Calcium Based Water Hardness and Associated Health Issues
Uploaded by
ARIVOLI RCalcium Based Water Hardness and Associated Health Issues
Uploaded by
ARIVOLI RPROJECT ON CALCIUM BASED WATER HARDNESS AND SOCIAL ISSUE
CALCIUM BASED WATER HARDNESS and
Associated health issues
UNDER THE GUIDANCE OF Prof. SARAVANAKUMAR M P
GROUP MEMBERS:
1. P.SIVARAMAN 15BCL0310
2. S. VENNILA 15BCL0403
3. P.PALANIYAPPAN 15BCL0404
4. R.ARUNKUMAR 15BCL0405
5. R.ARIVOLI 15BCL0407
6. S.GOKUL 15BCL0409
7. P.MOHAN 15BCL0410
8. R.RAJESH KANNAN 15BCL0411
9. D.PREETHI 15BCL0423
Friday, November 12, 2016 Page 1
PROJECT ON CALCIUM BASED WATER HARDNESS AND SOCIAL ISSUE
SL.NO. contents
1 Aim
2 Introduction
3 Our objective and Social significant
4 Principal
5 Material required
6 Apparatus Required
7 Chemicals Required
8 Sample Handling and Preservation
9 Precautions
10 Procedure
11 Preparation of Reagents
12 Testing of Water Sample
13 Table and Data sheet
14 Calculation
15 Result and Discussion
16 conclusion
17 reference
Friday, November 12, 2016 Page 2
PROJECT ON CALCIUM BASED WATER HARDNESS AND SOCIAL ISSUE
1. AIM
To determine the calcium hardness in the given water sample from different sources using titration
method.
INTRODUCTION
Water hardness is an expression for the sum of the calcium and magnesium cat ions concentration in a
water sample.
Calcium is usually found in highest concentrations in natural water. The presence of calcium in water
results from deposits of lime stone, gypsum ect. Calcium is one of the principal cat ions involved in
water hardness. Calcium hardness is the estimation of hardness due to calcium in water. These cat ions
form insoluble salts with soap and decrease the cleaning effectiveness of soap. They also form hard
water deposits in hot water heaters. The calcium contain may range from zero to several hundred ppm.
SOCIAL SIGNIFICANCE
We have decided to do this project basically to create awareness about the importance of drinking
clean water containing relevant amount of minerals. Water in different places has different taste and
mineral contain, because of the climatic condition and vegetation (exposed to) of that particular place.
In some place, water contains excessive minerals which deteriorate our health causing major bad health
issues. Whereas, in some places, water do not contain enough minerals which human body needs to
stay healthy. As we all know that minerals are very crucial for human body to function efficiently, but
only if it is taken in right quantity. Otherwise, it cause undesirable health problem (if we do not take it
in right amount) as and when we get older and make our live shortened.
Therefore, it is very important to examine the mineral contain of the water that we drink, so that we
could take necessary precaution to drink clean and healthy water.
With this objective, our group has decided to embark this project, to find out whether our people are
drinking safe and healthy water. So we are using this simple technique called titration to find out
calcium contain of the water in and around the VIT campus.
The relative amounts of calcium hardness, carbonate and non-carbonate hardness present in water are
the factors while determining the most economical type of softening process.
Determination of hardness serves as a basis for routine control of softening processes. Hard water
typically contains high concentrations of the Ca and Mg cat ions, which interfere with the use of the
water for many applications. These ions diminish the effectiveness of soaps and detergents for cleaning
operations. They diminish the drinking quality of water and they contribute to the accumulation of
insoluble salt deposits in the storage vessels or plumbing.
Friday, November 12, 2016 Page 3
PROJECT ON CALCIUM BASED WATER HARDNESS AND SOCIAL ISSUE
Principle
The quantity of calcium in water will be determined by titration the water sample with a standard
Ethylene Diamine Tetra Acetic acid (EDTA) of known volume and concentration. Based on the
stoichiometry of the reactions and the number of moles of EDTA required to reach the end point, the
concentration of calcium content in water is calculated.
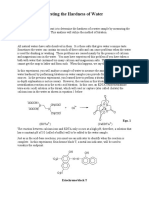
An indicator, ammonium purpurate (here we have used sodium purpurate) which combines only with
calcium is used.
The indicator imparts a pink color to the solution while there are calcium and magnesium ions that have
not complexes with EDTA. Once the endpoint has been reached and there in no more uncomplexed Ca
or Mg, the solution will turn to purple color. No hint of pink color will be left.
MATERIALS REQUIRED
Apparatus required:
1. Burette with stand and Porcelain tile
2. Pipettes with elongated tips
3. Conical flask
4. 250 ml Graduated cylinder
5. Standard Flask
6. Beakers
7. Wash bottle
CHEMICALS REQUIRED
1. Ammonium Purpurate
2. Sodium Hydroxide
3. Sodium chloride
4. EDTA
Friday, November 12, 2016 Page 4
PROJECT ON CALCIUM BASED WATER HARDNESS AND SOCIAL ISSUE
SAMPLE HANDLING AND PRESERVATION
Preservation of sample is not practical. Because biological activity will continue after a sample has been
taken, changes may occur during handling and storage. If analysis is to be carried out within two hours
of collection, cool storage is not necessary. If analysis cannot be started with in the two hours of sample
collection to reduce the change in sample, keep all samples at 4 degree celcis. Do not allow samples to
freeze. Do not open sample bottle before analysis. Begin analysis with six hours of sample collection.
Precautions
The following precautions should be observed while performing the experiment:
In this experiment, we are handling the indicator in powder form, in contrast with most of all other
basic experiments.
Handle the indicator powder carefully to get exact result. Handling of the alkali, NaOH should be born
with utmost care, since it causes irritation. Since NaOH pallets are hygroscopic in nature, do not expose
these pellets to air for a prolonged time period.
PROCEDURE
PREOARATION OF REAGENTS
Standard EDTA solution (0.02)
1. Switch on the Electronic balance, keep the weighing pan, and set the reading to zero. Take 1000mL
of distilled water in a 1000mL standard flask.
2. Weigh 3.723g of EDTA sodium salt.
3. Transfer the content to the water sample. Place the lid and mix the contents thoroughly until all
EDTA sodium salt dissolved in water.
4. Make all volume exactly 1000mL by adding distilled water. Transfer the solution to clean reagent
bottle named EDTA solution.
5. This 0.02 molar EDTA solution is going to be used as a titrate in this experiment. Take this solution in
a beaker for easy handling.
Ammonium Purpurate
1. Weigh 0.5g of Ammonium Purpurate. ( we used sodium purpurate)
2. Transfer it to the dry beaker.
3. Weigh 100g of sodium chloride.
4. Transfer it the beaker having sodium purpurate mix the contents thoroughly. Use it as a dry
powder
Friday, November 12, 2016 Page 5
PROJECT ON CALCIUM BASED WATER HARDNESS AND SOCIAL ISSUE
Sodium Hydroxide (1N) solution
1. Take 100mL of distilled water in a beaker.
2. Weigh 4gm of sodium hydroxide powder.
3. Transfer it to the distilled water in the breaker and mix it thoroughly.
4. Then transfer the entire content to 100mL standard flask.
5. Rinse the glass rod and funnel with distilled water.
6. Make the volume 100mL by adding distilled water up to mark.
7. Take the sodium hydroxide solution in 100mL beaker for easy handling.
TESTING OF SAMPLE:
Pipette 20mL of water sample and transfer it to a clean 250mL conical flask.
Measure 2mL of 1N sodium hydroxide solution using measuring cylinder. Add it to the water sample in
conical flask so that the pH will be maintained between 12 and 13.
Add few amount of sodium purpurate indicator to the water sample. Now the sample turns into pink
color. This color change is due to the calcium and magnesium contents presents in water.
Before starting the titration rinse the burette with few mL of EDTA solution and discard it. Fill the
burette with 0.02M EDTA solution. Adjust the reading to zero, and then fix it in burette stand. Ensure
that, there is no any air bubble inside the burette.
Titrate the water sample against the EDTA solution in the burette till all calcium and magnesium ions
present in the sample reacts with the EDTA to form a metal EDTA complex by changing the color of the
sample to purple. That is the end point.
Note down the burette reading.
The value of titration is 5.7mL
Repeat the titration for concordant values
CALCULATION:
To determine calcium Hardness in the given water sample, the reading are required to be tabulated.
Burette solution: EDTA
Pipette solution: sample
Indicator: Ammonium Purpurate
End point: Appearance of Purple color.
Friday, November 12, 2016 Page 6
PROJECT ON CALCIUM BASED WATER HARDNESS AND SOCIAL ISSUE
TABLE
Sample Volume of Burette Reading (mL) Volume of
no. sample (mL)
initial final EDTA(mL)
Here the volume of water sample is 20mL. The EDTA is taken in the burette. For the first titration, the
volume of initial reading is 0mL. Record the volume of EDTA consumed to get the end point. Repeat the
procedure to get concordant value.
After achieving the concordant value we can go for the calculations.
Calcium hardness of the given water sample in mg/L as calcium carbonate equivalent is equal to volume
of EDTA8* normality* 50*1000 divided by volume of sample taken
Next the calcium present in the sample is equal to ca hardness in mg/L as CaCO3 equivalent * Molecular
weight of calcium divided by Molecular weight of calcium carbonate.
Friday, November 12, 2016 Page 7
PROJECT ON CALCIUM BASED WATER HARDNESS AND SOCIAL ISSUE
TABLE AND DATA SHEET
Sample Tested by: Sample location Sample Calcium Calcium ion remark
number description hardness(mg/L) present(mg/L)
P.SIVARAMAN KANGEYANALLUR 1KM FROM VIT 290 116.22 EXCESS FROM
PRESCRIBED
1 AMOUNT
S.VENNILA KATPADI NEAR KATPADI 295 118 EXCESS FROM
RAILWAY PRESCRIBED
2 STATION AMOUNT
P.PALANIYAPPAN OUTSIDE VIT 260 104.2 EXCESS FROM
PRESCRIBED
3 AND
AMOUNT
R.ARUNKUMAR
R.ARIVOLI OUTSIDE VIT 215 86.16 MODERATE
S.GOKUL VIRUTHAMPATTU 2KM FROM VIT 295 118.23 EXCESS FROM
PRESCRIBED
5
AMOUNT
P.MOHAN RANIPET NEAR ONE 510 204.39 EXCESS FROM
FACTORY PRESCRIBED
6 AMOUNT
R.RAJESH GANDHI NAGAR BROUGH FROM 190 76.14 BEST AMOUNT
KANNAN DRINKING TAP CONTAIN
7
D.PREETHI BRAND: BAILLEY MINERAL 105 42.08 DEFICIET
WATER
8
Friday, November 12, 2016 Page 8
PROJECT ON CALCIUM BASED WATER HARDNESS AND SOCIAL ISSUE
RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
From our experiment we have found out that a place called “RANIPET” contains excessive of calcium
which is much above to what normal human body needs. As per the drinking water standards in India,
the limits of calcium in drinking water are 75ppm, but the water around this place contains 204.39ppm
which is very high. So the first question that struck in our mind after getting this unexpected is, what
cause the water around this place highly concentrated with calcium; to quench our curiosity, we did
little research and found out that this place is firstly located near to a factory, which otherwise has
acted as a source of impurity to the water nearby. Apparently people say that the place used to remain
covered with the white dust long time ago. Which is the indication of existence of calcium carbonate in
the region? Basically, we can say that this place is rich in minerals (ca) and as a result water also
contains excess of ca, but the fact that people should know is that the water in this place is not suitable
for normal human being to drink as it contains excess of ca which is bad for our health. So it is important
for the concern authority to take necessary precaution and ways to provide the people in this region
with clean and healthy water.
Similarly, we have found out that mineral “(brand: bailey)” contains the least calcium in it. It was wholly
unexpected results, because we believe that the mineral water is the BEST for health. We cannot say
exactly what caused acute deficiency of calcium in this particular brand of mineral water, but we can
assume that it may be because of too much filtration process involved during the manufacture. We
have also found out that the mineral water that we had used for our experiment was expired. This may
be the cause of the acute shortage.
Water in the Places like “KANGEYANALLUR, KATPADI, OUTSIDE VIT(1),VIRUTHAMPATTU” contains
excess of calcium from prescribed amount, but they are fit to drink as compared to other. All this places
are exposed to same climatic condition and vegetation.
However, the places like “OUTSIDE VIT(2) AND GHANDHI NAGAR” have water which contains
moderate amount of calcium in it. Among the entire sample that we have collected, these two samples
came out as the BEST among other for drinking purposes.
Friday, November 12, 2016 Page 9
PROJECT ON CALCIUM BASED WATER HARDNESS AND SOCIAL ISSUE
CONCLUSION:
Calcium ions are important contributors to water hardness. When water is heated, they break down and
precipitate out of the solution, forming scale. Maximum limits have been established. Calcium
concentrations ions more than 100mg/L have a laxative on some people. As per the drinking water
standards in India, the limit of Mg in drinking water is 30ppm and that of calcium us 75ppm.
Some of the major health issues caused by deficit of calcium intake are:
1. HYPOCALCEMIA-it is an electrolyte imbalance by low level of calcium in blood.
2. RICKETS
Some of the diseases caused by excess intake of calcium are:
1. FORMATION OS STONE IN KIDNEY
2. HYPERCALCEMIA
3. PARATHYROID
Approximately 60 percent of our body contains water. Our body uses water in all its cells, organs, and
tissues to help regulate its temperature and maintain other bodily functions. Water does more than just
quench our thirst and regulate our body temperature; it also keeps the tissues in our body moist. we
know how it feels when our eyes, nose, or mouth gets dry? Keeping our body hydrated helps it retain
optimum levels of moisture in these sensitive areas, as well as in the blood, bones, and the brain. In
addition, water helps protect the spinal cord, and it acts as a lubricant and cushion for our joints.
Therefore, it is very important to know about the quality of water that we drink in our day to day life
and live healthy and happy life.
Friday, November 12, 2016 Page 10
PROJECT ON CALCIUM BASED WATER HARDNESS AND SOCIAL ISSUE
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
To conclude, finally our group like to thank all the individuals who have helped us genuinely in making
this project successful and presentable. Last but not the least; we would like to thank our faculty
Prof. SARAVANAKUMAR M P for guiding us throughout our project. Without his valuable advice and
assistance it would not be possible for our group to present this project to you all. Thank you to all.
Reference
1. http://google.co.in/webhp?sourceid=chrome-instant&ion=1&espv=2&ie=UTF-8
2. https://www.google.co.in/search?q=experiment+to+determine+the+calcium&oq=experiment+t
o+determine+the+calcium&aqs=chrome..69i57.12769j0j7&sourceid=chrome&es_sm=122&ie=U
TF-8
3. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hTy9JBllUVg
4. https://www.google.co.in/search?q=mineral+water&oq=mineral+water&aqs=chrome..69i57j
69i61.4692j0j7&sourceid=chrome&es_sm=122&ie=UTF-8
5. Engineering chemistry O G Palanna, Department of Chemistry-RNS Institude of Technology
Bangalore.
6. https://www.google.co.in/search?tbm=bks&hl=en&q=engineering+chemistry+og+palanna
7. Engineering Chemistry by P.C JAIN
8. http://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/high-calcium-intake-from-supplements-linked-to-heart-
disease-in-men-201302065861
Friday, November 12, 2016 Page 11
You might also like
- EnglishFile4e Intermediate TG PCM Grammar 7ANo ratings yetEnglishFile4e Intermediate TG PCM Grammar 7A1 page
- Quantitative Determination of Total Hardness of Water50% (2)Quantitative Determination of Total Hardness of Water11 pages
- 3500-Ca Calcium 3500-Ca A.: 500 Mg/l. The Most CommonNo ratings yet3500-Ca Calcium 3500-Ca A.: 500 Mg/l. The Most Common2 pages
- The Problem and Review of Related Literature100% (3)The Problem and Review of Related Literature51 pages
- Analytical Chemistry Laboratory Report (Total Hardness)No ratings yetAnalytical Chemistry Laboratory Report (Total Hardness)6 pages
- H9. Template for Chemistry Project Report CSE-C (1) (2)No ratings yetH9. Template for Chemistry Project Report CSE-C (1) (2)11 pages
- Determination of Hardness in Water Lab ReportNo ratings yetDetermination of Hardness in Water Lab Report8 pages
- Lab Activity 8 - Hardness of Water undoneNo ratings yetLab Activity 8 - Hardness of Water undone5 pages
- Chem 26.1 Quantitative Determination of Total Hardness in Drinking Water by Complexometric EDTA TitrationNo ratings yetChem 26.1 Quantitative Determination of Total Hardness in Drinking Water by Complexometric EDTA Titration4 pages
- 3500-Ca Calcium : 1. Occurrence and Significance100% (1)3500-Ca Calcium : 1. Occurrence and Significance2 pages
- GROUP2 Act 6 - Water Hardness Determination - WorksheetNo ratings yetGROUP2 Act 6 - Water Hardness Determination - Worksheet5 pages
- Determination of Total Hardness of Water SamplesNo ratings yetDetermination of Total Hardness of Water Samples15 pages
- Complexometric Determination of Water Hardness Lab Report50% (2)Complexometric Determination of Water Hardness Lab Report5 pages
- Experiment 1 Determination of Water Hardness by EDTANo ratings yetExperiment 1 Determination of Water Hardness by EDTA2 pages
- Analytical Chemistry: Quantitative and Spectroscopic Methods of Analysis 4 March 2020No ratings yetAnalytical Chemistry: Quantitative and Spectroscopic Methods of Analysis 4 March 202013 pages
- Module 2.2 Total Hardness of Water PrincipleNo ratings yetModule 2.2 Total Hardness of Water Principle2 pages
- PRACTICAL NO.05_DETERMINATION OF HARDNESS OF WATER BY EDTA TITRATIONNo ratings yetPRACTICAL NO.05_DETERMINATION OF HARDNESS OF WATER BY EDTA TITRATION6 pages
- Chemistry 213: Experiment 7 Determining Water Hardness by EDTA TitrationNo ratings yetChemistry 213: Experiment 7 Determining Water Hardness by EDTA Titration6 pages
- Chemistry 232 Water Hardness: EDTA Titrimetric Method: PurposeNo ratings yetChemistry 232 Water Hardness: EDTA Titrimetric Method: Purpose4 pages
- Determination of Hardness of Water and WastewaterNo ratings yetDetermination of Hardness of Water and Wastewater5 pages
- Experiments 2 Calcium, Total Hardness, and Alkalinity AnalysisNo ratings yetExperiments 2 Calcium, Total Hardness, and Alkalinity Analysis21 pages
- No Nonsense Pool Care: Yes, You Can Take Care of Your Own PoolFrom EverandNo Nonsense Pool Care: Yes, You Can Take Care of Your Own PoolNo ratings yet
- Chemistry at Home - A Collection of Experiments and Formulas for the Chemistry EnthusiastFrom EverandChemistry at Home - A Collection of Experiments and Formulas for the Chemistry EnthusiastNo ratings yet
- The Seventy Weeks of Daniel: Enemies of Literal InterpretationNo ratings yetThe Seventy Weeks of Daniel: Enemies of Literal Interpretation5 pages
- Arabian Consolidated Industrial Cleaning Services - TandheefNo ratings yetArabian Consolidated Industrial Cleaning Services - Tandheef3 pages
- Jawatan Kosong Executive Banking Maybank Dan Hong Leong BankNo ratings yetJawatan Kosong Executive Banking Maybank Dan Hong Leong Bank5 pages
- Marketing To Youth in The Digital Age: The Promotion of Unhealthy Products and Health Promoting Behaviours On Social MediaNo ratings yetMarketing To Youth in The Digital Age: The Promotion of Unhealthy Products and Health Promoting Behaviours On Social Media3 pages
- niir-directory-database-india-professionals-architects-interior-decorators-building-contractors-property-dealers-real-estate-agents-brokers-developers-builders-delhi-amp-ncr-region-construction-materialsNo ratings yetniir-directory-database-india-professionals-architects-interior-decorators-building-contractors-property-dealers-real-estate-agents-brokers-developers-builders-delhi-amp-ncr-region-construction-materials11 pages
- Keeping The Peace: Conflict Management Strategies For Nurse ManagersNo ratings yetKeeping The Peace: Conflict Management Strategies For Nurse Managers5 pages
- Curriculum Vitae (C.V.) A. Personal InformationNo ratings yetCurriculum Vitae (C.V.) A. Personal Information4 pages
- Autonomous Cars - Research Results, Issues, and Future Challenges - Hussain, Autonomous Cars Research Results, Issues, and Future ChallengesNo ratings yetAutonomous Cars - Research Results, Issues, and Future Challenges - Hussain, Autonomous Cars Research Results, Issues, and Future Challenges39 pages
- S.C. The Use of Holy Quran in Legal ThinkingNo ratings yetS.C. The Use of Holy Quran in Legal Thinking2 pages
- Writing in The Air by Antonio Cornejo PolarNo ratings yetWriting in The Air by Antonio Cornejo Polar21 pages
- Kapitan Eddie T. Reyes Integrated School: Diagnosteic Test ResultNo ratings yetKapitan Eddie T. Reyes Integrated School: Diagnosteic Test Result9 pages
- Swim England Qualifications Level 2 Teaching Swimming To Babies and Toddlers SpecificationNo ratings yetSwim England Qualifications Level 2 Teaching Swimming To Babies and Toddlers Specification24 pages
- Training Orientation 28-12-2023 GBHS Bedal Bekas RohriNo ratings yetTraining Orientation 28-12-2023 GBHS Bedal Bekas Rohri18 pages
- Shri V Kishore Chandra Deo Minister of Tribal Affairs and Panchayati RajNo ratings yetShri V Kishore Chandra Deo Minister of Tribal Affairs and Panchayati Raj17 pages