Risk Managment
Risk Managment
Uploaded by
Rhodora BenipayoCopyright:
Available Formats
Risk Managment
Risk Managment
Uploaded by
Rhodora BenipayoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Risk Managment
Risk Managment
Uploaded by
Rhodora BenipayoCopyright:
Available Formats
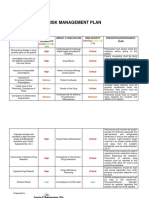
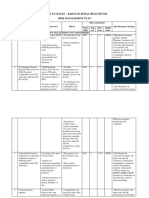
RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN.
……
STANDARD OPERATING
Document No. MM- 025-2017
PROCEDURE
Effective Date: July 8, 2017
PHARMACY Revision No:00
RISK MANAGEMENT
ANGONO MEDICS PLAN Page of: 1 of 5
HOSPITAL
REVISION HISTORY
Rev. Prepared by: Reviewed by Approved by
RHODORA M.
VIRGINIA C. LEONARDO AZER M. VILLAMAYOR, MD
BENIPAYO, RN. MAN.
Chief Pharmacist Medical Director
Chief Nurse/ QA Officer
REFERENCES
Document No.: Title
PURPOSE:
This policy is intended to propose a standard concept for “Pharmacovigilance
Plan” and “Risk Minimization Plan” in order to deal with “Important identified
risks”, “ Important potential risks” and “Important missing information” in
accordance to Pharmacovigilance Planning.
This policy should be used as a guideline when AMH considers further
surveillances and studies regarding the safety of the product and additional
actions to mitigate risks in the time of approval review of any product in the
pharmacy.
This policy is intended to improve safety measures based on the assured safety
guidelines, the benefit/risk assessment and the review of them.
SCOPE
The products which are subject to “Risk Management Plan (RMP)” and the time
when the Plan is applied are described below:
1. In the time of approval review of new drugs (include new additional indication
and dosage, revised/additional dosage and administration, new combination
drug, additional dosage form: the same shall apply hereinafter), and when Safety
Specification is newly submitted during the re-examination period.
ANGONO MEDICS HOSPITAL Inc. - In GOD We Trust!
1
RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN.……
2. When Safety Specification is newly submitted for generic drugs and drugs for
which the re-examination was completed.
3. At the time of approval of the generic, in the case that its reference drug has
already obligated to develop an additional risk minimization activity.
POLICY:
Safety Specification
1. AMH should present “ Important identified risks”, “ Important potential risks”
and “ Important missing information” as Safety Specification in order to review
whether additional actions are needed in Pharmacovigirance Plan and risk
minimization activity for the appropriate benefit-risk balance with taking into
account of the characteristics of the treatment population, disease and
administration.
2. Safety Specification should be a summary of the following important potential
risks which may affect the benefit/risk balance. As to preparing the Safety
Specification, AMH should refer to the revised“Medication Management Policy”.
DEFINITION OF TERMS:
a. “Important identified risks”:severe or frequent adverse drug
reactions (ADRs) (includes drug interaction): ADRs which are fully
verified in non-clinical studies as well as in clinical data. ADRs which are
suggested causal relationships to a drug by studies including clinical
trials. ADRs which are strongly suggested causal relationships to a drug
based on the ADR reports.
b. “Important potential risks”:adverse events (AEs) that are required
further collecting information because of safety concerns such as cases
(includes drug interaction).
Severe and frequent AEs which occurred in clinical trials or other
clinical use (the causal relationships unclear).
Potential serious ADRs which occurred in clinical trials and other
clinical use.
ANGONO MEDICS HOSPITAL Inc. - In GOD We Trust!
2
RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN.……
AEs which are identified in non-clinical studies but not identified in
clinical trials.
AEs which are not identified in clinical studies but
pharmacologically predictable.
AEs which are identified in another drug of the same class but not
identified in the drug.
Accumulated the ADR reports with unclear causal relationship to
the drug.
c. “Important missing information”: information which was not
acquired at the time of submission of Risk Management Plan and
suggests that it has a limitation in the estimation of the drug safety in the
post-marketing setting. e.g.) The safety information essential for a
certain patient population that is excluded from the clinical trials but need
to be considered about the drug safety, due to high frequency of the
drug use in a practical clinical setting.
3. AMH must identify the safety issues as Safety Specification in the time of
approval review of any drug to be included in the Formulary. The RMP which is
included in the "Basic plans of the Phamacovigilance Management System"
should be developed by identifying Safety Specification as the starting point, as
with described in the Medication Management Guideline.
Risk Management Plan (RMP)
1. Based on the “Important identified risks”, “Important potential risks” and
“Important missing information” which are identified as Safety Specifications,
AMH should develop the “Pharmacovigilance Plan” and “Risk Minimization Plan”,
the whole plan should be submitted as RMP.
2. RMP should be reviewed for consistency with its review report. Depending on the
Safety Specification, AMH should clarify whether an additional action should be
implemented besides the regular pharmacovigirance plan and risk minimization
activity. And the Pharmacy should also clarify the reason of that.
ANGONO MEDICS HOSPITAL Inc. - In GOD We Trust!
3
RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN.……
3. Even if it is not considered that the drug needs to be taken an additional action
in safety specifications, the Pharmacy is required to submit Adverse Drug
Reaction (ADR) under the provision of the FDA. In principle, pharmacovigilance is
required to be conducted for all new drugs.
4. Even if it is not considered that the drug needs an additional action in safety
specifications, information provision by the package insert is required as routine
risk minimization activity. The Pharmacy should provide information based on the
drug formulary using additional materials for new drugs.
5. If it is considered that the drug needs additional pharmacovigilance and that use-
cases surveillance including specified use-cases surveillance should be
implemented, the pharmacy should clarify the objectives of the survey and pays
attention to implement the RMP in an appropriate manner.
6. The pharmacy should also make a point to utilize methods of
pharmacoepidemiology as use- cases surveillance.
7. In the "Pharmacovigilance Plan" and "Risk Minimization Plan", when the
pharmacy reviews the need for additional actions, the following should be
considered.
a. The impact of ADRs, the severity, frequency, reversibility and
preventability on severe ADRs
b. The severity of disease included in drug indications, the severity and the
background incidence rate of complications
c. Estimated number of patient exposure
d. Identified risk populations
e. Expected benefits by conducting risk minimization activity
f. Treatment duration
g. World-wide market authorization status
h. Results of overseas surveillance and studies (if it is changed, the points
which should be taken into account)
i. The difference in safety profiles between Japan and overseas
j. Safety measures which was taken in overseas
8. If an additional action is required in pharmacovigilance plan and/or risk
minimization activity, AMH should clarify the reason and the method of the
ANGONO MEDICS HOSPITAL Inc. - In GOD We Trust!
4
RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN.……
action. In the case that it is not considered the drug needs an additional action,
AMH should clarify the reason.
Important potential risks
-Safety review of long-term administration
-Review of increased risk of possible AE
-Review of AEs which may occur in the natural course of the underlying disease
or complication, and are difficult to distinguish from ADRs
-Review whether the frequency of ADR is potentially higher than that of the
other drug long-term administration surveillance/studies, Pharmacoepidemiology
studies including a cohort study and case-control study
Important missing information
-Review of the drug safety in the case that safety information obtained from
clinical practice by the time of approval was extremely limited due to the
inefficient number of patients
-Review of the drug safety in the case that the drug may be used in sub-groups
including pregnant women. Information gathering by registry, other active
surveillances, use-cases surveillances
END OF DOCUMENT
ANGONO MEDICS HOSPITAL Inc. - In GOD We Trust!
5
You might also like
- SopsDocument35 pagesSopsziaddd82% (17)
- Pharmacy Risk Management PlanDocument6 pagesPharmacy Risk Management PlanJohn Roa80% (10)
- Risk Management PlanDocument2 pagesRisk Management Planrojon pharmacy84% (38)
- DR Sebi Cure For Herpes - DefDocument95 pagesDR Sebi Cure For Herpes - DefFabrizio Cottone80% (10)
- RMP DocsDocument8 pagesRMP DocsMike John Dela Cruz83% (12)
- Pharmacy Emergency Response Plan TemplateDocument42 pagesPharmacy Emergency Response Plan Templatelucky javellana100% (2)
- Generic Menu CardDocument32 pagesGeneric Menu CardZurerx Mindoro100% (4)
- Generics Menu CardDocument72 pagesGenerics Menu Cardjptragura.rxd100% (1)
- Standard Operating ProcedureDocument34 pagesStandard Operating ProcedureJessieLynMolina100% (2)
- Pharmacy Stadard Operating ProcedureDocument5 pagesPharmacy Stadard Operating ProcedureJose Ramon Dalo Bautista100% (3)
- SOP Power Contingency PlanDocument2 pagesSOP Power Contingency Planjhebuenga12100% (1)
- Risk Management PlanDocument2 pagesRisk Management Planrojon pharmacy100% (2)
- FDA Drugstore Inspection ChecklistDocument3 pagesFDA Drugstore Inspection ChecklistJohanna MonroyNo ratings yet
- CAPA Plan Farmacia Delim and General MerchandiseDocument4 pagesCAPA Plan Farmacia Delim and General MerchandiseArianne Courtney Nacar100% (1)
- Editable RMP DOH 2019 PDFDocument13 pagesEditable RMP DOH 2019 PDFtaslima tabayag100% (1)
- Drugstore Inspection Checklist - Routine PDFDocument3 pagesDrugstore Inspection Checklist - Routine PDFRyan Glenn Soguilon100% (5)
- Risk Management Plan: Fatima Hill Pharmacy APRIL 2019Document11 pagesRisk Management Plan: Fatima Hill Pharmacy APRIL 2019Sushmita Mae Cajes91% (11)
- Standard Operating Procedures HospitalDocument5 pagesStandard Operating Procedures HospitalCesar Francisco95% (40)
- Risk Management PlanDocument2 pagesRisk Management PlanKeith Reyes100% (4)
- Risk Management Plan: I. A. Internal EnvironmentDocument6 pagesRisk Management Plan: I. A. Internal EnvironmentJose Ramon Dalo Bautista100% (1)
- Personnel Competency EvaluationDocument4 pagesPersonnel Competency EvaluationMikes Flores100% (4)
- Generic Menu CardDocument13 pagesGeneric Menu CardCarissa Villaver100% (2)
- Standard Operating Procedure Good Storage PracticeDocument2 pagesStandard Operating Procedure Good Storage PracticeDaniel Yves IV Paez50% (2)
- Standard Operating Procedure Pests and Rodents ControlDocument3 pagesStandard Operating Procedure Pests and Rodents ControlDaniel Yves IV Paez100% (2)
- Standard Operating Procedures - PharmacyDocument2 pagesStandard Operating Procedures - Pharmacysheryl Guillermo100% (1)
- PhilHealth Circular No. 0035, s.2013 Annex 2 List of Procedure Case RatesDocument98 pagesPhilHealth Circular No. 0035, s.2013 Annex 2 List of Procedure Case RatesChrysanthus Herrera50% (2)
- Capa Plan FormatDocument4 pagesCapa Plan FormatJERSEY ANN MARIE V. MACALINCAGNo ratings yet
- Risk Management Plan: Polytechnic University of The PhilippinesDocument11 pagesRisk Management Plan: Polytechnic University of The PhilippinesdaniellaNo ratings yet
- Risk Management PlanDocument9 pagesRisk Management PlanCj Binalay Arao100% (3)
- Everyday Iloveyou Drugstore Risk Management PlanDocument8 pagesEveryday Iloveyou Drugstore Risk Management PlanKirstieKerry100% (1)
- Immunovacs Ltd. Co.: Section A: IntroductionDocument6 pagesImmunovacs Ltd. Co.: Section A: IntroductionBelle BrionesNo ratings yet
- Risk Management PlanDocument5 pagesRisk Management PlanJay Ar80% (5)
- Risk Management PlanDocument3 pagesRisk Management PlanrainNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy Risk Management Plan: Salun at Drugstore Page - 1Document5 pagesPharmacy Risk Management Plan: Salun at Drugstore Page - 1Mikes Flores100% (1)
- Standard Operating Procedure 4 PDF FreeDocument19 pagesStandard Operating Procedure 4 PDF FreeMillen100% (3)
- Inspection Checklist DSDocument1 pageInspection Checklist DSColleen Ariel SandovalNo ratings yet
- Duties and Responsibilities of The PharmacistDocument2 pagesDuties and Responsibilities of The PharmacistMaan Santiago100% (1)
- Requirements For Opening A Drugstore PDFDocument2 pagesRequirements For Opening A Drugstore PDFPsyar Lysa Javier67% (3)
- Standard Operating Procedures HospitalDocument5 pagesStandard Operating Procedures HospitalCindy Gabayeron100% (2)
- Pharmacy Risk Management PlanDocument7 pagesPharmacy Risk Management PlanLexie Glee100% (1)
- RMP For Drug Establishments - 26 August 2015 PDFDocument88 pagesRMP For Drug Establishments - 26 August 2015 PDFIan FranklinNo ratings yet
- RMP For Drug Establishments - 26 August 2015 PDFDocument88 pagesRMP For Drug Establishments - 26 August 2015 PDFBelle Briones0% (1)
- Duties and Responsibilities of PharmacistDocument3 pagesDuties and Responsibilities of PharmacistChan Orsolino100% (2)
- Generic DispensingDocument30 pagesGeneric Dispensingshervintancruzado83% (6)
- Pharmacy Standard Operating ProcedureDocument3 pagesPharmacy Standard Operating Procedurerain100% (3)
- Risk Identification Risk Assessment Plan Risk Response Development Plan Risk Response Control PlanDocument1 pageRisk Identification Risk Assessment Plan Risk Response Development Plan Risk Response Control PlanEugenio Rowe100% (1)
- Pharmacy PDFDocument25 pagesPharmacy PDFSauraj GautamNo ratings yet
- RMP RXDocument5 pagesRMP RXGloria RamosNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating Procedure - PharmaSave PharmacyDocument20 pagesStandard Operating Procedure - PharmaSave PharmacyDaniel Yves IV PaezNo ratings yet
- Handling Returned Products Forf CostumerDocument5 pagesHandling Returned Products Forf CostumerCyril Balla100% (2)
- Risk Management PlanDocument2 pagesRisk Management PlanRoxanneGailBigcasGoleroNo ratings yet
- Power Failure Contingency PlanDocument2 pagesPower Failure Contingency PlanDaniel Yves IV Paez100% (2)
- Edpms Complete GuideDocument75 pagesEdpms Complete Guidesheryl GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating Procedure Product RecallDocument2 pagesStandard Operating Procedure Product RecallDaniel Yves IV Paez100% (1)
- List of Medicines and Corresponding Maximum Drug Retail PriceDocument3 pagesList of Medicines and Corresponding Maximum Drug Retail PriceLindbergh Espino100% (4)
- Standard Operating Procedure Good Dispensing PracticeDocument2 pagesStandard Operating Procedure Good Dispensing PracticeDaniel Yves IV Paez100% (1)
- Generic Dispensing Flowchart: Over The Counter Drugs Prescription Drugs (RX)Document1 pageGeneric Dispensing Flowchart: Over The Counter Drugs Prescription Drugs (RX)chibibi the grNo ratings yet
- Ken's Pharmacy FDA ReqsDocument3 pagesKen's Pharmacy FDA ReqsStar Del Mar IsaganNo ratings yet
- MDRP A4 SizeDocument4 pagesMDRP A4 Sizejptragura.rxdNo ratings yet
- RMP BiosimilarsDocument18 pagesRMP BiosimilarsSutirtho MukherjiNo ratings yet
- Draft Guidance For PvpiDocument121 pagesDraft Guidance For PvpiLAKSHAY kUMARNo ratings yet
- PV Guidance DocumentDocument54 pagesPV Guidance DocumentRenneyNo ratings yet
- SRA GuidelinesDocument1 pageSRA GuidelinesRhodora BenipayoNo ratings yet
- Ritm MonkeypoxDocument24 pagesRitm MonkeypoxRhodora BenipayoNo ratings yet
- DM No. 2022-0298 Implementation of The HFP System in All Government and Private Hospitals, Infirmaries and Primary Care Facilities in The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesDM No. 2022-0298 Implementation of The HFP System in All Government and Private Hospitals, Infirmaries and Primary Care Facilities in The PhilippinesRhodora BenipayoNo ratings yet
- Nurturing A Thankful Heart!Document14 pagesNurturing A Thankful Heart!Rhodora BenipayoNo ratings yet
- Doh Health Facility Price Advisory-08032022-1 - 2Document1 pageDoh Health Facility Price Advisory-08032022-1 - 2Rhodora BenipayoNo ratings yet
- Facing The Future With ConfidenceDocument16 pagesFacing The Future With ConfidenceRhodora BenipayoNo ratings yet
- PERDEVDocument33 pagesPERDEVRhodora Benipayo100% (1)
- Benefits of BreastfeedingDocument1 pageBenefits of BreastfeedingRhodora BenipayoNo ratings yet
- Blood DonationDocument2 pagesBlood DonationRhodora BenipayoNo ratings yet
- Restoring Broken RelationshipsDocument13 pagesRestoring Broken RelationshipsRhodora BenipayoNo ratings yet
- Timeline of Philippine ArtsDocument2 pagesTimeline of Philippine ArtsRhodora Benipayo78% (54)
- DILG Memo - Circular 201146 44f587fc22 PDFDocument1 pageDILG Memo - Circular 201146 44f587fc22 PDFRhodora BenipayoNo ratings yet
- Application Form For HospitalDocument5 pagesApplication Form For HospitalRhodora BenipayoNo ratings yet
- Medication ManagementDocument34 pagesMedication ManagementRhodora BenipayoNo ratings yet
- Abuse and Neglect PolicyDocument4 pagesAbuse and Neglect PolicyRhodora BenipayoNo ratings yet
- Review Checklist For Hospital RenewalDocument1 pageReview Checklist For Hospital RenewalRhodora BenipayoNo ratings yet
- Application Form Blood Collection Unit Blood StationDocument5 pagesApplication Form Blood Collection Unit Blood StationRhodora BenipayoNo ratings yet
- Youth Camp FocusDocument43 pagesYouth Camp FocusRhodora BenipayoNo ratings yet
- Application Form Clinical Laboratory PDFDocument6 pagesApplication Form Clinical Laboratory PDFRhodora Benipayo100% (1)
- Hospital Safety PromotionDocument46 pagesHospital Safety PromotionRhodora BenipayoNo ratings yet
- PhilHealth Circular No. 0035, s.2013 Annex 1 List of Medical Case RatesDocument111 pagesPhilHealth Circular No. 0035, s.2013 Annex 1 List of Medical Case RatesChrysanthus Herrera80% (5)
- Globant S.A. - Corporate Governance GuidelinesDocument4 pagesGlobant S.A. - Corporate Governance Guidelineszerocinco5berto xdebertoNo ratings yet
- A StudyDocument133 pagesA StudyBibin PayyakaraNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae Soedjatmiko: KontakDocument4 pagesCurriculum Vitae Soedjatmiko: KontakKang AdingNo ratings yet
- Valve Positioners - SRD998Document2 pagesValve Positioners - SRD998agrovadoNo ratings yet
- Basic Life SupportDocument8 pagesBasic Life SupportAdilla RachmawatiNo ratings yet
- Road Design Note 0608 The Use of Flexible and Semi Rigid Guard FenceDocument15 pagesRoad Design Note 0608 The Use of Flexible and Semi Rigid Guard FenceAnonymous V92ZmILyQTNo ratings yet
- Friendship Vs FamilyDocument1 pageFriendship Vs Familysirthana697547No ratings yet
- Abnormal LaborDocument21 pagesAbnormal LaborCharisse Aser Flores AquinoNo ratings yet
- Division Virtual Orientation On The Implementation of Limited Face To Face Learning ModalityDocument52 pagesDivision Virtual Orientation On The Implementation of Limited Face To Face Learning ModalityVALIANT NAJIB ERESUELANo ratings yet
- Gryffin, For Decades, Has Specialised in Working Within The Education SectorDocument4 pagesGryffin, For Decades, Has Specialised in Working Within The Education SectorGryffinNo ratings yet
- ANDRITZ PumpsDocument2 pagesANDRITZ Pumpsventaseh 2019100% (1)
- Top 10 Guides For MenDocument288 pagesTop 10 Guides For MenSebastian Faragau100% (2)
- Case PresentationDocument21 pagesCase PresentationayhamsalimNo ratings yet
- Mapeh 10 Sustainable Development GoalsDocument10 pagesMapeh 10 Sustainable Development GoalsglenncabasiarNo ratings yet
- John Carnell - New Writings in SF 3Document97 pagesJohn Carnell - New Writings in SF 3hemanathanharikrishnNo ratings yet
- 2 - Addiction - Its Impact On FamilyDocument27 pages2 - Addiction - Its Impact On FamilyAlbert CostaNo ratings yet
- Enviro Mental Ethics: Jalina Re Ane Villa Ceran Renz Pu GaDocument10 pagesEnviro Mental Ethics: Jalina Re Ane Villa Ceran Renz Pu GaTaylor LeeNo ratings yet
- Disc Brake Rotor ProjectDocument9 pagesDisc Brake Rotor ProjectShobha raniNo ratings yet
- Sencon Short Can Sensors PDSDocument3 pagesSencon Short Can Sensors PDSAndrei LupuNo ratings yet
- Live Project On Advance Financial Management: Topic: - Leverage Analysis of Deloitte and Hindustan Unilever LimitedDocument7 pagesLive Project On Advance Financial Management: Topic: - Leverage Analysis of Deloitte and Hindustan Unilever Limitedrahul gargNo ratings yet
- The Friendship Recession - TRANSCRIPTDocument4 pagesThe Friendship Recession - TRANSCRIPTmatt_cheng_4No ratings yet
- CT554 Calibration Basics and WhyDocument15 pagesCT554 Calibration Basics and WhyKassis AkramNo ratings yet
- K130S Service Instruction EnglishDocument15 pagesK130S Service Instruction Englishaleksandras mickeviciusNo ratings yet
- Adjectives To Describe Character Information Gap Activities Oneonone Activities Tes - 125823Document2 pagesAdjectives To Describe Character Information Gap Activities Oneonone Activities Tes - 125823EvaNo ratings yet
- Let's Try This Fortune On Wheels!Document4 pagesLet's Try This Fortune On Wheels!Alaida Catacutan67% (3)
- ExerciseDocument2 pagesExercisesyahirahNo ratings yet
- ESSENTIAL AUTOMATION Company Profile-1Document3 pagesESSENTIAL AUTOMATION Company Profile-1Tushar KachhadiyaNo ratings yet
- Datasheet D296 Data Sheet enUS 2702469259Document3 pagesDatasheet D296 Data Sheet enUS 2702469259SOINSySO ECUADORNo ratings yet
- LEED GA v4 Flashcards 1-200 PDFDocument100 pagesLEED GA v4 Flashcards 1-200 PDFLawrence Martin LausNo ratings yet