0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
92 viewsArt Periods
Art Periods
Uploaded by
aasis21The document provides an overview of major art periods from the Stone Age through the 19th century, listing the characteristic styles, notable artists, and concurrent historical events for each period. It covers prehistoric cave paintings, Mesopotamian relief sculptures, Egyptian tomb art, Greek idealism and architecture, Roman realism and engineering, Byzantine mosaics and Islamic architecture, Renaissance revivals of classical styles, Baroque religious art, Neoclassical emulation of antiquity, Romantic exaltation of imagination, and Realist celebrations of everyday life. Key developments and figures are noted for each era to connect the visual arts with broader historical contexts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Art Periods
Art Periods
Uploaded by
aasis210 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
92 views7 pagesThe document provides an overview of major art periods from the Stone Age through the 19th century, listing the characteristic styles, notable artists, and concurrent historical events for each period. It covers prehistoric cave paintings, Mesopotamian relief sculptures, Egyptian tomb art, Greek idealism and architecture, Roman realism and engineering, Byzantine mosaics and Islamic architecture, Renaissance revivals of classical styles, Baroque religious art, Neoclassical emulation of antiquity, Romantic exaltation of imagination, and Realist celebrations of everyday life. Key developments and figures are noted for each era to connect the visual arts with broader historical contexts.
Original Description:
Art periods
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
The document provides an overview of major art periods from the Stone Age through the 19th century, listing the characteristic styles, notable artists, and concurrent historical events for each period. It covers prehistoric cave paintings, Mesopotamian relief sculptures, Egyptian tomb art, Greek idealism and architecture, Roman realism and engineering, Byzantine mosaics and Islamic architecture, Renaissance revivals of classical styles, Baroque religious art, Neoclassical emulation of antiquity, Romantic exaltation of imagination, and Realist celebrations of everyday life. Key developments and figures are noted for each era to connect the visual arts with broader historical contexts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
92 views7 pagesArt Periods
Art Periods
Uploaded by
aasis21The document provides an overview of major art periods from the Stone Age through the 19th century, listing the characteristic styles, notable artists, and concurrent historical events for each period. It covers prehistoric cave paintings, Mesopotamian relief sculptures, Egyptian tomb art, Greek idealism and architecture, Roman realism and engineering, Byzantine mosaics and Islamic architecture, Renaissance revivals of classical styles, Baroque religious art, Neoclassical emulation of antiquity, Romantic exaltation of imagination, and Realist celebrations of everyday life. Key developments and figures are noted for each era to connect the visual arts with broader historical contexts.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 7
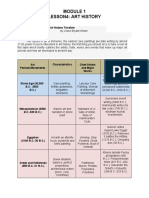
Art Periods/ Chief Artists and
Characteristics Historical Events
Movements Major Works
Ice Age ends (10,000
Lascaux Cave b.c.–8,000 b.c.); New
Cave painting, fertility
Stone Age (30,000 Painting, Woman of Stone Age and
goddesses,
b.c.–2500 b.c.) Willendorf, first permanent
megalithic structures
Stonehenge settlements (8000
b.c.–2500 b.c.)
Sumerians invent
writing (3400 b.c.);
Standard of Ur,
Warrior art and Hammurabi writes his
Mesopotamian (3500 Gate of Ishtar,
narration in stone law
b.c.–539 b.c.) Stele of
relief code (1780 b.c.);
Hammurabi’s Code
Abraham founds
monotheism
Narmer unites
Upper/Lower Egypt
Imhotep, Step
Art with an afterlife (3100 b.c.); Rameses II
Egyptian (3100 Pyramid, Great
focus: pyramids and battles
b.c.–30 b.c.) Pyramids, Bust of
tomb painting the Hittites (1274 b.c.);
Nefertiti
Cleopatra dies (30
b.c.)
Greek and Hellenistic Greek idealism: Parthenon, Myron, Athens defeats Persia
(850 b.c.–31 b.c.) balance, perfect Phidias, at Marathon (490 b.c.);
proportions; Polykleitos, Peloponnesian
architectural Praxiteles Wars (431 b.c.–404
orders(Doric, Ionic, b.c.); Alexander the
Corinthian) Great’s conquests
(336 b.c.–323 b.c.)
Julius Caesar
assassinated (44 b.c.);
Augustus of
Augustus proclaimed
Roman realism: Primaporta,
Roman (500 b.c.– a.d. Emperor (27 b.c.);
practical and down to Colosseum,
476) Diocletian splits
earth; the arch Trajan’s Column,
Empire (a.d. 292);
Pantheon
Rome falls
(a.d. 476)
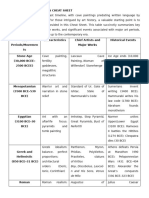
Birth of Buddha (563
b.c.); Silk Road opens
(1st century b.c.);
Indian, Chinese, and Serene, meditative Gu Kaizhi, Li
Buddhism spreads to
Japanese(653 art, and Arts of the Cheng, Guo Xi,
China (1st–2nd
b.c.–a.d. 1900) Floating World Hokusai, Hiroshige
centuries a.d.) and
Japan
(5th century a.d.)
Heavenly Byzantine Hagia Sophia, Justinian partly
Byzantine and Islamic
mosaics; Islamic Andrei Rublev, restores Western
(a.d. 476–a.d.1453)
architecture and Mosque of Roman Empire (a.d.
amazing Córdoba, the 533–a.d. 562);
maze-like design Alhambra Iconoclasm
Controversy (a.d.
726–a.d.
843); Birth of Islam
(a.d. 610) and Muslim
Conquests (a.d.
632–a.d. 732)
Viking Raids
(793–1066); Battle of
St. Sernin, Durham Hastings (1066);
Celtic art, Carolingian Cathedral, Notre Crusades I–IV
Middle Ages
Renaissance, Dame, Chartres, (1095–1204); Black
(500–1400)
Romanesque, Gothic Cimabue, Death
Duccio, Giotto (1347–1351); Hundred
Years’ War
(1337–1453)
Ghiberti’s Doors, Gutenberg invents
Brunelleschi, movable type (1447);
Early and High Donatello, Turks conquer
Rebirth of classical
Renaissance Botticelli, Constantinople (1453);
culture
(1400–1550) Leonardo, Columbus lands in
Michelangelo, New World (1492);
Raphael Martin
Luther starts
Reformation (1517)
The Renaissance Bellini, Giorgione, Council of Trent and
spreads north- ward Titian, Dürer, Counter-Reformation
Venetian and Northern
to France, the Low Bruegel, Bosch, (1545–1563);
Renaissance
Countries, Poland, Jan van Copernicus proves the
(1430–1550)
Germany, and Eyck, Rogier van Earth revolves around
England der Weyden the Sun (1543
Art that breaks the Tintoretto, El Magellan
Mannerism
rules; artifice over Greco, Pontormo, circumnavigates the
(1527–1580)
nature Bronzino, Cellini globe (1520–1522)
Splendor and flourish
Reubens, Thirty Years’ War
for God; art as a
Rembrandt, between Catholics and
Baroque (1600–1750) weapon in the
Caravaggio, Palace Protestants
religious
of Versailles (1618–1648)
wars
Enlightenment (18th
Art that recaptures
Neoclassical David, Ingres, century); Industrial
Greco-Roman grace
(1750–1850) Greuze, Canova Revolution
and grandeur
(1760–1850)
American Revolution
The triumph of Caspar Friedrich,
Romanticism (1775–1783); French
imagination and Gericault,
(1780–1850) Revolution
individuality Delacroix, Turner,
(1789–1799);
Benjamin Napoleon crowned
West emperor of France
(1803)
Celebrating working
class and Corot, Courbet, European democratic
Realism (1848–1900)
peasants; en plein air Daumier, Millet revolutions of 1848
rustic painting
Monet, Manet, Franco-Prussian War
Impressionism Capturing fleeting Renoir, Pissarro,
(1870–1871);
(1865–1885) effects of natural light Cassatt, Morisot,
Unification of Germany
Degas (1871)
Belle Époque
Van Gogh,
Post-Impressionism A soft revolt against (late-19th-century
Gauguin, Cézanne,
(1885–1910) Impressionism Golden Age); Japan
Seurat
defeats Russia (1905)
Harsh colors and flat Boxer Rebellion in
Fauvism and
surfaces (Fauvism); Matisse, Kirchner, China (1900); World
Expressionism
emotion distorting Kandinsky, Marc War
(1900–1935)
form (1914–1918)
Cubism, Futurism, Pre– and Post–World
Russian Revolution
Supremativism, War 1 art Picasso, Braque,
(1917); American
Constructivism, De experiments: new Leger, Boccioni,
women franchised
Stijl forms to express Severini, Malevich
(1920)
(1905–1920) modern life
Disillusionment after
World War I; The
GreatDepression
Ridiculous art; Duchamp, Dalí,
Dada and (1929–1938); World
painting dreams and Ernst, Magritte, de
Surrealism( 1917–1950 War II (1939–1945)
exploring the Chirico, Kahlo
) and Nazi horrors;
unconscious
atomic bombs
dropped on Japan
(1945)
Cold War and Vietnam
Post–World War II: War (U.S. enters
Abstract
pure abstraction and Gorky, Pollock, de 1965); U.S.S.R.
Expressionism
expression Kooning, Rothko, suppresses Hungarian
(1940s–1950s) and
without form; popular Warhol, revolt (1956)
Pop Art
art absorbs Lichtenstein Czechoslovakian
(1960s)
consumerism revolt
(1968)
Nuclear freeze
Gerhard Richter,
movement; Cold War
Postmodernism and Art without a center Cindy Sherman,
fizzles; Communism
Deconstructivism and reworking and Anselm Kiefer,
collapses
(1970– ) mixing past styles Frank Gehry,
in Eastern Europe and
Zaha Hadid
U.S.S.R. (1989–1991)
You might also like
- Ancient History Timeline FiguresDocument4 pagesAncient History Timeline FiguresAudrey100% (4)
- Art History TimelineDocument8 pagesArt History TimelinePauline YvetteNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 - The History of ArtDocument10 pagesLesson 9 - The History of ArtShina Mae Abellera BarramedaNo ratings yet
- Art History Timeline PDFDocument5 pagesArt History Timeline PDFKriti KumariNo ratings yet
- Art History Timeline: Art Periods/ Movements Characteristics Chief Artists and Major Works Historical EventsDocument2 pagesArt History Timeline: Art Periods/ Movements Characteristics Chief Artists and Major Works Historical EventsKirstieNicole100% (3)
- Dinosaur Planet - Broncosaurus Rex - Cretasus Adventure GuideDocument130 pagesDinosaur Planet - Broncosaurus Rex - Cretasus Adventure Guidetoney luka100% (2)
- Stacking Toy - Christel KrukkertDocument9 pagesStacking Toy - Christel KrukkertEmilse Anello100% (5)
- Art Periods/ Movements Characteristics Chief Artists and Major Works Historical EventsDocument4 pagesArt Periods/ Movements Characteristics Chief Artists and Major Works Historical EventsDaisy TañoteNo ratings yet
- Art History Timeline - For DummiesDocument3 pagesArt History Timeline - For DummiesBill Chan Chandler100% (3)
- History of ArtDocument3 pagesHistory of ArtElla Joyce100% (1)
- Art History TimelineDocument3 pagesArt History Timelinedurgisdurtan100% (1)
- Animal Farm PDFDocument26 pagesAnimal Farm PDFYaser100% (7)
- Dark Sun - 2419 - CGR2 - The Complete Gladiator's Handbook PDFDocument132 pagesDark Sun - 2419 - CGR2 - The Complete Gladiator's Handbook PDFPedro Lamas100% (6)
- Creveld The Art of War War and Military ThoughtDocument224 pagesCreveld The Art of War War and Military Thoughtamadgearu100% (7)
- Eu Com Final Report Relocation of RefugeesDocument144 pagesEu Com Final Report Relocation of Refugeesjohan100% (3)
- GEC106_HistoryWaysOfPresentingSubjects_Chapter3Document16 pagesGEC106_HistoryWaysOfPresentingSubjects_Chapter3Shenyl LibrandaNo ratings yet
- Art History TimelineDocument8 pagesArt History Timelineshwetha.backinblackNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lession 4Document5 pagesModule 1 Lession 4Nica EllyzaNo ratings yet
- Timeline of ArtDocument15 pagesTimeline of ArtCrizalene CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Art Periods/ Movements Characteristics Chief Artists and Major Works Historical EventsDocument4 pagesArt Periods/ Movements Characteristics Chief Artists and Major Works Historical EventsNathalie kate petallarNo ratings yet
- History Timeline of Art: Art Periods/ Movements Characteristics Chief Artists and Major Works Historical EventsDocument4 pagesHistory Timeline of Art: Art Periods/ Movements Characteristics Chief Artists and Major Works Historical Eventsjustine rasonablrNo ratings yet
- GEC 106 Art App Assignment History of Arts and Arts Movement Parisian LifeDocument7 pagesGEC 106 Art App Assignment History of Arts and Arts Movement Parisian LifeAyna Salic PangarunganNo ratings yet
- NAME: - Yr/Course/SecDocument4 pagesNAME: - Yr/Course/SecFarhana GuiandalNo ratings yet
- Why People Make Art andDocument6 pagesWhy People Make Art androzdan30No ratings yet
- Periods in Art History PDFDocument14 pagesPeriods in Art History PDFManuel100% (1)
- ArtApp Reviewer ArtHistoryDocument5 pagesArtApp Reviewer ArtHistoryrosepersonalemail04No ratings yet
- Artist and Artisan Workshop IntroDocument68 pagesArtist and Artisan Workshop Introapi-459132618100% (3)
- Art History TimelineDocument2 pagesArt History TimelineFrance Bejosa50% (2)
- HUM 101 - History of Arts-1Document3 pagesHUM 101 - History of Arts-1jurenazhuiNo ratings yet
- Art PeriodsDocument2 pagesArt PeriodsannaNo ratings yet
- Art History TimelineDocument3 pagesArt History TimelineАлександра Слободянюк100% (1)
- art history timelineDocument5 pagesart history timelinebitaniyamesfin7No ratings yet
- Art History Timeline: Art Periods/ Movements Dates Chief Artists and Major Works Characteristics Historical EventsDocument6 pagesArt History Timeline: Art Periods/ Movements Dates Chief Artists and Major Works Characteristics Historical EventsKenneth Mora RiofloridoNo ratings yet
- Art History Timeline Art Periods/ Movements Dates Chief Artists and Major Works Characteristics Historical EventsDocument11 pagesArt History Timeline Art Periods/ Movements Dates Chief Artists and Major Works Characteristics Historical EventsRegine YuNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 (History Timeline) - Enago, Jhan Reach, K.Document5 pagesActivity 4 (History Timeline) - Enago, Jhan Reach, K.Jhan Reach EnagoNo ratings yet
- Art History TimelineDocument4 pagesArt History TimelinemohanNo ratings yet
- Ge 3 Study Guide 5Document5 pagesGe 3 Study Guide 5Mariane EsporlasNo ratings yet
- ART APPRECIATION WEEK 2 (Autosaved)Document50 pagesART APPRECIATION WEEK 2 (Autosaved)maria100% (1)
- Ge 3 Study Guide 5Document5 pagesGe 3 Study Guide 5riavillanueva0416No ratings yet
- History of The WorldDocument6 pagesHistory of The WorldSTARK740No ratings yet
- Chapter 7inart AppDocument10 pagesChapter 7inart Appaileenmanalo00No ratings yet
- Art App Midterm ReviewerDocument20 pagesArt App Midterm ReviewerShay GenillaNo ratings yet
- Art History TimelineDocument4 pagesArt History TimelineEstrella Esperanza Montoya PantojaNo ratings yet
- Art Periods/ Movements Characteristics Chief Artists and Major Works Historical EventsDocument4 pagesArt Periods/ Movements Characteristics Chief Artists and Major Works Historical EventsannaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 for Unit 5Document22 pagesActivity 1 for Unit 5Giel Andrei CanitesNo ratings yet
- What Are Arts and HumanitiesDocument9 pagesWhat Are Arts and HumanitiesAllison SwiftNo ratings yet
- Art App Part 56 ReviewerDocument9 pagesArt App Part 56 ReviewerBela BellsNo ratings yet
- Art App Part 56 ReviewerDocument10 pagesArt App Part 56 ReviewerOnyx CuevasNo ratings yet
- 2.1 - Western Visual ArtDocument3 pages2.1 - Western Visual Artmaricar basilan100% (1)
- Before Christ (B.C.) Common Era (C.E.) 0 26-36 AD Death of JesusDocument23 pagesBefore Christ (B.C.) Common Era (C.E.) 0 26-36 AD Death of JesusJames PappasNo ratings yet
- Approaches and Methods in Language TeachingDocument64 pagesApproaches and Methods in Language TeachingDarkness the PianistNo ratings yet
- Gned 01 - Module 4 - Art in Today's SocietyDocument13 pagesGned 01 - Module 4 - Art in Today's SocietyRenato KelisteNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Art MovementDocument100 pagesModule 5 - Art MovementGabo AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Bargas TIMELINE PDFDocument20 pagesBargas TIMELINE PDFBargas, Mia Kazandra Loren L.100% (2)
- Greek ArtDocument25 pagesGreek Artshaybusiness022No ratings yet
- Lesson 7: The Eras of Art and Music: ObjectivesDocument8 pagesLesson 7: The Eras of Art and Music: ObjectivesAsteria TimeNo ratings yet
- Art Appreciation Module 2 Part 1Document26 pagesArt Appreciation Module 2 Part 1Jaslyn Kim Yasay BognadonNo ratings yet
- MIDTERMS REVIEWER Art AppreciationDocument13 pagesMIDTERMS REVIEWER Art AppreciationKurt Leo TeodoroNo ratings yet
- Wonders of The WorldDocument10 pagesWonders of The WorldJillian FajardoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Ancient Mediterranean ArtDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Ancient Mediterranean ArtCaitNo ratings yet
- GEd 108 FinalsDocument15 pagesGEd 108 Finalspchu4019No ratings yet
- CC Timeline PrintableDocument11 pagesCC Timeline Printablejerameel SANCHEZ RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- GREEK ART ROMAN ART 1 - CompressedDocument29 pagesGREEK ART ROMAN ART 1 - Compressedacenavalta19No ratings yet
- ChronoolgyDocument16 pagesChronoolgyaqueelpremjeeNo ratings yet
- Visual Power in Ancient Greece and Rome: Between Art and Social RealityFrom EverandVisual Power in Ancient Greece and Rome: Between Art and Social RealityNo ratings yet
- Key HW - RS (Các Năm)Document22 pagesKey HW - RS (Các Năm)TuộcNo ratings yet
- Aether Nexus Playtest v1 41Document63 pagesAether Nexus Playtest v1 41spazz451No ratings yet
- Essay On Child AbuseDocument7 pagesEssay On Child Abusefz640x4t100% (2)
- Emerson Knives Catalog 2014Document13 pagesEmerson Knives Catalog 2014konan76100% (1)
- Collectivism After Modernism The Art of Social Imagination After 1945Document331 pagesCollectivism After Modernism The Art of Social Imagination After 1945samradizdarevic100% (3)
- Euripides WorkDocument3 pagesEuripides WorkSumbul RaeesNo ratings yet
- Modern History Notes On Advent of European in India: SSC CGL Tier I 2017 Online Test Series - Get NowDocument6 pagesModern History Notes On Advent of European in India: SSC CGL Tier I 2017 Online Test Series - Get NowDeepak JhaNo ratings yet
- 21st Lit 24pagesDocument24 pages21st Lit 24pagesFrancient CamposoNo ratings yet
- Times Leader 02-27-2012Document36 pagesTimes Leader 02-27-2012The Times LeaderNo ratings yet
- Toward DemocracyDocument15 pagesToward DemocracyjibranqqNo ratings yet
- All The Badges of A PARA SF CommandoDocument10 pagesAll The Badges of A PARA SF CommandorohanNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 History Learners Book Unit 1 Term 2Document5 pagesGrade 8 History Learners Book Unit 1 Term 2melokuhlengcobo168No ratings yet
- ksp-151 Syrian Refugees Persuasive EssayDocument9 pagesksp-151 Syrian Refugees Persuasive Essayapi-350098277100% (1)
- Turkey of OttomanDocument406 pagesTurkey of OttomanAbdurrahman ŞahinNo ratings yet
- Project Snowblind - Manual - PS2 PDFDocument15 pagesProject Snowblind - Manual - PS2 PDFJasonNo ratings yet
- Encyclopedia Translation UuganaaDocument37 pagesEncyclopedia Translation UuganaaЛувсанням Ренчинханд100% (1)
- Persianempire 160907064320Document54 pagesPersianempire 160907064320Anonymous HumanNo ratings yet
- Crimean WarDocument24 pagesCrimean Warprabuharan890% (1)
- USS Louisiana SSBN 743 (G) : Letter From The CODocument6 pagesUSS Louisiana SSBN 743 (G) : Letter From The COLouisiana Gold OmbudsmanNo ratings yet
- Handley Page VictorDocument18 pagesHandley Page VictorMoshe Rubin0% (2)
- Keohane, R. and Nye, J. (1998) Power and Interdependence in The Information Age (81-94)Document15 pagesKeohane, R. and Nye, J. (1998) Power and Interdependence in The Information Age (81-94)Oscar Múnera PerafánNo ratings yet
- Ryane Abigail CarramanzanaDocument2 pagesRyane Abigail Carramanzanaapi-386299106No ratings yet
- Scion - Allies and YankeesDocument8 pagesScion - Allies and YankeesLivio Quintilio GlobuloNo ratings yet
- Kenya Al Shabaab Inteligence ReportDocument32 pagesKenya Al Shabaab Inteligence ReportWanjikũRevolution Kenya100% (2)