Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3-Obtain A Mechanical Analog of The Liquid-Level System.: Let Us Define
3-Obtain A Mechanical Analog of The Liquid-Level System.: Let Us Define
Uploaded by
Hassan El-kholy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
50 views3 pagesCONTROL
Original Title
sheet-5-Modeling-of-Hydraulic-and-Thermal-systems
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCONTROL
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
50 views3 pages3-Obtain A Mechanical Analog of The Liquid-Level System.: Let Us Define
3-Obtain A Mechanical Analog of The Liquid-Level System.: Let Us Define
Uploaded by
Hassan El-kholyCONTROL
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
معهد األهرامات العالي للهندسة والتكنولوجيا Electrical Power and Control Department
Automatic Control Code: ELP 224
Sheet 4 Topic : Modeling Liquid-level system;
Level 3 Date : 18/3/2017
1- Find the transfer function, T. F = (QO(S)/QI(S)).
Let us define
H = steady-state head (before any change has occurred), m
h = small deviation of head from its steady-state value, m
Q = steady-state flow rate (before any change has occurred), m3/s
qi = small deviation of inflow rate from its steady-state value, m3/s
qo = small deviation of outflow rate from its steady-state value, m3/s
2- Find the transfer function, T. F = (Q(S)/QI(S)) AND T. F = (QO(S)/Q(S )).
3-Obtain a mechanical analog of the liquid-level system.
4- Derive
the
transfer function for the system when q is the input and h2 is the output
Dr. Ehab Elwakil
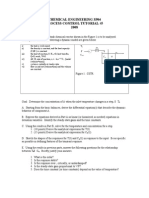
5- Consider the liquid-level system shown in Figure. Assume that the outflow rate
Q m3/s through the outflow valve is related to the head H m by
Assume also that, when the inflow rate Qi is 0.015 m3/s, the head stays constant. At
t = 0 the inflow valve is closed, so there is no inflow for t= o. Find the time necessary
To empty the tank to half the original head. The capacitance of the tank is 2 m2
•
6 - Consider the liquid-level system of Figure. The curve of head versus flow rate is shown
in figure. Assume that at steady state the liquid flow rate is 4 X 10-4 m3/s and the steady-
state head is 1 m. At t = 0, the inflow valve is opened further and the inflow rate is
changed to 4.5 X 10-4 m3/s. Determine the average resistance R of the outflow valve.
Also, determine the change in head as a function of time. The capacitance C of the tank is
0.02 m2.
Dr. Ehab Elwakil
Dr. Ehab Elwakil
You might also like
- Modeling A Process - Filling A Tank: in - Out AccumulationDocument3 pagesModeling A Process - Filling A Tank: in - Out Accumulationmnb100% (1)
- Chapter 5Document75 pagesChapter 5Deep NarulaNo ratings yet
- L-11 (SS) (Ia&c) ( (Ee) Nptel) PDFDocument12 pagesL-11 (SS) (Ia&c) ( (Ee) Nptel) PDFMohammad Zakir Hossan ShujonNo ratings yet
- Modelling and Design of Hydraulic Turbine - Governor SystemDocument5 pagesModelling and Design of Hydraulic Turbine - Governor SystemJaime L. ReyesNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Model Simulation 5 2020Document27 pagesDynamics Model Simulation 5 2020Kerem YamanNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Turbine Models & Control Models For Systems Dynamics StudiesDocument13 pagesHydraulic Turbine Models & Control Models For Systems Dynamics StudiesManuel CañadasNo ratings yet
- Ch05 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control VolumesDocument142 pagesCh05 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control VolumesJordanNo ratings yet
- Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes: Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 EditionDocument20 pagesMass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes: Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 EditionAhmad SiddiqNo ratings yet
- Flow RateDocument26 pagesFlow RateAung SoeNo ratings yet
- Control PDFDocument18 pagesControl PDFTaban ShahabNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Variable & Fixed Speed Machined in Hydro Power ProjectsDocument14 pagesDifference Between Variable & Fixed Speed Machined in Hydro Power ProjectsHema KumarNo ratings yet
- 5.lecture On Changing Top-Altitude Tail TunnelDocument36 pages5.lecture On Changing Top-Altitude Tail TunnelEng Bagaragaza RomualdNo ratings yet
- Coupled Tanks SystemsDocument8 pagesCoupled Tanks SystemsNamrajit DeyNo ratings yet
- Lab HandoutDocument9 pagesLab HandoutlitrakhanNo ratings yet
- Distillation ColumnDocument32 pagesDistillation ColumnTatiana RosarioNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram of A Control System: 11 August 2021 12:48Document68 pagesBlock Diagram of A Control System: 11 August 2021 12:48TUSHIT JHANo ratings yet
- Surge Tank ModelDocument10 pagesSurge Tank Modelkapil100% (1)
- CFD Analyses of Unsteady Cavitation in Rocket Feed Systems and Flow Control Elements PDFDocument9 pagesCFD Analyses of Unsteady Cavitation in Rocket Feed Systems and Flow Control Elements PDFmojicapNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Modeling of Two Tank System Ijariie4840Document8 pagesMathematical Modeling of Two Tank System Ijariie4840Abeng Yogta100% (1)
- Feedback Chap 2 HWDocument13 pagesFeedback Chap 2 HWAudreyWalangareDimalibotNo ratings yet
- Lecture ThermoDocument21 pagesLecture ThermoMUHAMMAD HUZAIFANo ratings yet
- Mastery Sheet 5 2016CNM GJDocument5 pagesMastery Sheet 5 2016CNM GJLevente Bajczi100% (1)
- Assignment 2Document4 pagesAssignment 2eja70No ratings yet
- BLANKADocument15 pagesBLANKADev jibreenNo ratings yet
- Procedures: Safety Googles, Gloves and Lab Coat Were Worn When Handling These Chemicals)Document4 pagesProcedures: Safety Googles, Gloves and Lab Coat Were Worn When Handling These Chemicals)JxinLeeNo ratings yet
- 2-Tank LevelDocument2 pages2-Tank LevelRazvan BotezatuNo ratings yet
- CL3601Document10 pagesCL3601md.jimshad.3883No ratings yet
- Exp # 7,8,9,10 Advanced Fluid Mechanics LabDocument12 pagesExp # 7,8,9,10 Advanced Fluid Mechanics LabrrNo ratings yet
- Transient Flows in A Pipe System With Pump Shut-DoDocument11 pagesTransient Flows in A Pipe System With Pump Shut-DoSuresh CNo ratings yet
- A Hydraulic Steering Gear Simulator For Analysis and ControlDocument9 pagesA Hydraulic Steering Gear Simulator For Analysis and Controlaj310790No ratings yet
- Process Control Project Report 1Document26 pagesProcess Control Project Report 1Henry Darius NamocNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - Lecture Notes - Unit 4Document71 pagesFluid Mechanics - Lecture Notes - Unit 4Mohan Prasad.MNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER-5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control VolumesDocument39 pagesCHAPTER-5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control VolumesSachin GirohNo ratings yet
- 3P04 Tutorial 5 MockQuiz 2008Document4 pages3P04 Tutorial 5 MockQuiz 2008Khaled KamalNo ratings yet
- Process Control: Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1Document12 pagesProcess Control: Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1poiuyNo ratings yet
- The Mathematics of Pumping Water: AECOM Design BuildDocument9 pagesThe Mathematics of Pumping Water: AECOM Design BuildAdel SharifiNo ratings yet
- L9-Tubular Flow ReactorDocument20 pagesL9-Tubular Flow ReactorCik Tiem Ngagiman82% (11)
- Centrifugal Pump Practical ReportDocument16 pagesCentrifugal Pump Practical ReportwellemanesiphoNo ratings yet
- The Mathematics of Pumping Water: AECOM Design BuildDocument9 pagesThe Mathematics of Pumping Water: AECOM Design Buildmabrouk2013No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document25 pagesChapter 5dickinaround87100% (1)
- Tubular Flow ReactorDocument5 pagesTubular Flow ReactorN Afiqah RazakNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lab ReportDocument35 pagesFluid Mechanics Lab ReportBilal Akhundzada0% (1)
- TFR ExperimentDocument25 pagesTFR ExperimentSiti Norbaya100% (1)
- Surge Tank DesignDocument15 pagesSurge Tank Designdharanimadala100% (3)
- Energy Analysis of Steady Flow SystemsDocument18 pagesEnergy Analysis of Steady Flow Systemsuwaqas.msee23seecsNo ratings yet
- FLUID MACHINERY-presentationDocument15 pagesFLUID MACHINERY-presentationcharmaine fosNo ratings yet
- TFRDocument19 pagesTFRsueeumuraNo ratings yet
- Flow and Heat Transfer in A Closed Loop Thermosyphon. Part I - Theoretical SimulationDocument9 pagesFlow and Heat Transfer in A Closed Loop Thermosyphon. Part I - Theoretical Simulationmartin sabusNo ratings yet
- Tota Pump Lecture Course 2004 6-5-04Document18 pagesTota Pump Lecture Course 2004 6-5-04Paulo H TavaresNo ratings yet
- Tubular Flow Reactor ReportDocument19 pagesTubular Flow Reactor ReportN Afiqah Razak100% (1)
- Hydraulic and Surge Analysis in A Pipeline Network Using PipelineStudioDocument8 pagesHydraulic and Surge Analysis in A Pipeline Network Using PipelineStudioAnonymous WNWk1h2No ratings yet
- Averaging Level Control of Multiple Tanks: A Passivity Based ApproachDocument6 pagesAveraging Level Control of Multiple Tanks: A Passivity Based ApproachFelipe VasconcelosNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 ReportDocument13 pagesLab 5 Reportapi-405394814No ratings yet
- First Law Open SystemsDocument6 pagesFirst Law Open SystemsxplodeitupNo ratings yet
- Computational NeuroendocrinologyFrom EverandComputational NeuroendocrinologyDuncan J. MacGregorNo ratings yet
- Methods for Increasing the Quality and Reliability of Power System Using FACTS DevicesFrom EverandMethods for Increasing the Quality and Reliability of Power System Using FACTS DevicesNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power System, Control System and Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab and PowerWorld SimulatorNo ratings yet
- DigitalDesignStudy TemplateDocument3 pagesDigitalDesignStudy TemplateHassan El-kholyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1modDocument2 pagesAssignment 1modHassan El-kholyNo ratings yet
- Design of High Gain Folded-Cascode Operational Amplifier Using 1.25 Um CMOSDocument9 pagesDesign of High Gain Folded-Cascode Operational Amplifier Using 1.25 Um CMOSHassan El-kholyNo ratings yet
- LAB BJT Current CircuitsDocument7 pagesLAB BJT Current CircuitsHassan El-kholyNo ratings yet
- Method For The Estimation of The Mean Lorentzian Bandwidth in Spectra Composed of An Unknown Number of Highly Overlapped BandsDocument12 pagesMethod For The Estimation of The Mean Lorentzian Bandwidth in Spectra Composed of An Unknown Number of Highly Overlapped BandsHassan El-kholyNo ratings yet
- Design and Simulation of 4T-Cascode Amplifier at 45 Nanometer Technology NodeDocument4 pagesDesign and Simulation of 4T-Cascode Amplifier at 45 Nanometer Technology NodeHassan El-kholyNo ratings yet
- Final Report - Multibody Dynamics of A Formula Student Car (2 Years Ago)Document57 pagesFinal Report - Multibody Dynamics of A Formula Student Car (2 Years Ago)Hassan El-kholyNo ratings yet
- Practical Cas Code AmplifierDocument5 pagesPractical Cas Code AmplifierHassan El-kholyNo ratings yet
- Optimum Photovoltaic Array Size For A Hybrid Wind/PV SystemDocument7 pagesOptimum Photovoltaic Array Size For A Hybrid Wind/PV SystemHassan El-kholyNo ratings yet
- (10-21) Simulation of Grid Intgrated PV Array For-Format For ZenodoDocument12 pages(10-21) Simulation of Grid Intgrated PV Array For-Format For ZenodoHassan El-kholyNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power and Control Department Automatic Control Code: Sheet 1 Topic: Laplace Transform Level 3 Date: 11/11/2014Document1 pageElectrical Power and Control Department Automatic Control Code: Sheet 1 Topic: Laplace Transform Level 3 Date: 11/11/2014Hassan El-kholyNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power and Control Department Automatic Control Code: Sheet 2 Topic: Electrical & Electronic System Modeling Level 3 Date: 25/2/2017Document2 pagesElectrical Power and Control Department Automatic Control Code: Sheet 2 Topic: Electrical & Electronic System Modeling Level 3 Date: 25/2/2017Hassan El-kholyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Fits and Tolerance)Document49 pagesChapter 1 (Fits and Tolerance)Hassan El-kholyNo ratings yet
- MHS11 Z TransformDocument16 pagesMHS11 Z TransformHassan El-kholyNo ratings yet
- Continuous Probability Distribution.Document10 pagesContinuous Probability Distribution.Hassan El-kholy100% (1)
- Sheet 3 (Transformer Tests)Document1 pageSheet 3 (Transformer Tests)Hassan El-kholyNo ratings yet
- Sheet 7 Routh Stability CriterionDocument1 pageSheet 7 Routh Stability CriterionHassan El-kholyNo ratings yet
- Sheet 3 (Circle Diagram)Document1 pageSheet 3 (Circle Diagram)Hassan El-kholyNo ratings yet
- Power StationsDocument16 pagesPower StationsHassan El-kholyNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment For Transfer Function of Ac Servo MotorDocument9 pagesLab Experiment For Transfer Function of Ac Servo MotorHassan El-kholyNo ratings yet