Frosio - Paint Systems
Frosio - Paint Systems
Uploaded by
Ganesh R NairCopyright:
Available Formats
Frosio - Paint Systems
Frosio - Paint Systems
Uploaded by
Ganesh R NairOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Frosio - Paint Systems
Frosio - Paint Systems
Uploaded by
Ganesh R NairCopyright:
Available Formats
SURFACE TREATMENT
Paint systems
Version: 1.1
Last updated: 27/04/18
Introduction
Can we find a paint for all environments and surfaces?
Different paints can be used to protect a variety of construction materials. No paint can be used in all
environments!
Factors influencing the selection of a paint system
Customer’s expectation (durability)
Service environment
Availability of paint and/or other protective materials
Substrate
Structure design
Surface preparation available
Paint application methods available
Ease of maintenance
Cost
Health, safety and environmental factors
Customer Expectations
Customers are usually concerned with corrosion and the durability of the asset with aesthetics normally
not as important
To meet their durability requirements coating system durability should be discussed
According to ISO 12944-1 durability is defined as the expected life of a protective paint system to the first
major maintenance painting
Durability is not the same as a “guarantee” period
Corrosivity of the Environment
It is important to identify the corrosivity category of an environment since it will relate to:
Corrosion rate of the building material
Material selection of building products
Selection of proper corrosion protection methods for the building materials
ISO 12944-2 defines the classification of environments by corrosivity category
Corrosivity Categories of Environment
Corrosivity Categories of Environment – ISO 12944-2
www.frosiobook.no Page 1 of 4 Printed 09/06/19 08:04:47
Atmospheric condition Immersion
C1 Very low
Im 1 Fresh water
C2 Low
C3 Medium
Im 2 Sea or brackish water
C4 High
C5 Very high Im 3 Soil
CX Extreme Im 4 Sea or brackish water
Description of corrosivity categories
C1 Very low
Interior: Heated buildings with clean atmospheres, e.g. offices, shops, schools, hotels
C2 Low
Exterior: Atmospheres with low level of pollution. Mostly rural areas
Interior: Unheated buildings where condensation may occur, e.g. depots, sports halls
C3 Medium
Exterior: Urban and industrial atmospheres, moderate sulfur dioxide pollution. Coastal areas with low
salinity
Interior: Production rooms with high humidity and some air pollution, e.g. food-processing plants,
laundries, breweries, dairies
C4 High
Exterior: Industrial areas and coastal areas with moderate salinity
Interior: Chemical plants, swimming pools, coastal ship- and boatyards
C5- Very high
Exterior: Industrial areas with high humidity and aggressive atmosphere and coastal areas with high
salinity
Interior: Buildings or areas with almost permanent condensation and with high pollution
CX- Extreme
Exterior: Offshore areas with high salinity and industrial areas with extreme humidity and aggressive
atmosphere and subtropical and tropical atmospheres
Interior: Industrial areas with extreme humidity and aggressive atmosphere
Im1 Fresh water
River installations, hydro-electric power plants
Im2 Sea or brackish water
www.frosiobook.no Page 2 of 4 Printed 09/06/19 08:04:47
Immersed structures without cathodic protection (e.g. harbor areas with structures like sluice gates,
locks, jetties)
Im3 Soil
Buried tanks, steel piles, steel pipes
Im4 Sea and brackish water
Immersed structures with cathodic protection (e.g. offshore structures)
Selecting a paint system according to ISO 12944-5
ISO 12944-5 is an industrial standard which can be referenced to find a suitable system for new
construction. There are lists of typical systems categorized by:
Substrate (low-alloyed carbon steel, hot-dip galvanized steel and thermally sprayed steel)
Corrosivity category (C1, C2, C3, C4, C5, CX, Im1, Im2, Im3, Im4)
Expected durability (low, medium and high)
Build-up of a Paint System
There are no “magic” paints that can do everything, hence, multi-layer systems are normal in most cases:
Primer / Intermediate coat / Topcoat
However, one coat system may also be specified:
Paint is specially designed for a single coat
Constant, mild environment
Minor job such as maintenance
Low expected durability
Primers
Primers are universal for most anticorrosive coating systems and are considered the most important component
of the system. The most important properties of primers are listed as follows:
Adhesion (strong bonding to substrate)
Cohesion (high internal strength in the film)
Intercoat adhesion (high bonding to intermediate coat)
Appropriate flexibility
Intermediate coats
The principal purposes of an intermediate coat is to provide:
Thickness for total coating system
Strong chemical resistance
Resistance to moisture vapor transfer
Increase electrical resistance for the coating system
Strong cohesion
Strong bonding to primer and topcoat
www.frosiobook.no Page 3 of 4 Printed 09/06/19 08:04:47
Topcoats
Topcoats also perform several important functions as they:
Provide a resistant seal for the coating system
Form the initial barrier towards the environment
Provide resistance towards chemicals, water, and weather
Provide a tough and wear-resistant surface
Provide a pleasant appearance
General rules – thickness of coating system
Deciding factor is the environment:
An example:
In a dry inland atmosphere, and indoors 120 µm will be sufficient, while in a coastal environment, 250 -
300 µm may be necessary to achieve the same number of years durability
Number of coats is also of importance
100 µm in 2 coats (50 + 50 µm) will give better protection than 100 µm in 1 coat
Where can we find the properties of a paint?
It is impossible to know all different paint products
Technical data sheet (TDS) from supplier is a suitable source
Information that may be found in a TDS or Application Guide:
Product description
Recommended use and typical paint system
Film thickness and spreading rate
Approvals
Physical properties
Surface preparation (methods and requirements)
Application (ambient condition, methods, technical parameters)
Drying time
Brief HSE requirements (Refer SDS)
Packing size
Inspectors need to understand and be familiar with the technical data in TDS
Environmental factors not covered in ISO 12944-2
The Corrosivity categories in ISO 12944 do not cover all situations
Some factors causing increased corrosion:
Heat (high)
Chemicals
Stray current
Mechanical stress
To find proper paint systems for these environments is not easy
We can always consult paint supplier and also confirm with pre-qualification testing
www.frosiobook.no Page 4 of 4 Printed 09/06/19 08:04:47
You might also like
- Frosio - Exam Questions - SampleDocument3 pagesFrosio - Exam Questions - SampleAnte Bosancic88% (8)
- Cathelco Evac ICPP ManualDocument85 pagesCathelco Evac ICPP ManualВладимир ПетрукNo ratings yet
- Frosio EgsamDocument8 pagesFrosio EgsamZiom Ziomek100% (2)
- I Corr Inspector Exam Sample Questions Level 3Document1 pageI Corr Inspector Exam Sample Questions Level 3Gabriel Pana67% (3)
- prosio 기출 문제 정리Document38 pagesprosio 기출 문제 정리77smilelife100% (5)
- QST 30Document7 pagesQST 30jengandxb67% (3)
- Frosio Practical Examination-GDocument101 pagesFrosio Practical Examination-Gweldingpearl100% (1)
- FROSIO Certification: For The Professional Coating InspectorDocument2 pagesFROSIO Certification: For The Professional Coating InspectorGeorgianaNo ratings yet
- FROSIO PresentationDocument36 pagesFROSIO PresentationSatish100% (3)
- Examp and HSEDocument46 pagesExamp and HSElonglong3003No ratings yet
- B GAS Painting Multiple Choice 2Document9 pagesB GAS Painting Multiple Choice 2Muhammad Nasir100% (2)
- FinalExamSheet 4663 1495206384Document28 pagesFinalExamSheet 4663 1495206384Gabriel Pana100% (2)
- CIP Session II Quiz-4Document5 pagesCIP Session II Quiz-4munna88% (8)
- Compatibility of PaintsDocument1 pageCompatibility of Paintslonglong3003100% (1)
- FROSIO - Flash QuesDocument4 pagesFROSIO - Flash QuesAnte BosancicNo ratings yet
- Q A BgasDocument33 pagesQ A BgasAnonymous rpcAOp100% (2)
- Inspections/full Package, Frosio-Nace Certified InspectorsDocument8 pagesInspections/full Package, Frosio-Nace Certified InspectorsZiom Ziomek100% (1)
- PCSDocument4 pagesPCStest1100% (2)
- Aga CourseDocument40 pagesAga CourseTarek YehiaNo ratings yet
- Painting Inspector Reviewer1Document5 pagesPainting Inspector Reviewer1ishaq_khanNo ratings yet
- CorrisionDocument56 pagesCorrisionUsab Gamal100% (1)
- Paint - Paint Film Defects PDFDocument49 pagesPaint - Paint Film Defects PDFDaison PaulNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Certified Coating Inspector For IMO PSPC RulesDocument21 pagesThe Importance of Certified Coating Inspector For IMO PSPC Rulesigeorge7950% (2)
- Application, Instructions, AND Program Rules: SSPC Qp6Document28 pagesApplication, Instructions, AND Program Rules: SSPC Qp6Victor Hugo PexoNo ratings yet
- Quiries AnswerDocument198 pagesQuiries AnswerAhmedNo ratings yet
- 4516 TTI Coating Inspector Transition 0317.2Document4 pages4516 TTI Coating Inspector Transition 0317.2Mohamed NouzerNo ratings yet
- Revision Questions AnswerDocument37 pagesRevision Questions AnswerahmedNo ratings yet
- Coating QaDocument17 pagesCoating Qasbmmla100% (9)
- Q & A 3 BgasDocument8 pagesQ & A 3 BgasAbdulRahman Mohamed Hanifa100% (2)
- Q & A BgasDocument33 pagesQ & A BgasAbdulRahman Mohamed Hanifa86% (7)
- New Trial Paper BGasDocument2 pagesNew Trial Paper BGasmoonstar_dme100% (1)
- 2 - 06 FROSIO Pre - CertificationDocument167 pages2 - 06 FROSIO Pre - CertificationHamza Al Amin100% (1)
- Bgas PA10Document23 pagesBgas PA10Ajith PayyanurNo ratings yet
- Q A CoatingDocument29 pagesQ A CoatingHau Le100% (2)
- G16S-0205-01 - Repair Hot Drip Galv SurfaceDocument5 pagesG16S-0205-01 - Repair Hot Drip Galv Surfacepuwarin naja100% (1)
- Question & Answer Ofhomework1Document9 pagesQuestion & Answer Ofhomework14romi89100% (2)
- CIP Session I Quiz-2Document5 pagesCIP Session I Quiz-2sahadik bahadur100% (1)
- FrosioBook 18.12.2017 PDFDocument232 pagesFrosioBook 18.12.2017 PDFmahmoud hagag100% (6)
- BGas Painting Multiple Choice 2Document17 pagesBGas Painting Multiple Choice 2Abdul Gafoor86% (14)
- AnswersDocument4 pagesAnswersWaseem YounisNo ratings yet
- CIP Session I Quiz-4Document5 pagesCIP Session I Quiz-4munna100% (6)
- Long Question/ Narrative Question.: Define Pigment?Document3 pagesLong Question/ Narrative Question.: Define Pigment?Hau LeNo ratings yet
- Painting Inspection Grade 2/3 Exam: Unit Test - 4Document1 pagePainting Inspection Grade 2/3 Exam: Unit Test - 4AjeetKumar0% (1)
- 005 NACE - Sample QuestionsDocument16 pages005 NACE - Sample QuestionsTunay UralNo ratings yet
- Frosio 03 Inspector DutiesDocument36 pagesFrosio 03 Inspector DutiesThien Van Le100% (1)
- ASTM D7393-07 (2012) Standard Practice For Indicating Oil in AbrasivesDocument2 pagesASTM D7393-07 (2012) Standard Practice For Indicating Oil in Abrasivesalexander zuritaNo ratings yet
- File SSPC Pci Study Guide PDFDocument3 pagesFile SSPC Pci Study Guide PDFmicah50% (2)
- Comparison-of-SSPC-PA2-and-ISO 19840Document6 pagesComparison-of-SSPC-PA2-and-ISO 19840Ahmad FazriNo ratings yet
- BGas Painting Inspection Grade 2 Multiple ChoiceDocument12 pagesBGas Painting Inspection Grade 2 Multiple Choicetcagokl93% (44)
- Standards Spec Brochure ME WEBDocument44 pagesStandards Spec Brochure ME WEBReza TambaNo ratings yet
- Standards Spec Brochure ME WEBDocument44 pagesStandards Spec Brochure ME WEBLaxman Duggirala100% (1)
- ISO 12944 2022 MasterDocument22 pagesISO 12944 2022 MasterJosé Román MenaNo ratings yet
- How To Select The Right Paint System - HempelDocument40 pagesHow To Select The Right Paint System - HempelBellana Sirish33% (3)
- Training Module 4 - Coating Selection StandardsDocument48 pagesTraining Module 4 - Coating Selection StandardsSanjay Kumar100% (1)
- Painting Istructions Accroding ISO 12944-5Document40 pagesPainting Istructions Accroding ISO 12944-5giulioiussich100% (6)
- Producing Coating Specifications That WoDocument11 pagesProducing Coating Specifications That WoAhmed hafez100% (1)
- Interesting Manual PDFDocument20 pagesInteresting Manual PDFthyskie100% (2)
- ISO 12944 - tcm279-213128Document16 pagesISO 12944 - tcm279-213128rodrigogomez87100% (1)
- IMO Performance Standard For Protective Coating and IACS Common Structural RulesDocument76 pagesIMO Performance Standard For Protective Coating and IACS Common Structural Rulesheobukon100% (2)
- Epoguard - Introduction To Industrial CoatingsDocument18 pagesEpoguard - Introduction To Industrial CoatingsPushkar Naresh Patil100% (1)
- CFA Coatings and ProtectionDocument24 pagesCFA Coatings and ProtectionangthiankongNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Protection of Offshore StructuresDocument10 pagesCorrosion Protection of Offshore StructuresHo Minh Viet100% (1)
- S HandlingDocument9 pagesS HandlingGanesh R NairNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: 1. IdentificationDocument7 pagesSafety Data Sheet: 1. IdentificationGanesh R NairNo ratings yet
- American Welding Society: 550 NW Lejeune Road Miami, Florida 33126Document1 pageAmerican Welding Society: 550 NW Lejeune Road Miami, Florida 33126Ganesh R NairNo ratings yet
- American Welding Society: 550 NW Lejeune Road Miami, Florida 33126Document1 pageAmerican Welding Society: 550 NW Lejeune Road Miami, Florida 33126Ganesh R NairNo ratings yet
- Welding Distortion Control in Thin Metal Plates by Altering Heat Input Through Weld ParametersDocument7 pagesWelding Distortion Control in Thin Metal Plates by Altering Heat Input Through Weld ParametersGanesh R NairNo ratings yet
- Full Materials Report DuPont GPODocument10 pagesFull Materials Report DuPont GPOGanesh R NairNo ratings yet
- Skip To Content: Needs YouDocument11 pagesSkip To Content: Needs YouGanesh R NairNo ratings yet
- Skip To Content: Needs YouDocument11 pagesSkip To Content: Needs YouGanesh R NairNo ratings yet
- Release Elsewhere Around The World, Especially in Brazil Romance The Population Down To Some Scattered Lonely HeartsDocument5 pagesRelease Elsewhere Around The World, Especially in Brazil Romance The Population Down To Some Scattered Lonely HeartsGanesh R NairNo ratings yet
- Skip To Content: Needs YouDocument10 pagesSkip To Content: Needs YouGanesh R NairNo ratings yet
- Skip To Content: Needs YouDocument11 pagesSkip To Content: Needs YouGanesh R NairNo ratings yet
- SILASTIC™ LS-2940 U Fluorosil Rubber - Dow IncDocument3 pagesSILASTIC™ LS-2940 U Fluorosil Rubber - Dow Incnorfazlinda20No ratings yet
- Hydraullic and Pneumatic ToolsDocument4 pagesHydraullic and Pneumatic ToolsShishir VardeNo ratings yet
- Akkialur BridgeDocument10 pagesAkkialur BridgeAVD CONSTRUCTIONSNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Material ExerciseDocument4 pagesMechanics of Material ExerciseFaiz Fauzi0% (1)
- Basic Washes in Denim FabricDocument24 pagesBasic Washes in Denim FabricAbdullah Al HafizNo ratings yet
- Surplus ApkDocument4 pagesSurplus ApkSivagnana IyappanNo ratings yet
- CP-D70DW CP-D707DW: Operation ManualDocument27 pagesCP-D70DW CP-D707DW: Operation ManualDean StaceyNo ratings yet
- Pumps Compressors UK FinalDocument24 pagesPumps Compressors UK FinalLeonard Hisatoshi EzureNo ratings yet
- Mason Industries, Inc.: Position 1 (Floor in Poured Position) Position 2 (Spring & Neoprene Cup Installed)Document1 pageMason Industries, Inc.: Position 1 (Floor in Poured Position) Position 2 (Spring & Neoprene Cup Installed)Mai Tuan AnhNo ratings yet
- 2019-11-29.11.20.52-St5001 Maintenance and Rehabilitation of StructuresDocument2 pages2019-11-29.11.20.52-St5001 Maintenance and Rehabilitation of StructuresSakkeer A VNo ratings yet
- Canalis KTDocument284 pagesCanalis KTKelvin TuarezNo ratings yet
- SW Management (Regulations 7-10) (EiMAS)Document100 pagesSW Management (Regulations 7-10) (EiMAS)Corona Virus100% (2)
- Piping Fabrication and Construction PDFDocument61 pagesPiping Fabrication and Construction PDFMohamed AdelNo ratings yet
- Grundfos MG3Document16 pagesGrundfos MG3Rameez IrfanNo ratings yet
- Precision PipesDocument2 pagesPrecision PipesRamu PamuruNo ratings yet
- Nitoflor Sol PDFDocument2 pagesNitoflor Sol PDFBijaya Raula100% (1)
- Atoms, Elements and Compounds HADocument4 pagesAtoms, Elements and Compounds HAHendry RaoNo ratings yet
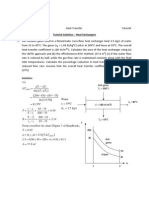
- ME3122 Tutorial Solutions 2010 - Heat Ex ChangersDocument8 pagesME3122 Tutorial Solutions 2010 - Heat Ex Changerskejun_h842No ratings yet
- Hyperdesmo - v3.1Document5 pagesHyperdesmo - v3.1omarmaaref.omNo ratings yet
- MTL FFieldbus HA Solutions and Diagnostics PDFDocument91 pagesMTL FFieldbus HA Solutions and Diagnostics PDFmasimerise100% (1)
- Tle 6Document3 pagesTle 6Yu NaNo ratings yet
- System OneDocument4 pagesSystem OnerasottoNo ratings yet
- Divercontact P16 Direct Food Contact Antimicrobial SolutionDocument7 pagesDivercontact P16 Direct Food Contact Antimicrobial SolutionVo Long ThuanNo ratings yet
- Objective of Concrete Mix DesignDocument11 pagesObjective of Concrete Mix DesignJude Prasanna0% (1)
- MetraWireHarness 120706502Document2 pagesMetraWireHarness 120706502Tanner WitherspoonNo ratings yet
- C45e - Propriedades 2Document1 pageC45e - Propriedades 2engenharia metalicaNo ratings yet
- Basic Chemistry TestDocument2 pagesBasic Chemistry TestVaidehi UlaganathanNo ratings yet
- Units Typical Overall Heat Transfer Coefficients (Fouling 0.003 FT Hdegf/Btu)Document1 pageUnits Typical Overall Heat Transfer Coefficients (Fouling 0.003 FT Hdegf/Btu)Anonymous bHh1L1No ratings yet