Basic Shell Programming
Uploaded by
Ronald PuthiyaveetilBasic Shell Programming
Uploaded by
Ronald PuthiyaveetilFDP on FOSS Lab
Sunil Thomas T
College of Engineering Attingal
suniltt@gmail.com
January 16, 2017
Sunil Thomas T (College of Engineering Attingal) January 16, 2017 1 / 18
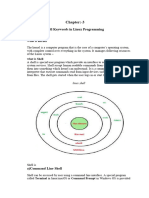
BASIC SHELL PROGRAMMING
What is a shell?
Shells available on a typical Linux system
Why bash ?
What is a shell script? A script is a file that contains
shell commands
data structure: variables
control structure: sequence, decision, loop
Sunil Thomas T (College of Engineering Attingal) January 16, 2017 2 / 18
Your first script
We will look at how to create and execute a shell script.
Open an editor and type the following code snippet. You can use any editor of
your choice.
1 #! / b i n / b a s h
2 ls
Save the file as myscript.sh. Open a terminal and make the file executable.
1 $ chmod +x m y s c r i p t . s h
Now execute the script
1 $ . / m y s c r i p t . sh
Add a few more common commands to the above script and experiment. ( You
need not set the execute permission every time you edit.)
Sunil Thomas T (College of Engineering Attingal) January 16, 2017 3 / 18
Your tool chest
Input
prompting user
command line arguments
Decision:
if-then-else
case
Repetition
do-while, repeat-until
for
select
Functions
Traps
Sunil Thomas T (College of Engineering Attingal) January 16, 2017 4 / 18
User Input
To read a variable
1 read var name
You can print the variable using echo.
1 echo $var name
Let us write a small script.
1 #! / b i n / s h
2 r e a d −p ” e n t e r y o u r name : ” f i r s t last
3
4 e c h o ” F i r s t name : $ f i r s t ”
5 e c h o ” L a s t name : $ l a s t ”
Note that you can give a prompt to read statement and replace a variable in a
long echoed statement.
Experiment with the above. Try inputting more values than variables. Try echo
with single quotes and with out quotes.
Sunil Thomas T (College of Engineering Attingal) January 16, 2017 5 / 18
Special Shell Variables
Inside a shell script you have access to several special variables.
Sunil Thomas T (College of Engineering Attingal) January 16, 2017 6 / 18
Experimenting with special shell variables
The following script demonstrates the use of special shell variables inside a script.
1 #! / b i n / b a s h
2
3 e c h o ” Name o f y o u r s c r i p t is $0 ”
4
5 e c h o ” a r g u e m e n t s e n t e r e d on command l i n e $ ∗ ”
6
7 e c h o ” f i r s t a r g u e m e n t $1 ”
8
9 e c h o ” Second a r g u e m e n t $2 ”
10
11 e c h o ” You e n t e r e d $# a r g u m e n t s ”
12
13 echo ” p r o c e s s i d i s $$ ”
Try it out as below from a command prompt.( pos par.sh is the script name)
1 $ . / p o s p a r . s h ram s i t a laxman
Sunil Thomas T (College of Engineering Attingal) January 16, 2017 7 / 18
Control structures
Basic if statement
1
2 i f [ <some t e s t > ]
3 then
4 <commands>
5 fi
Example: Test whether a number input from command line is greater than 100
1
2 #! / b i n / b a s h
3
4 i f [ $1 −g t 100 ]
5 then
6 e c h o Hey t h a t ’ s a l a r g e number .
7
8 fi
Sunil Thomas T (College of Engineering Attingal) January 16, 2017 8 / 18
test command
test command is very commonly used with if in shell script.
test command can be used perform a variety of test on the system. It can be
written in two ways as shown below.
Note that you need proper spacing around the square brackets.
1
2 t e s t <EXPRESSION>
3
4 [ <EXPRESSION> ]
test command evaluates the expression and returns true or false.
Please read the excellent test tutorial at
http://wiki.bash-hackers.org/commands/classictest.
Sunil Thomas T (College of Engineering Attingal) January 16, 2017 9 / 18
Some examples
1
2 #! / b i n / b a s h
3 # t e s t i f / e t c / passwd e x i s t s
4
5 if t e s t −e / e t c / passwd ; t h e n
6 e c h o ” A l r i g h t man . . . ”
7 else
8 e c h o ” Where i s i t ?? ”
9 fi
test statement above can also be written as below.
1 if [ −e / e t c / passwd ] ; t h e n
Various test options available are file tests string tests arithmetic relational and
logical tests. Please see the manual page.
1 $ man t e s t
Sunil Thomas T (College of Engineering Attingal) January 16, 2017 10 / 18
Some more examples
1 #! / b i n / b a s h
2
3 r e a d −p ” E n t e r y e a r s o f work : ” Y e a r s
4 i f [ ! ” $ Y e a r s ” − l t 20 ] ; t h e n
5 e c h o ”You can r e t i r e now . ”
6 else
7 e c h o ”You n e e d 20+ y e a r s t o r e t i r e ”
8 fi
1 #! / b i n / b a s h
2
3 Bonus =500
4 r e a d −p ” E n t e r S t a t u s : ” S t a t u s
5 r e a d −p ” E n t e r S h i f t : ” S h i f t
6 i f [ [ ” $ S t a t u s ” = ”H” && ” $ S h i f t ” = 3 ] ]
7 then
8 e c h o ” s h i f t $ S h i f t g e t s \ $$Bonus b o n u s ”
9 else
10 echo ” o n l y h o u r l y workers i n ”
11 echo ” s h i f t 3 g e t a bonus ”
12 fi
Sunil Thomas T (College of Engineering Attingal) January 16, 2017 11 / 18
if elif
1 #! / b i n / b a s h
2
3 r e a d −p ” E n t e r Income Amount : ” Income
4 r e a d −p ” E n t e r E x p e n s e s Amount : ” E x p e n s e
5
6 l e t Net=$Income−$ E x p e n s e
7
8 if [ ” $Net ” −eq ” 0 ” ] ; t h e n
9 e c h o ” Income and E x p e n s e s a r e e q u a l − b r e a k e v e n . ”
10 e l i f [ ” $Net ” −g t ” 0 ” ] ; t h e n
11 e c h o ” P r o f i t o f : ” $Net
12 else
13 e c h o ” L o s s o f : ” $Net
14 fi
Sunil Thomas T (College of Engineering Attingal) January 16, 2017 12 / 18
case statement
1 #! / b i n / b a s h
2 echo ” Enter Y to s e e a l l f i l e s i n c l u d i n g hidden files”
3 e c h o ” E n t e r N t o s e e a l l non−h i d d e n f i l e s ”
4 echo ” Enter q to q u i t ”
5
6 r e a d −p ” E n t e r y o u r c h o i c e : ” r e p l y
7
8 case $reply in
9 Y | YES ) e c h o ” D i s p l a y i n g a l l files”
10 l s −a ; ;
11 N |NO) e c h o ” D i s p l a y a l l non−h i d d e n f i l e s . . . ”
12 ls ;;
13 Q) exit 0 ;;
14
15 ∗) echo ” I n v a l i d c h o i c e ! ” ; e x i t 1 ; ;
16 esac
Sunil Thomas T (College of Engineering Attingal) January 16, 2017 13 / 18
while loop
1 #! / b i n / b a s h
2 COUNTER=0
3 w h i l e [ $COUNTER − l t 10 ]
4 do
5 e c h o The c o u n t e r i s $COUNTER
6 l e t COUNTER=$COUNTER+1
7 done
Sunil Thomas T (College of Engineering Attingal) January 16, 2017 14 / 18
for loop
1 #! / b i n / b a s h
2
3 for i in 7 9 2 3 4 5
4 do
5 echo $ i
6 done
Sunil Thomas T (College of Engineering Attingal) January 16, 2017 15 / 18
functions
1 #! / b i n / b a s h
2
3 funky () {
4 # This i s a simple f u n c t i o n
5 echo ” This i s a funky f u n c t i o n . ”
6 e c h o ”Now e x i t i n g f u n k y f u n c t i o n . ”
7 }
8
9 # d e c l a r a t i o n must p r e c e d e c a l l :
10
11 funky
Sunil Thomas T (College of Engineering Attingal) January 16, 2017 16 / 18
functions
Arguments provided via function call are accessible inside function as $1, $2, $3,
...
$# reflects number of parameters
Sunil Thomas T (College of Engineering Attingal) January 16, 2017 17 / 18
signals
Sunil Thomas T (College of Engineering Attingal) January 16, 2017 18 / 18
You might also like
- Unit - 4 Shell Scripting and StatementsNo ratings yetUnit - 4 Shell Scripting and Statements16 pages
- Linux Programming - Lecture Notes On UNIT 2No ratings yetLinux Programming - Lecture Notes On UNIT 269 pages
- 17CS35 Module 4 - Shell Programming Files Inode and Filters - VTUPulseNo ratings yet17CS35 Module 4 - Shell Programming Files Inode and Filters - VTUPulse23 pages
- Shell Scripting: Intermediate Systems Administration Decal Lecture #6 Joshua KwanNo ratings yetShell Scripting: Intermediate Systems Administration Decal Lecture #6 Joshua Kwan15 pages
- LEARN SHELL SCRIPT STEP BY STEP - Sanka Dharmarathna - Medium - Reader ViewNo ratings yetLEARN SHELL SCRIPT STEP BY STEP - Sanka Dharmarathna - Medium - Reader View9 pages
- Shell Script Guide for Red Teams - By CodelivlyNo ratings yetShell Script Guide for Red Teams - By Codelivly50 pages
- Shell Scripting: Presented by - Mukesh Halwan Premkanth MenganiNo ratings yetShell Scripting: Presented by - Mukesh Halwan Premkanth Mengani25 pages
- Bash Data Handling: COMP2101 Winter 2019No ratings yetBash Data Handling: COMP2101 Winter 201925 pages
- Introduction To UNIX: Lecture Eight: 8.1 ObjectivesNo ratings yetIntroduction To UNIX: Lecture Eight: 8.1 Objectives9 pages
- Python for Data Science: Data Science Mastery by Nikhil Khan, #1From EverandPython for Data Science: Data Science Mastery by Nikhil Khan, #1No ratings yet
- Python: Advanced Guide to Programming Code with Python: Python Computer Programming, #4From EverandPython: Advanced Guide to Programming Code with Python: Python Computer Programming, #4No ratings yet
- Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (Uart) PDFNo ratings yetUniversal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (Uart) PDF56 pages
- As 4418.1-1996 Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) - Generic Telecommunications Interface and PRNo ratings yetAs 4418.1-1996 Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) - Generic Telecommunications Interface and PR7 pages
- (IJCST-V7I5P8) :rednam S S Jyothi, Eswar Patnala, V.VikasNo ratings yet(IJCST-V7I5P8) :rednam S S Jyothi, Eswar Patnala, V.Vikas7 pages
- Replacing A Failed or Removed Disk Via Vxdiskadm (Option 5) May Fail With "Test: Argument Expected".No ratings yetReplacing A Failed or Removed Disk Via Vxdiskadm (Option 5) May Fail With "Test: Argument Expected".3 pages
- Pervasive Healthcare and Wireless Health MonitoringNo ratings yetPervasive Healthcare and Wireless Health Monitoring15 pages
- Oral Presentation Guidelines: 1. Audio/Visual & Equipment AvailableNo ratings yetOral Presentation Guidelines: 1. Audio/Visual & Equipment Available2 pages
- Customer Relationship Management - Book ReviewNo ratings yetCustomer Relationship Management - Book Review2 pages
- Coding Tutorials For Computational Fluid Dynamics: Ahmed Al MakkyNo ratings yetCoding Tutorials For Computational Fluid Dynamics: Ahmed Al Makky99 pages