#1 Cell Structure and Function
Uploaded by
Charlene Epilepsia#1 Cell Structure and Function
Uploaded by
Charlene Epilepsia© CHARLENE EPILEPSIA
Cell: Structure and Function
Principles of Cell Theory
All living things are made up of cells (Schleiden & Schwann)
Cells are the basic units of life (Schleiden & Schwann)
Cells only come from pre-existing cells (Virchow)
Development of Cell Theory
Year of Scientist Contribution
Discovery
1595 Hans & Zacharias Developed the first compound microscope by combining 2
Janssen convex lenses within a tube
1665 Robert Hooke Discovered small, hollow compartments in a cork of an oak
tree - pores/cells
1676 Anton van Leeuwenhoek Observed tiny living organisms in pond water, discovered
single celled organisms - animalcules
1683 Anton van Leuuwenhoek Discovered bacteria from a sample of saliva from his mouth
1836 Theodor Schwann Stated that all animal tissues are made up of cells
1838 Matthias Schleiden Discovered that plants were made up of cells
1840 Jan Evangelista Purkinje Named the cellular content ‘protoplasm’
1855 Rudolf Virchow Suggested that all cells come from cells
Cell
Basic structural and functional unit of life
Simplest entity capable of carrying out life’s processes
Can exist alone (unicellular) or as a complex organism (multicellular)
To be composed primarily of C, H, O, N
Contains over 60% water — homeostasis
Major biomolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids
Vary in size — ranges from 0.2μm to 2mm
Vary in shape — fixed or variable
Differences Similiarities
Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Both
“before nucleus” “true nucleus” Plasma Membrane
No nucleus With nucleus Cytoplasm
No organelles With organelles DNA
With Nucleoid Ribosomes
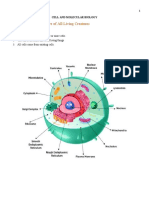
Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cell
1. Plasma Membrane
Structural barrier separating the cell from the outside environment
With protective and regulatory functions
2. Cell Membrane
Acts as a boundary
Controls what enters and leaves cell
Regulates chemical composition
Maintains homeostasis
© CHARLENE EPILEPSIA
3. Cytoplasm
Space in the cell where most cellular activities take place
Contains an intracellular matrix called cytosol where all other cellular components are suspended
Organelles - membrane-bound structures in eukaryotic cells
Inclusions - non-permanent and inactive substances/materials in the cell
4. DNA (Genetic Material)
Blueprint of an organism
Carries all the information necessary for the growth, development and survival of an organism
5. Ribosomes
Small non-membrane bound structures that act as sites for protein synthesis in the cell
Prokaryotic Cell
1. Capsule - a sticky outer layer that provides protection
2. Cell wall - a structure that confers rigidity and shape to the cell
3. Plasmid - a genetic material; extrachromosomal ring of DNA
4. Nucleoid - a DNA-containing region within the cytoplasm
5. Pilus (pili) - a hair-like appendage that functions in adhesion
6. Flagellum - facilitates movement of bacteria
Organelles (Little Organs)
Membrane-bound structures performing a specific function in eukaryotic cells
Distribution of work in the cell — maximizes time and space
Organelles Structure Function
Nucleus Double-membraned structure with Directs RNA and protein synthesis
nuclear pores that connect the Stores the genetic information
nuclear components to the cytoplasm (DNA)
Control center of the cell
Nucleolus Spherical organelle within the Assembles ribosomes
nucleus
Endoplasmic Network of internal membranes Compartmentalizes the cell
Reticulum Divided into two regions: rough ER creating a greater surface area for
(with ribosomes) and smooth ER cellular processes
(without ribosomes) Serves in the transport of cellular
products via the formation of
vesicles
Golgi Bodies Stacks of flattened membranous Modifies and packages cellular
sacs called cisternae products
Cis face - accepts incoming transport
vesicles from the ER
Trans face - releases secretory
vesicles containing the finished
product
Lysosome Small spherical bodies containing Digests macromolecules, cellular
digestive or acidic hydrolytic debris, old organelles and foreign
enzymes substances
Peroxisome Small spherical bodies containing Neutralizes toxic substances and
oxidase enzymes breaks down fatty acids
Vesicles Membrane-bound sacs Store and transport substances
© CHARLENE EPILEPSIA
Vacuole Membrane-bound sacs Store water, enzymes, pigments,
In animals, many but small in size waste products
In plants, one big central vacuole
Mitochondrion Hotdog-shaped structure with smooth Produces ATP (aerobic
outer membrane, folded inner respiration)
membrane and many respiratory
enzymes
Intermembrane space separates the
outer and inner membranes
Folds of the inner membrane are
called cristae
Matrix is the space within the inner
membrane
Chloroplast Double-membraned, green oval Facilitate food production in
structure with stacks of sac-like photosynthetic organisms
structures within
Thylakoid refers to the sac-like
structure containing pigments such
as chlorophyll and carotenoids
Thylakoids stack together to form a
granum
Cytoskeleton Network of protein filaments including Provides structural support and
microfilaments, intermediate Movement (in some) to the cell
filaments, microtubules
Cilia and flagella - motility
Centriole - anchor and assemble
Spindle fibers in animal mitosis
Cell Wall Rigid structure in plants and Provides structural support to the
members of the kingdom fungi made cell
up of cellulose or chitin, respectively
Animal Cell Plant Cell
You might also like
- SHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 2 - Cell Structure And-Functions67% (3)SHS STEM Bio1 Q1 Week 1 Module 2 - Cell Structure And-Functions23 pages
- Cell: The Building Blocks of Life: Awaluddin, M.KesNo ratings yetCell: The Building Blocks of Life: Awaluddin, M.Kes39 pages
- Robert Hooke (1665) - Who Named The Biological Unit Cell Cell Theory 1839 - byNo ratings yetRobert Hooke (1665) - Who Named The Biological Unit Cell Cell Theory 1839 - by11 pages
- Brief History Cytology Hierarchy of Structural Organization - Cell Structure - MitosisNo ratings yetBrief History Cytology Hierarchy of Structural Organization - Cell Structure - Mitosis52 pages
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chap 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Revision NotesNo ratings yetCBSE Class 9 Science Chap 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life - Revision Notes6 pages
- Answer Key - 2020 - Cell Organelles Worksheet ch2.2No ratings yetAnswer Key - 2020 - Cell Organelles Worksheet ch2.27 pages
- Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsNo ratings yetFunctional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells70 pages
- Topic 2.1, 2.2 Cell Structure and FunctionsNo ratings yetTopic 2.1, 2.2 Cell Structure and Functions45 pages
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Biology M2 Cell Structure & Function PDFNo ratings yetBiology M2 Cell Structure & Function PDF24 pages
- The Cell-Structure and Functions (BIOLOGY)No ratings yetThe Cell-Structure and Functions (BIOLOGY)12 pages
- Anatomy&Physiology Lecture 1 - TerminologiesNo ratings yetAnatomy&Physiology Lecture 1 - Terminologies70 pages
- Dr. Yanga'S Colleges, Inc.: Name: Role: Course - Date Submitted: Group NoNo ratings yetDr. Yanga'S Colleges, Inc.: Name: Role: Course - Date Submitted: Group No3 pages
- Chapter 2: Structure of Cells and OrganellesNo ratings yetChapter 2: Structure of Cells and Organelles24 pages
- General Biology 1: Modified Strategic Intervention MaterialsNo ratings yetGeneral Biology 1: Modified Strategic Intervention Materials22 pages
- Chapter 2 - Cell: The Unit of Life Exercise Ex. 1: Solution 1No ratings yetChapter 2 - Cell: The Unit of Life Exercise Ex. 1: Solution 18 pages
- Biology Exam 2024 (@QesemAcademy) - CompressedNo ratings yetBiology Exam 2024 (@QesemAcademy) - Compressed26 pages
- Full download Guyton Hall Physiology Review Guyton Physiology 4th Edition John E Hall Phd pdf docx100% (4)Full download Guyton Hall Physiology Review Guyton Physiology 4th Edition John E Hall Phd pdf docx65 pages