50%(2)50% found this document useful (2 votes)
2K viewsDrug Study - Cisplatin
Drug Study - Cisplatin
Uploaded by
Danielle AglusolosCisplatin is an antineoplastic drug that inhibits DNA synthesis, causing cross-linking of parent DNA strands and death of rapidly replicating cells. It is indicated for metastatic testicular and ovarian carcinoma, advanced bladder cancer, head and neck cancer, cervical cancer, lung cancer, and other tumors. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity, alopecia, hypocalcemia, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, and peripheral neuropathy. Nurses monitor for side effects, ensure adequate hydration and electrolyte replacement, and assess the IV site frequently during administration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Drug Study - Cisplatin
Drug Study - Cisplatin
Uploaded by
Danielle Aglusolos50%(2)50% found this document useful (2 votes)
2K views3 pagesCisplatin is an antineoplastic drug that inhibits DNA synthesis, causing cross-linking of parent DNA strands and death of rapidly replicating cells. It is indicated for metastatic testicular and ovarian carcinoma, advanced bladder cancer, head and neck cancer, cervical cancer, lung cancer, and other tumors. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity, alopecia, hypocalcemia, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, and peripheral neuropathy. Nurses monitor for side effects, ensure adequate hydration and electrolyte replacement, and assess the IV site frequently during administration.
Original Title
Drug Study -cisplatin.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Cisplatin is an antineoplastic drug that inhibits DNA synthesis, causing cross-linking of parent DNA strands and death of rapidly replicating cells. It is indicated for metastatic testicular and ovarian carcinoma, advanced bladder cancer, head and neck cancer, cervical cancer, lung cancer, and other tumors. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity, alopecia, hypocalcemia, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, and peripheral neuropathy. Nurses monitor for side effects, ensure adequate hydration and electrolyte replacement, and assess the IV site frequently during administration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
50%(2)50% found this document useful (2 votes)
2K views3 pagesDrug Study - Cisplatin
Drug Study - Cisplatin
Uploaded by
Danielle AglusolosCisplatin is an antineoplastic drug that inhibits DNA synthesis, causing cross-linking of parent DNA strands and death of rapidly replicating cells. It is indicated for metastatic testicular and ovarian carcinoma, advanced bladder cancer, head and neck cancer, cervical cancer, lung cancer, and other tumors. Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity, alopecia, hypocalcemia, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, and peripheral neuropathy. Nurses monitor for side effects, ensure adequate hydration and electrolyte replacement, and assess the IV site frequently during administration.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
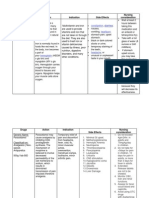
SIDE EFFECTS AND ADVERSE
DRUG MECHANISM OF ACTION INDICATION NURSING ACTION
EFFECTS
Inhibits DNA synthesis by Metastatic testicular and CNS: SEIZURES, malaise, Monitor vital signs frequently
producing cross-linking of ovarian carcinoma. Advanced weakness.
during administration. Report
EENT: ototoxicity, tinnitus.
parent DNA strands (cell-cycle bladder cancer. Head and
GENERIC NAME:
GI: severe nausea, vomiting, significant changes
cisplatin phase—nonspecific). neck cancer. Cervical cancer. diarrhea, hepatotoxicity.
Therapeutic Effects: Death of Lung cancer. Other tumors. GU: nephrotoxicity, sterility. Monitor intake and output and
Derm: alopecia.
rapidly replicating cells, specific gravity frequently
BRAND NAME:
F and E: hypocalcemia,
Platinol particularly malignant ones. during therapy.
hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia.
Hemat: LEUKOPENIA,
THROMBOCYTOPENIA, anemia.
Report discrepancies
DRUG CLASSIFICATION:
Local: phlebitis at IV site. immediately.
Antineoplastics Metab: hyperuricemia.
Neuro: peripheral neuropathy. Encourage patient to drink
Misc: anaphylactoid reactions.
2000– 3000 mL/day to
CONTRAINDICATION INTERACTIONS
Hypersensitivity; Orally disintegrating Drug-Drug: risk of nephrotoxicity and promote excretion of uric acid.
tablets contain aspartame and ototoxicity with other nephrotoxic and
Assess patency of IV site
should not be used in patients with ototoxic drugs (aminoglycosides,
phenylketonuria; loop diuretics).risk of hypokalemia frequently during therapy.
and hypomagnesemia with loop
Monitor amount of emesis
diuretics and amphotericin B.
Maypphenytoin levels. bone marrow and notify health care
depression with other antineoplastics professional if emesis
or radiation therapy. May antibody exceeds guidelines to prevent
response to live-virus vaccines and dehydration.
adverse reactions
Monitor for bone marrow
depression.
Assess for bleeding
Monitor for increased fatigue,
dyspnea, and orthostatic
hypotension.
Monitor for signs of
anaphylaxis
Assess patient frequently for
dizziness, tinnitus, hearing
loss, loss of coordination, loss
of taste, or numbness and
tingling of extremities
You might also like
- Clinical PharmacyDocument26 pagesClinical PharmacyboyapallymeghanaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - MorphineDocument3 pagesDrug Study - MorphineKian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Trilostane Dosing MonitoringDocument1 pageTrilostane Dosing Monitoringnessimmounir100% (1)
- Drug Study CISPLATINDocument2 pagesDrug Study CISPLATINCorrine IvyNo ratings yet
- Vincristine Drug StudyDocument4 pagesVincristine Drug StudyNiziu BearsNo ratings yet
- Tamoxifen DrugstudyDocument2 pagesTamoxifen Drugstudyjessica queenNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Action Indication and Rationale Contraindication Common Side Effects Nursing Consideration While Taking The DrugsDocument1 pageMechanism of Action Indication and Rationale Contraindication Common Side Effects Nursing Consideration While Taking The DrugsPeter Emmil GonzalesNo ratings yet
- DroperidolDocument1 pageDroperidolIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Table OkDocument29 pagesDrug Study Table OkRifa'atul Mahmudah100% (1)
- ChlorambucilDocument2 pagesChlorambucilApol PenNo ratings yet
- SHEENA Clomid Drug StudyDocument3 pagesSHEENA Clomid Drug StudyNur SetsuNo ratings yet
- Clomid Drug StudyDocument3 pagesClomid Drug StudySheen Ivashkov-BelikovNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Nursing DepartmentDocument1 pageDrug Study: Nursing Departmentgiselle chloeNo ratings yet
- Mupirocin Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMupirocin Drug StudymichelleNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HeparinDocument2 pagesDrug Study HeparinArianne Nicole100% (1)
- Leoprolide Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLeoprolide Drug Studyhappymee927No ratings yet
- PaclitaxelDocument3 pagesPaclitaxelGwyn Rosales100% (1)
- FluorouracilDocument2 pagesFluorouracilHyacinth Bueser BondadNo ratings yet
- Generic Name:: Norgestimate and Ethinyl EstradiolDocument5 pagesGeneric Name:: Norgestimate and Ethinyl EstradiolJay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- Linagliptin - DRUG STUDYDocument1 pageLinagliptin - DRUG STUDYAcads useNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Loop DiureticDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Loop DiureticNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug Studyzjoshuac100% (1)
- Drug Name Indication Action Adverse EffectsDocument4 pagesDrug Name Indication Action Adverse EffectsMaryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzNo ratings yet
- UROKINASE (Kinlytic)Document4 pagesUROKINASE (Kinlytic)Mikaela Gabrielle GeraliNo ratings yet
- EstradiolDocument1 pageEstradiol3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.No ratings yet
- DRug Study PhenytoinDocument1 pageDRug Study Phenytoinmichelle marquezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DoxoburicinDocument1 pageDrug Study DoxoburicinkyawNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Calcium GluconateDocument1 pageDrug Study Calcium GluconateLarah Mae AndogNo ratings yet
- EscitalopramDocument1 pageEscitalopramRicky Ramos Jr.No ratings yet
- Drug Mode of Action Indication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameDocument3 pagesDrug Mode of Action Indication Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameJinky Nacar DomingoNo ratings yet
- Cisplatin Drug StudyDocument1 pageCisplatin Drug StudykyawNo ratings yet
- PromethazineDocument3 pagesPromethazineGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Tamiflu, FlagylDocument2 pagesDrug Study - Tamiflu, Flagylmark_gain100% (2)
- FluoxetineDocument2 pagesFluoxetineSherena NicolasNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyDanica de LunaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Acetaminophen)Document1 pageDrug Study (Acetaminophen)Kian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Amoxicillin PDFDocument4 pagesDrug Study Amoxicillin PDFMc SantosNo ratings yet
- Alprazolam BiperidinDocument6 pagesAlprazolam BiperidinFionah RetuyaNo ratings yet
- FINAL Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFINAL Drug StudycasedraftNo ratings yet
- Bleomycin Drug StudyDocument1 pageBleomycin Drug StudykyawNo ratings yet
- MannitolDocument1 pageMannitolAina Haravata0% (1)
- Drug Study FluvoxamineDocument2 pagesDrug Study FluvoxamineAngeline de Gala0% (1)
- Drug Study AmpicillinDocument6 pagesDrug Study AmpicillinDgjj Compuiter100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyAngelique Ramos PascuaNo ratings yet
- Case Study - DrugsDocument4 pagesCase Study - DrugsYza DizaNo ratings yet
- Cancer Drug StudyDocument14 pagesCancer Drug StudyIamanamay Trinidad100% (1)
- Drug Study of SleDocument7 pagesDrug Study of Slejoyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Notre Dame of Tacurong CollegeDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Notre Dame of Tacurong CollegeApol PenNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY LevetiracetamDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY LevetiracetamMaria Althea NajorraNo ratings yet
- Ofloxacin Drug StudyDocument4 pagesOfloxacin Drug StudyMikko Anthony Pingol Alarcon100% (1)
- Drug Classification Action of Drug Indication and Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocument2 pagesDrug Classification Action of Drug Indication and Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Sertraline) - SANGUYO, CB.Document5 pagesDRUG STUDY (Sertraline) - SANGUYO, CB.Camille SanguyoNo ratings yet
- Silver Sulfadiazine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesSilver Sulfadiazine Drug StudyKenn Siasar100% (1)
- Medication Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Drug Reaction GenericDocument1 pageMedication Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Drug Reaction GenericTrisha CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SulfasalazineDocument2 pagesDrug Study SulfasalazineBunnie AlphaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For Thiothixene and OlanzapineDocument3 pagesDrug Study For Thiothixene and OlanzapineHARVEY SELIMNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PrednisoloneDocument2 pagesDrug Study Prednisoloneunnamed personNo ratings yet
- OctreotideDocument3 pagesOctreotideHatim DziauddinNo ratings yet
- AmilorideDocument1 pageAmilorideRox San100% (1)
- Drug Name Dopamine Indications Contraindications Mechanism of Action Common Side-Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument4 pagesDrug Name Dopamine Indications Contraindications Mechanism of Action Common Side-Effects Nursing ConsiderationsPRINCESS LARA CASILAONo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage, Route, Frequency and Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesName of Drug Dosage, Route, Frequency and Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing ResponsibilitiesKarl Lourenz DeysolongNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation and Respiratory Physiotherapy: Time To Push AheadDocument1 pagePulmonary Rehabilitation and Respiratory Physiotherapy: Time To Push AheadedwardplopNo ratings yet
- Infusion Quiz 1 PDFDocument6 pagesInfusion Quiz 1 PDFvia macario100% (1)
- Q. 1) Define and Classify Hospital (1 2 3 or Clinical and Non-Clinical) Ans:-I) HospitalDocument36 pagesQ. 1) Define and Classify Hospital (1 2 3 or Clinical and Non-Clinical) Ans:-I) Hospitalammarahmad882002No ratings yet
- Form 5 KSSM Chemistry Chapter 5: MedicineDocument4 pagesForm 5 KSSM Chemistry Chapter 5: MedicineSydney ChowNo ratings yet
- Jendela DispensingDocument4 pagesJendela DispensingAkhmad “Billy Rafi” HambaliNo ratings yet
- Im SQ AdminDocument2 pagesIm SQ AdminfitnessbopNo ratings yet
- Final GRP 8Document50 pagesFinal GRP 8Rachana ShettyNo ratings yet
- Medication - ALT-Template Polythene GlycolDocument1 pageMedication - ALT-Template Polythene GlycolNancyAmissahNo ratings yet
- Price ListDocument21 pagesPrice ListMansoor TheenNo ratings yet
- Ag Listing 04jan2024Document97 pagesAg Listing 04jan2024monkeNo ratings yet
- Saldo Per Barang: Nama Barang Kode Barangbatch No. Exp. Datesaldo Batch Otal BarangDocument34 pagesSaldo Per Barang: Nama Barang Kode Barangbatch No. Exp. Datesaldo Batch Otal BarangimansariNo ratings yet
- Aristopharma Product ListDocument16 pagesAristopharma Product ListSuhayel GaziNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Pharmacology 4th SemesterDocument34 pagesUnit 5 Pharmacology 4th SemesterMr. Parmar Himanshu ManojNo ratings yet
- IVCalc Prac TestDocument4 pagesIVCalc Prac TestamygrobinsonNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: A Career inDocument2 pagesPharmacology: A Career insnikt7863443No ratings yet
- NREMT Practice Test Bank - 4q Multiple Choice-36Document1 pageNREMT Practice Test Bank - 4q Multiple Choice-36Dickson Kuria MburiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Prelim-IDocument8 pagesClinical Prelim-IJosh Miguel BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Family Therapy. 100 Key Points and Techniques Mark Rivett y Eddy Street 2009, Routledge PDFDocument2 pagesFamily Therapy. 100 Key Points and Techniques Mark Rivett y Eddy Street 2009, Routledge PDFFormacion CPPNo ratings yet
- Course: Physioteraphy - Mentor: Dijana Njerš - Class: English II - Student: Ella DaradkehDocument9 pagesCourse: Physioteraphy - Mentor: Dijana Njerš - Class: English II - Student: Ella DaradkehEllaNo ratings yet
- Physiotherapy Brochure (English)Document2 pagesPhysiotherapy Brochure (English)Shamsuddin Hasnani100% (1)
- Psychopharmacology Is The Study of Drug-Induced Changes in Mood, Sensation, ThinkingDocument5 pagesPsychopharmacology Is The Study of Drug-Induced Changes in Mood, Sensation, Thinking0921pyNo ratings yet
- Kinetics Review 2Document37 pagesKinetics Review 2filenotfoundNo ratings yet
- Catalogo FS 07-09-2023Document10 pagesCatalogo FS 07-09-2023narciso javier Avila BejaranoNo ratings yet
- Drug AdministrationDocument24 pagesDrug AdministrationJonica AngNo ratings yet
- Risk Management in Community Pharmacy: Ismp Canada Safety BulletinDocument5 pagesRisk Management in Community Pharmacy: Ismp Canada Safety BulletinShiro AsamiNo ratings yet
- Investigational New DrugsDocument16 pagesInvestigational New DrugsVirgil Cendana100% (1)
- Dangerous DrugsDocument28 pagesDangerous DrugsRaymart GonzagaNo ratings yet
- BNYS Jan2024Document7 pagesBNYS Jan2024jaisundar333nNo ratings yet