Name of The Experiment: Introduction To Series and Parallel Circuits
Uploaded by
mir rownakName of The Experiment: Introduction To Series and Parallel Circuits
Uploaded by
mir rownakBRAC UNIVERSITY
CSE250: Circuits and Electronics
Laboratory
EXPERIMENT NO.: 2
Name of the Experiment: Introduction to series and parallel circuits.
OBJECTIVE: The experiment is to acquaint the students with series-parallel circuits and to give
them the idea about how to connect different circuits in bread board.
THEOREM:
An electrical circuit is a continuous path or array of paths through which an electrical current can flow.
The two different ways in which components of a circuit can be connected are called "series" and
"parallel". In a series connection, components are connected one after another; therefore, the same
current flows through all of them. In a parallel connection, the circuit components are connected side
by side. That is, the positive and negative sides of each component are respectively connected together;
therefore, each has the same potential drop across. In this lab, we will explore measurements of current
and potential difference in simple circuits. Also, we will attempt to verify the textbook expressions for
the equivalent resistance of components connected in series and in parallel, and for the power
dissipation in a resistive load. For instance, for a circuit consisting of any three resistance values R 1,
R2, R3, the equivalent resistance in series RS and in parallel RP are,
RS = R1 + R2 + R3 + … + RN (1)
1/ RP = 1/ R1 + 1/ R2 + 1/ R3 + … + 1/ RN (2)
APPARATUS :
DC power supplies
Resistors
Bread board/ Trainer board
Multimeter
PROCEDURES:
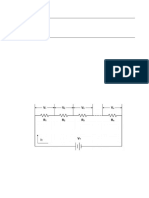
1) Set up the circuit as in the following Figures:
.
2) Place and connect the as shown in the circuit diagram.
3) Measure the voltage across the resistors (indicated in the circuits) and calculate the
current and record it.
REPORT:
1. Show results in tabular form.
2. Comment on the obtained results and discrepancies (if any).
CAUTIONS:
1. Don’t switch on the supply until the circuit has been checked by your teacher.
2. Take care of the reading of the apparatus.
3. Take care of any bare circuit element in energized condition.
QUESTION:
1) Using the recorded value of the resistors, calculate the value of the currents and check if there
is any discrepancies.
2) You are given six 100 ohm resistors. Arrange these resistors as to provide an effective
resistance value of 300ohm.
3) You are given two 1.5kohm resistors and six 15kohm resistors. Arrange these resistors as to
provide an effective resistance value of 3.25kohm.
REFERENCES:
1. Introduction to Electric Circuits. By
R.C. Dorf & J.A. Svoboda.
2. A Text book of Electrical
Technology, Vol. 1 By B.L Theraja
& A.K. Theraja
3. Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis
By J. D. Irwin
You might also like
- Mapúa Institute of Technology: Analysis of Resistive Network: Series-Parallel CircuitsNo ratings yetMapúa Institute of Technology: Analysis of Resistive Network: Series-Parallel Circuits10 pages
- Lenovo Thinkpad T430 Disassembly (Clean..No ratings yetLenovo Thinkpad T430 Disassembly (Clean..6 pages
- EE 2101L Experiment No. 3 Lab Report Elijah NeryNo ratings yetEE 2101L Experiment No. 3 Lab Report Elijah Nery7 pages
- EE21L-2 - Basic Electrical Engineering, LabNo ratings yetEE21L-2 - Basic Electrical Engineering, Lab11 pages
- ????? ????????? ??? ??????? ???????? Docx - Ar.enNo ratings yet????? ????????? ??? ??????? ???????? Docx - Ar.en7 pages
- SIMULATION EXPERIMENT 3 - Series and Parallel Circuit 1No ratings yetSIMULATION EXPERIMENT 3 - Series and Parallel Circuit 110 pages
- Lab Report 3: Electric Circuit Analysis I E E E - 121No ratings yetLab Report 3: Electric Circuit Analysis I E E E - 1218 pages
- Adamson University College of Engineering Electrical Engineering DepartmentNo ratings yetAdamson University College of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department8 pages
- Circuit Connection (Series and Parallel)No ratings yetCircuit Connection (Series and Parallel)4 pages
- AC-DC-Laboratory-Worksheets-for StudentsNo ratings yetAC-DC-Laboratory-Worksheets-for Students13 pages
- GeneralPhysics12 Q3 Ver4 Mod5-DIRECT-CURRENT-CIRCUITS V4No ratings yetGeneralPhysics12 Q3 Ver4 Mod5-DIRECT-CURRENT-CIRCUITS V421 pages
- Sulaimani Polytechnic University Engineering Technical College Communication DepartmentNo ratings yetSulaimani Polytechnic University Engineering Technical College Communication Department12 pages
- Batangas State University College of Engineering, Architecture & Fine ArtsNo ratings yetBatangas State University College of Engineering, Architecture & Fine Arts20 pages
- Electrical Resistance in Series and ParallelNo ratings yetElectrical Resistance in Series and Parallel10 pages
- University of The East - Caloocan College of Engineering: Series and Parallel Circuits Experiment No. 2No ratings yetUniversity of The East - Caloocan College of Engineering: Series and Parallel Circuits Experiment No. 212 pages
- Experiment #4 Series and Parallel Circuit (Resistors)No ratings yetExperiment #4 Series and Parallel Circuit (Resistors)4 pages
- Lab Manual 3 Series and Parallel Connections of Resistors _GNo ratings yetLab Manual 3 Series and Parallel Connections of Resistors _G5 pages
- 01 - Ohm's Law(1)- To Determine Experimentally the Value of Two Fixed ResistorsNo ratings yet01 - Ohm's Law(1)- To Determine Experimentally the Value of Two Fixed Resistors2 pages
- Geometric Transformations: (X) A X ,: R RNo ratings yetGeometric Transformations: (X) A X ,: R R4 pages
- Swift-X Accelerating OpenStack Swift With RDMA ForNo ratings yetSwift-X Accelerating OpenStack Swift With RDMA For10 pages
- CSE101 Chapter 3 Propagation of Information and MisinformationNo ratings yetCSE101 Chapter 3 Propagation of Information and Misinformation31 pages
- Assignment 4: Due October 19, 2016: LNZ ZNo ratings yetAssignment 4: Due October 19, 2016: LNZ Z2 pages
- Chapter 6 Part 1: Propagation of Information and Misinformation Part 1, 2 and 3 Scribe Prepared by Md. Saiful Islam (MSI)No ratings yetChapter 6 Part 1: Propagation of Information and Misinformation Part 1, 2 and 3 Scribe Prepared by Md. Saiful Islam (MSI)3 pages
- CSE101 Chapter 4 Digital Security Privacy and Law 1No ratings yetCSE101 Chapter 4 Digital Security Privacy and Law 114 pages
- Lecture Notes: Complex Variables and Laplace Transform100% (1)Lecture Notes: Complex Variables and Laplace Transform142 pages
- Elocity Potential: Elations For Treamlines and QuipotentialsNo ratings yetElocity Potential: Elations For Treamlines and Quipotentials2 pages
- Study And Analysis Of Piezo Bender For Energy Harvesting Application Using Matlab Simulink_Noor Fajwa Kamar ShahNo ratings yetStudy And Analysis Of Piezo Bender For Energy Harvesting Application Using Matlab Simulink_Noor Fajwa Kamar Shah37 pages
- Nemo Outdoor 9 50 Ext Compatible Devices May 2023No ratings yetNemo Outdoor 9 50 Ext Compatible Devices May 20238 pages
- Kaba Eye-Tech Sensor: High Performance Safety For Swing and Revolving DoorsNo ratings yetKaba Eye-Tech Sensor: High Performance Safety For Swing and Revolving Doors2 pages
- AM26LS31x Quadruple Differential Line Driver: 1 Features 3 DescriptionNo ratings yetAM26LS31x Quadruple Differential Line Driver: 1 Features 3 Description32 pages
- DTC B1608/84 Front Satellite Sensor Bus LH Initialization Incomplete Lost Communication With Front Airbag Sensor LH Front Airbag Sensor LH Initialization Incom-PleteNo ratings yetDTC B1608/84 Front Satellite Sensor Bus LH Initialization Incomplete Lost Communication With Front Airbag Sensor LH Front Airbag Sensor LH Initialization Incom-Plete7 pages
- Settings Considerations For Distance ElementsNo ratings yetSettings Considerations For Distance Elements25 pages