0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
310 viewsStatistics Exam
Statistics Exam
Uploaded by
Gom-o Eugenio JrThis document is a practice exam for a Grade 11 statistics and probability class. It contains 17 multiple choice questions testing concepts like random variables, probability distributions, normal distributions, and their related terminology. The key concepts covered include the difference between discrete and continuous random variables, properties of probability distributions, measures of central tendency and variability like mean, median and variance, and the characteristics of the standard normal distribution.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Statistics Exam
Statistics Exam
Uploaded by
Gom-o Eugenio Jr0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
310 views1 pageThis document is a practice exam for a Grade 11 statistics and probability class. It contains 17 multiple choice questions testing concepts like random variables, probability distributions, normal distributions, and their related terminology. The key concepts covered include the difference between discrete and continuous random variables, properties of probability distributions, measures of central tendency and variability like mean, median and variance, and the characteristics of the standard normal distribution.
Original Title
STATISTICS EXAM
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
This document is a practice exam for a Grade 11 statistics and probability class. It contains 17 multiple choice questions testing concepts like random variables, probability distributions, normal distributions, and their related terminology. The key concepts covered include the difference between discrete and continuous random variables, properties of probability distributions, measures of central tendency and variability like mean, median and variance, and the characteristics of the standard normal distribution.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
310 views1 pageStatistics Exam
Statistics Exam
Uploaded by
Gom-o Eugenio JrThis document is a practice exam for a Grade 11 statistics and probability class. It contains 17 multiple choice questions testing concepts like random variables, probability distributions, normal distributions, and their related terminology. The key concepts covered include the difference between discrete and continuous random variables, properties of probability distributions, measures of central tendency and variability like mean, median and variance, and the characteristics of the standard normal distribution.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
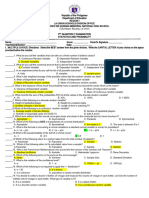
STATISTICS and PROBABILITY – GRADE 11, 2nd SEMESTER, S.Y.
2019 – 2020
Third Quarter Examination
Name: _____________________________ Date: _______________ Score: _____________
Multiple Choice: Choose the letter of the best answer and write it on the space provided for
before each number.
__________1. It is a set whose elements are the numbers assigned to the outcomes of an
experiment.
A. Experiment B. Outcome C. Random variable D. Variable
__________2. It is a type of random variable that has a finite number of elements or infinite but
can be represented by whole numbers.
A. Continuous B. Discrete C. Outcome D. Probability
__________3. Which of the following is an example of a discrete random variable?
A. F: The amount of milk obtained from a cow
B. X: Number of women among 10 newly hired teachers
C. Y: Height (in inches) of a randomly selected adult male
D. A: Amount of rainfall (in mm) in the different cities of Metro Manila
__________4. Which of the following is NOT an example of a continuous random variable?
A. F: The amount of milk obtained from a cow
B. X: Number of women among 10 newly hired teachers
C. Y: Height (in inches) of a randomly selected adult male
D. A: Amount of rainfall (in mm) in the different cities of Metro Manila
__________5. Given random variable X = {1, 2, 3}, what do you call 1, 2, 3?
A. variable B. random variable C. elements D. experiment
__________6. It is a table showing all the possible values of a discrete random variable
together with their corresponding probabilities.
A. discrete probability distribution B. probability distribution
C. continuous probability distribution D. random variable
__________7. In a discrete probability distribution, what must be the range of the value of each
of the probabilities?
A. 0-1 B. 1-2 C. 2-3 D. 1-3
__________8. In a discrete probability distribution, what must be the value of ƩP(x)?
A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4
__________9. What is the symbol used to denote the expected value of X?
A. E(x) B. P(x) C. f(x) D. x1
__________10. What is the symbol used to denote the variance of any random variable X?
A. E(x) B. 𝜎 C. 𝜎2 D. x1
__________11. Which of the following is usually used as a measure of variability?
A. mean B. median C. variance D. mode
__________12. In a normal distribution, what is the total area under its curve?
A. 0 B. 1 C. -1 D. -2
__________13. In a normal distribution, its curve is symmetric to what axis?
A. x-axis B. y-axis C. both x-and y-axis D. None of the above
__________14. In a normal distribution, what is the area above z = -1?
A. 0.1587 B. -0.1587 C. 0.8413 D. -0.8413
__________15. In a normal distribution, what is the area below z = -1?
A. 0.1587 B. -1.1587 C. 0.8413 D. -1.8413
__________16. It tells how many standard deviations a value is, away from the mean.
A. Z-score B. variance C. mode D. mean
__________17. What is the value of the mean of a standard normal distribution?
A. 2 B. 1 C. -1 D. 0
You might also like
- Local Media100839098740108681Document4 pagesLocal Media100839098740108681Majoy AcebesNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Examination in Statistics & ProbabilityDocument3 pagesPreliminary Examination in Statistics & Probabilitychristian enriquezNo ratings yet
- Summat IveDocument3 pagesSummat IvedhelNo ratings yet
- 3rdPTProbNStatsHUMSS1 2024Document4 pages3rdPTProbNStatsHUMSS1 2024Marlon D. GolongNo ratings yet
- Division Unified Test in Statistics and Probability Quarter 3Document6 pagesDivision Unified Test in Statistics and Probability Quarter 3Carren Deadio63% (8)
- Stats Q3 Unit Test With AnswerDocument3 pagesStats Q3 Unit Test With Answerraulbucao28No ratings yet
- q3 Sum1 Statprob Answer-KeyDocument3 pagesq3 Sum1 Statprob Answer-Keyryujinstorm0221No ratings yet
- Proba and Stat Prefi ExamDocument3 pagesProba and Stat Prefi ExamSamuel T. Catulpos Jr.100% (1)
- 1ST Quarter ExamDocument4 pages1ST Quarter ExamBlessed Joy PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Pre TEST1 AnswerDocument2 pagesPre TEST1 AnswerVal Daryl AnhaoNo ratings yet
- Stat Prob 11 - 3rd Quarter AssessmentDocument7 pagesStat Prob 11 - 3rd Quarter AssessmentRejie MaeNo ratings yet
- Summative 2Document2 pagesSummative 2Macky TruzoNo ratings yet
- Prob Stat Exam 3rd QuarterDocument3 pagesProb Stat Exam 3rd Quarteralvin madahan100% (1)
- Stat&Prob Module 1 EditedDocument14 pagesStat&Prob Module 1 EditedJeycelNo ratings yet
- 3RD Periodical Exam in StatDocument7 pages3RD Periodical Exam in Statroxan condes90% (10)
- TQ Statistics 11 - Q3 UPDATEDDocument2 pagesTQ Statistics 11 - Q3 UPDATEDanon_754485983No ratings yet
- Stat ExamDocument2 pagesStat ExamKelvin C. Grajo100% (1)
- Final Examination in Statistics and ProbabilityDocument2 pagesFinal Examination in Statistics and ProbabilityMagz Magan100% (15)
- Statistics and Probability Midterm ExamDocument3 pagesStatistics and Probability Midterm ExamDave Adajar Tejedo100% (3)
- 1st Quarter Exam For StatDocument4 pages1st Quarter Exam For StatLeonelyn Lecera Navarez100% (1)
- Statistics Quiz For Junior HighDocument10 pagesStatistics Quiz For Junior HighAira ApellidoNo ratings yet
- Stat and Prob-Thirrd QADocument4 pagesStat and Prob-Thirrd QASharlyn BalgoaNo ratings yet
- Third Quarter Examination - StatisticsandprobabilityDocument3 pagesThird Quarter Examination - StatisticsandprobabilitydeyangnicoleNo ratings yet
- Midterm ExamDocument3 pagesMidterm Examjayarvidor5No ratings yet
- Stat&Proba Midterm ExamDocument4 pagesStat&Proba Midterm ExamPatrice Del MundoNo ratings yet
- Business Research MethodsDocument15 pagesBusiness Research MethodsDisha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Quarter 3 TQ Statistics and Probability FinalDocument4 pagesQuarter 3 TQ Statistics and Probability Finalrommeldimla12100% (1)
- Statistics Quarter 3 Midterms ReviewerDocument6 pagesStatistics Quarter 3 Midterms ReviewerKristoppe SitoyNo ratings yet
- Q2 Quiz 1 and 2 - 2023-2024Document2 pagesQ2 Quiz 1 and 2 - 2023-2024mhackNo ratings yet
- Stat&PropbTQQ3W1 4Document4 pagesStat&PropbTQQ3W1 4Chladys EspirituNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability TQQ3W1-4Document3 pagesStatistics and Probability TQQ3W1-4Chladys EspirituNo ratings yet
- Midterm StatDocument5 pagesMidterm Statgerona.marquezaNo ratings yet
- Core 10 - SA 1 (ReviewMaterial)Document7 pagesCore 10 - SA 1 (ReviewMaterial)lorenzjohn777No ratings yet
- TQ Statistics & ProbabilityDocument13 pagesTQ Statistics & ProbabilityJanVie DueroNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam in Statistics and Probability (Grade 11)Document2 pagesMidterm Exam in Statistics and Probability (Grade 11)Magz Magan95% (58)
- Stat Reviewer 2Document4 pagesStat Reviewer 2obonglhetty06No ratings yet
- g11-3rd Quarter Exam (Statistics)Document4 pagesg11-3rd Quarter Exam (Statistics)reybeth.marilla029No ratings yet
- Midterm Exam in Stat and Prob (2018-2019)Document5 pagesMidterm Exam in Stat and Prob (2018-2019)Michelle Ann RamosNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter School Year 2020 - 2021 Statistics and Probability Answer SheetDocument10 pagesSecond Quarter School Year 2020 - 2021 Statistics and Probability Answer SheetLynette LicsiNo ratings yet
- CHP 1 StudyDocument16 pagesCHP 1 Studykenshin1989No ratings yet
- Prelim Examination in Statistics and Probability - Grade 11Document3 pagesPrelim Examination in Statistics and Probability - Grade 11mcarlos.23n-0057No ratings yet
- 4th Periodical Test (ProbStat)Document4 pages4th Periodical Test (ProbStat)Lourence CapaNo ratings yet
- SHS - StatisticsDocument7 pagesSHS - StatisticsKILVEN MASIONNo ratings yet
- ch03Document40 pagesch03aashir.aftab01No ratings yet
- stAT AND PROBDocument26 pagesstAT AND PROBdelimaashley13No ratings yet
- 3 RD PTProb NStatsDocument4 pages3 RD PTProb NStatsMarlon D. GolongNo ratings yet
- Second Quarter School Year 2020 - 2021 Statistics and Probability Answer SheetDocument11 pagesSecond Quarter School Year 2020 - 2021 Statistics and Probability Answer SheetLynette LicsiNo ratings yet
- 2nd Grading Math9Document5 pages2nd Grading Math9Jaylo SalduaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer StatDocument4 pagesReviewer StatJohn Mar CeaNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3: Statistics A. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Write The Letter of Your On The Space Provided Before The NumberDocument5 pagesQuiz 3: Statistics A. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Write The Letter of Your On The Space Provided Before The NumberPatrick GoNo ratings yet
- CH 03Document40 pagesCH 03AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Direction: Choose The Letter of The Correct Answer. Write The Chosen Letter On The Space Before Each NumberDocument4 pagesDirection: Choose The Letter of The Correct Answer. Write The Chosen Letter On The Space Before Each NumberREBECCA ORDONEZNo ratings yet
- Local Media7248226037668021614Document4 pagesLocal Media7248226037668021614Ken Ken GorianoNo ratings yet
- Math8 Q2 Exam (For Submission)Document5 pagesMath8 Q2 Exam (For Submission)Marlou KipkipanNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument3 pagesStatisticsAngel CaluscusanNo ratings yet
- CH 03Document32 pagesCH 03Tanya YablonskayaNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Statistics QuestionsDocument33 pagesDescriptive Statistics QuestionsPARUL SINGH MBA 2019-21 (Delhi)No ratings yet
- Learn Statistics Fast: A Simplified Detailed Version for StudentsFrom EverandLearn Statistics Fast: A Simplified Detailed Version for StudentsNo ratings yet
- Crysal Fild TheoryDocument56 pagesCrysal Fild TheoryAnil PatilNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2-3 - Introduction To Aerodynamics & FundamentalsDocument15 pagesLecture 2-3 - Introduction To Aerodynamics & FundamentalsAli RazaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 15 A Level Physics WB MSDocument4 pagesChapter - 15 A Level Physics WB MSmichelle winataNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Session 4Document34 pagesGrade 10 Session 4donnamichellepbonillaNo ratings yet
- Ch3 Fins ClassDocument35 pagesCh3 Fins ClassSYEDHAMMAD ALINo ratings yet
- Astm D4833.479148-1Document4 pagesAstm D4833.479148-1Leudy Utria100% (1)
- Worksheet 1 Class 10Document5 pagesWorksheet 1 Class 10Divyansh JainNo ratings yet
- PCAssignment 3Document2 pagesPCAssignment 3Aseem AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Prestressed Concrete Analysis and Design Fundamentals 2nd Ed CAP 15Document56 pagesPrestressed Concrete Analysis and Design Fundamentals 2nd Ed CAP 15Carlos Alberto Pacheco SierraNo ratings yet
- By Robert Anton Wilson: Holy Cross. HolyDocument12 pagesBy Robert Anton Wilson: Holy Cross. HolyChris F OrdlordNo ratings yet
- 3D Printing Eco-Friendly Concrete Containing Under-Utilised and WasteDocument13 pages3D Printing Eco-Friendly Concrete Containing Under-Utilised and WasteShrishail KalagiNo ratings yet
- Work and Energy Class 9 Mcqs Questions With AnswersDocument10 pagesWork and Energy Class 9 Mcqs Questions With AnswersSCIENCE WORK [AMP] ActivitiesNo ratings yet
- Substations and Electrical Installations: LPIT Applications in HV Gas Insulated SwitchgearDocument94 pagesSubstations and Electrical Installations: LPIT Applications in HV Gas Insulated Switchgearjeanjean100% (1)
- Common Approaches To Meeting Requirements For Packaging ValidationsDocument71 pagesCommon Approaches To Meeting Requirements For Packaging ValidationsYu-Chih Pu100% (1)
- Electromagnetic Waves Solutions Manual - InanDocument156 pagesElectromagnetic Waves Solutions Manual - Inansurajvidhata58% (12)
- Statistical Physics (MSC Phy) 1Document5 pagesStatistical Physics (MSC Phy) 1SACHIN VISHWAKARMANo ratings yet
- LTHE Comments On APG's Proposal No. 9090/3181-L&T-Detailed Engineering Services For EPCC-1-AVU Unit, Barauni RefineryDocument9 pagesLTHE Comments On APG's Proposal No. 9090/3181-L&T-Detailed Engineering Services For EPCC-1-AVU Unit, Barauni RefineryajayNo ratings yet
- Grand Viva QuestionsDocument13 pagesGrand Viva QuestionskhushalNo ratings yet
- Plastics Testing For DPTDocument94 pagesPlastics Testing For DPTMohsin Alam100% (3)
- Full Download Textbook of Veterinary Diagnostic Radiology 7. Ed. Edition Nald E. Thrall PDFDocument64 pagesFull Download Textbook of Veterinary Diagnostic Radiology 7. Ed. Edition Nald E. Thrall PDFayyashmelkin78100% (5)
- A Detailed Bin Hopper Flow DesignDocument46 pagesA Detailed Bin Hopper Flow DesignSaurabh RajNo ratings yet
- Solenoid Valves 2/2 225: Direct Operated 1/8Document2 pagesSolenoid Valves 2/2 225: Direct Operated 1/8vineeth8624No ratings yet
- Manufacture of Urea - Melamine - Formaldehyde Glue Used For Laminated Veneer Lumber ProductionDocument7 pagesManufacture of Urea - Melamine - Formaldehyde Glue Used For Laminated Veneer Lumber ProductionPhan KhánhNo ratings yet
- Ngukpletsrgn Issue 7 FinalDocument92 pagesNgukpletsrgn Issue 7 FinalAjay DixitNo ratings yet
- Calc 8.4 PacketDocument4 pagesCalc 8.4 PacketWilliam MaNo ratings yet
- Plaxis Dynamic Loading ExampleDocument11 pagesPlaxis Dynamic Loading ExampleFirat PulatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.2 Anchored Sheet Pile WallDocument30 pagesChapter 2.2 Anchored Sheet Pile WallizwanNo ratings yet
- SlidesDocument387 pagesSlidesFantasy WorldNo ratings yet
- FMATHSDocument5 pagesFMATHSOladimeji OgunleyeNo ratings yet
- Astb ReviewDocument40 pagesAstb Reviewkrgb75100% (2)