)
- Indoor Radio Planning: A Practical Guide for 2G, 3G and 4GFrom EverandIndoor Radio Planning: A Practical Guide for 2G, 3G and 4GRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 3351102Document7 pages3351102trivedi_urvi9087100% (1)
- AdHoc NetworksDocument35 pagesAdHoc Networkstrivedi_urvi9087100% (1)
- PCB Lab ManualDocument16 pagesPCB Lab Manualtrivedi_urvi9087No ratings yet
- 02-Matlab Subroutines Used in The SimulationDocument17 pages02-Matlab Subroutines Used in The Simulationtrivedi_urvi9087No ratings yet
- What Is GMSK ModulationDocument5 pagesWhat Is GMSK Modulationtrivedi_urvi9087No ratings yet
- GSM Frame StructureDocument14 pagesGSM Frame Structuretrivedi_urvi9087100% (1)
- 802.22 Based On CrsDocument60 pages802.22 Based On Crstrivedi_urvi9087No ratings yet
- B SMF Chapter 010011Document18 pagesB SMF Chapter 010011Ramakrishna KotaNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Guideline For VoLTE - v0.5Document113 pagesTroubleshooting Guideline For VoLTE - v0.5HoudaNo ratings yet
- Root Counter Level-1 Counter: L.RRC - Setupfail.ResfailDocument18 pagesRoot Counter Level-1 Counter: L.RRC - Setupfail.ResfailБотирали Азибаев100% (1)
- GSM-R SR20Document375 pagesGSM-R SR20kepscoNo ratings yet
- 4g Mobile Communication System A Seminar Report (1) Computer Science Seminar TopicsDocument7 pages4g Mobile Communication System A Seminar Report (1) Computer Science Seminar TopicsfinitehourabyssNo ratings yet
- MPEG Video CompressionDocument14 pagesMPEG Video CompressionGurukrushna PatnaikNo ratings yet
- r/NoContract Cell Phone Plans!Document1 pager/NoContract Cell Phone Plans!ybe_85No ratings yet
- CellularDocument81 pagesCellularJaser MaharusNo ratings yet
- UMTS RF Troubleshooting GuidelinesDocument111 pagesUMTS RF Troubleshooting GuidelinesAbhishek Jain100% (1)
- Cisco D9854-I Advanced Program Receiver: Product OverviewDocument7 pagesCisco D9854-I Advanced Program Receiver: Product OverviewIrving MartinNo ratings yet
- 10 GSM BSS Network KPI (Uplink-Downlink Balance) Optimization ManualDocument12 pages10 GSM BSS Network KPI (Uplink-Downlink Balance) Optimization ManualavonsusNo ratings yet
- Sertifikat Certificate: NOMOR: 65437/SDPPI/2020Document1 pageSertifikat Certificate: NOMOR: 65437/SDPPI/2020arryNo ratings yet
- Cognitive RadioDocument34 pagesCognitive RadioSiddharth Negi89% (9)
- PS IRAT U2G Optimization 2Document18 pagesPS IRAT U2G Optimization 2buscandoconocerteNo ratings yet
- LTE Frequency BandsDocument6 pagesLTE Frequency BandsBhagirathi SahuNo ratings yet
- List of Operator - AfricaDocument114 pagesList of Operator - AfricaRafi AnsariNo ratings yet
- Worst Cells Action Plan-50215Document569 pagesWorst Cells Action Plan-50215Roland BAKETUNGANo ratings yet
- SSS Parameters V1Document3 pagesSSS Parameters V1Ravi KumarNo ratings yet
- Principles of Communication SystemsDocument21 pagesPrinciples of Communication SystemsOdoch HerbertNo ratings yet
- Kpi Type KPI 3G: Ps Volume Hsdpa Ps Volume HsupaDocument12 pagesKpi Type KPI 3G: Ps Volume Hsdpa Ps Volume HsupaDaneil RadcliffeNo ratings yet
- CTU2DDocument4 pagesCTU2Djamal48No ratings yet
- IMT-2000 Network ArchitectureDocument6 pagesIMT-2000 Network ArchitectureMuhd Hisyam AwangNo ratings yet
- IEEE 802.11: Mobility and Evolutions: 4Tc - ArmDocument31 pagesIEEE 802.11: Mobility and Evolutions: 4Tc - ArmdocteurgynecoNo ratings yet
- SRVCC Feature Description RAN16Document63 pagesSRVCC Feature Description RAN16Hossein Nazari100% (1)
- The Hacker's Hardware Toolkit 2nd Edition: Yago HansenDocument184 pagesThe Hacker's Hardware Toolkit 2nd Edition: Yago HansenNewdelhi88% (8)
- 3GPP TS 36.300: Technical SpecificationDocument403 pages3GPP TS 36.300: Technical Specificationomcr1No ratings yet
- Description: Huawei 3G To 4G ReselectionDocument2 pagesDescription: Huawei 3G To 4G Reselectioninfo vistaNo ratings yet
- MNP Introduction MNP Seminar CETTM 270910Document17 pagesMNP Introduction MNP Seminar CETTM 270910Deepak MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Gcell Ooredo Myanmar GSM 19 Nov 2018Document1,037 pagesGcell Ooredo Myanmar GSM 19 Nov 2018roni100% (1)
- 802.11 StandardDocument3 pages802.11 StandardDaljit SinghNo ratings yet