Java Remote Method Invocation
Uploaded by
Lulu TojeenJava Remote Method Invocation
Uploaded by
Lulu Tojeen20/8/2014
Java remote method invocation
Browse
Topics
Documents
Terms
About
WARNING: DO NOT CITE
Search
Java remote method invocation
related topics
{system, computer, user}
{math, number, function}
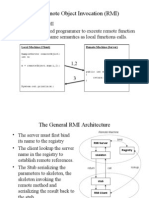
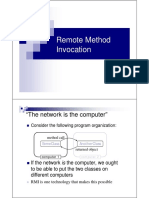
The Java Remote Method Invocation Application Programming Interface (API), or Java
RMI, is a Java application programming interface that performs the object-oriented
equivalent of remote procedure calls (RPC).
Wavelet compression
Usage of the term RMI may denote solely the programming interface or may signify both
the API and JRMP, whereas the term RMI-IIOP (read: RMI over IIOP) denotes the RMI
interface delegating most of the functionality to the supporting CORBA implementation.
Application programming
interface
The programmers of the original RMI API generalized the code somewhat to support
different implementations, such as a HTTP transport. Additionally, the ability to pass
arguments "by value" was added to CORBA in order to support the RMI interface. Still, the
RMI-IIOP and JRMP implementations do not have fully identical interfaces.
RMI functionality comes in the package java.rmi, while most of Sun's implementation is
located in the sun.rmipackage. Note that with Java versions before Java 5.0 developers
had to compile RMI stubs in a separate compilation step using rmic. Version 5.0 of Java
and beyond no longer require this step.
Jini offers a more advanced version of RMI in Java. It functions similarly but provides more
advanced searching capabilities and mechanisms for distributed object applications.[1]
related documents
Netwide Assembler
Scanline rendering
Alternating bit protocol
Wikipedia:Federal
Standard 1037C
terms/telecommunications
encryption terms
Pseudorandom noise
Gnumeric
GNUstep
Cacti (software)
Contents
1 Example
2 See also
3 References
4 External links
Automatic data processing
Challenge-handshake
authentication protocol
Applet
Example
Pico (text editor)
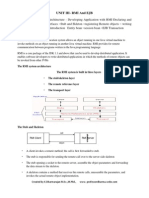
The following classes implement a simple client-server program using RMI that displays a
message.
RmiServerclassListens
to RMI requests and implements the interface which is used by
the client to invoke remote methods.
import java.rmi.Naming;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import java.rmi.RMISecurityManager;
import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject;
import java.rmi.registry.*;
public class RmiServer extends UnicastRemoteObject
implements RmiServerIntf {
public static final String MESSAGE = "Hello world";
public RmiServer() throws RemoteException {
}
public String getMessage() {
return MESSAGE;
}
Type code
Sinclair Scientific
Instruction register
Acme (text editor)
A20 handler
Distributed database
Rock Ridge
Binary image
Truncated binary
exponential backoff
Terabyte
Data stream
Mail transfer agent
XMMS
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("RMI server started");
// Create and install a security manager
if (System.getSecurityManager() == null) {
System.setSecurityManager(new RMISecurityManager());
System.out.println("Security manager installed.");
} else {
System.out.println("Security manager already exists.");
}
Layout engine
Baud
OS/390
try { //special exception handler for registry creation
LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099);
System.out.println("java RMI registry created.");
} catch (RemoteException e) {
//do nothing, error means registry already exists
System.out.println("java RMI registry already exists.");
}
try {
//Instantiate RmiServer
RmiServer obj = new RmiServer();
// Bind this object instance to the name "RmiServer"
Naming.rebind("//localhost/RmiServer", obj);
https://www.princeton.edu/~achaney/tmve/wiki100k/docs/Java_remote_method_invocation.html
1/2
20/8/2014
Java remote method invocation
System.out.println("PeerServer bound in registry");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("RMI server exception:" + e);
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
RmiServerIntfclassDefines
the server.
the interface that is used by the client and implemented by
import java.rmi.Remote;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
public interface RmiServerIntf extends Remote {
public String getMessage() throws RemoteException;
}
RmiClientclassThis
is the client which gets the reference to the remote object and
invokes its method to get a message.
import java.rmi.Naming;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import java.rmi.RMISecurityManager;
public class RmiClient {
// "obj" is the reference of the remote object
RmiServerIntf obj = null;
public String getMessage() {
try {
obj = (RmiServerIntf)Naming.lookup("//localhost/RmiServer");
return obj.getMessage();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("RmiClient exception: " + e);
e.printStackTrace();
return e.getMessage();
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Create and install a security manager
if (System.getSecurityManager() == null) {
System.setSecurityManager(new RMISecurityManager());
}
RmiClient cli = new RmiClient();
System.out.println(cli.getMessage());
}
}
Before running this subj, we need to make 'Stub' file of interface we used. For this task we
have RMI compiller - 'rmic'
Note: we make stub file from *.class with implementation remote interface, not
'*.java'*
rmic RmiServer
server.policyThis
file is required on the server to allow TCP/IP communication for the
remote registry and for the RMI server.
grant {
permission java.net.SocketPermission "127.0.0.1:*", "connect,resolve";
permission java.net.SocketPermission "127.0.0.1:*", "accept";
};
The server.policy file should be used using the D switch of Java RTE, e.g.:
java.exe -Djava.security.policy=server.policy RmiServer
client.policyThis
file is required on the client to connect to RMI Server using TCP/IP.
grant {
permission java.net.SocketPermission "127.0.0.1:*", "connect,resolve";
};
no.policyAlso if
you have a troubles with connecting, try this file for server or client.
Full article
The article content of this page came from Wikipedia and is governed by CC-BY-SA.
https://www.princeton.edu/~achaney/tmve/wiki100k/docs/Java_remote_method_invocation.html
2/2
You might also like
- Application of DSP in Video CompressionNo ratings yetApplication of DSP in Video Compression12 pages
- Solution Operations - Run SAP Like A FactoryNo ratings yetSolution Operations - Run SAP Like A Factory16 pages
- (PDC) Lecture 10 - Remote Method Invocation (RMI)No ratings yet(PDC) Lecture 10 - Remote Method Invocation (RMI)11 pages
- Lecture 07 Remote Method Invocation in JavaNo ratings yetLecture 07 Remote Method Invocation in Java14 pages
- Chapter 5 Remote Method Invocation (RMI)No ratings yetChapter 5 Remote Method Invocation (RMI)28 pages
- Chapter 5 - Distributed Programming (RMI & CORBA)No ratings yetChapter 5 - Distributed Programming (RMI & CORBA)46 pages
- An Overview of RMI Applications: Distributed Object ApplicationNo ratings yetAn Overview of RMI Applications: Distributed Object Application5 pages
- Remote Method Invocation in Java: Bennie Lewis EEL 6897No ratings yetRemote Method Invocation in Java: Bennie Lewis EEL 689718 pages
- Communications in Java RMI: Remote Object (Server) ClientNo ratings yetCommunications in Java RMI: Remote Object (Server) Client3 pages
- Remote Method Invocation (RMI), Corba, Idl, Rmi-Iiop & JarNo ratings yetRemote Method Invocation (RMI), Corba, Idl, Rmi-Iiop & Jar58 pages
- Java Programming Chapter 6.2 RMI IntroductionNo ratings yetJava Programming Chapter 6.2 RMI Introduction15 pages
- Advance Java Notes For B.C.a (2012) Unit III, IV, V.No ratings yetAdvance Java Notes For B.C.a (2012) Unit III, IV, V.29 pages
- Java Programming Chapter 6.2 RMI IntroductionNo ratings yetJava Programming Chapter 6.2 RMI Introduction15 pages
- Chapter 6 - RMI (Remote Method Invocation)No ratings yetChapter 6 - RMI (Remote Method Invocation)22 pages
- August 2010 Master of Computer Application (MCA) - Semester 4 MC0078 - Java Programming - 4 CreditsNo ratings yetAugust 2010 Master of Computer Application (MCA) - Semester 4 MC0078 - Java Programming - 4 Credits26 pages
- August 2010 Master of Computer Application (MCA) - Semester 4 MC0078 - Java Programming - 4 CreditsNo ratings yetAugust 2010 Master of Computer Application (MCA) - Semester 4 MC0078 - Java Programming - 4 Credits26 pages
- Chapter 5 Remote Procedure Call - and - Remote Method InvocationNo ratings yetChapter 5 Remote Procedure Call - and - Remote Method Invocation20 pages
- Lecture 7 - New - Remote Method InvocationNo ratings yetLecture 7 - New - Remote Method Invocation25 pages
- Remote Method Registry Service Stub Skeleton: Terminology Related To RMINo ratings yetRemote Method Registry Service Stub Skeleton: Terminology Related To RMI9 pages
- Understanding Software Engineering Vol 3: Programming Basic Software Functionalities.From EverandUnderstanding Software Engineering Vol 3: Programming Basic Software Functionalities.No ratings yet
- Python Advanced Programming: The Guide to Learn Python Programming. Reference with Exercises and Samples About Dynamical Programming, Multithreading, Multiprocessing, Debugging, Testing and MoreFrom EverandPython Advanced Programming: The Guide to Learn Python Programming. Reference with Exercises and Samples About Dynamical Programming, Multithreading, Multiprocessing, Debugging, Testing and MoreNo ratings yet
- Names Variables Type Checking Strong Typing Type CompatibilityNo ratings yetNames Variables Type Checking Strong Typing Type Compatibility18 pages
- RT 701 Object Oriented Modeling and Design - Module 4No ratings yetRT 701 Object Oriented Modeling and Design - Module 418 pages
- 2 Motion Of A Simple Pendulum: θ mg tangent LNo ratings yet2 Motion Of A Simple Pendulum: θ mg tangent L8 pages
- Creating Pseudo 3D Games With HTML 5 Canvas and Raycasting - Part 2 - DevNo ratings yetCreating Pseudo 3D Games With HTML 5 Canvas and Raycasting - Part 2 - Dev18 pages
- Hitachi Storage Replication Adapter 2.1: For Vmware® Vcenter Site Recovery Manager™ 5.1/5.5 Deployment GuideNo ratings yetHitachi Storage Replication Adapter 2.1: For Vmware® Vcenter Site Recovery Manager™ 5.1/5.5 Deployment Guide68 pages
- Problem Solving with C 6th Edition Savitch - The full ebook version is available, download now to explore100% (1)Problem Solving with C 6th Edition Savitch - The full ebook version is available, download now to explore51 pages
- 1712051623INFT Autonomous Syllabus Sem III IV v VI VII VII Wef 2023 2024No ratings yet1712051623INFT Autonomous Syllabus Sem III IV v VI VII VII Wef 2023 2024376 pages
- Joint Entrance Examination (MAIN) - 2019: Important Instructions For CandidatesNo ratings yetJoint Entrance Examination (MAIN) - 2019: Important Instructions For Candidates1 page
- Revision History: Learning Management System For The College of The Holy Spirit ManilaNo ratings yetRevision History: Learning Management System For The College of The Holy Spirit Manila36 pages
- Measurement Systems Analysis - AppendicesNo ratings yetMeasurement Systems Analysis - Appendices53 pages
- Recommended Computer Specifications For 2013-2014: University of Kentucky, College of DesignNo ratings yetRecommended Computer Specifications For 2013-2014: University of Kentucky, College of Design1 page
- Rockwell Hardness Tester Versitron Spec SheetNo ratings yetRockwell Hardness Tester Versitron Spec Sheet11 pages