Lect 1,2 Polarization
Uploaded by
SameerLect 1,2 Polarization
Uploaded by
SameerPolarization
Interference and Diffraction
Wave nature of Light
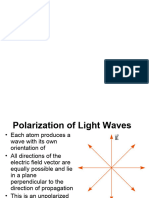
POLARIZATION ?
Longitudinal?
Transverse?
Light is an electromagnetic wave and
transverse in nature.
nature
E M wave
S-wave
S wave in seismic wave
Electric field only going up and down
linearly or plane polarized
Natural light or ordinary light is unpolarized in nature.
nature
Vibrations take place symmetrically in all directions in the
plane perpendicular to the direction of propagation of light.
light
Why????
The process of transforming unpolarized light into
polarized light is known as
Representation of Plane polarized light
Plane of vibration & polarization:
Plane p
polarized light
g with
Vibration perpendicular to
the Plane of paper (Spolarized)
l i d)
Plane of vibration: A plane containing the direction of
propagation
p
p g
and direction of vibration
Plane of polarization: A plane containing the direction of
propagation and perpendicular to plane of vibration
Plane
a e po
polarized
a ed light
g
with
w
vibrations parallel to the plane
of paper (P-polarized)
How to detect unpolarized & polarized light
Mathematical representation of
Pl
Plane
polarized
l i d li
light
ht
Suppose light is propagating in zz
direction. Mathematically a plane
polarized light can be represented as:
E x ( z , t ) = iE0 x cos( kz t )
E y ( z , t ) = j E 0 y cos( kz t )
x
z
Unpolarized: if no change in the intensity during full rotation
Polarized: if intensity changes during full rotation of the crystal
Production off polarized
p
z light
g
1 By
1.
B R
Reflection:
fl ti
B
Brewsters
t Law
L
2 By
2.
B Refraction: Malus
Mal s Law
La
Polarization by reflection: Brewsters Law
Unpolarized light is incident at
polarizing
l i i
angle
l
on the
th
di l t i
dielectric
medium the reflected light is
completely plane polarized.
polarized
3 By selective absorption: Dichroic material
3.
= tan p
4 By double refraction:
4.
-Nicol Prism
- Wave plates
Polarization by reflection: Brewsters Law
Note : The polarizing angle is different for different
reflecting
fl i surfaces.
f
Polarization by reflection: Brewsters Law
n1
n2
= tan
n2
n1
Show that 2 + p =
tan p =
sin p
cos p
n2
=
n1
and snell ' s law
n1 sin p = n2 sin 2
therefore
cos p = sin 2 = cos (90 2 )
p + 2 =
Polarization by reflection: Brewsters Law
Polarization by reflection: Brewsters Law
For air-water interface, n1 = 1 and n2 = 1.33 (say)
then Brewsters
Brewster s angle is:
p = tan-11(1.33)
(1 33) ~ 530
Thus if the sunlight is incident on the sea at an angle
close to the polarizing angle, the reflected light is
almost polarized. Now if view through the rotation
polaroid, the sea will appear more transparent
when the polaroid blocks the reflected light.
Polarization by multiple reflection
Malus Law
I = I 0 cos 2
Law
states
that
intensity
of
light
transmitted through
the analyzer is directly
proportional to the
square of the angle
between
the
transmission planes of
the polarizer and
analyzer.
Two consecutive polarizers.
Unpolarized light have E field vibration in all directions.
Therefore I = I0 <cos2> = I0/2
Quest: 22.10 (page-22.38) Optics 4th ed by Ajoy Ghatak
(a) Consider two crossed Polaroids placed in the path of
an unpolarized
p
beam off intensityy I0. Iff we p
place a third
Polaroid in between the two then, in general, some
light
g
will be transmitted through
g . Explain
p
this
phenomenon.
(b) Assuming the pass axis of the third polaroid to be 450
to the p
pass axis off either off the p
polaroids,, calculate the
intensity of the transmitted beam. Assume that all the
ppolaroids are p
perfect.
f
Ans: I0/8
Quest: An unpolarized light passes through a
vertically placed polarizer having horizontal
polarization axis.
axis Subsequently it passes through a
polarizer with its pass axis at 90o with respect to
verticall andd two polarizers
l
h
having
their
h polarization
l
axes at an angle 30o and 60o with vertical
respectively.
What will be the intensity of the emergent light?
Use of Polaroid
Ans : (3/32)I0
Use of Polaroid
Without polarizer
With polarizer
Use of Polaroid
Without polarizer
With polarizer
Wire Grid Polarizer
Input light contains
both polarizations
g can excite electrons to move along
g the wires,, which then
The light
emit light that cancels the input light. This cannot happen perpendicular to the wires. Such polarizers work best in the IR.
Polaroid sheet polarizers use the same idea, but with long polymers.
Wire grid polarizer in the visible
Using semiconductor fabrication techniques, a wire-grid polarizer was
recently developed for the visible
visible.
The spacing is less than 1 micron.
How do we make Polarized Light?
I. Polarizers-
Polarization by double refraction
When an UPL enters an
anisotropic crystal,
crystal it splits into
two beams, each of them being
characterized by a certain state of
polarization. If by some method,
we could eliminate one of the
beams then we would obtained a
LPL.
LPL
Methods of eliminating one of the beam.
beam
1. By selective absorption - Dichroism.
2. Total Internal Reflection.
Polarization by Selective Absorption Dichroism
Polarization by Absorption: Dichroic materials
A number of crystalline materials absorb more light in one
incident plane than another,
another so that light progressing
through the material become more and more polarized as
they proceed.
proceed This anisotropy in absorption is called
dichroism. There are several naturally occurring dichroic
materials and the commercial material polaroid also
materials,
polarizes by selective absorption.
Tourmaline crystal
is a dichroic material
The electric field component of an incident light that is perpendicular
to the optic axis (determined by its atomic configuration) is strongly
absorbed by the sample.
Thicker the sample, the more complete the absorption. Here the
crystals principal axis becomes polarizers transmission axis.
By total internal reflection
Polarization by Scattering
Doubly Refracting Crystals
DOUBLE REFRACTION BIREFRINGENCE
When a ray of unpolarised light is incident on a certain
special
i l crystal
t l (doubly
(d bl refracting
f ti crystal)
t l) there
th
are two
t
refracted rays. Such crystals are of two types
1 Unaxial e.g.:
1.
e g : calcite (Iceland spar) , tourmaline and
quartz
When a ray enters such a crystal, it splits into two rays. This
phenomenon is known as double refraction or birefringence.
birefringence
A material
t i l which
hi h displays
di l
t different
two
diff
t indices
i di
off refraction,
f ti
i said
is
id
to be birefringent.
2 Bi
2.
Bi-axial
axial e.g.:
e g : topaz and aragonite,
aragonite Copper Sulphate,
Sulphate
cane sugar and Mica
GEOMETRY OF CALCITE CRYSTAL
GEOMETRY OF CALCITE CRYSTAL
It is colorless transparent crystal. It is chemically crystallized CaCO3
and occur in nature in different forms,
forms all of which give rhombohedran
on cleavage as shown in figure.
Two images
calcite crystal
through
Polarizer transmits the
ordinary ray.
Polarizer rotated about 90
transmits the extraordinary
ray.
A and H are Blunt Corner
GEOMETRY OF CALCITE CRYSTAL
GEOMETRY OF CALCITE CRYSTAL
Optic axis: direction along a line passing through any one
of the blunt corners and making equal angles each of the
three edges which meet at the corner.
Principal Section: A plane containing the optic axis of the crystal
and perpendicular to its two opposite faces is called the Principal
section of the crystal for that pair of faces. As Crystal has six
faces there are three principal sections corresponding to each
pair of the opposite faces.
You might also like
- Compression Dead End & Compression Midspan JointNo ratings yetCompression Dead End & Compression Midspan Joint23 pages
- 3-Polarisation-Sept 2022 (Students Copy)No ratings yet3-Polarisation-Sept 2022 (Students Copy)8 pages
- Polarization of Light MNH Class LectureNo ratings yetPolarization of Light MNH Class Lecture44 pages
- PH 201 Optics & Lasers: Lecture - Polarization - 3No ratings yetPH 201 Optics & Lasers: Lecture - Polarization - 329 pages
- 3 Polarisation Chem Eng April 2022 DR Paul V3No ratings yet3 Polarisation Chem Eng April 2022 DR Paul V354 pages
- Module 26: Polarization-I Lecture 26: Polarization-I: 26.1 Natural RadiationNo ratings yetModule 26: Polarization-I Lecture 26: Polarization-I: 26.1 Natural Radiation7 pages
- DR - Paramjit Kour Dept of Physics Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra. Patna CampusNo ratings yetDR - Paramjit Kour Dept of Physics Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra. Patna Campus44 pages
- Experiment 12 Polarized Light 1: 1 I 2 T 1 I 2 T 2No ratings yetExperiment 12 Polarized Light 1: 1 I 2 T 1 I 2 T 26 pages
- QuantumPro Electromagnetic (EM) and Quantum Analysis Environment for Quantum Circuit DesignersNo ratings yetQuantumPro Electromagnetic (EM) and Quantum Analysis Environment for Quantum Circuit Designers5 pages
- Exergy Analysis in ProSimPlus SimulationNo ratings yetExergy Analysis in ProSimPlus Simulation22 pages
- Raman Spectroscopy: Dr. Majid Muneer Assistant Professor Department of Chemistry, GCU Faisalabad100% (2)Raman Spectroscopy: Dr. Majid Muneer Assistant Professor Department of Chemistry, GCU Faisalabad47 pages
- Anisotropy and Periodic Potential in A SolidNo ratings yetAnisotropy and Periodic Potential in A Solid23 pages
- Chapter 7.2 Lifting Capacity of Drilling Fluids100% (1)Chapter 7.2 Lifting Capacity of Drilling Fluids10 pages
- Studytheme 2.22 - Nickel and Nickel AlloysNo ratings yetStudytheme 2.22 - Nickel and Nickel Alloys12 pages
- A Mini Project On Design, Manufacturing & Failure Analysis of Leaf Spring60% (10)A Mini Project On Design, Manufacturing & Failure Analysis of Leaf Spring61 pages
- Definition and Proper Usage of Electrical Materials and EquipmentNo ratings yetDefinition and Proper Usage of Electrical Materials and Equipment6 pages
- Solution To Problem 110 Normal Stress - Strength of Materials Review100% (1)Solution To Problem 110 Normal Stress - Strength of Materials Review5 pages
- Shell Gadus S5 T460: Previously Shell Stamina HdsNo ratings yetShell Gadus S5 T460: Previously Shell Stamina Hds1 page
- Evaporative Cooling of Water in A Natural Draft Cooling TowerNo ratings yetEvaporative Cooling of Water in A Natural Draft Cooling Tower12 pages
- Zig Zag and Zero Sequence Current ReflectionNo ratings yetZig Zag and Zero Sequence Current Reflection10 pages
- PH 201 Optics & Lasers: Lecture - Polarization - 3PH 201 Optics & Lasers: Lecture - Polarization - 3
- Module 26: Polarization-I Lecture 26: Polarization-I: 26.1 Natural RadiationModule 26: Polarization-I Lecture 26: Polarization-I: 26.1 Natural Radiation
- DR - Paramjit Kour Dept of Physics Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra. Patna CampusDR - Paramjit Kour Dept of Physics Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra. Patna Campus
- Experiment 12 Polarized Light 1: 1 I 2 T 1 I 2 T 2Experiment 12 Polarized Light 1: 1 I 2 T 1 I 2 T 2
- QuantumPro Electromagnetic (EM) and Quantum Analysis Environment for Quantum Circuit DesignersQuantumPro Electromagnetic (EM) and Quantum Analysis Environment for Quantum Circuit Designers
- Raman Spectroscopy: Dr. Majid Muneer Assistant Professor Department of Chemistry, GCU FaisalabadRaman Spectroscopy: Dr. Majid Muneer Assistant Professor Department of Chemistry, GCU Faisalabad
- A Mini Project On Design, Manufacturing & Failure Analysis of Leaf SpringA Mini Project On Design, Manufacturing & Failure Analysis of Leaf Spring
- Definition and Proper Usage of Electrical Materials and EquipmentDefinition and Proper Usage of Electrical Materials and Equipment
- Solution To Problem 110 Normal Stress - Strength of Materials ReviewSolution To Problem 110 Normal Stress - Strength of Materials Review
- Evaporative Cooling of Water in A Natural Draft Cooling TowerEvaporative Cooling of Water in A Natural Draft Cooling Tower