Schematic Pathophy Dka
Schematic Pathophy Dka
Uploaded by
Maria Francheska OsiCopyright:
Available Formats
Schematic Pathophy Dka
Schematic Pathophy Dka
Uploaded by
Maria Francheska OsiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Schematic Pathophy Dka
Schematic Pathophy Dka
Uploaded by
Maria Francheska OsiCopyright:
Available Formats
SUMAGUE, Maria Francheska O.
BSN 4
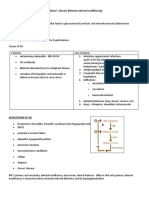
DIABETIC KETOACIDOSIS
Absolute Insulin
Deficit
Lack of insulin to Glucose remains in
suppress lipolysis blood not being
allows the body to utilized by muscle
start producing and fat cells
energy from
Hypothalamic cells
triglycerides
sense low
intracellular
glucose, triggering Decrease of
hunger glucose in cells
Release of free fatty
increase the
acids from adipose
release of
tissue
glucagon,
Polyphagia epinephrine,
cortisol and growth
hormone
Hydrolysis of free
fatty acids in the
liver
Body tries to
increase blood
glucose to increase
cell glucose
absorption
Decreased
protein
synthesis
Increased
proteolysis in Increase
muscle gluconeogenesis
and increased
glycogenolysis in
liver
Hyperglycemia
Less than 12 mmol/L
and increased
glucose filtration,
increased urine
Glucosuria
Glucose in filtrate
promotes osmotic
diuresis
Polyuria
Alters total
Electrolyte imbalance body water &
ion osmosis
Severe Dehydration
Polydipsia If pt alert & H2O
is accessible
Decreased ECF
volume concentrates
Metabolic Acidosis
ketone bodies,
exacerbates acidosis
Disrupts enteric Blowing off CO2 Breathing Disruption of
nervous system, to try to offset off ketones electrical signaling in
decreased emptying acidosis brain, spinal cord
of ileus and nerves
Ketone breath
Kussmaul
(fruity odor)
Abdominal Nausea, respiration
Weakness/
pain Vomiting Confusion
Reference:
Cheever, K. H., & Hinkle, J. L. (2018). Brunner & Suddarth's textbook of medical-surgical nursing.
Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer.
You might also like
- All Quiz QuestionsDocument60 pagesAll Quiz QuestionsMorgan ChristNo ratings yet
- Clareblend Mini BrochureDocument2 pagesClareblend Mini BrochureHO AndjeliNo ratings yet
- Newsletter Spring 2006Document4 pagesNewsletter Spring 2006786lailaNo ratings yet
- CKD Treated With Dialysis Case Study 18 MNT 409 - 2Document3 pagesCKD Treated With Dialysis Case Study 18 MNT 409 - 2api-240419901No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of NephrosclerosisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of NephrosclerosisJessica Damasen Caballero0% (1)
- Eritro Papulo Skuamosa 2021Document47 pagesEritro Papulo Skuamosa 2021Yolanda Agnesia Purba0% (1)
- Formulir Permintaan Dan Hasil Pemeriksaan Laboratorium KlinikDocument3 pagesFormulir Permintaan Dan Hasil Pemeriksaan Laboratorium KlinikMUKTI HUSADA100% (2)
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis:: Evidence Based ReviewDocument4 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis:: Evidence Based ReviewgracedumaNo ratings yet
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument13 pagesDiabetic KetoacidosisMabelle Blancada ConsultaNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis in PaediatricDocument11 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis in PaediatricSana Anam JahanNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Pregnancy: Diagnosis of DKADocument7 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis in Pregnancy: Diagnosis of DKA123someone123No ratings yet
- Case Presentation: Andreas Crede EM RegistrarDocument15 pagesCase Presentation: Andreas Crede EM RegistrarHeru WahyudiNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)Document9 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)Tan DavidNo ratings yet
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument27 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosisjun sianNo ratings yet
- DkaDocument38 pagesDkaHam SotheaNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) & Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State (HHS)Document36 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) & Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State (HHS)Ismail GunawanNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (D.K.A) Beaumont Hospital Protocol: DiagnosisDocument1 pageDiabetic Ketoacidosis (D.K.A) Beaumont Hospital Protocol: Diagnosislouglee9174100% (1)
- Glomerulonephritis 10Document5 pagesGlomerulonephritis 10Eden Jay Calija AgoyNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was Shared Via: HypoparathyroidismDocument1 pageThis Study Resource Was Shared Via: HypoparathyroidismDeo FactuarNo ratings yet
- 128 Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument9 pages128 Diabetic KetoacidosisDite Bayu NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology DKADocument2 pagesPathophysiology DKALovely CacapitNo ratings yet
- Hyperkalemia 1Document26 pagesHyperkalemia 1ksNo ratings yet
- Dka & HHS: Ketoasidosis Diabetikum & Hiperosmolaritas Hyperglikemik StageDocument17 pagesDka & HHS: Ketoasidosis Diabetikum & Hiperosmolaritas Hyperglikemik StageAmeel BubbleeNo ratings yet
- Hypokalemia 180813073624Document26 pagesHypokalemia 180813073624korotkofNo ratings yet
- DkaDocument29 pagesDkaShadowSpectre0No ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis Case StudyDocument6 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis Case StudyJohn AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury-An UpdateDocument99 pagesAcute Kidney Injury-An UpdateProf Brigadier Mamun MostafiNo ratings yet
- 4.1agents For Hyperuricemia GoutDocument4 pages4.1agents For Hyperuricemia GoutjohntrueNo ratings yet
- Patho Case Study CirrhosisDocument2 pagesPatho Case Study Cirrhosismgomez27No ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) : Abdirahman Nour Mmed Internal MedicineDocument48 pagesAcute Kidney Injury (AKI) : Abdirahman Nour Mmed Internal MedicineMohamoud MohamedNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit Nursing ManagementDocument5 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Nursing ManagementA.No ratings yet
- Drug-Induced Renal FailureDocument14 pagesDrug-Induced Renal FailureFiorella Mamani Acero100% (1)
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument4 pagesDiabetic KetoacidosisHasan A. AsFourNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Fluid Volume Deficit R/T Active Fluid Loss (Increased Urine Output)Document9 pagesNursing Care Plan: Fluid Volume Deficit R/T Active Fluid Loss (Increased Urine Output)Gayu Patel0% (1)
- Increased Serum Glucose Level (Hyperglycemia) 278.14 MG/DL (Normal: 70-100 MG/DL)Document3 pagesIncreased Serum Glucose Level (Hyperglycemia) 278.14 MG/DL (Normal: 70-100 MG/DL)Angel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- DKADocument12 pagesDKAAisha SyedNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument15 pagesDiabetes Mellitusfayeniwa100% (1)
- Case Study 18 CKDDocument7 pagesCase Study 18 CKDapi-301049551No ratings yet
- Anemia 130809044630 Phpapp01Document21 pagesAnemia 130809044630 Phpapp01Siddharth Das100% (1)
- Case Study - Chronic Kidney Disease Treated With DialysisDocument7 pagesCase Study - Chronic Kidney Disease Treated With Dialysisapi-387604918100% (1)
- PhysioEx Exercise 2 Activity 1Document5 pagesPhysioEx Exercise 2 Activity 1PatriNo ratings yet
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument22 pagesDiabetic KetoacidosispoktaviantiNo ratings yet
- KNH 411 - Case Study 22Document17 pagesKNH 411 - Case Study 22api-301118772100% (3)
- Regulation of Blood GlucoseDocument5 pagesRegulation of Blood GlucoseSwathi PariNo ratings yet
- 1778 Uralyt U 1331882845Document5 pages1778 Uralyt U 1331882845James HornerNo ratings yet
- DiverticulitisDocument2 pagesDiverticulitisyapyapvinx50% (2)
- Unit 1-B5Document28 pagesUnit 1-B5Jan Marsha Marie DomiquelNo ratings yet
- Diabetic and Endocrine EmergenciesDocument21 pagesDiabetic and Endocrine Emergenciesjoko5157No ratings yet
- Department of Kriyasharir: Mahatma Gandhi Ayurved College Hospital & Research Centre Salod (H), WardhaDocument39 pagesDepartment of Kriyasharir: Mahatma Gandhi Ayurved College Hospital & Research Centre Salod (H), WardhaAvanti ShendurjaneNo ratings yet
- Hemodialysis: Carina Joane Villareal-Barroso, R.N.,M.NDocument108 pagesHemodialysis: Carina Joane Villareal-Barroso, R.N.,M.NJune BarsNo ratings yet
- SIADH, DI, Cerebral Salt WastingDocument20 pagesSIADH, DI, Cerebral Salt Wastingmaged_najehNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Emergencies in The ICUDocument47 pagesEndocrine Emergencies in The ICUchadchimaNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis: 4 Signs of DKA: Acidosis (Metabolic, Raised Anion Gap), Ketosis, Dehydration and HyperglycaemiaDocument3 pagesDiabetic Ketoacidosis: 4 Signs of DKA: Acidosis (Metabolic, Raised Anion Gap), Ketosis, Dehydration and HyperglycaemiajsdlzjNo ratings yet
- Addison's DiseaseDocument9 pagesAddison's Diseaseash ashNo ratings yet
- EndometriosisDocument6 pagesEndometriosissalamredNo ratings yet
- Dka Patho DiagramDocument1 pageDka Patho DiagramGrae TaclobNo ratings yet
- Addison's Disease (Primary Adrenal Insufficiency)Document5 pagesAddison's Disease (Primary Adrenal Insufficiency)sunnnydayNo ratings yet
- Ventricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandVentricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram Book Based: Diet: Preferences For SweetsDocument1 pageSchematic Diagram Book Based: Diet: Preferences For SweetsarnnieNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Pancreas: Regulate Blood Glucose - The Fuel ThatDocument2 pagesAnatomy of The Pancreas: Regulate Blood Glucose - The Fuel ThatSkyerex100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Syndrome EtiologyDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Syndrome EtiologyJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Endocrine DisordersDocument2 pagesEndocrine DisordersRalph Elvin MacanlalayNo ratings yet
- Concept Map MarwahDocument5 pagesConcept Map MarwahAsniah Hadjiadatu AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Assessment Using Functional Health Patterns: AppendixDocument16 pagesAssessment Using Functional Health Patterns: AppendixNalzaro Emyril89% (19)
- Pathophysiology CKD - DrawioDocument54 pagesPathophysiology CKD - DrawioGwyneth CiriloNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Explanation of The Problem Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Sto: StoDocument5 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Explanation of The Problem Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Sto: StoMaria Francheska OsiNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology: SeptumDocument2 pagesPathophysiology: SeptumMaria Francheska OsiNo ratings yet
- CV Disease Drug StudyDocument11 pagesCV Disease Drug StudyMaria Francheska OsiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Comp: Nursing DiagnosisDocument1 pageRespiratory Comp: Nursing DiagnosisMaria Francheska OsiNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMaria Francheska OsiNo ratings yet
- Injection: 10 MG/ML Oral Solution: 10 Tablets: 20 MG, 40Document4 pagesInjection: 10 MG/ML Oral Solution: 10 Tablets: 20 MG, 40Maria Francheska OsiNo ratings yet
- Beta-Adrenergic Blockers: Increased Risk: Tablets: 2.5 MG, 5Document2 pagesBeta-Adrenergic Blockers: Increased Risk: Tablets: 2.5 MG, 5Maria Francheska OsiNo ratings yet
- Building Your Immune System: What Is Healthy Eating? What Food Should I Eat?Document3 pagesBuilding Your Immune System: What Is Healthy Eating? What Food Should I Eat?Maria Francheska OsiNo ratings yet
- OB Ward DRUG STUDYDocument1 pageOB Ward DRUG STUDYMaria Francheska OsiNo ratings yet
- School Nursing Common DRUG STUDYDocument10 pagesSchool Nursing Common DRUG STUDYMaria Francheska OsiNo ratings yet
- NCP TemplateDocument2 pagesNCP TemplateMaria Francheska OsiNo ratings yet
- Actual Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesActual Nursing Care PlanMaria Francheska OsiNo ratings yet
- PE NotesDocument1 pagePE NotesMaria Francheska Osi100% (1)
- Potential Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesPotential Nursing Care PlanMaria Francheska OsiNo ratings yet
- Program Report For 1999Document192 pagesProgram Report For 1999IRRI_resourcesNo ratings yet
- Sodium Hydroxide Liquid 31% 50%: Safety Data SheetDocument9 pagesSodium Hydroxide Liquid 31% 50%: Safety Data SheetDhani ArdianNo ratings yet
- The Smart Book For Mum and Dad PDFDocument127 pagesThe Smart Book For Mum and Dad PDFRe MarkNo ratings yet
- The Landscape Reporter: Turf TalkDocument3 pagesThe Landscape Reporter: Turf Talkmartha_goleaNo ratings yet
- PropoxypheneDocument3 pagesPropoxypheneapi-3797941No ratings yet
- HuntersWoodsPH Science Reviewer Set ADocument21 pagesHuntersWoodsPH Science Reviewer Set AScc Balayong ESNo ratings yet
- Online Game Addiction Among Senior High School Students SnhsDocument29 pagesOnline Game Addiction Among Senior High School Students SnhsEunsang Lee86% (7)
- US Sales of Herbal Supplements Increase by 9.7% in 2021Document14 pagesUS Sales of Herbal Supplements Increase by 9.7% in 2021Stanford LeeNo ratings yet
- Learning From Incomplete Training Data With Missing Values and Medical ApplicationDocument4 pagesLearning From Incomplete Training Data With Missing Values and Medical ApplicationSher Afghan MalikNo ratings yet
- Assessment 3 Miranda Bsma1 6 PDFDocument4 pagesAssessment 3 Miranda Bsma1 6 PDFEloise Dorothy PatiñoNo ratings yet
- 90Document11 pages90Eka Nurul HayatiNo ratings yet
- Children Exposed To Violence: Caryn Brauweiler, LCSW Debbie Conley, LCSWDocument59 pagesChildren Exposed To Violence: Caryn Brauweiler, LCSW Debbie Conley, LCSWIman MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Amodia - Purposive CommunicationDocument7 pagesAmodia - Purposive CommunicationCLUVER AEDRIAN AMODIANo ratings yet
- Tuberculosis With Discordant Drug Resistance Patterns - A Diagnostic DilemmaDocument4 pagesTuberculosis With Discordant Drug Resistance Patterns - A Diagnostic DilemmaKevinNo ratings yet
- July MCQ-2023 - 230922 - 091408Document55 pagesJuly MCQ-2023 - 230922 - 091408Maria SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Eval-Matrix ShortGuide FinalDocument2 pagesEval-Matrix ShortGuide FinalAngele Hema MarajNo ratings yet
- Fluids in Surgery 1 1Document43 pagesFluids in Surgery 1 1محمد عماد عليNo ratings yet
- Herpes ZosterDocument42 pagesHerpes ZostermehranerezvaniNo ratings yet
- Summary of MH Screening and Assessment Tools For Primary CareDocument20 pagesSummary of MH Screening and Assessment Tools For Primary CareTeresa Meehan100% (1)
- MPC 002 AssignmentsDocument22 pagesMPC 002 AssignmentsAshwati JayakrishnanNo ratings yet
- A Case of Short Root Anomaly - 2006Document5 pagesA Case of Short Root Anomaly - 2006Rocio HerreraNo ratings yet
- State of The City Address 2014 of Mayor Belen FernandezDocument49 pagesState of The City Address 2014 of Mayor Belen FernandezbalondagupanNo ratings yet
- TinitusDocument4 pagesTinitusFridaZorayaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Focus On FunctionDocument100 pagesAssessment Focus On FunctionAngel FiloteoNo ratings yet
- Avanced Lipoproteins Reserch 2017Document108 pagesAvanced Lipoproteins Reserch 2017Carlos SorianoNo ratings yet