FCM 1.7 - NSCEP (Schistosomiasis) PDF
FCM 1.7 - NSCEP (Schistosomiasis) PDF
Uploaded by
ZazaCopyright:
Available Formats
FCM 1.7 - NSCEP (Schistosomiasis) PDF
FCM 1.7 - NSCEP (Schistosomiasis) PDF
Uploaded by
ZazaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
FCM 1.7 - NSCEP (Schistosomiasis) PDF
FCM 1.7 - NSCEP (Schistosomiasis) PDF
Uploaded by
ZazaCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
7
National Schistosomiasis Control and
Elimination Program
Group 4 22 July 2015
OUTLINE INTERMEDIATE SNAIL HOSTS
I. Schistosomiasis Snails (Oncomelania hupensis quadrasi) serve as
A. Etiology
the intermediary agent between mammalian hosts
B. Mode of Transmission
C. Symptoms Found in freshwater aquatic environments such as
D. Pathogenesis tropical lotic (lakes and reservoirs) and lentic
E. Clinical Manifestations environments (rivers)
F. Diagnosis They are most common in waters where water plants
G. Treatment are abundant and in water moderately polluted
II. Epidemiology
withorganic matter, such as feces and urine, as is often
III. History of NSCEP
IV. The NSCEP the case near human habitations
V. NSCEP Targets and Accomplishments
VI. Challenges/Issues Encountered by NSCEP SYMPTOMS
VII. Where do we want to be? Not by worms but by reactions to eggs
VIII. Plans for the year 2015 Eggs produced by adult worms that do not pass
IX. The Medical Teleparasitology Project out of the body can lodge in the intestine or the
X. Updates bladder
XI. Criteria for Elimination of Schistosomiasis in the
Years of infection may cause damage to the
Philippines
XII. The Four Pronged Approach liver, intestine, spleen, lungs, and bladder.
XIII. Appendix Most people are asymptomatic when first
infected
Source: 3A 2017 (normal text), 3B 2017 (italicized text), 3A o Days after infection, a rash or pruritus
2016 (dark yellow text) may develop
o Within 1 to 2 months of infection,
SCHISTOSOMIASIS symptoms such as fever, chills, cough
ETIOLOGY and muscle aches may develop.
Schistosomiasis is an acute and chronic, parasitic Untreated schistosomiasis may persist for years
disease caused by digenetic blood flukes (trematode o Abdominal pain, enlarged liver, blood in
worms) of the genus Schistosoma stool or urine, problems in passing urine.
Three main species infecting humans are Schistosoma o May also increase risk for bladder cancer
japonicum, Schistosoma haematobium, and Rarely, eggs may be found in the brain or spinal
Schistosoma mansoni. cord
o Cause seizures, paralysis, or spinal cord
Table 1. Parasite species and geographical distribution of inflammation
Schistosomiasis (WHO, 2013)
Species Geographic PATHOGENESIS
Distribution
Schistosoma Africa, Middle East,
mansoni Caribbean, Brazil,
(mesenteric Venezuela,
venules of colon) Suriname
Schistosoma China, Indonesia,
japonicum Philippines
(mesenteric
venules of SI)
Intestinal Schistosoma Several districts of
Schistosomiasis mekongi Cambodia and Lao
(mesenteric People’s Democratic
venules of SI) Republic
Schistosoma Rain forest areas of
guineensis and central Africa
related S.
intercalatum
(mesenteric
venules of colon)
Schistosoma Africa, Middle East
Urogenital haematobium
Schistosomiasis (vesical venous
plexus)
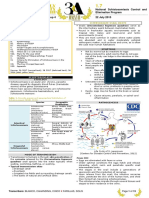
Life Cycle of S. japonicum
(Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2012)
MODE OF TRANSMISSION
Transmission to humans is through skin penetration of
From CDC
the cercaria released by the Oncomelania hupensis
Eggs are eliminated with feces or urine
quadrasi snail species into the water typically when
Under optimal conditions the eggs hatch and release
wading, swimming, bathing, or washing.
miracidia, which swim and penetrate specific snail
Typical transmission sites intermediate hosts.
o Drainage canal
The stages in the snail include 2 generations of
o Riverbank
sporocysts and the production of cercariae.
o Irrigated rice fields and surrounding drainage canals Upon release from the snail, the infective cercariae
o The banks of natural and artificial lakes
swim, penetrate the skin of the human host, and shed
their forked tail, becoming schistosomulae.
The schistosomulae migrate through several tissues and
stages to their residence in the veins.
Transcribers: BLANCO, CAHANDING, CINCO ♥ FARILLAS, SOLIS Page 1 of 15
NATIONAL SCHISTOSOMIASIS CONTROL AND ELIMINATION PROGRAM 1.7
Adult worms in humans reside in the mesenteric venules The quantum of cercariae that infect the host and
in various locations, which at times seem to be specific mature to lay eggs, determine severity of
for each species. infection.
For instance, S. japonicum is more frequently found in
the superior mesenteric veins draining the small STAGE MANIFESTATION
intestine, and S. mansoni occurs more often in the Cercarial Dermatitis
superior mesenteric veins draining the large intestine. penetration
However, both species can occupy either location, and Superficial lung petechiae (parenchyma
Schistosomular to vasculature)
they are capable of moving between sites, so it is not
migration Pneumonitis (pulmonary
possible to state unequivocally that one species only microvasculature)
occurs in one location. Granulomatous hypersensitivity reaction
S. haematobium most often occurs in the venous plexus Initial deposition: accelerated
of bladder, but it can also be found in the rectal venules. formatrion of larger and
Eggs
The females (size 7 to 20 mm; males slightly smaller) destructive granulomas
deposit eggs in the small venules of the portal and Chronic: small or modulated
perivesical systems. granulomas
The eggs are moved progressively toward the lumen of
the intestine (S. mansoni and S. japonicum) and of the Most serious consequence of granuloma formation
bladder and ureters (S. haematobium), and are in the liver: obstruction of the intrahepatic portal
eliminated with feces or urine, respectively. branches
Human contact with water is thus necessary for infection o Leads to portal hypertension with
by schistosomes. accompanying splenomegaly
Various animals, such as dogs, cats, rodents, pigs, o Collateral circulation
hourse and goats, serve as reservoirs for S. japonicum, Eggs are shunted into the
and dogs for S. mekongi. systemic circulation and filtered in
the pulmonary vasculature,
The strains of Schistosoma japonicum require eventually causing pulmonary
Oncomelania snails as intermediate hosts. hypertension.
Oncomelania H. quadrasi o Ascites
o An operculated fresh water amphibious
snail with separate male and female sexes. CHRONIC SCHISTOSOMIASIS
o They are sexually mature by the time they Due to eggs retained in host tissues- highly
measure 3.5 mm. immunogenic and induce vigorous circulating and local
o A single copulation will allow the fertilized immune responses and cause granulomatous reactions
female to lay eggs every five days for one Granuloma formation in organs reach a size many times
month. that of parasite eggs, thus inducing organomegaly and
o Their usual habitats are small clear obstruction (eg. Hepatomegaly)
water streams, water-logged rice Subsequent to the granulomatous response, fibrosis
fields, swamps, and water seepage sets in, resulting in more permanent disease sequelae.
areas along mountains or foothills.
The accumulation of antigen-antibody complexes
In a stream or small swamp, they
results in deposits in renal glomeruli and may cause
are found both in the water and in
significant kidney disease.
the banks.
o They are numerous in areas where the soil
LIVER DISEASE IN SCHISTOSOMIASIS
is moist.
Is initiated after the ova that are carried by portal
o Those in the water are found more in the
blood embolize to the liver
shallower portions, in protruding rocks,
o Because of their size they lodge at presinusoidal
or on floating leaves and branches.
sites, where granulomas are formed
o These granulomas contribute to the hepatomegaly
Three phases of infection
observed in infected individuals
Cercariae penetrate and migrate
through the skin Schistosomal liver enlargement is also associated
Often asymptomatic with certain class I and class II human leukocyte
Migratory phase antigen (HLA) haplotypes and markers
May cause transient dermatitis
(swimmer’s itch), pulmonary lesions, Presinusoidal portal blockage causes several
& pneumonitis hemodynamic changes, including portal
“Katayama fever hypertension and assoc. development of
First egg release portosystemic collaterals at the esophagogastric
Allergic responses (serum sickness
junction and other sites
due to overwhelming immune
Acute phase
complex formation)
Esophageal varices are most likely to break and
Pyrexia, fatigue, aches, cause repeated episodes of hematemesis
lymphadenopathy, GI discomfort, Because changes in hepatic portal blood flow occur
eosinophilia slowly, compensatory arterialization of the blood flow
Cumulative deposition of eggs in through the liver is established
tissues o While this compensatory mechanism may be assoc.
Chronic phase Egg-induced immune response, with certain metabolic side effects, retention of
granuloma formation, and hepatocyte perfusion permits maintenance of
associated fibrotic changes
normal liver function for several years
FIBROSIS – relates to the second most significant
The main pathology: due to host granulomatous
pathologic change in the liver
reaction to eggs deposited in the liver and other
o It is characteristically periportal (Symmers' clay
organs.
pipe–stem fibrosis) but may be diffuse
Pathology and clinical manifestations of cercarial
o Fibrosis, when diffuse, may be seen in areas of egg
penetration and of schistosomular migration are
deposition and granuloma formation but is also seen
considered minor and are not invariable.
in distant locations such as portal tracts
Transcribers: BLANCO, CAHANDING, CINCO ♥ FARILLAS, SOLIS Page 2 of 15
NATIONAL SCHISTOSOMIASIS CONTROL AND ELIMINATION PROGRAM 1.7
o Schistosomiasis results in pure fibrotic lesions in the portal hypertension with
liver hematemesis and
o Cirrhosis occurs when other nutritional factors or splenomegaly (S. mansoni,
infectious agents (e.g. hepB or C virus) are involved S. japonicum)
cystitis and ureteritis (S.
S.HAEMATOBIUM SCHISTOSOMIASIS haematobium) with
While S. mansoni and S. japonicum schistosomiasis hematuria, which can
focuses on granuloma formation and fibrosis of the progress to bladder cancer,
liver, similar processes occur in urinary pulmonary hypertension (S.
schistosomiasis mansoni, S. japonicum, more
Granuloma formation at the lower end of the ureters rarely S. haematobium)
obstructs urinary flow, with subsequent development of glomerulonephritis, and CNS
hydroureter and hydronephrosis lesions
Similar lesions in the urinary bladder cause the Table 2. Symptoms with acute and chronic
protrusion of papillomatous structures into its cavity; schistosomiasis
these may ulcerate and/or bleed Condition Symptoms
The chronic stage of infection is associated with Fever
scarring and deposition of calcium in the bladder Abdominal pain (liver/spleen
wall area)
Symptoms Bloody diarrhea or blood in the
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS associated with stools
acute Cough
Also known as Katayama’s schistosomiasis Malaise
fever Headache
Occurs weeks after the initial Rash
infection and is seen as Body aches
ACUTE
symptoms of fever, cough, Abdominal pain
SCHISTOSOMIASIS
abdominal pain, diarrhea, Abdominal swelling (ascites)
hepatosplenomegaly, Bloody diarrhea or blood in the
eosinophilia stools
Occasionally central nervous Blood in the urine and painful
system lesions occur urination
Symptoms
Presents as ulceration Shortness of breath and
associated with
caused by eggs result in coughing
chronic
dysentery or diarrhea Weakness
COLONIC schistosomiasis
Chronic stage of colonic Chest pain and palpitations
SCHISTOSO-
schistosmiasis is usually Seizures
MIASIAS
asymptomatic but occasional Paralysis
bouts of diarrhea may occur Mental status changes
and are associated with Lesions on the vulva or the
malignancies perianal area
Most serious consequence
of chronic schistosomiasis DIAGNOSIS
HEPATOSPLENIC
Presents as S. japonicum is primarily a parasite of the portal vein
DISEASE
hepatosplenomegaly, and its branches
ascites, and symptoms of o in view of this, eggs are not demostrable in the feces
collateral circulation unless they are deposited in the terminal vein or
Commonly manifests as cor capillaries of the intestinal mucosa or submucosa,
PULMORY pulmonale from obstruction and subsequently escape to the intenstinal lumen
SCHISTOSOMIASIS of lung vasculature due to Consequently, infections where there is scarring or
granuloma formation and fibrosis of sites of ulcerations prevent passage of eggs
fibrosis to the intestinal lumen
Motor or sensory disturbance Stool examination therefore frequently give negative
depending on site of egg results even in active infection
deposition and granuloma Schistosome eggs can also be recovered by rectal or
formation liver biopsy
Route: portal vein via These procedures require skills not within the
mesenteric and pelvic veins capabilities of ordinary medical laboratory technologists
to spinal veins and are not practical for mass screening or field surveys
CEREBRAL
Acutely manifest as
SCHISTOSOMIASIS
fulminating MICROSCOPIC EXAMINATION
meningoencephalitis, fever, The gold standard for diagnosis of schistosomiasis in
headache, confusion, suspected patients via identification of ova in stool or
lethargy, and coma urine
Chronic cases give a clinical Most suitable for enumeration of eggs, evaluation
picture of tumor with of epidemiology, effectiveness of control
localizing signs and increased measures and drug trials
intracranial pressure Done 2 months after contact with freshwater
May result in manifestations Limited sensitivity in patients with low infectious burden
CONTINUING/
that include, colonic o May be increased bu collection of specimen on
CHRONIC
polyposis with bloody three different days
INFECTION
diarrhea (Schistosoma Diagnosis may be done by observation of even a
mansoni mostly), single ovum in thick smears (Kato-Katz technique)
Transcribers: BLANCO, CAHANDING, CINCO ♥ FARILLAS, SOLIS Page 3 of 15
NATIONAL SCHISTOSOMIASIS CONTROL AND ELIMINATION PROGRAM 1.7
Formalin concentration techniques may be done to less robust, and repeat treatment may be needed after
increase yield in low infectious burdens 2 to 4 weeks to increase effectiveness
Recommended by WHO for use in field studies If the pre-treatment stool or urine examination was
Preparations may be stored for around 2 weeks, thus positive for schistosome eggs, follow up examination at
making it ideal for identification of egg density. 1 to 2 months post-treatment is suggested to help
Urine examination for S. haematobium may be confirm successful cure
concentrated via sedimentation, centrifugation or
filtration. Table 3. Praziquantel Dose and Duration for Different
Maximum egg excretion for S. haematobium: between Schistosoma Species
10am and 2pm. Schistosoma species Praziquantel dose and
infection Duration
CIRCUMOVAL PRECIPITIN TEST (COPT)
Schistosoma mansoni,
Demonstrates the formation of bleb or septate 40 mg/kg per day orally in 2
S. haematobium, S.
precipitates attached to one or more points on the egg divided doses for one day
Intercalatum
surface after incubation of schistosome eggs in a
patient’s serum S. japonicum, S. 60 mg/kg per day orally in 3
It is currently the method of choice for definitive Mekongi divided doses for one day
diagnosis of infection in the Philippines
Used if microscopic examination yields a negative result EPIDEMIOLOGY AND PREVALENCE IN THE
and there is a high index of suspicion for infection with PHILIPPINES
schistosomiasis Prevalent especially in poor communities without
access to safe drinking water and adequate sanitation.
ANTIBODY DETECTION Mostly affects poor and rural communities,
Employed if a patient has a history of travelling particularly agricultural and fishing populations.
to endemic areas in the past and have not Inadequate hygiene and contact with infected water
received prior appropriate treatment make children especially vulnerable to infection.
Serum must be collected at least 6 to 8 weeks The general distribution:
after likely infection to ensure full development o Africa, the Middle East, South America
of parasite to adult stage. and South East Asia
ELISA, indirect hemagglutination, o It is estimated that at least 90% of those requiring
immunofluorescence. treatment for schistosomiasis live in Africa
Not recommended for patients with active o Worldwide, more than 200 million are known to be
infection and treated previous infection. infected and up to 800 million daily are at risk to
become infected
o The number of deaths due to schistosomiasis is
ANTIGEN TESTS
difficult to estimate because of hidden pathologies
Circulating Anodic Antigen (CAA) such as liver and kidney failure and bladder cancer.
Circulating Cathodic Antigen (CCA) o Estimates therefore vary widely between 20,000 and
Commercially available kits containing 200,000 deaths per year (WHO, 2015).
monoclonal antibodies for schistosomule
antigens From the data of WHO, we are still considered to have a
low to moderate prevalence (10 to 49%) of
PCR ASSAYS schistosomiasis with a greater prevalence occurring in
Highly specific and sensitive for detection of Visayas and Mindanao regions.
schistosome DNA According to IAMAT, schistosomiasis in the Philippines is
Can establish diagnosis regardless of clinical mainly caused by Oncomelania quadrasi snails infected
stage of disease with S. japonicum.
Stool, urine, blood serum Still endemic in 12 regions with approximately 12
million at risk and almost 2.5 million directly exposed to
TISSUE BIOPSIES the parasite.
May also be done for diagnosis when urine or Specifically 28 provinces, 190 municipalities and 2,230
stool examination is negative (CDC) barangays are affected.
Bladder biopsy: S. hematobium According to DOH, the national mean prevalence based
Rectal biopsy: all other species on the active surveillance by field health schistosomiasis
teams is 2.5%. having the highest prevalence and
TREATMENT intensity of infection among 5-15 years old
PRAZIQUANTEL The intensity of infection varies widely between villages
Can be used for infections with all as a function of geography, age, sex, and ecology with
major Schistosoma species a difference in prevalence for the same region ranging
Most effective against the adult worm and requires from 0% to 45%.
the presence of a mature antibody response to the In all of the endemic provinces, the prevalence rate of
parasite the disease was higher among males than females;with
Drug of choice for treatment of schistosomiasis the usually affected age groups to be are 55-59 years or
Recommended dosage: 60mg/kg/day PO, in 3 25- 29 years of age.
divided doses in a day This is due to occupational hazards such as farming
Mechanism of action: and fishing that are key factors for infection.
o Increases permeability of schistosome This suggests that occupational exposure is a significant
membranes, leading to efflux of calcium ions thus predictor of infection (DOH Philippines 2008).
paralyzing the worms Although adults have a higher infection prevalence, the
Treatment for travellers should be at least 6-8 weeks highest intensity of infection was found to be among the
after last exposure to potentially contaminated 5- 15-year age group.
freshwater
Although a single course of treatment is usually curative,
the immune response in lightly infected patients may be
Transcribers: BLANCO, CAHANDING, CINCO ♥ FARILLAS, SOLIS Page 4 of 15
NATIONAL SCHISTOSOMIASIS CONTROL AND ELIMINATION PROGRAM 1.7
Morbidity of Schistosomiasis per Region, 2010
Top endemic provinces being Mindoro Oriental,
Agusan del Sur and Sorsogon.
Kato-Katz thick smear examination was used in
diagnosing Schistosoma japonicum
Prevalence for each province was computed by dividing
the number of positives by the total number of
individuals whose stools were examined from the five
barangays per province.
CARAGA is the region with the most # of cases
(morbidity) in the Philippines
Field data collected by the schistosomiasis research
team, CPH, UPM 2005-2008
Table. Prevalence of Schistosomiasis by province (2005
to 2007)
PROVINCES PREVALENCE (%)
Agusan del Sur 3.95
Northern Samar 2.45
Eastern Samar 1.79
Bukidnon 1.66
Surigao del Sur 1.3 Morbidity rate per 100,000 population in the Philippines
Leyte 0.91 from 1998 to 2012
Lanao del Norte 0.81
Davao del Norte 0.78 7
Western Samar 0.77 5.9
Compostela Valley 0.68 6
Mindoro Oriental 0.63 4.3
Catabato- Kidapawan 0.54
5
Marawi City 0.12 4
Sorsogon 0.36 2.7 2.4
Surigao del Norte 0.29 3 2
South Cotabato 0.28 2 1.4
Sultan Kudarat 0.24
Iloilo City 0.2 1
Davao del Sur- Digos 0.09
0
Agusan del Norte 0.08
Cagayan 0.04 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014
Prevalence Rate of Schistosomiasis in the Phlippines by
Year 2009-2014
From the figure above, morbidity rate is decreasing
over the years but the decline is not constant
There is still a huge discrepancy between number of
cases identified in 1998 and 2012
o May signify effectiveness of control
programs implemented by the DOH and
WHO
Transcribers: BLANCO, CAHANDING, CINCO ♥ FARILLAS, SOLIS Page 5 of 15
NATIONAL SCHISTOSOMIASIS CONTROL AND ELIMINATION PROGRAM 1.7
o Establish effective liaison with
participating agencies
o Submit recommendations to the President
on administrative or legislative measures
that will effectively carry out national
control program for the disease
SCHISTOSOMIASIS CONTROL COUNCIL
Formed under PD 893 by President Marcos in 1976.
Reconstitution of NSCC into NCC
Schistosomiasis mortality rate per 100,000 popuation in Functions and objectives:
the Philippines from 1989 to 2009 o Formulate an integrated national program for the
control of schistosomiasis in the Philippines
Observed decline in mortality rate from 1989 to o Coordinate and integrate the implementation of
2009. schistosomiasis control programs, projects, and
More stable and consistent compared to the activities of all agencies and instrumentalities of
morbidity rate the government as well as those of the private
sector involved in controlling the disease
HISTORY OF NSCEP o Formulate an effective information and education
SCHISTOSOMIASIS CONTROL PROJECT campaign scheme and other such complimentary
Formulated: 1961 schemes necessary for the control of the disease
Integrated into the total health program of the o Promot special studies and researchers on related
rural health units at the local level aspects of schistosomiasis control and treatment
Managerial positions: provincial health officer and o Represent the government in its dealings with the
regional health director World Health Organization or with the United
Approach before introduction of praziquantel: Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund
o Decrease transmission by breaking the or any other international health agencies or
parasite life cycle through reduction of the entities or with foreign governments or their
number of snail intermediate hosts agencies in matters involving schistosomiasis
o Limiting human exposure to the infective control, subject to existing laws, rules, and
form of the parasite, and regulations
o Health education o Undertake such other activity as may be deemed
Methods of control necessary for the attainment of the objectives of
o Agro-engineering methods of snail control the Council
o Environmental sanitation measure
o Health education THE NATIONAL SCHISTOSOMIASIS CONTROL AND
o Treatment of cases with Stibophen ELIMINATION PROGRAM
MAIN PROBLEM: financial constraints The Kalusugan Pangkalahatan of the Department
of Health aims to provide every Filipino the
NATIONAL SCHISTOSOMIASIS CONTROL highest possible quality of health care that is
COMMISSION accessible, efficient, equitably distributed,
adequately funded, fairly financed, and
RA 4359
appropriately used by an informed and
Liaison agency between Philippine government
empowered public.
and WHO/UNICEF
o Under this program are technical clusters,
Also serves as a coordinating body to ensure
in which, The Support to Service Delivery
concerted effort of agencies concerned in planning
Technical Cluster (SSDTC) belongs to.
and implementing a comprehensive program for
o Among the units in the SSDTC is the
schistosomiasis control in endemic and potentially
National Center for Disease Prevention
endemic areas in the country.
and Control (NCDPC).
Multisectorial and involves:
o One of the diseases that the NCDPC
o The Secretary of Health as chairman, the
addresses is the elimination of the
Secretary of Education, the Secretary of
schistosomiasis as a public health
Agriculture and Natural Resources, the
problem in all endemic areas, hence, the
Secretary of Public Works and
formerly called Schistosomiasis Control
Communications, the Chairman, National
Commission (SCC), is now the National
Economic Council, the Social Welfare
Schistosomiasis Control and Elimination
Administrator, the Commissioner of
Program (NSCEP).
Agricultural Productivity, the Director
One of it is particularly address the elimination of
General of Program Implementation
Schistosomiasis as a public health problem in all
Agency, the National Irrigation
endemic areas
Administrator, the Presidential Assistant
on Community Development, the General
VISION
Manager, National Waterworks &
Schistosomiasis-Free Philippines by 2016
Sewerage Authority, the Budget
Commissioner, and the President,
MISSION
Philippine Medical Association.
synchronize and harmonize public and private
Duties:
stakeholders’ efforts in the elimination of
o To formulate and carry out a
Schistosomiasis in the Philippines
comprehensive national schistosomiasis
control program
OVER-ALL GOAL
o Foster effective exchange of information
Schistosomiasis is eliminated as a public health
and coordination of projects, programs,
problem in all endemic areas.
and activities of various agencies
Basis for elimination of schistosomiasis:
connected with schistosomiasis control
Transcribers: BLANCO, CAHANDING, CINCO ♥ FARILLAS, SOLIS Page 6 of 15
NATIONAL SCHISTOSOMIASIS CONTROL AND ELIMINATION PROGRAM 1.7
o Prevalence rate is reduced to less than 1% o Living in a highly endemic barangay (PR > 10%),
for at least five (5) consecutive years. without the benefit of a stool exam
Current target o School children from provinces that have reached
o Eliminate 5 areas (Bohol, Zamboanga del the elimination level of <1/100,000 prevalence for
Norte, Zamboanga Sibugay, Davao del 5 consecutive years.
sure, Davao city) by 2016 According to Belizario et al (2004), the
o Elimination of the disease as a public rationale behind selecting school children
health problem in 23 endemic provinces as a target population is that
by 2020 chemotherapy in the age group has been
shown to reduce significant short term
morbidity, and prevent long term
OBJECTIVES complications in adulthood associated
Objective Indicator/s with chronic infection.
1.Reduce the Percent prevalence rate To further promote these objectives, July was
prevalence rate of of Schistomiasis and the declared as the mass treatment and awareness
Schistosomiasis in number of provinces month for schistosomiasis, in 2009.
endemic provinces that have reached The drug of choice for mass treatment is
below 1% by 2016 elimination level praziquantel, single dose, 40 mg per kg body
2.Increase the coverage Percent coverage in weight, given with a full stomach.
of mass treatment to mass treatment of Observe for ADRs
85% per year in all exposed population (5- o Headache, dizziness, abdominal
endemic areas 65 years old) discomfort, and less commonly, nausea,
vomiting, diarrhea, fever, and urticarial
STRATEGIES rashes
1. Preventive chemotherapy and infection control
2. Transmission control
3. Public-private partnership ACTIVITY 2: SELECTIVE TREATMENT OF CASES
4. Advocacy and social mobilization Selective treatment of cases, covering positive cases
5. Monitoring and evaluation – those found to be infected upon stool examination –
from areas of moderate prevalence rates (2.1 – 9.9%),
ENABLING ACTIVITIES and low prevalence rates (< 2%).
Linkaging and networking Drug of choice is praziquantel, 600 mg/tab, 60
Policy guidelines and CPGs mg per kg body weight, taken one day in two
Institutional capacity building divided doses, with 4-6 hours interval and given
Competency enhancement of frontline service provider with a full stomach.
Monitoring and supervision Praziquantel is not contraindicated at any stage of
pregnancy, with the benefits of treatment far
outweighing the risks associated with schistosomiasis,
POLICIES AND GUIDELINES
such as maternal anemia and poor birth and survival
rates of infants.
A.O. 2007-0015 and A.O 2007-0015 A Current Efforts:
Revised Guidelines in the Management and Prevention o Constant revision of the manual of
of Schistosomiasis operation procedures, guidelines and
sentinel surveillance by the Department of
A.O. 2009-0013 Health
Declaring the month of JULY every year as Mass o mass treatment planning and workshop
Treatment and Awareness Month for Schistosomiasis in o Further research on the improvement of
the established endemic areas schistosomiasis control
o Clinical practice guidelines training in
STRATEGY 1: PREVENTIVE CHEMOTHERAPY AND public hospitals and Centers for Health
INFECTION CONTROL Development
Objective: to scale up access to preventive o Case management training for municipal
chemotherapy with a treatment coverage of 85%, and health officers and selected hospitals
intensifying case management interventions.
Activities STRATEGY 2: TRANSMISSION CONTROL
o Mass treatment of population age 5-65 years Objective: to promote the use of safe water and
(DOH-AO 2009-0013). proper sanitation facilities using the WASHED
o Selective treatment of cases, covering positive (Water, Sanitation, Hygiene Education,
cases Deworming) framework
WHO has categorized communities based on the Activities:
prevalence of schistosomiasis to determine the o Snail mapping and control
strategy of protective therapy to be given (Please o Environmental sanitation
see appendix)
ACTIVITY 1: SNAIL MAPPING AND CONTROL
Targeted towards the intermediate host of
ACTIVITY 1: MASS TREATMENT OF POPULATION
Schistosoma japonicum.
AGE 5-65 YEARS
A. SNAIL MAPPING
Goal: at least 85% coverage in high-prevalence Existing and potential disease transmission sites
barangays for 3 consecutive years, followed by its are first identified in endemic areas
evaluation using the parasitologic and process Breeding sites for the snails are also mapped out.
indicators. Common breeding sites: rice paddies, creeks,
Coverage: springs, dams, and others (Belizario et al, 2004).
o Citizens in the specified age group (5 to 65 years) Mapping is done using survey tools such as GPS
units given to endemic provinces, in order to plot
Transcribers: BLANCO, CAHANDING, CINCO ♥ FARILLAS, SOLIS Page 7 of 15
NATIONAL SCHISTOSOMIASIS CONTROL AND ELIMINATION PROGRAM 1.7
sites wherein snails which may or may not be Practice of scientific
positive for schistosomiasis, breed. farming that promotes
improved rice culture
B. SNAIL CONTROL o Constant plowing
This is achieved through focal and area-wide o Periodic weeding of the
approaches. fields
FOCAL APPROACH Chemical control
o Involves water contact studies to identify o The use of chemicals to control snails is
the most common transmission sites, in only recommended in areas with low
areas where these are limited. prevalence (<1%) as a final phase of
AREA-WIDE APPROACH elimination
o Areas where transmission is spread over o use of molluscicides for snail control is
greater areas, such as a watershed or restriced due to acute inhalation toxicity,
irrigation system. aquatic organism toxicity and ground
After identification of sites, control measures are water contamination
undertaken to reduce the number of snails
infected. ACTIVITY 2: ENVIRONMENTAL SANITATION
These measures include: Promotes elimination of infection among people in
endemic areas, and the general health of the
INFRASTRU Lining of canals with concrete population
CTURE- to ensure that the canals are Improper waste disposal allows the parasite to
DIRECTED properly emptied spread via water, survive in intermediate hosts, and
MEASURES Weeds are kept to a minimum, eventually infect people, perpetuating schistosomiasis,
thereby giving the snails less as well as a myriad of other preventable infections.
venues to reproduce. In line with this, sanitary toilets must be used, and
ENVIRONM Management of irrigation defecation must be avoided in rice paddies, rivers, and
ENTAL Clearing of swamps other bodies of water.
MODIFICAT Covering of snail habitats The safety of water sources must also be ascertained
ION with landfills before the water is used for bathing, washing, and
Farming methods: drinking. Boiling water, treatment with iodine or
o Constant plowing chlorine, and filtering all reduce the chances of
o Periodic weeding. parasite survival
Proper protective gear such as rubber boots to
All these measures are aimed at lowering the snail prevent contact with water that may be carrying the
populations to minimize vectors available for the parasite.
parasite. o These measures also apply to farm, stray, and
However, in the event that these methods fail, domesticated animals, which are potential
and only as a terminal measure, chemical means agents of transmission of the parasite.
of reducing snail populations may be done using Current efforts: Integrated forum on Neglected
molluscicides. Tropical Disease (NTD) for sanitary inspectors (DOH)
o This method is applicable only to areas Specific campaigns
with low prevalence (< 1%), due to o Latrine construction and utilization
the risks of: o Safe water supply
Acute inhalation toxicity o Control of stray and domesticated animals
Aquatic organism toxicity o Foot bridges
Ground water contamination
o Current efforts: STRATEGY 3: PUBLIC-PRIVATE PARTNERSHIP
o Training on snail site mapping and Multisectorial approach
surveillance Linkages has been made and establish to the
o Further research on animal and snail infection various sectors and organizations that share the
o Analysis of the parasite and vector same goal as to the elimination of the disease
o Operational research on animal and snail burden caused by the infection of Schistosoma
infection (DOH-CPH) spp.
o Species diversity analysis of S. japonicum and
Oncomelania quadrasi (UP-CPH) 1. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH
o Animal infection survey and diagnostic Development of a new Clinical Practice Guideline
technique development for bovine for management of schistosomiasis
infection(UP-CPH) o Includes new trends specific for
neurological and other ectopic organ
ENVIRONMENTAL involvement
PHYSICAL SNAIL
MODIFICATION o Aimed to be provided on various medical
CONTROL
METHODS and academic institutions with the aim of
Engineering of hydraulic Proper management of improving the practice of clinicians in
infrastructures irrigation systems detecting and intervening against the
Concrete lining of canals Clearing of vegetation in disease.
to ensure: swampy areas to expose
o High water velocity the vector snails to 2. DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION
o Weed control sunlight Plays a key role in management of cases on
o Periodic flushing Construction of fish ponds endemic areas with the help of their Public School
o Emptying of canals when water cannot be Surveillance System.
drained It was reported that the members of the faculty
Covering of snail habitats are the ones assisting the medical officials in
with land fills distributing the medications for children of school
age during the yearly mass treatment programs.
Transcribers: BLANCO, CAHANDING, CINCO ♥ FARILLAS, SOLIS Page 8 of 15
NATIONAL SCHISTOSOMIASIS CONTROL AND ELIMINATION PROGRAM 1.7
community that will encourage community
3. LOCAL GOVERNMENT UNITS participation in control programs of the DOH
Responsible in the local management of their The program in this strategy is being partnered with
cases through their rural health units. the Department of Education.
This entails that the management of new and o The school curriculum is encouraged to
chronic cases are being spearheaded by the local integrate health education among children on
communities in their endemic areas. disease infection, transmission, prevention and
Furthermore, there are yearly mass treatment control of endemic parasitic diseases.
programs being conducted with the supervision of o This practice is highly advised in schools
the regional officials of the DOH. coming from the endemic provinces
Influencing change in the attitudes and practices of
The following enumerated sectors are the partners of the people is dependent upon the efforts of the
Department of Health in the delivery of technical community organizations and the willingness of the
assistance, planning and research on feasibility and residents to accept and participate to the projects.
safety of treatments, delivery of treatments as well as The use of tri-media is recommended as an effective
surveillance and monitoring. tool to create awareness, to advocate, promote and
o Department of Agriculture (BAI, NIA, educate the people on disease transmission,
BFAR) diagnosis, treatment, prevention and control of
o Department of Science and Technology schistosomiaisis.
o Department of Local Government/ Local o Educational programs are aired through radio
Government Units and television.
o Philippine Information Agency, Kapisanan o All of these are necessary in order to obtain the
ng mga Broadcaster ng Pilipinas cooperation of the people for the control and
o Department of Public Works And prevention of the disease.
Highways o Promotion of the most important interventions
Cement lining of canals in the control of schistosomiasis, which is the
o Department of Natural Resources mass treatment, may be done through media.
Snail mapping o The National Center for Disease Prevention and
o Department of Tourism Control of the DOH is the main agency involved
o Department of Social Welfare and in this management.
Development Together with the National Center for
Current Efforts: Health Promotion, they conceptualize and
o Technical assistance and capability building to develop prototype advocacy materials
LGUs and other stakeholder (DOH) (radio plugs, advisory flyers and other
o Development of schistosomiasis strategic plan and promotional materials) that will hopefully
framework (DOH-CPH) catch the attention of the targeted
o Feasibility and safety of school-based combined exposed population and convince them for
treatment for soil-transmitted helminth infectios schistosomiasis mass treatment.
and schistosomiais (DOH-NIH-DepEd) Community assemblies and other gatherings are
o Validating the WHO dose pole in the Philippines for avenues to disseminate information in endemic
school-based mass drug administration of provinces.
praziquantel for morbidity control of To further promote awareness on schistosomiases,
schistosomiasis (DOH-NIH-DepEd) the DOH has made partnership with the World Health
o Efficacy and safety of 40 mg/kg and 60 mg/kg Organization (WHO), Asian Institute of Journalism and
single doses of praziquantel in the treatment of Communication (AIJC) and FHI 360.
schistosomiasis o The WHO allows researches regarding the
o Resurgence of shistosomiasis japonicum in school current status of schistosomiasis in the
children in Agusan del Norrte Philippines: country to be made and published.
Opportunities for control in the school setting o They also provide health promotional
(DOH-NIH-DepEd) materials regarding the disease.
o AIJC on the other hand developed and
produced advocacy kits and other advocacy
materials for Local Chief Executives to gain
the support of local leaders to prioritize the
health improvements in their localities for the
NTDs including schistosomiasis.
o They also help in the capacity building in
communication planning and Information-
Education-Communication (IEC) materials
development.
FHI 360 has launched a 5-year program in 2011, End
Neglected Tropical Diseases in Asia (END in Asia), to
Partners and Satkeholders in the SCEP reduce the incidence and mortality related to
neglected tropical diseases including schistosomiasis.
As part of this program, FHI 360 train service
STRATEGY 4: ADVOCACY AND SOCIAL
providers, improve logistics for supplies, enhance
MOBILIZATION
monitoring and evaluation systems and provide health
Health Promotion promotion materials.
Information being disseminated in health promotion Current Efforts:
includes facts about the disease process, disease o Technical and logistic support for the conduct
infection, transmission, prevention and control of of Multi-stakeholders forum and kick-off
endemic parasitic diseases. launching of Mass Treatment and awareness
The knowledge of the people on schistosomiasis is month to various partners
very vital particularly among the primary health care o Development of Communication plan and
workers as they are the health educators in the o materials (DOH-AIJ)
Transcribers: BLANCO, CAHANDING, CINCO ♥ FARILLAS, SOLIS Page 9 of 15
NATIONAL SCHISTOSOMIASIS CONTROL AND ELIMINATION PROGRAM 1.7
o Development of NTD IEC Materials “Urbani The involvement of other departments of the
Kits” for schools (DOH-FHI/USAID) government, along with different NGOs and the
o Development of NTD Maps for three diseases citizens themselves is of great importance.
(DOH-FHI) The program requires input from each stakeholder
o Development of NTD Provincial maps for for recommendations to further improve the
Malaria, STH, Filaria and SCH (DOH-WHO) control programs implemented, as stated by
Future projects: Department of Health former secretary Francisco
o Coalition building in the endemic provinces Duque III.
and revival of Schistosomiasis task force
3. QUALITY ASSURANCE
STRATEGY 5: MONITORING AND EVALUATION To ensure the quality of the diagnostic methods,
Goal: strengthening monitoring of infections as well 10% of the total slides are subjected to a blind
as evaluation and enhancement of the current validation by a Certified Validator for
surveillance system. Schistosomiasis from other provinces.
Activities: In addition, slides examined by the RHUs and
o Sentinel surveillance and monitoring other health facilities are validated by a certified
o Health impact assessment provincial validator and 15% of the total slides
o Quality assurance validated are sent to be validated by UPM-CPH or
RITM.
1. SENTINEL SURVEILLANCE AND MONITORING
Done first by the establishment of sentinel sites, Process indicators: consumption of drugs,
areas in the community where in-depth data are treatment coverage
gathered and analyzed. Parasitologic Indicators: prevalence of infection,
In areas with a large population (>120,000 intensity of infection, incidence
population per province) barangay schools may be VECTOR Indicators: snail density, snail infection
selected as sentinel sites for surveillance as health rate, estimated snail population
centers alone may not be enough. Current efforts:
Selection of snail sentinel sites may be conducted o Rural health unit (RHU) database system:
as well. Schistosomiasis information (SIS) expanded to
o Using these schools as sentinel sites, zero surveillance web-based information using
school children especially those belonging geographic information systems (GIS) Maps
to grades 1-3 can be monitored (DOH-NIH) is now being utilized.
specifically in. o Hospital registry for neuroschistosomiasis and
o Kato-Katz technique is done to this other complicated cases are available for such
population annually to determine the cases.
trends in human infection. o Assessment of disease-free provinces is being
In areas that are not endemic with new or done using sensitive diagnostic test (DOH-NIH).
suspected case of Schistosomiasis, rapid As of 2010, only 533758 out of the 1382447
epidemiological surveys are warranted to prevent (38.61%) patients diagnosed were treated and
further transmissions. cured accordingly.
In endemic areas, households are monitored in o Prevalence survey on schistosomiasis and soil
terms of their existing sanitary toilet facilities, transmitted helminthiasis (STH-RITHM)
safe water supply facilities and the utilization of o Development of prevalence maps (DOH-CPH-FHI)
these facilities. o Schistosomiasis School Sentinel Surveillance
In order to assess the status of prevalence per
area, prevalence surveys are done every five NSCEP TARGETS AND ACCOMPLISHMENTS
years in endemic areas using random selection Please see appendix.
(multi-stage sampling) of endemic barangays. IMPORTANT!
Surveillance of known cases is made through the
Rural Health Unit Database System: CHALLENGES AND ISSUES ENCOUNTERED BY
Schistosomiasis Information System and hospital NSCEP
registry for cases of neuroschistosomiasis. Wavering political commitment of LGUs in the
o Using these gathered data, the implementation and sustenance of public health
Department of Health can generate interventions for addressing schistosomiasis
prevalence maps to determine and predict Sustenance of program integration and environmental
prevalence patterns nationwide. sanitation activities at various levels
o The development of the Neglected Increasing treatment coverage of MDA in regions VIII,
Tropical Diseases (NTD) Map has also X and CARAGA.
been helpful in the surveillance of Use of more sensitive diagnostic tools in areas with
schistosomiasis cases. low to elimination levels of prevalence to prevent
underestimation of the actual value.
2. HEALTH IMPACT ASSESSMENT Problems are encountered in addressing the zoonotic
Health impact assessments help the communities component of the disease
make informed choices about improving public
health through community’s collective effort. WHERE DO WE WANT TO BE?
Because schistosomiasis is a multifactorial Currently, 18 provinces remain endemic for
problem, the approach to eradicate the disease schistosomiasis but the prevalence rates in those
must also be multisectorial. areas remain low (<10%)
Health impact assessment should be carried out 11 provinces have achieved a prevalence of 0 to
in close association with environmental <1% and is categorized in the elimination level.
assessment, because health impact assessment Sustain these gains via:
considers changes in both environmental and o Strengthened active surveillance of human and
social determinants of health. snail vectors
o Infection control
o Transmission control
Transcribers: BLANCO, CAHANDING, CINCO ♥ FARILLAS, SOLIS Page 10 of 15
NATIONAL SCHISTOSOMIASIS CONTROL AND ELIMINATION PROGRAM 1.7
o Safe water supply o Academic Institutions (Davao Medical School
o Water sealed toilets Foundation Inc and Saint Louis University, Baguio)
o Ordinances to control animal host o Local PAMET Chapter
o Mass treatment of school children
o Quality control of laboratory and laboratory staff UPDATES
Leonardo et al. in 2015
NSCEP PLANS FOR THE YEAR 2015 o Described schistosomiasis as endemic in 28
*Please see appendix provinces in 12 regions, 14 cities, 189
municipalities, and 2221 barangays
MEDICAL TELEPARASITOLOGY PROECT o Most of these areas, characterized by the
A type of telehealth services absence of dry season, found in CARAGA and
A network of health care professionals in diagnostic Region VIII.
parasitology that remotely share information in order o More than 12 million people are at risk and
to deliver healthcare services to far flung areas using about 2.5 million are directly exposed from
information and communication technologies for the 3012 snail-infested bodies of water nationwide
exchange of information regarding the diagnosis, which are largely found in Mindanao (80%).
treatment, and prevention of disease. o The same article assessed the prevalence as
This system aims to develop a database of cases well as the age and sex distribution of
referred to the system and thus subsequently map the schistosomiasis in two new endemic foci in
distribution of parasitic infections in the country— the country namely Gonzaga, Cagayan
which will provide quality data and evidence for and Calatrava, Negros Occidental which
advocacy and formulation of policies regarding the showed Calatrava of having lower prevalence.
control and prevention of parasitic infections.
Spearheaded by Dr. Vicente Y. Belizario
Aims to develop and demonstrate a feasible referral
system which links laboratories over select regional
diagnostic referral centers without requiring the
physical presence of the experts in their localities. It
aims for a timely and accurate diagnosis of parasitic
infections by providing training, reference, diagnostic
assistance, and continuing education for medical
technologists.
Significance:
o Correct and timely diagnosis of parasitic
infections, preventing misdiagnosis and allowing
for appropriate and correct management of
patients especially in far-flung and underserved CRITERIA FOR ELIMINATION OF
areas; SCHISTOSOMIASIS IN THE PHILIPPINES
o A feedback mechanism for referring parties who FOUR PARAMETERS
are part of the network to share their microscopic 1. Criteria for Morbidity Control
and laboratory findings, express their opinions The prevalence rate of cases and heavy intensity
and to communicate with experts in the field and infection is less than 5% in endemic population
vice versa; (residents);
o Capacity building of laboratory personnel as The prevalence rate in domestic animals is less
referring parties; than 5%;
o Support for Neglected Tropical Disease Data and files reflecting the changes in human
Information System (NTDIS) currently being and snail infections at the barangay and
developed by the DOH through a database of all municipal level are available (including validation
referred cases that will be utilized in mapping of snail sites)
parasitic infections in the Philippines and Preventive chemotherapy treatment coverage is
o An updated data and generation of new 85% or more and 100% geographic coverage for
information that will be used to improve current 5 to 65 years of the population
guidelines and policies on NTD control and 2. Criteria for Elimination as a Public Health
contribute to global discussions on the diagnosis Problem
of parasitic infections. The prevalence rate of cases and heavy intensity
infection is less than 1% in endemic population
(residents) for at least three (3) years.
The prevalence rate in domestic animals is less t
han 1%.
No infected Oncomelania snails are found for two
successive years
Data and files reflecting the changes in human a
nd snail infections at the municipal and
barangay level are available.
3. Criteria for Areas Eligible for Elimination of the
Disease
No new human schistosomiasis case (incidence) is
found for five (5) successive years.
No schistosomiasis case in domestic animals
Collaborating agencies: with local infection is found for five successive
o Department of Science and Technology-Philippine years.
Council for Health and Development No infected Oncomelania snails are found after
o Department of Health careful surveys for two successive years.
Transcribers: BLANCO, CAHANDING, CINCO ♥ FARILLAS, SOLIS Page 11 of 15
NATIONAL SCHISTOSOMIASIS CONTROL AND ELIMINATION PROGRAM 1.7
Data and files reflecting the changes in human Stop water contamination by infected
and snail infections at the municipal and barangay individuals or animals
level are available. 4. Safe water supplies, IEC and PPEs
Available elimination plan Prevent contact of human and bovine reservoirs
Existing and functional surveillance system (zero with snai- or cercaria-contaminated water
surveillance)
CURRENT RESEARCHES AND PROGRAMS ON
4. Criteria for Areas who have Achieved Disease SCHISTOSOMIASIS
Elimination 1. Neuroschistosomiasis Registry
No new infection in man (autochthonous cases) or Department of Clinical Epidemiology-UPCM
domestic animals is detected for five years after In partnership with the Philippine Neurologic
reaching the criteria for transmission interruption. Association,PGH
To monitor the target provinces in Mindanao
THE FOUR PRONGED APPROACH Research areas include zero surveillance, area
*Please see appendix evaluation and focal surveys
1. Preventive chemotherapy or selective treatment Currently under Phase II
Similar to strategy 1 of NSCEP Please see appendix.
Kill worms in man and reservoir hosts (esp.
carabaos) via praziquantel-based therapy. 2. RITM-Schistosomiasis Study Program
Cattle and carabaos Objectives:
o Have a high prevalence of S. japonicum o development of cost-effective schistosomiasis
infection in Northern Samar control measures based on existing
o Average daily egg output: 195,000 technology that can be applied by the DOH in
o Warrants an integrated approach for schistosomiasis endemic areas in the
hampering bovine transmission of Philippines
schistosomiasis via bovine chemotherapy or o development of alternative diagnostic tests
vaccination for determining prevalence and intensity of
2. Snail control infection in field settings
Killing of intermediate host (Oncomelania o conduct of studies that will provide new
snails) via biological, chemical and insights in the pathogenesis of disease and
environmental control. resistance to Schistosoma japonicum infection
Biological control that can include the development of a safe
o Competitor snails like the Thiarid snail and effective vaccine against establishment of
family infection.
o Snail-eating fish
Chemical control 3. Neglected Tropical Diseases-USAID
o Molluscicides DOH in partnership with USAIC
Environmental control NTDs Elimination and Control Program
o Concrete lining of canals create large-scale activities to eliminate
o Weeding lymphatic filariasis (LF) and control the
o Irrigation management transmission of schistosomiasis (SCH) and soil-
o Swamp clearing transmitted helminthes (STH)
3. Environmental sanitation, IEC and behavior “WASHED” — water, sanitation, hygiene,
change education and deworming
Prevents infection of Oncomelania snails by
schistosome miracidia
Transcribers: BLANCO, CAHANDING, CINCO ♥ FARILLAS, SOLIS Page 12 of 15
1.7
National Schistosomiasis Control and
Elimination Program
Group 4 22 July 2015
STEPS TOWARD THE ELIMINATION OF SCHISTOSOMIASIS
1. Countries 2. Countries eligible 3. Countries eligible
4. Countries that
eligible for for elimination as a for elimination
GROUP have achieved
control of public health (interruption of
elimination
morbidity problem transmission)
Elimination
Elimination as a public Post-elimination
Goal Control of morbidity (interruption of
health problem surveillance
transmission)
Intensified preventive V Surveillance to detect
Preventive Adjusted preventive
chemotherapy in E and respond to
chemotherapy chemotherapy
residual areas of R resurgence of
Recommende
transmission I transmission and to
d Complementary Complementary public
F prevent reintroduction
Intervention public health health interventions
Complementary public I (schistosomiasis
interventions, strongly
health interventions C should be made
where possible recommended
essential A notifiable)
100% geographical T
coverage and at I
least 75% national O
Prevalence of heavy-
coverage N
intensity infection Reduction of incidence Incidence of infection
Target
<1% in all sentinel of infection to zero remains zero
Prevalence of
sites
heavy-intensity
infection <5%
across sentinel sites
Group Up to 5-10 years Until all countries have
Up to 3-6 years from Up to 5 years from
progression from joining the interrupted
joining the group joining the group
(1 to 4) group transmission
ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES OF STAKEHOLDERS IN SUPPORT OF DISEASE PREVENTION AND
HELMINTH CONTROL PROGRAMS IN THE PHILIPPINES
STAKEHOLDER ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES
Formulate policies and control programs
DOH
Provide opportunity for capacity building (LGU and school health staff
Capacity building (BHWs, local health unit and hospital staff, local officials) for
implementation, surveillance, and monitoring of policies and control programs at the local
LGU level
Forge partnerships and spearhead advocacy, social mobilization, program marketing at the
local level
Capacity building (direct involvement of trained teachers in drug distribution and
administration) for implementation of control programs in the school setting
DEPED
Advocacy (advocacy meetings through parent-teacher assemblies, health education, and
information dissemination)
Capacity building (assistance of day care workers in drug distribution and administration)
DSWD
Advocacy (health education and information dissemination to parents)
Technical assistance
INTERNATIONAL Logistical support
AGENCIES Academic institutions
AND Research for policy generation
ACADEMIC Monitoring and evaluation of control programs and initiatives
INSTITUTIONS Capacity building
Advocacy
Technical assistance
PRIVATE SECTOR
Logistical support
(MEDIA, SOCIO-
Advocacy (program marketing)
CIVIC GROUPS,
Social mobilization
NGOS)
Research (NGOs)
APPENDIX
Distribution of Schistosoma Infection by Age Group, Sex and Year
Transcribers: BLANCO, CAHANDING, CINCO ♥ FARILLAS, SOLIS Page 13 of 15
NATIONAL SCHISTOSOMIASIS CONTROL AND ELIMINATION PROGRAM 1.7
NOTE: SCHISTOSOMIASIS IS MOST PREVALENT IN THE 15 to 49 AGE GROUP AND IN MALES.
WHO CLASSIFICATION OF THE DIFFERENT COMMUNITIES BASED ON THEIR RISKS
CATEGORY PREVALENCE OF ANY
ACTIONS TO BE TAKEN
SCHISTOSOMIASIS
INFECTION AMONG SCHOOL-
SCHOOL AGE CHILDREN ADULTS
AGED CHILDREN
High-risk > 50% by parasitological methods Treat all school age children Treat adults considered to
community (intestinal and urinary (enrolled and not enrolled) once be at risk (from special
schistosomiasis) a year groups to entire
communities living in
endemic areas)
Moderate- > 10 and < 50% by pathological Treat all school age children Treat adults considered to
risk methods (intestinal and urinary (enrolled and not enrolled) twice be at risk (from special
community schistosomiasis) a year groups to entire
communities living in
endemic areas)
Low-risk < 10% by parasitological methods Treat all school age children Praziquantel should be
community (intestinal and urinary (enrolled and not enrolled) twice available in dispensaries and
schistosomiasis) during their primary schooling clinics for treatment of
age (e.g. once on entry & once suspected cases
on exit)
NSCP TARGETS AND PROGRAM ACCOMPLISHMENTS (!!!!)
STRATEGIC BASELINE ACCOMPLISHMENT
INDICATOR TARGETS
OBJECTIVES (2009) 2013 2014 2015 2016
Prevalence Rate (%) of
4.3 % <1% 2% 1.4% <1%
Schistosmiasis
Schistosomiasis Number of Provinces
in endemic areas with Enhanced Control
is eliminated for Elimination of 0 5 0 0 5
Schistosomiasis as a
public health problem.
Coverage in MDA Coverage of 85% in
is increased in MDA among exposed 85%
30% 44% 57% 85%
endemic population (5-65 years (Annual)
provinces old)
THE FOUR PRONGED APPROACH
Transcribers: BLANCO, CAHANDING, CINCO ♥ FARILLAS, SOLIS Page 14 of 15
NATIONAL SCHISTOSOMIASIS CONTROL AND ELIMINATION PROGRAM 1.7
CATEGORY OF AREAS BASED ON LEVEL OF PREVALENCE
LOW TO MODERATE (>1% ELIMINATION LEVEL (<1%
PREVALENCE) PREVALENCE)
Surigao Norte (8.1%-2012) Davao del Sur (0 %-2013)
Agusan Sur (3.7%-2012) Bohol (0 %)
Agusan Norte (14.2%-2011) Zamboaga del Norte (0%)
North Cotabato (1.6%-2013) Davao Oriental (0.6%)
Compostela Valley (1%) Davao City (0 %-2013)
North Leyte (1.8%-2013) South Cotabato (0.8%-2013)
North Samar (5.4%) Mindoro Oriental (0 .3%-2013)
Eastern Samar (4%- 2013) Davao del Norte (0.7%)
TARGET West Samar (5.5%) Sultan Kudarat (0%-2013)
AREAS Bukidnon (5.8%) Maguindanao (0.1%)
Lanao del Norte (3.3%) Zamboanga de Sibugay (0%-2013)
Zamboanga del Sur (1%)
Lanao Sur (1%)
Cagayan (2.7%)
Sorsogon (3.3%)
Negros Occidental (4.8%)
Misamis Occidental (1.3%)
Surigao del Sur (2%)
Elimination Level: <1%;
Low: >1% but <10%;
Moderate: >10% but <50%;
High: >50%
PROGRAM THRUSTS MAJOR ACTIVITIES
Preventive Chemotherapy and Clinical Practice Guidelines (CPG) Dissemination to Public and Private sectors
Infection Control MDA in all endemic areas
Capability building of LGU and other partners in Malacological surveillance and
Transmission Control
control and environmental sanitation
Advocacy and Social Integrated forum on Schistosomiaisis, STH, FWBD and Environmental
Mobilization Sanitation for LGU and other partners (Luzon/Visayas and Mindanao Cluster)
Focal Prevalence Survey in some Provinces and Assessment of 5 Areas who
Monitoring and Evaluation have reached elimination
Pre-Post MDA program review
Public-Private/P2P Partnership Engagement of Technical partners in various projects
Different Areas of Research and Investigation in a study entitled, Development of a Registry for
Neuroschistosomiasis, Philippines, June 2013-2014
ACTIVITIES PARTNER TARGET REMARKS
a. Neuroschistosomiasis Registry Academe 2 Provinces Ongoing
b. Zero surveillance Academe 12 Provinces Ongoing
c. Evaluation of areas under the DZFI Academe 5 Provinces 2-Ongoing
3-To start 2nd quarter
(2014)
d. Evaluation of endemic areas after a minimum of 5 years of Academe 22 Provinces To start 2nd quarter
PC (Focal surveys) (2014)
Transcribers: BLANCO, CAHANDING, CINCO ♥ FARILLAS, SOLIS Page 15 of 15
You might also like
- Medical Parasitology QuestionsDocument5 pagesMedical Parasitology Questionsskeltenboi77% (22)
- Case 2Document4 pagesCase 2Patrícia Martins25% (4)
- Surgery Final NotesDocument81 pagesSurgery Final NotesDETECTIVE CONANNo ratings yet
- LDTDocument6 pagesLDTRaian SuyuNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Respiratory Cases: DR Hodan S. Ahmed, Department of Pediatrics and Child Health, Amoud Medical School, AUDocument24 pagesPediatric Respiratory Cases: DR Hodan S. Ahmed, Department of Pediatrics and Child Health, Amoud Medical School, AUmukhtar abddiNo ratings yet
- Anes Preoperative-AssessmentDocument6 pagesAnes Preoperative-AssessmentChristine Mendoza100% (1)
- 7 RespirationDocument15 pages7 RespirationCLEMENTNo ratings yet
- The Sense of HearingDocument22 pagesThe Sense of HearingarkabbotNo ratings yet
- Pma Code of EthicsDocument40 pagesPma Code of Ethicsmaydansayco100% (1)
- Gynecology 1.1 - History-Taking, Physical Examination, and Office GynecologyDocument9 pagesGynecology 1.1 - History-Taking, Physical Examination, and Office GynecologyZaza100% (2)
- Schistosoma in Egypt: Prepared By: 407-417 Supervised byDocument24 pagesSchistosoma in Egypt: Prepared By: 407-417 Supervised byBahaa Shaaban100% (1)
- Physiology Lab 2 FinalDocument3 pagesPhysiology Lab 2 Finalaileen agustin100% (6)
- Approach To The Patient With Endocrine DisordersDocument17 pagesApproach To The Patient With Endocrine Disordersseun williamsNo ratings yet
- Bland Aerosol TherapyDocument9 pagesBland Aerosol TherapyRyl WonNo ratings yet
- Incentive SpirometryDocument2 pagesIncentive SpirometryAlyssa LeonesNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System AnatomyDocument49 pagesRespiratory System AnatomyHiraya WNo ratings yet
- Ymphatic Ystem: Natomy AND HysiologyDocument7 pagesYmphatic Ystem: Natomy AND Hysiologydlneisha61No ratings yet
- Aerosoltherapy Nebu 120503115712 Phpapp01Document65 pagesAerosoltherapy Nebu 120503115712 Phpapp01Aan Ika SugathotNo ratings yet
- 3mijares - TransesDocument9 pages3mijares - TransesJüdith Marie Reyes BauntoNo ratings yet
- SCHISTOSOMIASISDocument3 pagesSCHISTOSOMIASISsands32No ratings yet
- Anaesthesia and CopdDocument7 pagesAnaesthesia and CopdAshish PandeyNo ratings yet
- 161111163114Document31 pages161111163114lejizixNo ratings yet
- Advanced Airway ControlDocument1 pageAdvanced Airway ControlBrett FieldsNo ratings yet
- Mechvent Review (Topnotcher)Document284 pagesMechvent Review (Topnotcher)Inimical G100% (1)
- Cystic Fibrosis Final AssignmentDocument6 pagesCystic Fibrosis Final AssignmentSteg250No ratings yet
- Pulm Board ReviewDocument19 pagesPulm Board ReviewAli LaftaNo ratings yet
- Programme 63rd Annual Conference of WACS, Lome, TogoDocument51 pagesProgramme 63rd Annual Conference of WACS, Lome, TogoAchille DoleagbenouNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Salivary GlandsDocument62 pagesPathophysiology Salivary GlandsDwi Rizky LestariNo ratings yet
- Surg MCQDocument17 pagesSurg MCQzhahmy0% (1)
- Recognizining Individuals of Plant PopulationDocument11 pagesRecognizining Individuals of Plant PopulationFatima GraceNo ratings yet
- RT Board Examination - Table of SpecificationsDocument21 pagesRT Board Examination - Table of SpecificationsCPD MASNo ratings yet
- Pathology Cases 6Document21 pagesPathology Cases 6infobusiness2010No ratings yet
- Mechanical Ventilation: Standard Weaning Criteria (Respiratory Therapy)Document6 pagesMechanical Ventilation: Standard Weaning Criteria (Respiratory Therapy)S3DOSHA osmanNo ratings yet
- Catheter Related InfectionsDocument581 pagesCatheter Related InfectionshardboneNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Labyrinth by DR Inam Ur RehmanDocument29 pagesAnatomy of Labyrinth by DR Inam Ur RehmanasssadulllahNo ratings yet
- Circulatory Shock: Santosh DevDocument32 pagesCirculatory Shock: Santosh DevdevdsantoshNo ratings yet
- Bombay Blood Group - Case ReportDocument3 pagesBombay Blood Group - Case ReportPremier PublishersNo ratings yet
- What'S The Antagonist Meaning?Document2 pagesWhat'S The Antagonist Meaning?Lenchie GayramonNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic 4 SurgicalDocument3 pagesAntibiotic 4 SurgicalNanaDinaWahyuniNo ratings yet
- Anaesthetic Consideration For Neonatal Surgical emDocument7 pagesAnaesthetic Consideration For Neonatal Surgical emLong LongNo ratings yet
- Medicine I: 1. General Data / Patient InformationDocument3 pagesMedicine I: 1. General Data / Patient InformationMadeline SibuloNo ratings yet
- Krok 2 - 2014 (Therapy)Document74 pagesKrok 2 - 2014 (Therapy)areenNo ratings yet
- Poisoning DecontaminationDocument14 pagesPoisoning DecontaminationadystiNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry: Hematology Values Red Blood Cell ValuesDocument2 pagesGeneral Chemistry: Hematology Values Red Blood Cell ValuesDanica ZaragozaNo ratings yet
- VACTERL-association EN PDFDocument12 pagesVACTERL-association EN PDFAuliaRahmanNo ratings yet
- Thromboembolic Disease PDFDocument5 pagesThromboembolic Disease PDFBáĦẳá Y. Ẳl-mársǾúmiNo ratings yet
- LAMU Term 1B IMED Written ExamDocument12 pagesLAMU Term 1B IMED Written ExamSecret AgentNo ratings yet
- Actinomycosis: Mohanad N. Saleh 6 Year Meical Student Supervisor: Dr. Anas MuhannaDocument19 pagesActinomycosis: Mohanad N. Saleh 6 Year Meical Student Supervisor: Dr. Anas MuhannaMohanad SalehNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) Analysis PDFDocument4 pagesArterial Blood Gas (ABG) Analysis PDFAshriiwati ArlandNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal QuestionsDocument4 pagesMusculoskeletal QuestionsJen Del Mundo100% (1)
- Cerebrovascular Accident ReportDocument16 pagesCerebrovascular Accident ReportAngelu Gabrielle CastroNo ratings yet
- New Fluid and Electrolytes Therapy Toyinoriginali2againDocument55 pagesNew Fluid and Electrolytes Therapy Toyinoriginali2againt.baby100% (1)
- GIT Applied AnatomyDocument62 pagesGIT Applied Anatomyueumana0% (1)
- Soil Transmitted Helminth PDFDocument90 pagesSoil Transmitted Helminth PDFMinarni HoNo ratings yet
- Preoperative Preparation of Patient For SurgeryDocument23 pagesPreoperative Preparation of Patient For SurgeryFauzi SebunyaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Notes and SlideDocument33 pagesRespiratory Notes and SlideChristina Gonez100% (1)
- MCQ PneuDocument60 pagesMCQ PneuYanesh Bishundat0% (1)
- Chapter 2 QUALITY AND EVIDENCE BASE RESPIRATORY CAREDocument11 pagesChapter 2 QUALITY AND EVIDENCE BASE RESPIRATORY CAREShanin Salapuddin100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Respiratory Therapy 2 (RT 59) - LaboratoryDocument18 pagesFundamentals of Respiratory Therapy 2 (RT 59) - LaboratoryLezahnor CasibangNo ratings yet
- Immunology: QuestionsDocument41 pagesImmunology: Questionsgamelat Official100% (1)
- SCHISTOSOMIASIS abradDocument36 pagesSCHISTOSOMIASIS abradakramdoc1982No ratings yet
- Schistosoma MansoniDocument3 pagesSchistosoma MansoniVanessa Mae RaraNo ratings yet
- Lopez vs. ErictaDocument8 pagesLopez vs. ErictaZazaNo ratings yet
- Ricafort vs. DicdicanDocument46 pagesRicafort vs. DicdicanZazaNo ratings yet
- Forest Hills Vs Vertex SalesDocument5 pagesForest Hills Vs Vertex SalesZazaNo ratings yet
- Baltazar vs. Lingayen GulfDocument7 pagesBaltazar vs. Lingayen GulfZazaNo ratings yet
- Asian Terminals Inc vs. Simon Enterprises, IncDocument1 pageAsian Terminals Inc vs. Simon Enterprises, IncZazaNo ratings yet
- Lambert v. FozDocument3 pagesLambert v. FozZazaNo ratings yet
- Makati Sports v. ChengDocument7 pagesMakati Sports v. ChengZazaNo ratings yet
- RADIOLOGY 2.1e Skull FracturesDocument1 pageRADIOLOGY 2.1e Skull FracturesZazaNo ratings yet
- Med 1.11 - SleDocument5 pagesMed 1.11 - SleZazaNo ratings yet
- UCPB General Insurance vs. Aboitiz Shipping Corporation, Et - AlDocument2 pagesUCPB General Insurance vs. Aboitiz Shipping Corporation, Et - AlZazaNo ratings yet
- Gynecology 1.3 Human SexualityDocument8 pagesGynecology 1.3 Human SexualityZazaNo ratings yet
- Gynecology 1.5 AddendumDocument1 pageGynecology 1.5 AddendumZazaNo ratings yet
- ENT 1.2 Diseases of The Nose, Paranasal Sinuses, and Face PDFDocument18 pagesENT 1.2 Diseases of The Nose, Paranasal Sinuses, and Face PDFZazaNo ratings yet
- ENT 1.3 Lips and Oral CavityDocument15 pagesENT 1.3 Lips and Oral CavityZazaNo ratings yet
- MUST To KNOW in ParasitologyDocument22 pagesMUST To KNOW in ParasitologyTristan Jay CalabiaNo ratings yet
- Prevention and Control of Disease TransmissionsDocument79 pagesPrevention and Control of Disease Transmissionshemed0% (1)
- Parasitology Lecture 1Document84 pagesParasitology Lecture 1Dr Sarah Bakhsh - Resident FCPS Community MedicineNo ratings yet
- Antihelmintic DrugsDocument79 pagesAntihelmintic DrugsDr. Hashibu SsekweyamaNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Schistosomiasis Lecture SMunsakaDocument39 pages3.0 Schistosomiasis Lecture SMunsakaTrophimus KangwaNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Table Review 3Document9 pagesParasitology Table Review 3Dustin DietNo ratings yet
- ParasiticvaccineDocument10 pagesParasiticvaccineRajesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Activity 9 Phylum NematodaDocument18 pagesActivity 9 Phylum Nematodanicole syNo ratings yet
- Schistosomiasis: Caused by Blood Flukes (Trematode Worms) of The Genus SchistosomaDocument2 pagesSchistosomiasis: Caused by Blood Flukes (Trematode Worms) of The Genus SchistosomakyawNo ratings yet
- Table For Cestodes and TrematodesDocument5 pagesTable For Cestodes and TrematodesMafie Barreiro100% (4)
- PDF The Behavioural Ecology of Parasites First Edition E. E. Lewis (Editor) DownloadDocument60 pagesPDF The Behavioural Ecology of Parasites First Edition E. E. Lewis (Editor) Downloadstrennteeme100% (11)
- Pathophysiology Schistosomiasis: Table in New WindowDocument7 pagesPathophysiology Schistosomiasis: Table in New WindowKaren Leigh MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Paralec MergedDocument63 pagesParalec MergedJim-in Jim-outNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Pharmacology ToxicologyDocument4 pagesVeterinary Pharmacology ToxicologyAgus BurhamNo ratings yet
- World Health Organization - Training Manual On Diagnosis of Intestinal Parasites - Tutor's Guide-StationeryDocument180 pagesWorld Health Organization - Training Manual On Diagnosis of Intestinal Parasites - Tutor's Guide-StationeryHadish BekuretsionNo ratings yet
- Types of ParasitesDocument39 pagesTypes of ParasitesDavid Hero BarrientosNo ratings yet
- Phylum PlatyhelminthesDocument13 pagesPhylum PlatyhelminthesGerard JaposNo ratings yet
- 03 SchistosomesDocument16 pages03 SchistosomesAlvin LaurenceNo ratings yet
- PARASITOLOGYDocument35 pagesPARASITOLOGYMcarl Matel100% (8)
- SudomoDocument12 pagesSudomoAji Dwi SNo ratings yet
- WaterResources AgriculturalDocument10 pagesWaterResources AgriculturalCông AnNo ratings yet
- 6 PlatyhelminthesDocument19 pages6 PlatyhelminthesHarun Ft KencolNo ratings yet
- ZLY 111-4 Phylum Platyhelminthes_lecture PptDocument29 pagesZLY 111-4 Phylum Platyhelminthes_lecture Pptajibadeashrof2004No ratings yet
- Timeline of The History of PARASITOLOGYDocument5 pagesTimeline of The History of PARASITOLOGYScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Acta TropicaDocument7 pagesActa TropicaThodoris ArgirakisNo ratings yet
- FCM 1.7 - NSCEP (Schistosomiasis) PDFDocument15 pagesFCM 1.7 - NSCEP (Schistosomiasis) PDFZazaNo ratings yet
- DISTOCIDDocument2 pagesDISTOCIDmahgadNo ratings yet
- Parasitic Disease (Schistosomiasis)Document15 pagesParasitic Disease (Schistosomiasis)Brijesh Singh YadavNo ratings yet
- S. Japonicum or Oriental Lung FlukeDocument4 pagesS. Japonicum or Oriental Lung FlukeMon Kristoper CastilloNo ratings yet