0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
Hertz Contact Stresses Sullivan
Hertz Contact Stresses Sullivan
Uploaded by
keikunbrThis document is a lecture on Hertz contact stresses presented by Mark Sullivan on February 9, 2009. It discusses Hertz contact stress theory, provides equations and graphs to calculate contact stresses, and analyzes kinematic couplings. It acknowledges sources used to create the lecture and provides strategies to reduce Hertz contact stresses such as decreasing force, increasing ball radius, and decreasing modulus of elasticity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
Hertz Contact Stresses Sullivan
Hertz Contact Stresses Sullivan
Uploaded by
keikunbr0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
This document is a lecture on Hertz contact stresses presented by Mark Sullivan on February 9, 2009. It discusses Hertz contact stress theory, provides equations and graphs to calculate contact stresses, and analyzes kinematic couplings. It acknowledges sources used to create the lecture and provides strategies to reduce Hertz contact stresses such as decreasing force, increasing ball radius, and decreasing modulus of elasticity.
Original Description:
Hertz Contact Stresses
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
This document is a lecture on Hertz contact stresses presented by Mark Sullivan on February 9, 2009. It discusses Hertz contact stress theory, provides equations and graphs to calculate contact stresses, and analyzes kinematic couplings. It acknowledges sources used to create the lecture and provides strategies to reduce Hertz contact stresses such as decreasing force, increasing ball radius, and decreasing modulus of elasticity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
Hertz Contact Stresses Sullivan
Hertz Contact Stresses Sullivan
Uploaded by
keikunbrThis document is a lecture on Hertz contact stresses presented by Mark Sullivan on February 9, 2009. It discusses Hertz contact stress theory, provides equations and graphs to calculate contact stresses, and analyzes kinematic couplings. It acknowledges sources used to create the lecture and provides strategies to reduce Hertz contact stresses such as decreasing force, increasing ball radius, and decreasing modulus of elasticity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1/ 13
Precision Machine Design
ME 250
Hertz Contact Stresses
Mark Sullivan
February 9, 2009
Precision Machine Design
Hertz Contact Stresses
Acknowledgements
Text and figures in these lecture notes are taken from the
following sources:
Slocum, A. H., Precision Machine Design, SME, 1992.
Slocum, A. H., FUNdaMENTALs of Design, MIT, 2008.
Culpepper, M., 2.75 Constraint Lecture, MIT, 2001.
Precision Engineering Research Group, MIT
http://pergatory.mit.edu/
http://pergatory.mit.edu/kinematiccouplings/
Sullivan
Feb 9, 2009
Page 2
Precision Machine Design
Hertz Contact Stresses
Hertz Contact Stresses
Sullivan
Feb 9, 2009
Chart from FUNdaMENTALs of Design, Slocum
Page 3
Precision Machine Design
Hertz Contact Stresses
Hertz Contact Stresses (2)
This is the general case.
For solved cases, see Roark
or MathCAD
Sullivan
Feb 9, 2009
Equations from FUNdaMENTALs of Design, Slocum
Page 4
Precision Machine Design
Hertz Contact Stresses
Hertz Contact Stresses (3)
Shear
Radial
Compressive
Sullivan
Feb 9, 2009
Graph and equations from FUNdaMENTALs of Design, Slocum
Page 5
Precision Machine Design
Hertz Contact Stresses
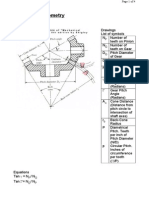
Kinematic Coupling Analysis
Sullivan
Feb 9, 2009
Chart from FUNdaMENTALs of Design, Slocum
Page 6
Precision Machine Design
Hertz Contact Stresses
KC Analysis Culpepper
Sullivan
Feb 9, 2009
Page 7
Precision Machine Design
Hertz Contact Stresses
KC Analysis Culpepper (2)
Sullivan
Feb 9, 2009
Page 8
Precision Machine Design
Hertz Contact Stresses
KC Analysis Culpepper (3)
Sullivan
Feb 9, 2009
Page 9
Precision Machine Design
Hertz Contact Stresses
Hertz Contact Stress Reduction
Contact pressure is proportional to:
Force to the 1/3rd power (F1/3)
Radius to the -2/3rd power (R-2/3)
Modulus to the 2/3rd power (E2/3)
Deflection3 is proportional to:
Force to the 2/3rd power (F2/3)
Radius to the -1/3rd power (R-1/3)
Modulus to the -2/3rd power (E-2/3)
Contact ellipse diameter is
proportional to:
Force to the 1/3rd power (F1/3)
Radius to the 1/3rd power (R1/3)
Modulus to the -1/3rd power (E-1/3)
Sullivan
Feb 9, 2009
To reduce Hertz stresses:
Decrease force (F)
Increase ball radius (R)
Decrease modulus (E)
To reduce deflection:
Decrease force (F)
Increase ball radius (R)
Increase modulus (E)
To reduce contact area:
Decrease force (F)
Decrease ball radius (R)
Increase modulus (E)
From FUNdaMENTALs of Design, Slocum
Page 10
Precision Machine Design
Hertz Contact Stresses
KC Analysis Sullivan
Sullivan
Feb 9, 2009
Page 11
Precision Machine Design
Hertz Contact Stresses
KC Analysis MathCAD
Sullivan
Feb 9, 2009
Page 12
Precision Machine Design
Hertz Contact Stresses
Pop Quiz: Contact Stress
Which 3 DOF mount has lower Hertz contact stresses? Why?
How could you make the stresses even lower?
3-Ball Nest
Tetrahedron
Sullivan
Feb 9, 2009
Page 13
You might also like
- Combilift Ltd. Operators & Service Manual.83% (58)Combilift Ltd. Operators & Service Manual.72 pages
- PECP5030!10!10.1 Edition Cat Hose Products & Tooling Guide100% (2)PECP5030!10!10.1 Edition Cat Hose Products & Tooling Guide524 pages
- Thermal and Efficiency Characterization of A Low-Backlash Planetary GearboxNo ratings yetThermal and Efficiency Characterization of A Low-Backlash Planetary Gearbox10 pages
- Spur - Gears - Metric - XLS: Tooth Normal ForceNo ratings yetSpur - Gears - Metric - XLS: Tooth Normal Force5 pages
- The Hertz Contact Problem - Solving in AbaqusNo ratings yetThe Hertz Contact Problem - Solving in Abaqus17 pages
- Ramberg Osgood Stress-Strain - WIKIPEDIANo ratings yetRamberg Osgood Stress-Strain - WIKIPEDIA3 pages
- CHABOCHE, J. L. - Continuum Damage Mechanics P.2 - Damage Growth, Crack InitiationNo ratings yetCHABOCHE, J. L. - Continuum Damage Mechanics P.2 - Damage Growth, Crack Initiation8 pages
- F= Π X Dt3 X Τk 8Xdmxk: Technical InformationNo ratings yetF= Π X Dt3 X Τk 8Xdmxk: Technical Information6 pages
- How To Tackle Convergence Issues Without Compromising Accuracy in Any Static Structural Non Linear Analysis Using ANSYS Workbench 13No ratings yetHow To Tackle Convergence Issues Without Compromising Accuracy in Any Static Structural Non Linear Analysis Using ANSYS Workbench 135 pages
- New Algorithms For Calculating Hertzian Stresses, Deformations, and Contact Zone Parameters PDFNo ratings yetNew Algorithms For Calculating Hertzian Stresses, Deformations, and Contact Zone Parameters PDF11 pages
- Finite Element Evaluation of The State of Cure in A TireNo ratings yetFinite Element Evaluation of The State of Cure in A Tire35 pages
- Effect of Shot Peening On The Fatigue Life of 2024 Aluminum Alloy PDFNo ratings yetEffect of Shot Peening On The Fatigue Life of 2024 Aluminum Alloy PDF12 pages
- Workshop 16 Thermal Stress Analysis of A Bi-Metalic PlateNo ratings yetWorkshop 16 Thermal Stress Analysis of A Bi-Metalic Plate40 pages
- Shigley's Mechanical Engineering Design Tutorial 3-19: Hertz Contact Stresses100% (1)Shigley's Mechanical Engineering Design Tutorial 3-19: Hertz Contact Stresses10 pages
- Criteria For Self Loosening of Fasteners Under VibrationNo ratings yetCriteria For Self Loosening of Fasteners Under Vibration5 pages
- 06-Chapter 3 - 2D Meshing-v2017.2.3-27JUNE-2018 PDFNo ratings yet06-Chapter 3 - 2D Meshing-v2017.2.3-27JUNE-2018 PDF82 pages
- Gear Trains: Qassim University Unayzah College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering DeptNo ratings yetGear Trains: Qassim University Unayzah College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Dept42 pages
- Design-II, 2016 Bevel Gear Design ProcedureNo ratings yetDesign-II, 2016 Bevel Gear Design Procedure1 page
- RADIOSS For Impact Analysis v12 Rev20130214 A PDFNo ratings yetRADIOSS For Impact Analysis v12 Rev20130214 A PDF328 pages
- Housing Influences On Churning Losses in Geared TransmissionsNo ratings yetHousing Influences On Churning Losses in Geared Transmissions6 pages
- PDF - M11ekm Fatigue and Fracture - Autumn 2010No ratings yetPDF - M11ekm Fatigue and Fracture - Autumn 201025 pages
- Reduction of Stress Concentration in Bolt Nut ConnectorsNo ratings yetReduction of Stress Concentration in Bolt Nut Connectors6 pages
- Calculation of Stress Time Signals of Multi-Bolted JointsNo ratings yetCalculation of Stress Time Signals of Multi-Bolted Joints8 pages
- Workshop 7 Thermal Contact Resistance: WS7-1 NAS104, Workshop 7, March 2004 2004 MSC - Software CorporationNo ratings yetWorkshop 7 Thermal Contact Resistance: WS7-1 NAS104, Workshop 7, March 2004 2004 MSC - Software Corporation24 pages
- Finite Element Analysis Using Hypermesh Radioss OR Optistruct PDFNo ratings yetFinite Element Analysis Using Hypermesh Radioss OR Optistruct PDF4 pages
- Lead Screw Calculator Metric ISO2904 1977No ratings yetLead Screw Calculator Metric ISO2904 19772 pages
- Pub 222 Nickel Al Bronze Guide EngineersNo ratings yetPub 222 Nickel Al Bronze Guide Engineers100 pages
- Designing Parametric Bevel Gears With Catia V5: 1 Sources, Credits and LinksNo ratings yetDesigning Parametric Bevel Gears With Catia V5: 1 Sources, Credits and Links10 pages
- Cyclic Plasticity of Engineering Materials: Experiments and ModelsFrom EverandCyclic Plasticity of Engineering Materials: Experiments and ModelsNo ratings yet
- Subject: Machine Design Presentation On: Spur Gear Design Mechanical 7 - B2No ratings yetSubject: Machine Design Presentation On: Spur Gear Design Mechanical 7 - B225 pages
- Elements of Metric Gear Technology: Table 1-5 (Cont.) Spur Gear Design FormulasNo ratings yetElements of Metric Gear Technology: Table 1-5 (Cont.) Spur Gear Design Formulas13 pages
- Correlation Between Yield Stress and Slump CompariNo ratings yetCorrelation Between Yield Stress and Slump Compari10 pages
- 2.003 Engineering Dynamics Problem Set 5No ratings yet2.003 Engineering Dynamics Problem Set 58 pages
- JCB 803 Plus & Super Mini Excavator: DIG DEPTH 2.78 M (9 FT 1 In)No ratings yetJCB 803 Plus & Super Mini Excavator: DIG DEPTH 2.78 M (9 FT 1 In)2 pages
- Introduction To Heat Transfer Final 2023 CheatSheetNo ratings yetIntroduction To Heat Transfer Final 2023 CheatSheet5 pages
- Maintenance Manual: FAX: 816-472-1999 PHONE: 816-472-8999 TOLL FREE: 1-800-235-2829 E-MailNo ratings yetMaintenance Manual: FAX: 816-472-1999 PHONE: 816-472-8999 TOLL FREE: 1-800-235-2829 E-Mail303 pages
- Cooling Tower Presentation - Brandon Rees - 2012-10-03 PDF100% (2)Cooling Tower Presentation - Brandon Rees - 2012-10-03 PDF67 pages
- Chadha Papers Ltd. - Wetscrubber 15.09.15No ratings yetChadha Papers Ltd. - Wetscrubber 15.09.153 pages
- Tyre Hydroplaning Abaqus CEl Master Thesis100% (1)Tyre Hydroplaning Abaqus CEl Master Thesis133 pages
- ST 7211 Advanced Structural Engineering Laboratory: Observation100% (1)ST 7211 Advanced Structural Engineering Laboratory: Observation35 pages
- Corse Project Report: Report Title: Belt GrinderNo ratings yetCorse Project Report: Report Title: Belt Grinder18 pages
- Direct Analysis Method: CE 434 Steel Design I 1 / 2 Spring 2015No ratings yetDirect Analysis Method: CE 434 Steel Design I 1 / 2 Spring 20152 pages
- 2011 - Chaallal - ETS FRP For Shear Strenghtening of RC Beams-Performance and ComparisonNo ratings yet2011 - Chaallal - ETS FRP For Shear Strenghtening of RC Beams-Performance and Comparison10 pages
- Novec Heat Transfer Product Line Card PDFNo ratings yetNovec Heat Transfer Product Line Card PDF2 pages
- Fischer Concrete Screw: The High-Performance Concrete Screw For Absolute Installation EaseNo ratings yetFischer Concrete Screw: The High-Performance Concrete Screw For Absolute Installation Ease10 pages
- PECP5030!10!10.1 Edition Cat Hose Products & Tooling GuidePECP5030!10!10.1 Edition Cat Hose Products & Tooling Guide
- Thermal and Efficiency Characterization of A Low-Backlash Planetary GearboxThermal and Efficiency Characterization of A Low-Backlash Planetary Gearbox
- CHABOCHE, J. L. - Continuum Damage Mechanics P.2 - Damage Growth, Crack InitiationCHABOCHE, J. L. - Continuum Damage Mechanics P.2 - Damage Growth, Crack Initiation
- How To Tackle Convergence Issues Without Compromising Accuracy in Any Static Structural Non Linear Analysis Using ANSYS Workbench 13How To Tackle Convergence Issues Without Compromising Accuracy in Any Static Structural Non Linear Analysis Using ANSYS Workbench 13
- New Algorithms For Calculating Hertzian Stresses, Deformations, and Contact Zone Parameters PDFNew Algorithms For Calculating Hertzian Stresses, Deformations, and Contact Zone Parameters PDF
- Finite Element Evaluation of The State of Cure in A TireFinite Element Evaluation of The State of Cure in A Tire
- Effect of Shot Peening On The Fatigue Life of 2024 Aluminum Alloy PDFEffect of Shot Peening On The Fatigue Life of 2024 Aluminum Alloy PDF
- Workshop 16 Thermal Stress Analysis of A Bi-Metalic PlateWorkshop 16 Thermal Stress Analysis of A Bi-Metalic Plate
- Shigley's Mechanical Engineering Design Tutorial 3-19: Hertz Contact StressesShigley's Mechanical Engineering Design Tutorial 3-19: Hertz Contact Stresses
- Criteria For Self Loosening of Fasteners Under VibrationCriteria For Self Loosening of Fasteners Under Vibration
- 06-Chapter 3 - 2D Meshing-v2017.2.3-27JUNE-2018 PDF06-Chapter 3 - 2D Meshing-v2017.2.3-27JUNE-2018 PDF
- Gear Trains: Qassim University Unayzah College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering DeptGear Trains: Qassim University Unayzah College of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Dept
- Housing Influences On Churning Losses in Geared TransmissionsHousing Influences On Churning Losses in Geared Transmissions
- Reduction of Stress Concentration in Bolt Nut ConnectorsReduction of Stress Concentration in Bolt Nut Connectors
- Calculation of Stress Time Signals of Multi-Bolted JointsCalculation of Stress Time Signals of Multi-Bolted Joints
- Workshop 7 Thermal Contact Resistance: WS7-1 NAS104, Workshop 7, March 2004 2004 MSC - Software CorporationWorkshop 7 Thermal Contact Resistance: WS7-1 NAS104, Workshop 7, March 2004 2004 MSC - Software Corporation
- Finite Element Analysis Using Hypermesh Radioss OR Optistruct PDFFinite Element Analysis Using Hypermesh Radioss OR Optistruct PDF
- Designing Parametric Bevel Gears With Catia V5: 1 Sources, Credits and LinksDesigning Parametric Bevel Gears With Catia V5: 1 Sources, Credits and Links
- Cyclic Plasticity of Engineering Materials: Experiments and ModelsFrom EverandCyclic Plasticity of Engineering Materials: Experiments and Models
- Subject: Machine Design Presentation On: Spur Gear Design Mechanical 7 - B2Subject: Machine Design Presentation On: Spur Gear Design Mechanical 7 - B2
- Elements of Metric Gear Technology: Table 1-5 (Cont.) Spur Gear Design FormulasElements of Metric Gear Technology: Table 1-5 (Cont.) Spur Gear Design Formulas
- Correlation Between Yield Stress and Slump CompariCorrelation Between Yield Stress and Slump Compari
- JCB 803 Plus & Super Mini Excavator: DIG DEPTH 2.78 M (9 FT 1 In)JCB 803 Plus & Super Mini Excavator: DIG DEPTH 2.78 M (9 FT 1 In)
- Introduction To Heat Transfer Final 2023 CheatSheetIntroduction To Heat Transfer Final 2023 CheatSheet
- Maintenance Manual: FAX: 816-472-1999 PHONE: 816-472-8999 TOLL FREE: 1-800-235-2829 E-MailMaintenance Manual: FAX: 816-472-1999 PHONE: 816-472-8999 TOLL FREE: 1-800-235-2829 E-Mail
- Cooling Tower Presentation - Brandon Rees - 2012-10-03 PDFCooling Tower Presentation - Brandon Rees - 2012-10-03 PDF
- ST 7211 Advanced Structural Engineering Laboratory: ObservationST 7211 Advanced Structural Engineering Laboratory: Observation
- Direct Analysis Method: CE 434 Steel Design I 1 / 2 Spring 2015Direct Analysis Method: CE 434 Steel Design I 1 / 2 Spring 2015
- 2011 - Chaallal - ETS FRP For Shear Strenghtening of RC Beams-Performance and Comparison2011 - Chaallal - ETS FRP For Shear Strenghtening of RC Beams-Performance and Comparison
- Fischer Concrete Screw: The High-Performance Concrete Screw For Absolute Installation EaseFischer Concrete Screw: The High-Performance Concrete Screw For Absolute Installation Ease