0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
363 viewsAbas Drug Study Nicu PDF
Abas Drug Study Nicu PDF
Uploaded by
Alexander Miguel M. AbasThis document summarizes information about the anticonvulsant drug carbamazepine, which is given to Down syndrome patients experiencing seizure attacks. It lists the generic and brand names, mechanism of action, indications, contraindications, side effects, and the nursing responsibilities associated with carbamazepine administration and monitoring. Nurses are responsible for ensuring the drug is only used as indicated, starting with a low dose and monitoring for side effects such as dizziness, nausea, and bone marrow suppression. They must also provide counseling on safe use and signs requiring medical attention.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Abas Drug Study Nicu PDF
Abas Drug Study Nicu PDF
Uploaded by
Alexander Miguel M. Abas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
363 views4 pagesThis document summarizes information about the anticonvulsant drug carbamazepine, which is given to Down syndrome patients experiencing seizure attacks. It lists the generic and brand names, mechanism of action, indications, contraindications, side effects, and the nursing responsibilities associated with carbamazepine administration and monitoring. Nurses are responsible for ensuring the drug is only used as indicated, starting with a low dose and monitoring for side effects such as dizziness, nausea, and bone marrow suppression. They must also provide counseling on safe use and signs requiring medical attention.
Original Title
ABAS DRUG STUDY NICU.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
This document summarizes information about the anticonvulsant drug carbamazepine, which is given to Down syndrome patients experiencing seizure attacks. It lists the generic and brand names, mechanism of action, indications, contraindications, side effects, and the nursing responsibilities associated with carbamazepine administration and monitoring. Nurses are responsible for ensuring the drug is only used as indicated, starting with a low dose and monitoring for side effects such as dizziness, nausea, and bone marrow suppression. They must also provide counseling on safe use and signs requiring medical attention.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
363 views4 pagesAbas Drug Study Nicu PDF
Abas Drug Study Nicu PDF
Uploaded by
Alexander Miguel M. AbasThis document summarizes information about the anticonvulsant drug carbamazepine, which is given to Down syndrome patients experiencing seizure attacks. It lists the generic and brand names, mechanism of action, indications, contraindications, side effects, and the nursing responsibilities associated with carbamazepine administration and monitoring. Nurses are responsible for ensuring the drug is only used as indicated, starting with a low dose and monitoring for side effects such as dizziness, nausea, and bone marrow suppression. They must also provide counseling on safe use and signs requiring medical attention.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 4
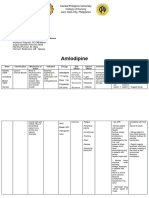
ABAS, ALEXANDER MIGUEL 04/01/20
NCM 109 RLE (NICU, MA’AM EVIA)
DRUG STUDY ABOUT CARBAMAZEPINE, AN ANTICONVULSANT DRUG GIVEN TO DOWN SYNDROME
PATIENTS WITH SEIZURE ATTACKS.
GENERIC/BRAN MECHANISM OF INDICATION CONTRAIND SIDE EFFECTS/ NURSING RESPONSIBILITY
D NAME ACTION I-CATION ADVERSE
EFFECTS
GENERIC NAME: • Carbamazepine • PO Epilepsy • Patients w/ • Dizziness • Use only for classifications listed. Do
• Carbamazepine depresses • Trigeminal AV block, • Drowsiness not use as a general analgesic. Use
activity in the Neuralgia history of • Ataxia only for epileptic seizures that are
BRAND NAME: nucleus • Prophylaxis bone • Nausea refractory to other safer agents.
• Carbastal ventralis of the Of Bipolar marrow • Vomiting • Give drug with food to prevent GI
• Carbilepp thalamus, Disorder depression • Dry Mouth upset.
• Epazin reduces synaptic • Rectal or history of • Abdominal Pain • Do not mix suspension with other
• Epikor propagation of Epilepsy hepatic medications or elements—
• Anorexia
• Lestremor excitatory porphyrias. precipitation may occur.
• Diarrhoea Or
• Mezacar impulses or • WARNING: Reduce dosage,
Constipation
• Tegrepin decreases • Concurrent discontinue, or substitute other
summation of • Mild Skin
• Tegretol use w/ or antiepileptic medication gradually.
temporal Reactions
w/in 14 Abrupt discontinuation of all
stimulation days of • Disturbances Of
Cerebellar And antiepileptic medication may
leading to MAOI use. precipitate status epilepticus.
neural discharge Oculo-Motor
Function • Suspension will produce higher peak
by limiting • Concurrent levels than tablets—start with a lower
influx of Na use w/ • Transient
Leucopenia dose given more frequently.
ions across cell nefazodone.
membrane or • Eosinophilia • Ensure that patient swallows ER
other unknown • Leukocytosis tablets whole—do not cut, crush, or
mechanisms. • Thrombocyte- chew.
paenia • Arrange for frequent liver function
• It stimulates the • Purpura tests; discontinue drug immediately if
release of • Lymphadeno- hepatic dysfunction occurs.
antidiuretic pathy • WARNING: Arrange for patient to
hormone (ADH) • Splenomegaly, have CBC, including
and potentiates Pneumonitis platelet, reticulocyte counts, and
its action in • Abonormalities serum iron determination, before
promoting of Liver And initiating therapy; repeat weekly for
reabsorption of Kidney the first 3 mo of therapy and monthly
water. Function thereafter for at least 2–3 yr.
• Hepatitis Discontinue drug if there is evidence
• Cholestatic of marrow suppression, as follows:
Jaundice • Arrange for frequent eye
• Hyponatraemia examinations, urinalysis, and BUN
• Oedema determinations.
• Paraesthesia • Arrange for frequent monitoring of
serum levels of carbamazepine and
• Headache
other antiepileptics given
• Arrhythmias concomitantly, especially during the
And Heart first few weeks of therapy. Adjust
Block dosage on basis of data and clinical
• Impotence response.
• Male Infertility • Counsel women who wish to become
• Gynaecomastia pregnant; advise the use of barrier
• Galactorrhoea contraceptives.
• Dystonias • Evaluate for therapeutic serum levels
• Dykinesias W/ (usually 4–12 mcg/mL).
Asterixis
• Local Irritation Teaching points
W/ Rectal Use. • Take drug with food as prescribed.
Swallow ER tablets whole, do not cut,
• Potentially crush, or chew them.
Fatal: • Do not discontinue this drug abruptly
o HLA- or change dosage, except on the
B*1502 And advice of your physician.
HLA- • Avoid alcohol, sleep-inducing, or
A*3101 Allele OTC drugs; these could cause
: dangerous effects.
§ Serious • Arrange for frequent checkups,
Dermatolog including blood tests, to monitor your
ic Reactions response to this drug. Keep all
(E.G. appointments for checkups.
Stevens- • Use contraceptives at all times; if you
Johnson wish to become pregnant, you should
Syndrome, consult your physician.
Toxic • Wear a medical alert tag at all times
Epidermal so that any emergency medical
Necrolysis). personnel will know that you have
epilepsy and are taking antiepileptic
§ Apalastic medication.
Anaemia, • You may experience these side
Agranulocy effects: Drowsiness, dizziness, blurred
tosis, CV vision (avoid driving or performing
Effects other tasks requiring alertness or
(E.G. CHF). visual acuity); GI upset (take the drug
with food or milk; eat frequent small
meals).
• Report bruising, unusual bleeding,
abdominal pain, yellowing of the skin
or eyes, pale feces, darkened urine,
impotence, CNS disturbances, edema,
fever, chills, sore throat, mouth ulcers,
rash, pregnancy.
You might also like
- Drug Study About Carbamazepine Used For Down Syndrome Patients With Seizure PDFDocument4 pagesDrug Study About Carbamazepine Used For Down Syndrome Patients With Seizure PDFAlexander Miguel M. AbasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study About Carbamazepine Used For Down Syndrome Patients With Seizure PDFDocument4 pagesDrug Study About Carbamazepine Used For Down Syndrome Patients With Seizure PDFAlexander Miguel M. AbasNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyCyril_Cybernat_1553No ratings yet
- Drug Study - DiazepamDocument2 pagesDrug Study - DiazepamCerie Anne Olay40% (5)
- MS Drug Study 1Document6 pagesMS Drug Study 1Elijah MarfilNo ratings yet
- Laranang, Mica Joy R. Drug Study: BSN 123 Group 90Document5 pagesLaranang, Mica Joy R. Drug Study: BSN 123 Group 90Gerard Louise Esmao RNNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ClozapineDocument2 pagesDrug Study ClozapineRobert Martin Rivera PuertaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study orDocument4 pagesDrug Study orChristine Katherine LibuitNo ratings yet
- ANTIPSYCHOTICSDocument25 pagesANTIPSYCHOTICSCheetahboi Shopee100% (4)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyMaxine RicafortNo ratings yet
- Att.vlcjFqsGt7d4rROyzpx11bw40HNGNN0Wg3pykWrhQ60Document13 pagesAtt.vlcjFqsGt7d4rROyzpx11bw40HNGNN0Wg3pykWrhQ60محمدNo ratings yet
- KlonopinDocument2 pagesKlonopinAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- AE Presentation Final Palliative CareDocument17 pagesAE Presentation Final Palliative CareioannastasopoulouNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On Emergency Drugs Final - )Document12 pagesDrug Study On Emergency Drugs Final - )wen_pil100% (3)
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyKaguraNo ratings yet
- Dengue DRUG StudyDocument4 pagesDengue DRUG Studyjaninenicole100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyPau-pau BasiNo ratings yet
- Pharmasheet AMLODIPINE BESYLATEDocument3 pagesPharmasheet AMLODIPINE BESYLATEplokatzNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyPark JeongyeonNo ratings yet
- Cardaic Emergency Drugs.Document13 pagesCardaic Emergency Drugs.Alma Susan100% (1)
- AntiepilepticsDocument25 pagesAntiepilepticsMurali Krishna Kumar MuthyalaNo ratings yet
- MCN Form 014Document4 pagesMCN Form 014jericho dinglasanNo ratings yet
- ClonazepamDocument2 pagesClonazepamjhezelle05100% (2)
- Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic NameDocument2 pagesDrug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibility Generic NameSHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: West Visayas State University La Paz, Iloilo CityDocument14 pagesDrug Study: West Visayas State University La Paz, Iloilo CityKhryss Paula BaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Gabato - Drug Study 1-3Document6 pagesGabato - Drug Study 1-3Denise GabatoNo ratings yet
- Handy Hints When Prescribing Antidepressants: Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (Ssris)Document3 pagesHandy Hints When Prescribing Antidepressants: Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (Ssris)Mariya ZhekovaNo ratings yet
- Drugs Study Drugs Classification Adverse Effect Mechanism of Action Contrandication Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument6 pagesDrugs Study Drugs Classification Adverse Effect Mechanism of Action Contrandication Nursing ResponsibilitiesRachel BotonNo ratings yet
- FMBularan-Urinary-Drug StudyDocument3 pagesFMBularan-Urinary-Drug StudyfransmallarebularanNo ratings yet
- CarbamazepineDocument5 pagesCarbamazepineapi-3797941100% (3)
- Drugs and NCPDocument4 pagesDrugs and NCPApril Anne CostalesNo ratings yet
- 3, Antiepileptic DrugsDocument39 pages3, Antiepileptic DrugsAbebe TilahunNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - AcetaminophenDocument2 pagesDrug Study - AcetaminophenVANESSA PAULA ALGADORNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyHoney BeeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15+16 Antiepileptic DrugsDocument40 pagesLecture 15+16 Antiepileptic DrugsHafsa ShakilNo ratings yet
- Atropine SulphateDocument1 pageAtropine SulphatealexisNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument3 pagesAcetazolamideGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Med Ward Week 2)Document2 pagesDrug Study (Med Ward Week 2)Kimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 Narcotics & NMJDocument7 pagesActivity 2 Narcotics & NMJKristineNo ratings yet
- ANS Regulation ANS Medication CardsDocument12 pagesANS Regulation ANS Medication Cards方郝建No ratings yet
- Anti-Epileptic Agents Cns Stimulants Muscle RelaxantsDocument3 pagesAnti-Epileptic Agents Cns Stimulants Muscle RelaxantsMichaela BernadasNo ratings yet
- AntiConvulsants Drugs in Brief PDFDocument28 pagesAntiConvulsants Drugs in Brief PDFSunilNo ratings yet
- Pharma SheetDocument2 pagesPharma SheetcdctinNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyShamsa AfdalNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PPS 3RDDocument14 pagesDrug Study PPS 3RDLoren SarigumbaNo ratings yet
- EnalaprilDocument2 pagesEnalaprilpinksapphire929100% (2)
- Bumetanide Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDocument2 pagesBumetanide Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComYuuki Chitose (tai-kun)No ratings yet
- Marfori - Activity 3 Antineoplastic Agents Drug StudyDocument3 pagesMarfori - Activity 3 Antineoplastic Agents Drug Studyckkyle0% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyBarbara Detaro100% (3)
- RenalPalliativeCarefinal Mar 2011Document5 pagesRenalPalliativeCarefinal Mar 2011Nexi anessaNo ratings yet
- Magnesium Sulfate Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMagnesium Sulfate Drug Studynicay.lieciousNo ratings yet
- To Pi Ram AteDocument3 pagesTo Pi Ram Ateapi-3797941No ratings yet
- M&N MGMTDocument3 pagesM&N MGMTMark Jefferson LunaNo ratings yet
- MED SURG Final CoachingDocument12 pagesMED SURG Final Coachingkim torino100% (1)
- Drug Study 3Document5 pagesDrug Study 3jasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- Amh Summary 2019 İn One FileDocument220 pagesAmh Summary 2019 İn One FileTatenda BrunoNo ratings yet
- Final Drug StudyDocument4 pagesFinal Drug StudyBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- Top 100 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2023 Edition)From EverandTop 100 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2023 Edition)No ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcFrom EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcNo ratings yet
- EPILEPSYDocument22 pagesEPILEPSYlakshitataneja1998No ratings yet
- Valpros PediaDocument2 pagesValpros PediaAnnsh Hadji EliasNo ratings yet
- History TakingDocument67 pagesHistory TakingOluremi KehindeNo ratings yet
- Cns FormattedDocument59 pagesCns FormattedbrihaspathiacademyNo ratings yet
- Irinotekan QILU-spcDocument24 pagesIrinotekan QILU-spcSrechko MilichNo ratings yet
- Anti Epileptic DrugsDocument16 pagesAnti Epileptic DrugsFatima Asim 922-FSS/BSPSY/F17No ratings yet
- Difficult Topics of Mrcp-1Document134 pagesDifficult Topics of Mrcp-1Khalil AhrariNo ratings yet
- Update On Antiepileptic - Drugs 2019 PDFDocument29 pagesUpdate On Antiepileptic - Drugs 2019 PDFRahul RaiNo ratings yet
- Pre Test Post TestDocument3 pagesPre Test Post TestNina Oaip100% (1)
- Pharmacology in A NutshellDocument124 pagesPharmacology in A NutshellNerak Lu100% (1)
- Antikonvulsan OkeDocument77 pagesAntikonvulsan OkeAci LusianaNo ratings yet
- Journal ReadingDocument11 pagesJournal ReadingifahInayahNo ratings yet
- Anti Seizure DrugsDocument76 pagesAnti Seizure DrugsMwanja Moses100% (1)
- ANTICONVULSANTSDocument1 pageANTICONVULSANTSPadmavathi CNo ratings yet
- Sinusitis With Polyposis Presenting As Refractory Trigeminal Neuralgia Treated With Acupuncture and Chinese Herbal DecoctionDocument6 pagesSinusitis With Polyposis Presenting As Refractory Trigeminal Neuralgia Treated With Acupuncture and Chinese Herbal DecoctionCarleta StanNo ratings yet
- Seizure MedicationsDocument3 pagesSeizure Medicationsm.dhiyarahadianNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic DrugsDocument7 pagesAntiepileptic DrugsFatima Asim 922-FSS/BSPSY/F17No ratings yet
- Bonitas Chronic PMB Formulary D January 2023Document28 pagesBonitas Chronic PMB Formulary D January 2023BP ViviersNo ratings yet
- Drug Interaction SaDocument3 pagesDrug Interaction SaShahabWassiNo ratings yet
- Predisposing Factors of ADRsDocument7 pagesPredisposing Factors of ADRssuhas reddyNo ratings yet
- MCQ Pract Pharma 1Document9 pagesMCQ Pract Pharma 1Syamil AzharNo ratings yet
- 2 Pharmacy Cheat Sheets Nurse NationDocument2 pages2 Pharmacy Cheat Sheets Nurse Nationk100% (2)
- AnticonvulsantDocument37 pagesAnticonvulsantPamela MendozaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument16 pagesNervous Systemعلي الفواديNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapy of EpilepsiesDocument43 pagesDrug Therapy of EpilepsiesZobayer Ahmed100% (1)
- Albani 1993Document2 pagesAlbani 1993Febrina FadhillahNo ratings yet
- Psych Meds Review MaterialDocument2 pagesPsych Meds Review MaterialMary Romaine Dela Pasion100% (10)
- Nutrient Drug Interactions and Food - Mss TelegramDocument7 pagesNutrient Drug Interactions and Food - Mss TelegramPratiwi TiwiNo ratings yet
- AnxiolyticsDocument16 pagesAnxiolyticsChengDNo ratings yet