Kingdom Animalia
Kingdom Animalia
Uploaded by
markCopyright:
Available Formats
Kingdom Animalia
Kingdom Animalia
Uploaded by
markOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Kingdom Animalia
Kingdom Animalia
Uploaded by
markCopyright:
Available Formats
KINGDOM: ANIMALIA (Metazoans)
9 10 Million species
800,000 identified
36 official Phyla
108 classes
Mostly marine, few are in fresh water, fewer are
in land
Made up of organic molecules
Capable of Growth
Capable of reproduction
Irritable
Have a definite size and shape
Mostly motile
I. PHYLUM: ACANTHOCEPHALA
(Gr) akanthos= thorn + kephale= head
II.
Annelid worms have a body cavity called a
coelom which provides room for organ
development.
Examples:
- Hirudo Verbana
- Hirudo Medicinalis
- Nereis (The Sandworm)
- Pheretima (Earthworm)
- Tubiflex (Bloodworm)
- Leeches
3 CLASSES:
1.Class: Hirudinea
- Terrestrial
- Monoecious
- Segmentation inconspicuous
- Example:
o Hirudo Verbana
Thorny/spiny-headed worms
o Hirudo Medicinalis
With eversible proboscis
2.Class: Olygochaeta
1150 species
- Terrestrial
Parasitic members
- Monoecious
Found in invertebrates, fishes, amphibians, birds,
- Segmentation conspicuous
3.Class: Polychaeta
mammals
- Marine
Example:
- Dioecious
- Macrachanthorhyncus hirudinaceous
- Segmentation conspicuous
PHYLUM: ANNELIDA (segmented animals)
III.
PHYLUM:
BRYOZOA Moss Animals
(Annelus=a ring; segmented worms)
AKA Polyzoa, Ectoprocta
Moss animals
With fine bristle like setae for locomotion
Mostly marine, few are in fresh and brackish
Digestive tract complete
waters
Metanephridia for excretion
Mostly colonial (zooids)
Hydrostatic skeleton
5000 species
Circulatory system: with hemoglobin and other
Example:
pigments
- Triphyllozoon Trifoliatum
Has 5 hearts
Employ cutaneous respiration
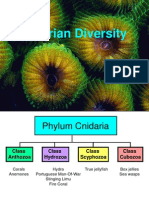
IV. PHYLULM: CNIDARIA/COELENTERATA
Animal body is soft, elongated, bilateral, flattened. (two-layered animals)
(koilos=hollow; enteron= gut)
Body is divided into segments by rings like
groove and annule.
10,000 species
Body bears locomotory appendages, parapodia,
With Cnidocytes/Namatocysts
setae.
Symmetry: Radial
Alimentary canal is complete, straight and
No anus, head or other organ systems
extends from mouth to anus. These are first
animals to have true body cavity.
With gastrovascular cavity
The specialized cells called metanephridia helps
Habitat: Aquatic
in excretion.
Stages/ Body types:
Closed circulatory system has appeared and
1. Polyp- vase shaped
nervous system starts developing.
2.Medusa- umbrella shaped (ex. Sea Anemone)
Reproduction occurs by sexual means. Sexes may
They may be solitary or colonial.
be separate (unisexual) or united
They have tissue level of organization but lacks
(hermaphroditic).
organ and organ system. Symmetry is radial.
It has a single aperture, the mouth. It has no anus.
Mouth bears tentacles (flexible processes).
They have special stinging cells, called
cnidoblasts for defense purposes.
Reproduction is mainly asexual but sometimes
undergoes sexual reproduction.
Fertilization may be internal or external. Hard
skeleton occurs in corals
Examples:
- Anemones
- Aurelia
- Chironex Fleckeri
- Fire Corals
- Hydra
- Jellyfish
- Sea Pens
- Sea Fans
- Other Corals In Deep Waters
4 CLASSES:
1. CLASS: ANTHOZOA
- Exclusively polyps
- Exclusively marine
- Some have a symbiotic relationship with
algae (e.g. Scleractinian corals and
Symbiodinium )
- In shallow waters
- Example:
o Anemones
o Sea Pens
o Sea Fans
o Other Corals In Deep Waters
2.CLASS: CUBOZOA
- Box jellies
- Have 4 tentacles/groups of tentacles
- Have well-developed eyes
- 20species in tropical, subtropical regions
- Example:
o Chironex Fleckeri
3.CLASS: HYDROZOA
- With polyp and medusa stages
- Usually colonial
- In fresh and marine waters
- Polyps reproduce asexually
- Medusae reproduce sexually
- Example:
o Fire Coral
o Hydra (fresh water polyp)
o Siphonphore
4.CLASS: SCYPHOZOA
- With polyp and medusa stages
- 12 mm 2m in diameter
- Exclusively marine
- Mostly pelagic, free swimming forms
- Cnidocytes in oral arms instead of
peripheral
- Example:
o Aurelia (jelyfish)
V.
PHYLUM: NEMATODA (round worms)
Pseudocoelomate
10,000 spp.
Mostly free living, few parasitic
Mostly dioecious, some are parthenogenetic
Dimorphic
Animal body is cylindrical, flattened, bilateral,
triploblastic(third layer), unsegmented.
Size of the body varies from microscopic to
several centimeters in length.
Body wall is covered with tough cuticle. Cilia
are absent.
Pseudocoelom (false body cavity) is present.
Digestive track is complete, with a mouth at one
end where food enters, and an opening at the
other end where wastes exit.
Sexes are separate (bisexual).
These are generally parasites and causes
diseases.
They may be free living in soil or water.
Not segmented
Examples
Anisakis Simplex
Ascaris (intestinal sound-worm),
Ascaris Lumbricoides (intestinal soundworm)
Dracunculus Medinensis
Hookworm
Loa loa
Pinworm filarial worm
Trichinella (pork worm)
Trichuris Trichiura
Tubatrix Aceti
Wuchereia Bancrofti (elephant)
2 CLASSES:
1.
CLASS: ADENOPHOREA
- Without phasmids
- Egg with bipolar plugs
- Anterior end with stichocytes
- Caudal end has no papillae/spines
- Example:
o Trichuris Trichiura
2.
CLASS: SECERNENTEA
- With phasmids
- Egg without bipolar plugs
- Caudal end with papillae/spines
VI.
- Example:
o Anisakis Simplex
o Ascaris Lumbricoides (intestinal
sound-worm)
o Dracunculus Medinensis
o Loa loa
o Tubatrix Aceti
o Wuchereia Bancrofti (elephant)
PHYLUM: PORIFERA (sponges)
( Porus=pore; ferre=bear; sponges)
Larva: free swimming
Adult: Sessile
Skeleton: Spicules and/or Spongin fibers
Habitat: Aquatic
Body is lined with choanocytes
Porifera are commonly called sponges, mostly
marine but may live in fresh water.
Mostly sessile (stalk less) and attach to
substratum.
They are asymmetrical.
They have cellular level organization.
They have a single large opening called osculum.
(intake and exit of food through a single
opening). They lack mouth, digestive cavity
and anus.
Sponges are covered with hard outer skeleton.
Reproduction is both asexual as well as sexual.
Examples:
Anthella Basta
Boring Sponge
Chalinula Nematifera
Clathrina Clathrus
Euplectella
Phakellia
Scypha
Staurocalyptus
4 CLASSES:
1. CLASS: CALCAREA
- Calcareous spicules
- Exclusively marine (Tropical)
- <10cm tall
- 400 species
- Examples:
o Clathrina Clathrus
o Scypha
2. CLASS: DEMOSPONGJAE
- 81% of sponge species
- Endoskeleton= Si spicules + spongin
fibers
- Marine and fresh water
- <1m in width
- Example:
o Boring Sponge
o Ianthella basta
o Phakellia
3. CLASS: HEXACTINELLIDA (6 spines)
- Phylum Symplasma
- Siliceous spicules
- Exclusively marine
- Habitat in 450-900 m (Antarctic and N.
Pacific)
- 10-30 cm in height
- Example:
o Euplectella
o Staurocalyptus
4. CLASS: SCLEROSPONGIA
- Coralline sponges
- Endoskeleton= CaCO3
- Long lived: 500 1000 years
- Exclusively marine
- Example:
o Chalinula Nematifera
Sponge Development
zygote free swimming larva, interted
luna, sessile stage
VII.
PHYLUM: PLATYHELMINTHES (flat worms)
(platys=flat; helmins=worm; flatworm)
Symmetry: bilateral
Very thin and flat
Triploblastic
Acoelomate
Gut is blind-ended
Marine, fresh water, terrestrial
These are most primitive, soft, leaf or ribbon like
organisms without segmentation.
These are mostly parasites, few are free living.
They attach to the host by suckers or hooks.
They are the first animals to have third primary
germ layer, this shows tissue differentiation
leading to organ formation.
Digestive track is incomplete. They have flamecells for excretion.
They are mostly hermaphrophite (bisexual).
First animals to have a head.
Example:
Diplyidium Caninum
Diphyllobothrium Latum
Dugesia (Planaria)
Fasciola (Liver Fluke)
Faciolopsis Buski
Fasciola Spp.
Liver Fluke
Paragonimus
Schistosoma Spp.
Taenia Solium
Taenia Saginata
Taenia Solium (Tape Worms)
3 CLASSES:
1. CLASS: CESTODA
- Parasitic
- Monoecious
- Example:
o Diplyidium Caninum
o Diphyllobothrium Latum (sushi)
o Taenia Saginata (meat/beef)
o Taenia Solium (bbq)
2.CLASS: TREMATODA
- Parasitic
- Mostly monoecious
- Example:
o Faciolopsis Buski
o Fasciola Spp.
o Paragonimus
o Schistosoma spp.
3.CLASS: TURBELLARIA
- Free-living
- Marine, fresh water, terrestrial
- Monoecious
- Example:
o Dugesia
You might also like
- Animal Kingdom (Phylum 1-7)Document4 pagesAnimal Kingdom (Phylum 1-7)AllenNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom1Document17 pagesAnimal Kingdom1Jojie PamaNo ratings yet
- Campus Journalism - LectureDocument2 pagesCampus Journalism - LectureChristine Mae SamsonNo ratings yet
- The ChordatesDocument6 pagesThe Chordatesfathiaseidu78No ratings yet
- PHYLUMSDocument6 pagesPHYLUMSJanelle RedobladoNo ratings yet
- General Characteristics and Classification of Porifera FinalDocument35 pagesGeneral Characteristics and Classification of Porifera Finalanoushkapatnaik60No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Kingdom AnimaliaDocument104 pagesChapter 5 Kingdom AnimaliaLebT “Beast”No ratings yet
- Platyhelminthes and MolluscaDocument7 pagesPlatyhelminthes and MolluscaYasmine AurelliaNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Animali1Document5 pagesKingdom Animali1Lester ParadilloNo ratings yet
- 1.1 General Characteristics of Phylum of InvertebratesDocument10 pages1.1 General Characteristics of Phylum of InvertebratesManish thapa100% (2)
- SZL105 Topic Twelve Phyla Hemichordata and ChordataDocument5 pagesSZL105 Topic Twelve Phyla Hemichordata and Chordatajenkinsonyango77No ratings yet
- Protochordata-Characters & PhylogenyDocument4 pagesProtochordata-Characters & PhylogenyAakash V100% (1)
- Exercise-__-Diversity-of-Animal-Life-Bio-41A-1Document11 pagesExercise-__-Diversity-of-Animal-Life-Bio-41A-1Van RadazaNo ratings yet
- Kingdom AnimaliaDocument42 pagesKingdom AnimaliaGuffran septiahadiNo ratings yet
- Phylum AnnelidaDocument6 pagesPhylum AnnelidaRechelle CabagingNo ratings yet
- Comparative Vertebrate AnatomyDocument5 pagesComparative Vertebrate AnatomyNeha ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Guide Questions For Experiment NoDocument6 pagesGuide Questions For Experiment NosannicolasjonasNo ratings yet
- Nonc Hordate EvolutionDocument12 pagesNonc Hordate EvolutionBheemasenachar KopparNo ratings yet
- MolluscsDocument2 pagesMolluscsIvy Villanueva DivinoNo ratings yet
- Animal TaxonomyDocument21 pagesAnimal TaxonomylegendibsongeeNo ratings yet
- Zoology Lecture 1-10Document52 pagesZoology Lecture 1-10snazzy minaNo ratings yet
- ClassificationDocument40 pagesClassificationSajed- JRNo ratings yet
- Session 3Document5 pagesSession 3KESHAVA MURTHY M VNo ratings yet
- The Phylum PlatyhelminthesDocument24 pagesThe Phylum PlatyhelminthesFlora NeriNo ratings yet
- Phylum ChordataDocument15 pagesPhylum Chordatay_khartashNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 SCDocument7 pagesChapter 11 SCapi-523871352No ratings yet
- EnglishDocument27 pagesEnglishkhairani100% (1)
- Phylum Coenlenterata and Phylum CtenophoraDocument21 pagesPhylum Coenlenterata and Phylum CtenophoraYukimi SugitaNo ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University IslamabadDocument16 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University IslamabadAbdullah Nagra100% (1)
- Classification of AnimaliaDocument31 pagesClassification of AnimaliaAnilaNo ratings yet
- Basic Health BiologyDocument18 pagesBasic Health BiologyJohn BasseyNo ratings yet
- Structure and Levels of Organization of The Platyhelminthes The Phylum PlatyhelminthesDocument12 pagesStructure and Levels of Organization of The Platyhelminthes The Phylum PlatyhelminthesMobile OverloadNo ratings yet
- 12 - Academic Script200319070703034141Document11 pages12 - Academic Script200319070703034141rishabh1367opNo ratings yet
- Animal Diversity II - Introduction (Protochordates) PDFDocument5 pagesAnimal Diversity II - Introduction (Protochordates) PDFinam ullahNo ratings yet
- Animal KingdomDocument8 pagesAnimal KingdomAarav SonethaNo ratings yet
- Phylum ChordataDocument25 pagesPhylum ChordataNicole100% (1)
- Lab ArtropodeDocument15 pagesLab ArtropodeVonna IonescuNo ratings yet
- InvertebratesDocument55 pagesInvertebratesNajibah CasimNo ratings yet
- Zool Lab Act 1Document21 pagesZool Lab Act 1pascualfrancejosephNo ratings yet
- HerpetolgyDocument67 pagesHerpetolgybelgieabebaw09No ratings yet
- Animal Diversity - The Kingdom Animalia 1. Phylum Porifera - SpongesDocument6 pagesAnimal Diversity - The Kingdom Animalia 1. Phylum Porifera - SpongesSamantha Dasmariñas MagaanNo ratings yet
- OSB Tryout Study Packet 2011Document26 pagesOSB Tryout Study Packet 2011Serena HuangNo ratings yet
- Invertebrates AntonetteDocument27 pagesInvertebrates Antonetteduganirene1No ratings yet
- invertibraeDocument10 pagesinvertibraemknightNo ratings yet
- Research No. 2Document46 pagesResearch No. 2Bai Putri Rohaina S. MalangNo ratings yet
- Comparative Vertebrate AnatomyDocument9 pagesComparative Vertebrate AnatomyJayson Tafalla Lopez100% (2)
- Ch. 16. Molluscs - BSBIO1-4Document65 pagesCh. 16. Molluscs - BSBIO1-4amitafNo ratings yet
- Reporters: Maun, Maja Mariella Gonzales, Alessy Joy Cortez, KateDocument34 pagesReporters: Maun, Maja Mariella Gonzales, Alessy Joy Cortez, KateKate CortezNo ratings yet
- AnnelidaDocument6 pagesAnnelidaViswadeep DasNo ratings yet
- Bio 111-1Document13 pagesBio 111-1efep478No ratings yet
- AnimaliaDocument46 pagesAnimaliaChristine FidelNo ratings yet
- Phylum - Chordata: By: Y.Sarvesan 11A1Document26 pagesPhylum - Chordata: By: Y.Sarvesan 11A1ragavimaladhi23No ratings yet
- MolluscaDocument27 pagesMolluscaWalter Felix NainggolanNo ratings yet
- Taxonomic Retrospect of Phylum PlatyhelminthesDocument1 pageTaxonomic Retrospect of Phylum PlatyhelminthesMuabshir AmjadNo ratings yet
- 5 - Invertebrate & Vertebrate Animals - PrintDocument35 pages5 - Invertebrate & Vertebrate Animals - PrintInmaculada Campos RomeroNo ratings yet
- 27 ArthropodsDocument63 pages27 Arthropodsapi-244168124No ratings yet
- Summary NotesDocument4 pagesSummary Noteslungelolulu38No ratings yet
- Science Is Awesome!: 101 Incredible Things Every Kid Should KnowFrom EverandScience Is Awesome!: 101 Incredible Things Every Kid Should KnowNo ratings yet
- The Book of Frogs: A Life-Size Guide to Six Hundred Species from Around the WorldFrom EverandThe Book of Frogs: A Life-Size Guide to Six Hundred Species from Around the WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Animals Without Backbones1 PDFDocument31 pagesAnimals Without Backbones1 PDFSamKris Guerrero Malasaga100% (1)
- DK-Amazing Animals Q & ADocument66 pagesDK-Amazing Animals Q & AAgata Ferdyn-Antosik100% (5)
- Animal Kingdom ClassificationDocument11 pagesAnimal Kingdom ClassificationcharminemarideNo ratings yet
- Latihan SoalDocument5 pagesLatihan Soaltrifebrianti22No ratings yet
- Lab Rep 3 FinalDocument16 pagesLab Rep 3 FinalBella LopezNo ratings yet
- NNNNMDocument96 pagesNNNNMramdeepramdeep02No ratings yet
- Classification of Animal KingdomDocument13 pagesClassification of Animal KingdomRyanmilrex BertulfoNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes For Medical EntranceDocument40 pagesBiology Notes For Medical EntranceNickOoPandeyNo ratings yet
- Jellyfish Blooms in The Mediterranean and Black SeaDocument63 pagesJellyfish Blooms in The Mediterranean and Black SeaangryhamsterNo ratings yet
- Phylum CnidariaDocument2 pagesPhylum CnidariaHafizah ZakiahNo ratings yet
- Rhizostoma Pulmo: Irritant Contact Dermatitis From The JellyfishDocument2 pagesRhizostoma Pulmo: Irritant Contact Dermatitis From The JellyfishSarly FebrianaNo ratings yet
- PhylumDocument15 pagesPhylumNuman AshrafNo ratings yet
- Reading ComprehensionDocument8 pagesReading Comprehension17. Thảo NhiNo ratings yet
- Pembahasan Soal UN Bahasa Inggris SMP 2012 (Paket Soal C29) PDFDocument15 pagesPembahasan Soal UN Bahasa Inggris SMP 2012 (Paket Soal C29) PDFArdi Ansyah YusufNo ratings yet
- Class-5 F.M: 30 Subject-English P.M: 12 Time: 50 MinsDocument4 pagesClass-5 F.M: 30 Subject-English P.M: 12 Time: 50 MinsExcelsior SchoolNo ratings yet
- Phylum CtenophoraDocument13 pagesPhylum CtenophoraBayu SugaraNo ratings yet
- PAS 1 Bahasa Inggris XI MA - RINADocument4 pagesPAS 1 Bahasa Inggris XI MA - RINARina SetyaniNo ratings yet
- Practical Guide Invertebrates PDFDocument61 pagesPractical Guide Invertebrates PDFMOUSTAFA ALEMAMNo ratings yet
- 006 Cnidarian DiversityDocument32 pages006 Cnidarian DiversitySheerin SulthanaNo ratings yet
- Sprigg 49 TRSSA EdiacaraDocument43 pagesSprigg 49 TRSSA EdiacaraBreandán Anraoi MacGabhann100% (1)
- Soal UN SMP MTs 2009 Bahasa Inggris P12 C2 2Document14 pagesSoal UN SMP MTs 2009 Bahasa Inggris P12 C2 2Nurul HatmahNo ratings yet
- Sea Dominoe Craft and ReadingDocument4 pagesSea Dominoe Craft and ReadingSivapriya GopiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cubozoa NEW!Document14 pagesIntroduction To Cubozoa NEW!Syarif Hidayat AmrullahNo ratings yet
- Imad Ullah AssigmentDocument7 pagesImad Ullah AssigmentAsad Ullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Animal Diversity 1st Edition B. N. Pandey All Chapters Instant DownloadDocument60 pagesAnimal Diversity 1st Edition B. N. Pandey All Chapters Instant Downloadvladanebija100% (11)
- Uts Big 11Document6 pagesUts Big 11Iu LeejieunNo ratings yet
- Cnidarians and CtenophoresDocument16 pagesCnidarians and CtenophoresKamvelihle GwalaNo ratings yet
- Soal Bahasa Inggris Kels IxDocument2 pagesSoal Bahasa Inggris Kels IxIrvan RiandiNo ratings yet
- Soal B. Inggris Kls XiDocument6 pagesSoal B. Inggris Kls Xilitra jayaNo ratings yet
- Cnidaria PDFDocument19 pagesCnidaria PDFthetrashwilldoNo ratings yet