Chapter Ii: Block Diagrams in Control Systems Engineering: G(S) G G G G
Chapter Ii: Block Diagrams in Control Systems Engineering: G(S) G G G G
Uploaded by
Jeffry GigantoCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter Ii: Block Diagrams in Control Systems Engineering: G(S) G G G G
Chapter Ii: Block Diagrams in Control Systems Engineering: G(S) G G G G
Uploaded by
Jeffry GigantoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Chapter Ii: Block Diagrams in Control Systems Engineering: G(S) G G G G
Chapter Ii: Block Diagrams in Control Systems Engineering: G(S) G G G G
Uploaded by
Jeffry GigantoCopyright:
Available Formats
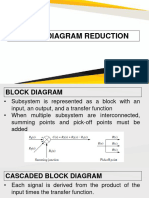
CHAPTER II: BLOCK DIAGRAMS IN CONTROL SYSTEMS ENGINEERING
1. Blocks – It contains the transfer function (ratio of
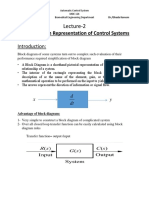
A block diagram of a system is a pictorial representation
output and input) of the control system. It also
of the functions performed by each of its components and
represents the physical components of the system.
the flow of signals on it. Such diagram depicts the
2. Summing Point (also known as summer) – a circle
interrelationships that exist among the various
representation that indicates a summing operation.
components. Differing from a purely abstract mathematical
The plus or minus sign at each arrowhead indicates
representation, a block diagram has the advantage of
whether that signal is to be added or subtracted. It is
indicating more realistically the signal flows of the actual
important that the quantities being added or
system.
subtracted have the same dimensions and the same
In a block diagram all system variables are linked to each units.
other through functional blocks. The functional block or
simply block is a symbol for a mathematical operation on What will be the relationship between the output
the input signal to the block that produces the output. The and the inputs for the summing points represented
transfer functions of the components are usually entered below?
in the corresponding blocks, which is connected by arrows
to indicate the direction of the flow of the signals. Note that
the signal can pass only in the direction of the arrows.
The advantage of the block diagram
representation of a control system lie in the fact that it is 3. Take-off (Pick-off) Point – It indicates that the same
easy to form the overall block diagram for the entire signal is to go several places in the diagram.
system by merely connecting the blocks of the 4. Arrows – represent unidirectional signal flow. These
components according to the signal flow and it is possible are referred to as signals.
to evaluate the contribution of each component to the
overall performance of the system. A block diagram
contains information on the physical construction of the BLOCK DIAGRAM REDUCTION
system.
1. Blocks in Cascade - Each signal is derived from
the product of the input times the transfer
BLOCK DIAGRAM ELEMENTS function. Therefore, any finite blocks in series
may be algebraically combined by multiplication.
Summing C C
Block Take-off R R
Point G1 G2 G1G2
R E Point C
G(s)
± C
B
2. Blocks in Tandem (Blocks in Parallel) -
Parallel subsystems have a common input and
an output formed by the algebraic sum of the
outputs from all subsystems.
Take first things first. Triumph is just “umph” added to try.
Moving Block Diagram Element/s to Create Familiar
G1 Forms
R C R C It is important to note that blocks can be connected in
G1±G2 series only if the output of one block is not affected by the
± next following block. A complicated block diagram
G2 involving many feedback loops can be simplified by a
step-by-step rearrangement, using some of the
3. Feedback Form (Canonical Form)
transformations shown below.
In simplifying a block diagram, remember the
R E C
G following:
The product of the transfer functions in the feed-
± B
forward direction must remain the same.
H
The product of the transfer functions around the
Where:
loop must remain the same.
E= Actuating signal or Error Signal
B = Feedback Signal
C = Controlled Output Signal SYSTEMS WITH MULTIPLE INPUTS
R = Reference Input Signal When multiple inputs are present in a linear control
G = direct transfer function or forward transfer system, each input can be treated independently of the
function others (analyze the system one source at a time), using
H = feedback transfer function the process called superposition. The complete output of
the system can then be obtained adding together the
outputs corresponding to each input.
FEEDBACK RATIOS
Procedure in Simplifying Systems with Multiple Inputs
C
= Closed-loop transfer -function or control ratio 1. Set all inputs, except one, equal to zero.
R 2. Transform the block diagram to canonical form.
E 3. Calculate the response due to chosen input acting
= Actuating Signal Ratio or Error Ratio
R alone.
B 4. Repeat steps 1-3 for each of the remaining inputs.
= Primary Feedback Ratio
R 5. Algebraically add all of the responses determined in
steps 1-4. This sum is the total output of the system
Steps in Reducing (Simplifying) Complicated Block with all inputs acting simultaneously.
Diagram:
1. Combine all cascade blocks
2. Combine all parallel blocks
3. Eliminate all feedback loops
4. Shift summing points to the left and take-off
(pick-off) points to the right of the major loop.
5. Repeat steps 1 to 4 until canonical form has
been achieved for a particular input.
6. Repeat steps 1-5 to for each input (for multiple
inputs), as required.
Take first things first. Triumph is just “umph” added to try.
Transformation Block Diagram Equivalent Block Diagram
X1 X3
X1 + G X3 G +
1. Moving the summing point to the ±
right of a block ±
X2 G
X2
X1 X2 X1 X2
G G
2. Moving Pickoff point to the left of
X2 X2
a block G
X1 X
X1 X2 G
3. Moving a Pickoff point to the G 2
right of a block X1 1
X1 G
X1 X1 + X3
G + X3 G
4. Moving Summing Point to the
± ±
left of a block
X2 1/G
X2
G1 C G1
R
5. Removing a Block from a ± G1
R G2
Forward Path G2 ±C
Take first things first. Triumph is just “umph” added to try.
Example 1:
Determine C/R for the given system Example 6:
G2 Reduce the given block diagram to canonical
+
C form isolating H3. H3
R +
G1 + –
R C
+ G1 + G2 G3
+ H1
–
Example 2: – H2
Determine the output C of the system
U H1
+ C
R + +
G1 G2 Example 7:
G
– +
C
R +
G G G
Example 3: – –
Shown is a block diagram for the control system for H
speed of a shaft with the terms in the boxes being
the transfer functions for the elements concerned. H
Example 8:
Example 4:
Determine the output C of the given system
U1
+ C
R +
G1 + G2
–
H1 + H2
+ U2
H1
+
Example 5: R + + + C
G1 G2 G3
Reduce into one block
– –
H2
+
H3
+
H4
Take first things first. Triumph is just “umph” added to try.
You might also like
- To Perform A Block Diagram Reduction Using MATLAB - Matlab ExamplesDocument5 pagesTo Perform A Block Diagram Reduction Using MATLAB - Matlab Examplesdanycg85No ratings yet
- Tutorial Sol CH 11Document3 pagesTutorial Sol CH 11Abraham wisdomNo ratings yet
- Instruction Sheet Process Trainer 37 100Document4 pagesInstruction Sheet Process Trainer 37 100Abcd123411No ratings yet
- Module 3Document3 pagesModule 3SohnNo ratings yet
- C.S Unit - 2Document22 pagesC.S Unit - 2Rajendar PonagantiNo ratings yet
- 96 Feedback and Stability TheoryDocument18 pages96 Feedback and Stability TheoryJohnny DoeNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram ReductionDocument18 pagesBlock Diagram ReductionRobby KumarNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 3 - Control-EngineeringDocument35 pagesTOPIC 3 - Control-EngineeringCllyan ReyesNo ratings yet
- IE474 Summer2022 Nise Ch2 PartB Ch5 PDFDocument24 pagesIE474 Summer2022 Nise Ch2 PartB Ch5 PDFAmon SimatwoNo ratings yet
- MSD2Document47 pagesMSD2moeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 BDDocument39 pagesLecture 3 BDhabtemariam woredeNo ratings yet
- 05 Block Diagram (Updated)Document33 pages05 Block Diagram (Updated)iamdanishrathorNo ratings yet
- 3 - Block Diagram and Signal Flow GraphDocument55 pages3 - Block Diagram and Signal Flow GraphEyasu demsewNo ratings yet
- BlockDiagram and Signal Flow GraphsDocument29 pagesBlockDiagram and Signal Flow GraphsDienies TorresNo ratings yet
- Automatic Control Systems I e LearningDocument9 pagesAutomatic Control Systems I e LearningAlfred K ChilufyaNo ratings yet
- Unit IIDocument40 pagesUnit IIdivya guptaNo ratings yet
- Unit1 Block DiagramDocument75 pagesUnit1 Block DiagramPrasidha PrabhuNo ratings yet
- 5 - Block Diagram ReductionDocument20 pages5 - Block Diagram ReductionAngel RupidoNo ratings yet
- 003 ME31002 - Block Diagram-2021febDocument54 pages003 ME31002 - Block Diagram-2021febShek Yu LaiNo ratings yet
- 18033193Document16 pages18033193John ValenzonaNo ratings yet
- SECTION 4 REDUCTION OF MULTIPLE SUBSYSTEMS (Autosaved)Document39 pagesSECTION 4 REDUCTION OF MULTIPLE SUBSYSTEMS (Autosaved)mlungisilushoziNo ratings yet
- Control System Analysis and Design: Karen WillcoxDocument12 pagesControl System Analysis and Design: Karen Willcoxkhannasir1No ratings yet
- CSEXP2Document15 pagesCSEXP2Kavita DhamalNo ratings yet
- Controls Finals ResearchDocument15 pagesControls Finals ResearchRenz Xynor Liotib CadizNo ratings yet
- BDR SFGDocument112 pagesBDR SFGAk GamingNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document14 pagesLecture 2Abdullah Mohammed AlsaadouniNo ratings yet
- Block DiagramDocument12 pagesBlock DiagramJohn Cedrik RetardoNo ratings yet
- Slides 3: Reduction of Multiple SystemsDocument25 pagesSlides 3: Reduction of Multiple SystemsAhmad AbunassarNo ratings yet
- Zahra AbdulHameed ShukrDocument11 pagesZahra AbdulHameed ShukrTana AzeezNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram and Laplace TransformDocument2 pagesBlock Diagram and Laplace TransformNabi Newaz Mahamud lumenNo ratings yet
- LESSON2 ControlSystemBlockDiagramDocument20 pagesLESSON2 ControlSystemBlockDiagramalexancog456No ratings yet
- LG Embedded Jan09 PDFDocument5 pagesLG Embedded Jan09 PDFAnonymous VfH06fQXbANo ratings yet
- Blok DiagramDocument43 pagesBlok DiagramBagoessngenger DwiNo ratings yet
- Transfer Functions Block Diagrams Signal Flow Graph Mason's Gain FormulaDocument28 pagesTransfer Functions Block Diagrams Signal Flow Graph Mason's Gain FormulaMesut OzilNo ratings yet
- Control Sys.2Document102 pagesControl Sys.2Salman TariqNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 05 56Document8 pagesLab Report 05 56MEEN201101056 KFUEITNo ratings yet
- Feedback and Control System Module - 19Document28 pagesFeedback and Control System Module - 19AkiHiro San CarcedoNo ratings yet
- 2018 EE305 New SolutionDocument25 pages2018 EE305 New SolutionJasa R ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document13 pagesLecture 4Syed Hussain Akbar MosviNo ratings yet
- Block DiagramsDocument7 pagesBlock DiagramsElyk TakataNo ratings yet
- Block DiagramDocument75 pagesBlock DiagramJane Erestain BuenaobraNo ratings yet
- Study, Analysis and Evaluation of Block Diagram Reduction Name: University of Polytechnic/college ofDocument10 pagesStudy, Analysis and Evaluation of Block Diagram Reduction Name: University of Polytechnic/college ofTana AzeezNo ratings yet
- ECE 43 Module 7 - Block Diagram AlgebraDocument34 pagesECE 43 Module 7 - Block Diagram Algebrafrancisemil.vistaNo ratings yet
- control block systemDocument7 pagescontrol block systemJohn ValenzonaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5-Feedback ControlDocument12 pagesLecture 5-Feedback ControlKAILA FUNTANILLANo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-Block Diagram Reduction TechniquesDocument71 pagesLecture 2-Block Diagram Reduction TechniquesNoor AhmedNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram and Signal FlowDocument23 pagesBlock Diagram and Signal Floweltn s.No ratings yet
- Linear CoctrolDocument6 pagesLinear CoctrolwhycharlespitsoNo ratings yet
- Lab # 8 SolvedDocument10 pagesLab # 8 SolvedZabeehullahmiakhailNo ratings yet
- Distinguish Between Open Loop and Closed Loop Control SystemsDocument2 pagesDistinguish Between Open Loop and Closed Loop Control SystemsSornagopal VijayaraghavanNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram Reduction TechniquesDocument59 pagesBlock Diagram Reduction Techniquesdavid.barodi12No ratings yet
- MMC TechMax 2Document248 pagesMMC TechMax 2Swaraj KhandekarNo ratings yet
- ME406 Mod 5 Block DiagramsDocument110 pagesME406 Mod 5 Block DiagramsJim CruzNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram Reduction 1 TechniqueDocument17 pagesBlock Diagram Reduction 1 TechniqueNtiyisoColbertNo ratings yet
- CS Mod2@AzDOCUMENTS - inDocument26 pagesCS Mod2@AzDOCUMENTS - insssNo ratings yet
- Transfer Functions 2Document7 pagesTransfer Functions 2joker princeNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics (2015) Unit IIDocument38 pagesMechatronics (2015) Unit IIkishan100% (1)
- Lab # 8 Control SystemDocument10 pagesLab # 8 Control SystemZabeehullahmiakhailNo ratings yet
- Control Engineering Lab ManualDocument4 pagesControl Engineering Lab ManualGTNo ratings yet
- FME 326 - Module 5 - Signal Flow and Block Diagram ModelsDocument47 pagesFME 326 - Module 5 - Signal Flow and Block Diagram ModelsJesse Jon FerolinoNo ratings yet
- FME 326 - Module 5 - Signal Flow and Block Diagram ModelsDocument47 pagesFME 326 - Module 5 - Signal Flow and Block Diagram ModelsJesse Jon FerolinoNo ratings yet
- Testing Harmoin ProductionDocument3 pagesTesting Harmoin ProductionEngAbdallahMohamedNo ratings yet
- Advanced Control StrategiesDocument14 pagesAdvanced Control Strategiesaaron ibarra san diego100% (1)
- Aerospace System Guidance and Control Lesson IV Introduction To SimulinkDocument17 pagesAerospace System Guidance and Control Lesson IV Introduction To SimulinkRıfat BenvenisteNo ratings yet
- Plant InversionDocument19 pagesPlant InversionMaher HammamiNo ratings yet
- Discrete Control Using Programmable Logic ControllersDocument12 pagesDiscrete Control Using Programmable Logic Controllersfarah nazNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics and Power SystemsDocument49 pagesPower Electronics and Power Systemsrasim_m1146No ratings yet
- Control Theory - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument14 pagesControl Theory - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaJoon Suk HuhNo ratings yet
- วงจรกรองความถี่แบบแอคทีฟv3Document14 pagesวงจรกรองความถี่แบบแอคทีฟv3Phornphat PhrommunNo ratings yet
- Lect 8 Dynamic Behaviour of Feedback Controller ProcessDocument12 pagesLect 8 Dynamic Behaviour of Feedback Controller ProcessZaidoon MohsinNo ratings yet
- Industrial Control SystemDocument31 pagesIndustrial Control Systempraveen100% (2)
- Fundamentals of MeasurementDocument27 pagesFundamentals of MeasurementBakaali HuzaifaNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of DC Motor Using Pid Controller BasedDocument16 pagesSpeed Control of DC Motor Using Pid Controller Basedayesha amjadNo ratings yet
- Further Engineering DynamicsDocument186 pagesFurther Engineering Dynamicsmoljaime1326100% (1)
- Experiments - RC Circuit Sheet PDFDocument5 pagesExperiments - RC Circuit Sheet PDFĂkŕăm LôKâNo ratings yet
- 4.1. Perancangan Filter IIR Dengan Analog Prototipe: % Order of Filter % Cut Off FrequencyDocument10 pages4.1. Perancangan Filter IIR Dengan Analog Prototipe: % Order of Filter % Cut Off FrequencyNyami IndraNo ratings yet
- Control System Engineering: Topic Block Diagram ExamplesDocument42 pagesControl System Engineering: Topic Block Diagram ExamplesjpatrNo ratings yet
- Controlador MCCDocument4 pagesControlador MCCJuan RiosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - DTSDocument28 pagesLecture 2 - DTSq6hvqqzy5fNo ratings yet
- Homework 1-Heat ExchangerDocument2 pagesHomework 1-Heat ExchangerPe1L1ngNo ratings yet
- Lec12 PDFDocument39 pagesLec12 PDFmousa bagherpourjahromiNo ratings yet
- Optimal Space Flight NavigationDocument277 pagesOptimal Space Flight Navigationmoafr100% (1)
- Unit-IV Band Pass FiltersDocument16 pagesUnit-IV Band Pass Filterskiran kumarNo ratings yet
- Esd5500E Series Speed Control Unit: Product Technical Information PTI 1002EDocument7 pagesEsd5500E Series Speed Control Unit: Product Technical Information PTI 1002EalstomNo ratings yet
- Re30012 B - 2010 09Document80 pagesRe30012 B - 2010 09thierrylindo100% (1)
- Research 1 Proposal: SEMESTER 4 - SESI 2019/2020Document3 pagesResearch 1 Proposal: SEMESTER 4 - SESI 2019/2020Dzulfathil PuteraNo ratings yet
- Control System Analysis-Lecture 2Document13 pagesControl System Analysis-Lecture 2Dhirendra SoniNo ratings yet
- EE171 Process ControlDocument1 pageEE171 Process ControlAkhil KathiNo ratings yet
- Classification of CNC MachineDocument11 pagesClassification of CNC Machineaqtu12fuc81% (16)