Penetrant Non Destructive Testing. Theory and Application?
Penetrant Non Destructive Testing. Theory and Application?
Uploaded by
SimranAhluwaliaCopyright:
Available Formats
Penetrant Non Destructive Testing. Theory and Application?
Penetrant Non Destructive Testing. Theory and Application?
Uploaded by
SimranAhluwaliaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Penetrant Non Destructive Testing. Theory and Application?
Penetrant Non Destructive Testing. Theory and Application?
Uploaded by
SimranAhluwaliaCopyright:
Available Formats
Practical work 1
PENETRANT TESTING METHOD, EQUIPMENT AND TESTING TECHNOLOGY
I. Theory
1. Penetrant non destructive testing. Theory and application?
Answer :- The basic principle upon which penetrant testing is based is that of capillary attraction
or action. Capillary action is a surface tension phenomenon that permits liquids to be drawn into
tight openings as a result of the energies that are present at the surfaces of the openings. The liquid
used is a typical visible contrast penetrant. The capillary action forces are very strong and, in fact, if
a penetrant test were being performed on a specimen in an overhead position, the penetrant would
be drawn into the opening, against the force of gravity. The capillary force is much stronger than
gravity and the discontinuities will be detected even though they may be in an overhead specimen.
Penetrant testing is extremely versatile and has many applications. It is used in virtually every major
industry and for a wide variety of product forms. Industries that widely use penetrant testing
techniques include: Power generation, both fossil- and nuclear-fueled Petrochemical
Marine/Shipbuilding Metalworking, including foundries and forging shops Aerospace Virtually all
of the various welding processes and metals-joining industries. Another unique application of
penetrant testing is for the detection of through-wall leaks.
2. Types of penetrant testing?
Answer :-
1) Fluorescent technique
This technique contains three process according to material used for the testing.
Process A uses a fluorescent water-removable penetrant that can be used with either dry, aqueous, or
nonaqueous developers.
Processes B use a fluorescent postemulsifiable penetrant, a lipophilic (L) or hydrophilic (H)
emulsifier, and dry, aqueous, or nonaqueous developers. The penetrants used in this technique are
not water-removable without emulsification. A lipophilic or hydrophilic emulsifier must be used
after the dwell time has expired.
Process C uses a fluorescent penetrant, which is solvent-removable, a solvent cleaner/remover, and
a nonaqueous developer. The excess surface penetrant is first removed with a dry cloth, followed by
cleaning with a cloth dampened with a solvent remover.
2) Visible color-contrast technique
This technique contains three process according to material used for the testing.
Process A uses a visible color-contrast, water-removable penetrant and an aqueous or nonaqueous
developer. Dry developer is not usually used with Technique II penetrants. Some specifications, in
fact, do not permit the use of dry developers with Technique II penetrants
Process B uses a visible color-contrast, postemulsifiable penetrant, an emulsifier, and an aqueous or
nonaqueous developer. The materials used (except for the penetrant) are very similar to those
2
described for Technique I Process B. An emulsifier (usually lipophilic) is applied to the surface
penetrant after the dwell time to make it water-removable.
Process C uses a visible, color-contrast, solvent-removable penetrant, a solvent cleaner/remover,
and an aqueous or nonaqueous developer. The excess penetrant is not water-removable and must be
removed with a solvent remover.
3. Advantages and disadvantages of penetrant testing?
Answer :- The major advantages of penetrant testing include: Portability Cost (inexpensive)
Sensitivity Versatilevirtually any solid nonporous material can be inspected Effective for
production inspection Nondestructive.
The limitations include: Only discontinuities open to the surface of the test specimen can be
detected There are many processing variables that must be controlled Temperature variation effects
Surface condition and configuration Surface preparation is necessary The process is usually messy
II. Practical work
4. What equipment is used for penetrant testing?
Test material (Turbine blade)
Indicator penetrant
Penetrant remover (cleaner)
Penetrant drier
Penetrant developer
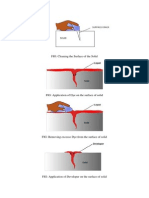
5. What is penetrant testing technology?
Preparation for testing.
Indicator penetrant technology of testing.
Removing of penetrant.
Developer technology of testing.
Registration of defects.
6. Results of pracical work
3
7. Conclusion
In this practical work visible color-contrast technique is used, thus the defect is identified with the
naked eye. Therefore, after performing practical work it can be seen that there is defect on the test
material that can be visible as a crack. It can be seen that the crack is located at about 3.01 cm from
the tip of the test material (Turbine Blade) and the crack is approximately 0.5 cm in length.
You might also like
- Liquid Penetrant Testing PDFDocument20 pagesLiquid Penetrant Testing PDFgueridiNo ratings yet
- Dye Penetrant InspDocument5 pagesDye Penetrant InspVysakh VasudevanNo ratings yet
- Dye Penetrant InspectionDocument5 pagesDye Penetrant Inspectionrajasekar21No ratings yet
- PTDocument217 pagesPTkhaled saadneh100% (1)
- Dye Penetrant InspectionDocument5 pagesDye Penetrant Inspectionrashm006ranjanNo ratings yet
- Dye Penetrant InspectionDocument5 pagesDye Penetrant InspectiontechzonesNo ratings yet
- Dye Penetrant Inspection: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument59 pagesDye Penetrant Inspection: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaPratik Karekar0% (1)
- Dye Penetrant Inspection - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 pagesDye Penetrant Inspection - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaviswamanoj100% (1)
- Module1 Testing and Flaw Detection of Materials and ComponentsDocument12 pagesModule1 Testing and Flaw Detection of Materials and ComponentsHari GovindNo ratings yet
- Dye PenetrantDocument17 pagesDye Penetrantsen_subhasis_58No ratings yet
- Module 2 Surface Gears MethodsDocument12 pagesModule 2 Surface Gears MethodsNAVEEN H V MENo ratings yet
- Non Destructive Testing and Evaluation Course Module Topic - Dye Penetrant TestingDocument118 pagesNon Destructive Testing and Evaluation Course Module Topic - Dye Penetrant TestingV.Muthu KumarNo ratings yet
- Liquid Penetrant Inspection 3Document24 pagesLiquid Penetrant Inspection 3Taha KhanNo ratings yet
- Dye Penetrant InspectionDocument15 pagesDye Penetrant InspectionUwaiz Qurni IINo ratings yet
- Dye Penetrant InspectionDocument6 pagesDye Penetrant InspectionHabib ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- PT Level IIDocument161 pagesPT Level IIJerry100% (5)
- Liquid Penetrant Testing ModuleDocument59 pagesLiquid Penetrant Testing ModuleDITANo ratings yet
- NDT of MaterialsDocument10 pagesNDT of MaterialsSuresh HaldipurNo ratings yet
- Liquid Penetrant TestingDocument20 pagesLiquid Penetrant Testingajayghosh3140No ratings yet
- Penetrant RaportDocument6 pagesPenetrant RaportMeritan BaballariNo ratings yet
- Liquid Penetrant TestingDocument20 pagesLiquid Penetrant TestingsanjibkrjanaNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT No.: - Liquid Penetrant TestDocument6 pagesEXPERIMENT No.: - Liquid Penetrant TestVandan GundaleNo ratings yet
- PT 001Document18 pagesPT 001ziyadhelaly998No ratings yet
- DPTDocument10 pagesDPTShabbir HassanNo ratings yet
- Inspecting Welds With Liquid PenetrantDocument4 pagesInspecting Welds With Liquid PenetrantHizbul WathanNo ratings yet
- Liquid Penetrant TestingDocument20 pagesLiquid Penetrant TestingdharshdivyNo ratings yet
- NDT Lecture05 2015Document39 pagesNDT Lecture05 2015Miruna Clinciu100% (1)
- LPTDocument22 pagesLPTPratik SalveNo ratings yet
- Material Science AlfathiDocument5 pagesMaterial Science AlfathiAnonymous UdOhqLMNo ratings yet
- Dye Penetrant TestDocument14 pagesDye Penetrant TestSaif FaridiNo ratings yet
- Liquid Penetration TestDocument12 pagesLiquid Penetration TestYuvaraj Maganathan100% (1)
- Non Destructive Testing - Dye Penetrant InspectionDocument6 pagesNon Destructive Testing - Dye Penetrant InspectionKevin ThomasNo ratings yet
- Basic DPTDocument56 pagesBasic DPTrajuajiNo ratings yet
- Dye Penetrant TestDocument4 pagesDye Penetrant Testarunkumarnoola100% (2)
- Non Destructive TestingDocument30 pagesNon Destructive TestingRahul GajjeNo ratings yet
- NDT Module 2Document21 pagesNDT Module 2Sajeesh Saji100% (1)
- PT-Liquid Penetrant Testing Procedure R01 - 2 2Document12 pagesPT-Liquid Penetrant Testing Procedure R01 - 2 2George Ogbeche100% (1)
- Non-Destructive Inspection Practical: NAME:-Amol Rajhans Talekar Roll No.: - Name of DepartmentDocument40 pagesNon-Destructive Inspection Practical: NAME:-Amol Rajhans Talekar Roll No.: - Name of DepartmentAniket DhoneNo ratings yet
- PT Theory FromDocument75 pagesPT Theory FromYousef Adel HassanenNo ratings yet
- Often Referenced StandardsDocument18 pagesOften Referenced StandardssriramNo ratings yet
- Penetrant Testing, or PT, Is A NondestructiveDocument10 pagesPenetrant Testing, or PT, Is A NondestructiveMastram HatheshNo ratings yet
- Non - Destructive Testing: UNIT-5Document26 pagesNon - Destructive Testing: UNIT-5Jones Jones Jr.No ratings yet
- Welcome To CIAST and Liquid Penetrant TestingDocument154 pagesWelcome To CIAST and Liquid Penetrant Testinghisham_eyesNo ratings yet
- General Knowledge: 1.1 Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) 1.1.1 Definition and Nature of NDT TechnologyDocument44 pagesGeneral Knowledge: 1.1 Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) 1.1.1 Definition and Nature of NDT TechnologyMirza Safeer AhmadNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.3 Dye Penetration TestDocument4 pagesExperiment No.3 Dye Penetration TestChristian D. AllanaNo ratings yet
- Basics of LPIDocument21 pagesBasics of LPISuresh RathodNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document5 pagesModule 1nijo.joseNo ratings yet
- Liquid Penetrant PresentationDocument98 pagesLiquid Penetrant PresentationAkhil Balachandran100% (9)
- LPT Study Material LatestDocument33 pagesLPT Study Material Latestbeltranrommel100% (2)
- 4 Intro To Penetrant 03092013 OKDocument27 pages4 Intro To Penetrant 03092013 OKnishant kumar singhNo ratings yet
- L8 - NonDestructive Test - Liquid Penetrant TestDocument32 pagesL8 - NonDestructive Test - Liquid Penetrant Testvenosyah devanNo ratings yet
- Penetrant Testing: Principles, Techniques, Applications and Interview Q&AFrom EverandPenetrant Testing: Principles, Techniques, Applications and Interview Q&ANo ratings yet
- Self-Cleaning Materials and Surfaces: A Nanotechnology ApproachFrom EverandSelf-Cleaning Materials and Surfaces: A Nanotechnology ApproachWalid A. DaoudRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Science of Superhydrophobicity: Enhancing Outdoor Electrical InsulatorsFrom EverandThe Science of Superhydrophobicity: Enhancing Outdoor Electrical InsulatorsNo ratings yet
- New Appoaches in the Process Industries: The Manufacturing Plant of the FutureFrom EverandNew Appoaches in the Process Industries: The Manufacturing Plant of the FutureNo ratings yet
- Hydro Testing Handbook: Principles, Practices, Applications, Formulas, and Common Q&AFrom EverandHydro Testing Handbook: Principles, Practices, Applications, Formulas, and Common Q&ANo ratings yet
- LABORATORY MANUAL FOR A MINI PROJECT: MSCB 1113 BIOCHEMISTRY & MICROBIAL PHYSIOLOGYFrom EverandLABORATORY MANUAL FOR A MINI PROJECT: MSCB 1113 BIOCHEMISTRY & MICROBIAL PHYSIOLOGYNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Inspection ReportDocument9 pagesUnit 6 Inspection ReportSimranAhluwaliaNo ratings yet
- Swot Analysis of Tata Group: Presented By: Flocim Gabriel DsouzaDocument14 pagesSwot Analysis of Tata Group: Presented By: Flocim Gabriel DsouzaSimranAhluwaliaNo ratings yet
- UG21T3504-Specialized Cargo Handling and Stowage - QP1Document2 pagesUG21T3504-Specialized Cargo Handling and Stowage - QP1SimranAhluwaliaNo ratings yet
- Autonomous Air Space Management & Control System: Presented By:-Prabh Simranjeet Singh AhluwaliaDocument39 pagesAutonomous Air Space Management & Control System: Presented By:-Prabh Simranjeet Singh AhluwaliaSimranAhluwaliaNo ratings yet
- Export of Rice From IndiaDocument6 pagesExport of Rice From IndiaSimranAhluwaliaNo ratings yet
- Role of Aviation Sector For LatviaDocument17 pagesRole of Aviation Sector For LatviaSimranAhluwaliaNo ratings yet
- Progress Test Nr.1 Penetrant TestingDocument2 pagesProgress Test Nr.1 Penetrant TestingSimranAhluwaliaNo ratings yet
- Progress Test Nr.001 DefectsDocument3 pagesProgress Test Nr.001 DefectsSimranAhluwaliaNo ratings yet
- M15 Lecture 4 InletDocument24 pagesM15 Lecture 4 InletSimranAhluwaliaNo ratings yet
- History of Human Factors Andrey KanDocument6 pagesHistory of Human Factors Andrey KanSimranAhluwaliaNo ratings yet