Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN: Topology
Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN: Topology
Uploaded by
Shulav PoudelCopyright:
Available Formats
Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN: Topology
Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN: Topology
Uploaded by
Shulav PoudelOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN: Topology
Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN: Topology
Uploaded by
Shulav PoudelCopyright:
Available Formats
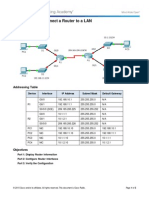
Packet Tracer - Connect a Router to a LAN
Topology
Addressing Table
Device
Interface
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Default Gateway
G0/0
192.168.10.1
255.255.255.0
N/A
G0/1
192.168.11.1
255.255.255.0
N/A
S0/0/0 (DCE)
209.165.200.225
255.255.255.252
N/A
G0/0
10.1.1.1
255.255.255.0
N/A
G0/1
10.1.2.1
255.255.255.0
N/A
S0/0/0
209.165.200.226
255.255.255.252
N/A
PC1
NIC
192.168.10.10
255.255.255.0
192.168.10.1
PC2
NIC
192.168.11.10
255.255.255.0
192.168.11.1
PC3
NIC
10.1.1.10
255.255.255.0
10.1.1.1
PC4
NIC
10.1.2.10
255.255.255.0
10.1.2.1
R1
R2
Objectives
Part 1: Display Router Information
Part 2: Configure Router Interfaces
Part 3: Verify the Configuration
2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 1 of 5
Packet Tracer - Connect a Router to a LAN
Background
In this activity, you will use various show commands to display the current state of the router. You will then
use the Addressing Table to configure router Ethernet interfaces. Finally, you will use commands to verify and
test your configurations.
Note: The routers in this activity are partially configured. Some of the configurations are not covered in this
course, but are provided to assist you in using verification commands.
Part 1: Display Router Information
Step 1: Display interface information on R1.
Note: Click a device and then click the CLI tab to access the command line directly. The console password is
cisco. The privileged EXEC password is class.
a.
Which command displays the statistics for all interfaces configured on a router?
b.
Which command displays the information about the Serial 0/0/0 interface only?
c.
Enter the command to display the statistics for the Serial 0/0/0 interface on R1 and answer the following
questions:
1) What is the IP address configured on R1?
2) What is the bandwidth on the Serial 0/0/0 interface?
d.
Enter the command to display the statistics for the GigabitEthernet 0/0 interface and answer the following
questions:
1) What is the IP address on R1?
2) What is the MAC address of the GigabitEthernet 0/0 interface?
3) What is the bandwidth on the GigabitEthernet 0/0 interface?
Step 2: Display a summary list of the interfaces on R1.
a.
Which command displays a brief summary of the current interfaces, statuses, and IP addresses assigned
to them?
b.
Enter the command on each router and answer the following questions:
1) How many serial interfaces are there on R1 and R2?
2) How many Ethernet interfaces are there on R1 and R2?
3) Are all the Ethernet interfaces on R1 the same? If no, explain the difference(s).
Step 3: Display the routing table on R1.
a.
What command displays the content of the routing table?
b.
Enter the command on R1 and answer the following questions:
1) How many connected routes are there (uses the C code)?
2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 2 of 5
Packet Tracer - Connect a Router to a LAN
Which route is listed?
2) How does a router handle a packet destined for a network that is not listed in the routing table?
Part 2: Configure Router Interfaces
Step 1: Configure the GigabitEthernet 0/0 interface on R1.
a.
Enter the following commands to address and activate the GigabitEthernet 0/0 interface on R1:
R1(config)# interface gigabitethernet 0/0
R1(config-if)# ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)# no shutdown
%LINK-5-CHANGED: Interface GigabitEthernet0/0, changed state to up
%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface GigabitEthernet0/0, changed
state to up
b.
It is good practice to configure a description for each interface to help document the network information.
Configure an interface description indicating to which device it is connected.
R1(config-if)# description LAN connection to S1
c.
R1 should now be able to ping PC1.
R1(config-if)# end
%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
R1# ping 192.168.10.10
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.10.10, timeout is 2 seconds:
.!!!!
Success rate is 80 percent (4/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 0/2/8 ms
Step 2: Configure the remaining Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces on R1 and R2.
a.
Use the information in the Addressing Table to finish the interface configurations for R1 and R2. For each
interface, do the following:
1) Enter the IP address and activate the interface.
2) Configure an appropriate description.
b.
Verify interface configurations.
Step 3: Back up the configurations to NVRAM.
Save the configuration files on both routers to NVRAM. What command did you use?
2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 3 of 5
Packet Tracer - Connect a Router to a LAN
Part 3: Verify the Configuration
Step 1: Use verification commands to check your interface configurations.
a.
Use the show ip interface brief command on both R1 and R2 to quickly verify that the interfaces are
configured with the correct IP address and active.
How many interfaces on R1 and R2 are configured with IP addresses and in the up and up state?
What part of the interface configuration is NOT displayed in the command output?
What commands can you use to verify this part of the configuration?
b.
Use the show ip route command on both R1 and R2 to view the current routing tables and answer the
following questions:
1) How many connected routes (uses the C code) do you see on each router?
2) How many EIGRP routes (uses the D code) do you see on each router?
3) If the router knows all the routes in the network, then the number of connected routes and
dynamically learned routes (EIGRP) should equal the total number of LANs and WANs. How many
LANs and WANs are in the topology?
4) Does this number match the number of C and D routes shown in the routing table?
Note: If your answer is no, then you are missing a required configuration. Review the steps in
Part 2.
Step 2: Test end-to-end connectivity across the network.
You should now be able to ping from any PC to any other PC on the network. In addition, you should be
able to ping the active interfaces on the routers. For example, the following should tests should be
successful:
From the command line on PC1, ping PC4.
From the command line on R2, ping PC2.
Note: For simplicity in this activity, the switches are not configured; you will not be able to ping them.
2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 4 of 5
Packet Tracer - Connect a Router to a LAN
Suggested Scoring Rubric
Activity Section
Part 1: Display Router
Information
Question
Location
Possible
Points
Step 1a
Step 1b
Step 1c
Step 1d
Step 2a
Step 2b
Step 3a
Step 3b
Part 1 Total
Part 2: Configure Router
Interfaces
Part 3: Verify the
Configuration
Step 3
30
2
Part 2 Total
Step 1a
Step 1b
Part 3 Total
14
Packet Tracer Score
54
Total Score (with bonus)
2015 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Earned
Points
100
Page 5 of 5
You might also like
- Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN: Addressing TableDocument4 pagesPacket Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN: Addressing TableBenj MendozaNo ratings yet
- 4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRPDocument7 pages4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRPLeo Leo17% (6)
- 2.6.1.2 Lab - Securing The Router For Administrative AccessDocument54 pages2.6.1.2 Lab - Securing The Router For Administrative AccessDaniel Ergicho100% (1)
- 6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANDocument5 pages6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANSergio MonteNo ratings yet
- 6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANDocument5 pages6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANAzeemuddin MohammedNo ratings yet
- 6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN - InstructionsDocument5 pages6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN - InstructionsLaura HampNo ratings yet
- Navdeep Singh Parewa (2030075 - 10.3.4 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANDocument4 pagesNavdeep Singh Parewa (2030075 - 10.3.4 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANNavdeep ParewaNo ratings yet
- 6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN Instructions IGDocument5 pages6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN Instructions IGopiNo ratings yet
- 10.3.4 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LanDocument4 pages10.3.4 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A Lanvudat20042820No ratings yet
- 10.3.4 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN-1Document4 pages10.3.4 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN-1garicabrianNo ratings yet
- 10.3.4 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LanDocument4 pages10.3.4 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LanBryan GalamgamNo ratings yet
- 6.4.3.3 - ZachDocument5 pages6.4.3.3 - ZachZack ShoreNo ratings yet
- Lab6 - Connect A Router To A LANDocument4 pagesLab6 - Connect A Router To A LANkaisbarboura99No ratings yet
- 10.3.4 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANDocument4 pages10.3.4 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANkds20850No ratings yet
- JARKOM11 DaviAdrian - 1803007Document10 pagesJARKOM11 DaviAdrian - 1803007Davi AdrianNo ratings yet
- Finals Activity 1 - 6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANDocument5 pagesFinals Activity 1 - 6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANjaxmain1750No ratings yet
- 10.3.4 Packet Tracer Connect A Router To A LanDocument4 pages10.3.4 Packet Tracer Connect A Router To A LanVince Mitchell LinaNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN: Addressing TableDocument6 pagesPacket Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN: Addressing TableAfif MananNo ratings yet
- 10.3.4 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LanDocument8 pages10.3.4 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LanMarinela BrânzeanuNo ratings yet
- 10.3.4 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANDocument4 pages10.3.4 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANDan jonesNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN: Addressing TableDocument12 pagesPacket Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN: Addressing TableMENDOZA GASPAR PAOLA Ingeniería en Sistemas ComputacionalesNo ratings yet
- Laboratorio Simulador 10.3.4: PT Conexión de Un Router A Una LanDocument15 pagesLaboratorio Simulador 10.3.4: PT Conexión de Un Router A Una Lanangel ricardo estrada garciaNo ratings yet
- 10.3.4 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANDocument4 pages10.3.4 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANGadisa D FayisaNo ratings yet
- 10.3.4 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANDocument5 pages10.3.4 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANIE Carlos A. Piñerez Calao100% (1)
- 10.3.4 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LanDocument4 pages10.3.4 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A Lantunguyen209205No ratings yet
- KLoaiza 6.4.3.3 Packet TracerDocument5 pagesKLoaiza 6.4.3.3 Packet TracerKevin LoaizaNo ratings yet
- PT6433 v2 CompletedDocument3 pagesPT6433 v2 Completedlorel17157No ratings yet
- 4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRP - ILMDocument18 pages4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRP - ILMjanakp2004No ratings yet
- Configuring Basic RIPv2 and RIPngDocument13 pagesConfiguring Basic RIPv2 and RIPngbinj78% (9)
- 4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRPDocument7 pages4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRPjb100% (1)
- Lab 4 (RIP Configuration)Document5 pagesLab 4 (RIP Configuration)Tame DaxNo ratings yet
- HRRPDocument7 pagesHRRPJavier CastilloNo ratings yet
- 4.1.4.5 Packet Tracer - Configuring and Verifying A Small Network InstructionsDocument3 pages4.1.4.5 Packet Tracer - Configuring and Verifying A Small Network Instructionsmvpdagawd0% (3)
- 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default RoutesDocument15 pages2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routesbalvinder singh50% (6)
- 5.3.2.3 Lab - Implement Local SPAN (Satinder Singh) PDFDocument6 pages5.3.2.3 Lab - Implement Local SPAN (Satinder Singh) PDFSatinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Inside GlobalDocument13 pagesInside GlobalKleinhaus GyörgyNo ratings yet
- Inside GlobalDocument13 pagesInside GlobalKleinhaus GyörgyNo ratings yet
- 6.2.7 Lab - Configure Automated Security Features - ILMDocument17 pages6.2.7 Lab - Configure Automated Security Features - ILMandrew.talaat192No ratings yet
- 4.4.7 Lab - Configure Secure Administrative Access - ILMDocument22 pages4.4.7 Lab - Configure Secure Administrative Access - ILMRony Schäfer JaraNo ratings yet
- Cisco Lab Guide - 6.4.3.3 & 6.4.3.4Document3 pagesCisco Lab Guide - 6.4.3.3 & 6.4.3.4Julis-Alexia von Riessfelt100% (1)
- 4.4.7 Lab - Configure Secure Administrative AccessDocument11 pages4.4.7 Lab - Configure Secure Administrative AccessJesús Enrique100% (1)
- 2.6.1.2 Lab - Securing The Router For Administrative Access PDFDocument38 pages2.6.1.2 Lab - Securing The Router For Administrative Access PDFAAANo ratings yet
- Lab 01 - Securing The Router For Administrative AccessDocument39 pagesLab 01 - Securing The Router For Administrative AccessespolieeeNo ratings yet
- Konfigurasi Static Routing LABDocument18 pagesKonfigurasi Static Routing LABDhani msNo ratings yet
- Laporan Praktikum Komunikasi Data Dan Jaringan Komputer Modul 3Document13 pagesLaporan Praktikum Komunikasi Data Dan Jaringan Komputer Modul 3fahmy akhmad100% (1)
- 4.4.7 Lab Configure Secure Administrative AccessDocument10 pages4.4.7 Lab Configure Secure Administrative AccessHector De Jesus Tapia GorgonioNo ratings yet
- 8.3.2.7 Lab - Testing Network Connectivity With Ping and TracerouteDocument15 pages8.3.2.7 Lab - Testing Network Connectivity With Ping and TracerouteasdfjklNo ratings yet
- Dynamic RIPDocument8 pagesDynamic RIPkhaledrousan2121No ratings yet
- 5.3.3.2 Lab - Troubleshoot LAN Traffic Using SPANDocument6 pages5.3.3.2 Lab - Troubleshoot LAN Traffic Using SPANYaser Samer0% (6)
- Certification 2 Sem 4Document27 pagesCertification 2 Sem 4Norman AdimoNo ratings yet
- 6.5.1.2 Lab - Building A Switch and Router NetworkDocument8 pages6.5.1.2 Lab - Building A Switch and Router NetworkParthPatel100% (8)
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkFrom EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNo ratings yet
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationFrom EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationNo ratings yet
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3From EverandCisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksFrom EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNo ratings yet
- MPLS: Multi-Protocol Label MPLS: Multi-Protocol Label SwitchinggDocument29 pagesMPLS: Multi-Protocol Label MPLS: Multi-Protocol Label SwitchinggShulav PoudelNo ratings yet
- 04 RouterDocument109 pages04 RouterShulav PoudelNo ratings yet
- Extra - Question For WFQDocument1 pageExtra - Question For WFQShulav PoudelNo ratings yet
- F51033541 PDFDocument7 pagesF51033541 PDFShulav PoudelNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge: TopologyDocument2 pagesPacket Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge: TopologyShulav PoudelNo ratings yet
- Digital CommunicationDocument8 pagesDigital CommunicationShulav PoudelNo ratings yet
- Network Design - Assignment - 3Document2 pagesNetwork Design - Assignment - 3Shulav PoudelNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 2 2015Document7 pagesAssignment - 2 2015Shulav PoudelNo ratings yet
- Network Design Assignment 1Document4 pagesNetwork Design Assignment 1Shulav PoudelNo ratings yet
- Ask FSK PSK NotesDocument47 pagesAsk FSK PSK NotesRandy LeeNo ratings yet
- Imrpoving ZRP ProtocolDocument5 pagesImrpoving ZRP ProtocolChaitas ShahNo ratings yet
- Capitulo 8 (Equipo 4)Document44 pagesCapitulo 8 (Equipo 4)Juan Manuel RamirezNo ratings yet
- ACOMAR: ACO-based MAC-aware Routing Protocol: Djamila Mechta - Oussama Mahgoun - Saad HarousDocument25 pagesACOMAR: ACO-based MAC-aware Routing Protocol: Djamila Mechta - Oussama Mahgoun - Saad HarousUsman AshrafNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 1 RIP v.2Document4 pagesActivity No. 1 RIP v.2secretNo ratings yet
- FBR-4000-V1 Spec V1.0Document3 pagesFBR-4000-V1 Spec V1.0SHING EBNo ratings yet
- CCDE Written Exam Topics v2.0: Exam Sections and Sub-Task ObjectivesDocument5 pagesCCDE Written Exam Topics v2.0: Exam Sections and Sub-Task Objectivesacer04266No ratings yet
- Basic Cisco Router CommandsDocument6 pagesBasic Cisco Router Commandsabhaytech8451No ratings yet
- Power Plane: 2.6.2 Attacks On WSNDocument9 pagesPower Plane: 2.6.2 Attacks On WSNPonraj ParkNo ratings yet
- CiscoDocument11 pagesCiscoSudhir MaherwalNo ratings yet
- Network LabDocument24 pagesNetwork Labget_togetherNo ratings yet
- ns-2 Tutorial: Polly Huang Usc/Isi Huang@isi - Edu 14 June, 1999Document78 pagesns-2 Tutorial: Polly Huang Usc/Isi Huang@isi - Edu 14 June, 1999Pratik MaskeyNo ratings yet
- Circuit and Packet SwitchingDocument27 pagesCircuit and Packet Switchingdevbrat anandNo ratings yet
- Solutions OSI ExercisesDocument50 pagesSolutions OSI ExercisesHussam AlwareethNo ratings yet
- FortiGate Administration Guide 01 400 89802 20090219Document658 pagesFortiGate Administration Guide 01 400 89802 20090219arnoo25No ratings yet
- ME Electronics Mumbai UniversityDocument38 pagesME Electronics Mumbai UniversityRahul Rajesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- CN-Lab-6-Basic-Router-Configuration Mubashir Hussain 4979Document26 pagesCN-Lab-6-Basic-Router-Configuration Mubashir Hussain 4979Mubashir HussainNo ratings yet
- EC8702Document7 pagesEC8702Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Router 1X3-RTL Design and Verification: September 2015Document11 pagesRouter 1X3-RTL Design and Verification: September 2015Bhosle Balaji DhondibaNo ratings yet
- Intelligent Health Monitoring Device and Technology in Wireless Community Remote Medical Monitoring System On Basis of Zigbee NetworkDocument6 pagesIntelligent Health Monitoring Device and Technology in Wireless Community Remote Medical Monitoring System On Basis of Zigbee Networkchalla SushmitaNo ratings yet
- 4.3.8 Packet Tracer - Configure Layer 3 Switching and Inter-VLAN Routing - ILMDocument6 pages4.3.8 Packet Tracer - Configure Layer 3 Switching and Inter-VLAN Routing - ILMJhonathanNo ratings yet
- 5.2.1.6 Packet Tracer - DR - SN0305-20170140118-Abdi Brillian RDocument5 pages5.2.1.6 Packet Tracer - DR - SN0305-20170140118-Abdi Brillian Rabdi brillianNo ratings yet
- 06 - VXLAN Part VI VXLAN BGP EVPN - Basic ConfigurationsDocument22 pages06 - VXLAN Part VI VXLAN BGP EVPN - Basic ConfigurationsNguyen LeNo ratings yet
- FCIP IP Configuration-GSTNDocument2 pagesFCIP IP Configuration-GSTNTaruna PNo ratings yet
- Survey On Traffic Engineering Using MPLS TechnologyDocument7 pagesSurvey On Traffic Engineering Using MPLS Technologyزكريا بركةNo ratings yet
- JNCIS SP Part1 - 2013 04 26 PDFDocument192 pagesJNCIS SP Part1 - 2013 04 26 PDFf.mrassiNo ratings yet
- CISCO Questions & Answers 85Document11 pagesCISCO Questions & Answers 85AsadNo ratings yet
- CCNA Lab Topology 100406 PDFDocument34 pagesCCNA Lab Topology 100406 PDFAshin AntonyNo ratings yet
- MPLS ConfiguracaoDocument6 pagesMPLS ConfiguracaoLucio CostaNo ratings yet
- The New Cyber Insecurity:: Geopolitical and Supply Chain Risks From The Huawei MonocultureDocument16 pagesThe New Cyber Insecurity:: Geopolitical and Supply Chain Risks From The Huawei MonoculturesdfwerNo ratings yet
- Is-Is Routing ProtocolDocument27 pagesIs-Is Routing Protocolkukulkan9No ratings yet