Design of Flexible Design - AASHTO
Uploaded by
dineshDesign of Flexible Design - AASHTO
Uploaded by
dineshAASHTO Method of Pavement Design
Stretch : KMP Expressway (Design as done by RITES)
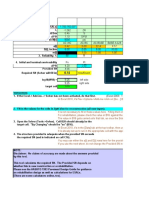
INPUT DATA
Remarks
Serviceability Indices
Pi = 4.5 (Initial) (Assuming Strict adherence of quality control)
Po = 2.5 (Lowest) (Lowest acceptable serviceability)
W18 = 75 i.e. 7.50E+7 ESAL
MR = 15000 (1500* CBR)
So = 0.4 In general it is 0.4 to 0.5 0.4 adopted, assuming that the projections represents the most likely
scenario)
R = 0.95 Overall Reliability of 0.9 assumed as being stage construction. So far 1st
Stage 0.95 considered i.e. (0.900.50).
Layer Strength coefficients
a1 = 0.425 For Bituminous RITEs while calculating equivalent SN for design by IRC method
Concrete considered it as 0.4
a2 = 0.38 For Dense Bituminous RITEs while calculating equivalent SN for design by IRC method
Concrete considered it as 0.4. The value as shown on P 7/13 is 0.35.
a3 = 0.14 For Wet Mix Macadam
a4 = 0.12 For Granular Sub Base
Drainage coefficients
m1 = 1 For Bituminous
Concrete
m2 = 1 For Dense Bituminous
Concrete
m3 = 1 For Wet Mix Macadam
m4 = 1 For Granular Sub Base
CALCULATIONS
ZR = -1.645 For R=0.95
∆(PSI) = 2 (4.5-2.5)
Caclulated SNf Value = 5.1454 Update Structural Number
Log(W18) 7.8751
ZRxSo = -0.658
9.36log(SN+1)-0.2 = 7.181
((LOG(∆PSI/(4.2-1.5),10)/(0.4+(1094/(SN+1)5.19)))) = -0.267
2.32*LOG(MR)-8.07 = 1.619
Log(W18) 7.8745
Layer Thicknesss and structural number calculations
Layer thicknesses Layer thicknesses Structural Numbers Adopted layer thickness Remarks
(in mm) (in Inches) (in mm)
D1 = 50 1.963 SN1 = 0.8340 D1= 50
D2 = 120 4.711 SN2 = 2.6240 D2= 120
D3 = 288 11.307 SN3 = 4.2070 D3= 300
D4 = 200 7.852 SN4 = 5.1490 D4= 200
Total = 658 SNf = 5.1490 Total= 670
AASHTO Method of Pavement Design
Stretch : KMP Expressway (Design RITES-100MSA)
INPUT DATA
Remarks
Serviceability Indices
Pi = 4.5 (Initial) (Assuming Strict adherence of quality control)
Po = 2.5 (Lowest) (Lowest acceptable serviceability)
W18 = 75 i.e. 7.50E+7 ESAL
MR = 15000 (1500* CBR)
So = 0.4 In general it is 0.4 to 0.5 0.4 adopted, assuming that the projections represents the most likely
scenario)
R = 0.95
Layer Strength coefficients
a1 = 0.425 For Bituminous RITEs while calculating equivalent SN for design by IRC method
Concrete considered it as 0.4
a2 = 0.38 For Dense Bituminous RITEs while calculating equivalent SN for design by IRC method
Concrete considered it as 0.4. The value as shown on P 7/13 is 0.35.
a3 = 0.14 For Wet Mix Macadam
a4 = 0.12 For Granular Sub Base
Drainage coefficients
m1 = 1 For Bituminous
Concrete
m2 = 1 For Dense Bituminous
Concrete
m3 = 1 For Wet Mix Macadam
m4 = 1 For Granular Sub Base
CALCULATIONS
ZR = -1.645 For R=0.95 ZR Value stated to be -1.645 corresponding to R=0.95 but R value adopted
is 0.90.
∆(PSI) = 2 (4.5-2.5)
Caclulated SNf Value = 5.1463 Update Structural Number
Log(W18) 7.8751
ZrxSo = -0.658
9.36log(SN+1)-0.2 = 7.181
((LOG(∆PSI/(4.2-1.5),10)/(0.4+(1094/(SN+1)5.19)))) = -0.267
2.32*LOG(MR)-8.07 = 1.619
Log(W18) 7.8751
Layer Thicknesss and structural number calculations
Layer thicknesses Layer thicknesses Structural Numbers Adopted layer thickness Remarks
(in mm) (in Inches) (in mm)
D1 = 50 1.963 SN1 = 0.8340 D1= 50
D2 = 130 5.104 SN2 = 2.7740 D2= 130
D3 = 298 11.700 SN3 = 4.4120 D3= 300
D4 = 200 7.852 SN4 = 5.3540 D4= 200
Total = 678 SNf = 5.3540 Total= 680
AASHTO Method of Pavement Design
Stretch : KMP Expressway (Design as submitted in km 0 to 20 report)
INPUT DATA
Remarks
Serviceability Indices
Pi = 4.2 (Initial) The experience of AASHTO in road performance indicates that initial
serviceability index (Po) normally achieved for rigid pavement is 4.5 and for
flexible pavement is 4.2
Po = 2.5 (Lowest) (Lowest acceptable serviceability)
W18 = 100 i.e. 1.00E+8 ESAL
MR = 15000 (1500* CBR)
So = 0.4 In general it is 0.4 to 0.5 0.4 adopted, assuming that the projections represents the most likely
scenario)
R = 0.9
Layer Strength coefficients
a1 = 0.4 For Bituminous Same value considered by RITEs while calculating equivalent SN for design
Concrete by IRC method. But considered different in case of AASHTO
a2 = 0.4 For Dense Bituminous -do'
Concrete
a3 = 0.14 For Wet Mix Macadam
a4 = 0.12 For Granular Sub Base
Drainage coefficients
m1 = 1 For Bituminous
Concrete
m2 = 1 For Dense Bituminous
Concrete
m3 = 1 For Wet Mix Macadam
m4 = 1 For Granular Sub Base
CALCULATIONS
ZR = -1.282 For R=0.90
∆(PSI) = 1.7 (4.2-2.5)
Caclulated SNf Value = 5.3563 Update Structural Number
Log(W18) 8.0000
ZrxSo = -0.513
9.36log(SN+1)-0.2 = 7.318
((LOG(∆PSI/(4.2-1.5),10)/(0.4+(1094/(SN+1)5.19)))) = -0.424
2.32*LOG(MR)-8.07 = 1.619
Log(W18) 8.0000
Layer Thicknesss and structural number calculations
Layer thicknesses Layer thicknesses Structural Numbers Adopted layer thickness Remarks
(in mm) (in Inches) (in mm)
D1 = 50 1.963 SN1 = 0.7850 D1= 50
D2 = 130 5.104 SN2 = 2.8270 D2= 130
D3 = 289 11.347 SN3 = 4.4160 D3= 300
D4 = 200 7.852 SN4 = 5.3580 D4= 200
Total = 669 SNf = 5.3580 Total= 680
AASHTO Method of Pavement Design
Stretch : KMP Expressway (Design as submitted in km 0 to 20 report)
INPUT DATA
Remarks
Serviceability Indices
Pi = 4.2 (Initial) The experience of AASHTO in road performance indicates that initial
serviceability index (Po) normally achieved for rigid pavement is 4.5 and for
flexible pavement is 4.2
Po = 2.5 (Lowest) (Lowest acceptable serviceability)
W18 = 100 i.e. 1.00E+8 ESAL
MR = 15000 (1500* CBR)
So = 0.4 In general it is 0.4 to 0.5 0.4 adopted, assuming that the projections represents the most likely
scenario)
R = 0.8
Layer Strength coefficients
a1 = 0.38 For Bituminous Same value considered by RITEs while calculating equivalent SN for design
Concrete by IRC method. But considered different in case of AASHTO
a2 = 0.38 For Dense Bituminous -do'
Concrete
a3 = 0.14 For Wet Mix Macadam
a4 = 0.11 For Granular Sub Base
Drainage coefficients
m1 = 1 For Bituminous
Concrete
m2 = 1 For Dense Bituminous
Concrete
m3 = 0.85 For Wet Mix Macadam
m4 = 0.85 For Granular Sub Base
CALCULATIONS
ZR = -0.841 For R=0.80
∆(PSI) = 1.7 (4.2-2.5)
Caclulated SNf Value = 5.0597 Update Structural Number
Log(W18) 8.0000
ZrxSo = -0.336
9.36log(SN+1)-0.2 = 7.124
((LOG(∆PSI/(4.2-1.5),10)/(0.4+(1094/(SN+1)5.19)))) = -0.406
2.32*LOG(MR)-8.07 = 1.619
Log(W18) 8.0000
Layer Thicknesss and structural number calculations
Layer thicknesses Layer thicknesses Structural Numbers Adopted layer thickness Remarks
(in mm) (in Inches) (in mm)
D1 = 0 0.000 SN1 = 0.0000 D1= 50
D2 = 180 7.067 SN2 = 2.6860 D2= 120
D3 = 180 7.067 SN3 = 3.5270 D3= 250
D4 = 0 0.000 SN4 = 3.5270 D4= 200
Total = 360 SNf = 3.5270 Total= 620
AASHTO Method of Pavement Design
Stretch : KMP Expressway (Design with R=0.95 and Traffic- 100MSA)
INPUT DATA
Remarks
Serviceability Indices
Pi = 4.2 (Initial) The experience of AASHTO in road performance indicates that initial
serviceability index (Po) normally achieved for rigid pavement is 4.5 and for
flexible pavement is 4.2
Po = 2.5 (Lowest) (Lowest acceptable serviceability)
W18 = 100 i.e. 1.00E+8 ESAL
MR = 15000 (1500* CBR)
So = 0.4 In general it is 0.4 to 0.5 0.4 adopted, assuming that the projections represents the most likely
scenario). As per AASHTO average value is to be considered.
R = 0.9
Layer Strength coefficients
a1 = 0.4 For Bituminous Same value considered by RITEs while calculating equivalent SN for design
Concrete by IRC method. But considered different in case of AASHTO
a2 = 0.35 For Dense Bituminous -do'
Concrete
a3 = 0.14 For Wet Mix Macadam
a4 = 0.11 For Granular Sub Base
Drainage coefficients
m1 = 1 For Bituminous
Concrete
m2 = 1 For Dense Bituminous
Concrete
m3 = 0.85 For Wet Mix Macadam
m4 = 0.85 For Granular Sub Base
CALCULATIONS
ZR = -1.282 For R=0.90
∆(PSI) = 1.7 (4.2-2.5)
Caclulated SNf Value = 5.3563
Log(W18) 8.0000
ZrxSo = -0.513
9.36log(SN+1)-0.2 = 7.318
((LOG(∆PSI/(4.2-1.5),10)/(0.4+(1094/(SN+1)5.19)))) = -0.424
2.32*LOG(MR)-8.07 = 1.619
Log(W18) 8.0000
Layer Thicknesss and structural number calculations
Layer thicknesses Layer thicknesses Structural Numbers Adopted layer thickness Remarks
(in mm) (in Inches) (in mm)
D1 = 40 1.570 SN1 = 0.6280 D1= 50
D2 = 120 4.711 SN2 = 2.2770 D2= 130
D3 = 0 0.000 SN3 = 2.2770 D3= 300
D4 = 0 0.000 SN4 = 2.2770 D4= 300
Total = 160 SNf = 1.0910 Total= 780
Reliability
R (percent) 80 85 90 91 92 93 94 95
Standard Normal
Deviate - Zr -0.841 -1.037 -1.282 -1.34 -1.405 -1.476 -1.555 -1.645
96 97 98
-1.751 -1.881 -2.054
17 135000 2295000
22950 5000 114750000
11.475
AASHTO Method of Pavement Design
Stretch : KMP Expressway (Design as submitted in km 0 to 20 report)
INPUT DATA
Remarks
Serviceability Indices
Pi = 4.2 (Initial) The experience of AASHTO in road performance indicates that initial
serviceability index (Po) normally achieved for rigid pavement is 4.5 and for
flexible pavement is 4.2
Po = 2.5 (Lowest) (Lowest acceptable serviceability)
W18 = 400 i.e. 4.00E+8 ESAL
MR = 10500 (1500* CBR)
So = 0.42 In general it is 0.4 to 0.5 0.4 adopted, assuming that the projections represents the most likely scenario)
R = 0.85
Layer Strength coefficients
a1 = 0.42 For Bituminous Same value considered by RITEs while calculating equivalent SN for design by
Concrete IRC method. But considered different in case of AASHTO
a2 = 0.38 For Dense Bituminous -do'
Concrete
a3 = 0.15 For Wet Mix Macadam
a4 = 0.12 For Granular Sub Base
Drainage coefficients
m1 = 1 For Bituminous
Concrete
m2 = 1 For Dense Bituminous
Concrete
m3 = 1 For Wet Mix Macadam
m4 = 1 For Granular Sub Base
CALCULATIONS
ZR = -1.037 For R=0.85
∆(PSI) = 1.7 (4.2-2.5)
Caclulated SNf Value = 7.0018 Update Structural Number
Log(W18) 8.6021
ZrxSo = -0.436
9.36log(SN+1)-0.2 = 8.254
((LOG(∆PSI/(4.2-1.5),10)/(0.4+(1094/(SN+1)5.19)))) = -0.476
2.32*LOG(MR)-8.07 = 1.259
Log(W18) 8.6019
Layer Thicknesss and structural number calculations
Layer thicknesses Layer thicknesses Structural Numbers Adopted layer thickness Remarks
(in mm) (in Inches) (in mm)
D1 = 50 1.963 SN1 = 0.8240 D1= 50
D2 = 65 2.552 SN2 = 1.7940 D2= 130
D3 = 0 0.000 SN3 = 1.7940 D3= 300
D4 = 0 0.000 SN4 = 1.7940 D4= 200
Total = 115 SNf = 1.7940 Total= 680
You might also like
- Flexible Pavement Design Calculation Spreadsheet According To AASHTO67% (3)Flexible Pavement Design Calculation Spreadsheet According To AASHTO45 pages
- TTRegs Light Motor Vehicle Study Guide - Printable80% (5)TTRegs Light Motor Vehicle Study Guide - Printable21 pages
- Flexible - Pavement - Design - Tool AASHTO 1993No ratings yetFlexible - Pavement - Design - Tool AASHTO 199312 pages
- Topic 3 - Flexible Pavement Stress Analysis100% (1)Topic 3 - Flexible Pavement Stress Analysis22 pages
- Roads in Desert, Swamp & Black Cotton SoilNo ratings yetRoads in Desert, Swamp & Black Cotton Soil20 pages
- Highways Department: Enable Macros To Use This Application100% (1)Highways Department: Enable Macros To Use This Application14 pages
- Altaf Reg 0950 Cep Flexible Pavement DesignNo ratings yetAltaf Reg 0950 Cep Flexible Pavement Design37 pages
- Flexible Pavement Thickness Design (Aastho Method)No ratings yetFlexible Pavement Thickness Design (Aastho Method)8 pages
- Chapter 3 - Example Flexible Pavement Thickness DesignNo ratings yetChapter 3 - Example Flexible Pavement Thickness Design3 pages
- Pavement Design AASHTO SOAL QUEZ 05 DES 2016 Hal 7 14 08 12 2016 Conto 4 6 Hal 186 RevisiiiNo ratings yetPavement Design AASHTO SOAL QUEZ 05 DES 2016 Hal 7 14 08 12 2016 Conto 4 6 Hal 186 Revisiii4 pages
- Pavement Design Thickness Using Asstho Method 1993No ratings yetPavement Design Thickness Using Asstho Method 19937 pages
- Lecture 2 (B) - Flexible Pavement DesignNo ratings yetLecture 2 (B) - Flexible Pavement Design24 pages
- 4.3.8 Design of Pavement 4.3.8.1 5.9.1 Design of New Flexible Pavement (IRC-37)0% (1)4.3.8 Design of Pavement 4.3.8.1 5.9.1 Design of New Flexible Pavement (IRC-37)23 pages
- Pavement Design Thickness Using Asstho Method 1993No ratings yetPavement Design Thickness Using Asstho Method 199348 pages
- Aashto Flexible Pavement Design ProcedureNo ratings yetAashto Flexible Pavement Design Procedure43 pages
- Comparison Between The Effect of Silica Fume & Fly AshNo ratings yetComparison Between The Effect of Silica Fume & Fly Ash19 pages
- Edoc - Pub - Transformer Foundation DesignNo ratings yetEdoc - Pub - Transformer Foundation Design26 pages
- Seismic Risk Assessment of Built Environment in PakistanNo ratings yetSeismic Risk Assessment of Built Environment in Pakistan10 pages
- On The Correlation of Seismic Intensity Scale WithNo ratings yetOn The Correlation of Seismic Intensity Scale With25 pages
- Time and Materials (T&M) Contracts - How They Work and Free Template - NetSuiteNo ratings yetTime and Materials (T&M) Contracts - How They Work and Free Template - NetSuite7 pages
- Design of Foundation For 220 KV ElectricalNo ratings yetDesign of Foundation For 220 KV Electrical7 pages
- Calculation of Seismic Protective Qualities of Dampefer and AbsorterNo ratings yetCalculation of Seismic Protective Qualities of Dampefer and Absorter4 pages
- Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis For YemenNo ratings yetProbabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis For Yemen16 pages
- Seismic Code Developments For Steel & Composite StructuresNo ratings yetSeismic Code Developments For Steel & Composite Structures23 pages
- Tube Structural System - Types & Features - The ConstructorNo ratings yetTube Structural System - Types & Features - The Constructor11 pages
- Annexure-6 FOSROC - Lokfix & Nitobond Technical DataNo ratings yetAnnexure-6 FOSROC - Lokfix & Nitobond Technical Data10 pages
- RAM Connection Standalone CE Report - 11No ratings yetRAM Connection Standalone CE Report - 112 pages
- Schedule 80 Mild Steel Pipe Sizes - Dimensions - Weight and PriceNo ratings yetSchedule 80 Mild Steel Pipe Sizes - Dimensions - Weight and Price10 pages
- Bored CIP Piles - Capacity Calculation - International Practice - Updated-1No ratings yetBored CIP Piles - Capacity Calculation - International Practice - Updated-113 pages
- Comparative Study of Diagrid Structures With and Without Corner ColumnsNo ratings yetComparative Study of Diagrid Structures With and Without Corner Columns6 pages
- Cross-Sectional Optimization of Cold-Formed Steel Channels To Eurocode 3No ratings yetCross-Sectional Optimization of Cold-Formed Steel Channels To Eurocode 312 pages
- Lesson 1 - Intro To Highway EngineeringNo ratings yetLesson 1 - Intro To Highway Engineering15 pages
- City of Corpus Christi's Bond Program GuideNo ratings yetCity of Corpus Christi's Bond Program Guide14 pages
- Pavement Distress Survey Manual: Pavement Services Unit Revised June 2010No ratings yetPavement Distress Survey Manual: Pavement Services Unit Revised June 201058 pages
- Highway Engineering Khanna and Justo (1) SKNo ratings yetHighway Engineering Khanna and Justo (1) SK23 pages
- Strengthening of Karaimedu - Maruthur-Kulakudi Road KM 1/2 - 4/6 Including Upkeeping For A Period of 60 MonthsNo ratings yetStrengthening of Karaimedu - Maruthur-Kulakudi Road KM 1/2 - 4/6 Including Upkeeping For A Period of 60 Months6 pages
- MDOT 2020-2024 Five Year Transportation ProgramNo ratings yetMDOT 2020-2024 Five Year Transportation Program28 pages
- Interstate 82: Interstate 82 (Pennsylvania-New York) Interstate 84 in Connecticut History Interstate '82No ratings yetInterstate 82: Interstate 82 (Pennsylvania-New York) Interstate 84 in Connecticut History Interstate '8211 pages
- AGRD04A-23 Guide To Road Design Part 4A Unsignalised and Signalised Intersections Ed3.2No ratings yetAGRD04A-23 Guide To Road Design Part 4A Unsignalised and Signalised Intersections Ed3.2203 pages
- Flexible Pavement Design Calculation Spreadsheet According To AASHTOFlexible Pavement Design Calculation Spreadsheet According To AASHTO
- TTRegs Light Motor Vehicle Study Guide - PrintableTTRegs Light Motor Vehicle Study Guide - Printable
- Highways Department: Enable Macros To Use This ApplicationHighways Department: Enable Macros To Use This Application
- Flexible Pavement Thickness Design (Aastho Method)Flexible Pavement Thickness Design (Aastho Method)
- Chapter 3 - Example Flexible Pavement Thickness DesignChapter 3 - Example Flexible Pavement Thickness Design
- Pavement Design AASHTO SOAL QUEZ 05 DES 2016 Hal 7 14 08 12 2016 Conto 4 6 Hal 186 RevisiiiPavement Design AASHTO SOAL QUEZ 05 DES 2016 Hal 7 14 08 12 2016 Conto 4 6 Hal 186 Revisiii
- Pavement Design Thickness Using Asstho Method 1993Pavement Design Thickness Using Asstho Method 1993
- 4.3.8 Design of Pavement 4.3.8.1 5.9.1 Design of New Flexible Pavement (IRC-37)4.3.8 Design of Pavement 4.3.8.1 5.9.1 Design of New Flexible Pavement (IRC-37)
- Pavement Design Thickness Using Asstho Method 1993Pavement Design Thickness Using Asstho Method 1993
- Comparison Between The Effect of Silica Fume & Fly AshComparison Between The Effect of Silica Fume & Fly Ash
- Seismic Risk Assessment of Built Environment in PakistanSeismic Risk Assessment of Built Environment in Pakistan
- On The Correlation of Seismic Intensity Scale WithOn The Correlation of Seismic Intensity Scale With
- Time and Materials (T&M) Contracts - How They Work and Free Template - NetSuiteTime and Materials (T&M) Contracts - How They Work and Free Template - NetSuite
- Calculation of Seismic Protective Qualities of Dampefer and AbsorterCalculation of Seismic Protective Qualities of Dampefer and Absorter
- Seismic Code Developments For Steel & Composite StructuresSeismic Code Developments For Steel & Composite Structures
- Tube Structural System - Types & Features - The ConstructorTube Structural System - Types & Features - The Constructor
- Annexure-6 FOSROC - Lokfix & Nitobond Technical DataAnnexure-6 FOSROC - Lokfix & Nitobond Technical Data
- Schedule 80 Mild Steel Pipe Sizes - Dimensions - Weight and PriceSchedule 80 Mild Steel Pipe Sizes - Dimensions - Weight and Price
- Bored CIP Piles - Capacity Calculation - International Practice - Updated-1Bored CIP Piles - Capacity Calculation - International Practice - Updated-1
- Comparative Study of Diagrid Structures With and Without Corner ColumnsComparative Study of Diagrid Structures With and Without Corner Columns
- Cross-Sectional Optimization of Cold-Formed Steel Channels To Eurocode 3Cross-Sectional Optimization of Cold-Formed Steel Channels To Eurocode 3
- Pavement Distress Survey Manual: Pavement Services Unit Revised June 2010Pavement Distress Survey Manual: Pavement Services Unit Revised June 2010
- Strengthening of Karaimedu - Maruthur-Kulakudi Road KM 1/2 - 4/6 Including Upkeeping For A Period of 60 MonthsStrengthening of Karaimedu - Maruthur-Kulakudi Road KM 1/2 - 4/6 Including Upkeeping For A Period of 60 Months
- Interstate 82: Interstate 82 (Pennsylvania-New York) Interstate 84 in Connecticut History Interstate '82Interstate 82: Interstate 82 (Pennsylvania-New York) Interstate 84 in Connecticut History Interstate '82
- AGRD04A-23 Guide To Road Design Part 4A Unsignalised and Signalised Intersections Ed3.2AGRD04A-23 Guide To Road Design Part 4A Unsignalised and Signalised Intersections Ed3.2