Class 12 - Genetics Notes
Uploaded by
Dimas HernadyClass 12 - Genetics Notes
Uploaded by
Dimas HernadyGENETIC MATERIALS
2. Copying of DNA (Replication)
Genetics is the study of heredity and hereditary variation.
DNA is copied by semi-conservative method; each DNA strand serves as a
A. DNA, GENES and CHROMOSOMES
template for synthesis of a new DNA molecule.
Gene is a length of DNA coding for a protein. Genes are on chromosomes.
Cells copy their DNA when they are going to divide.
Chromosomes are made of DNA and histone proteins. Chromosomes are
Synthesis of new DNA molecules is done by DNA polymerase enzymes.
located inside nucleus. Humans have 46
chromosomes. The two DNA strands are separated by helicase enzyme. RNA primase forms
short RNA pieces (primers) on the separated strands. Then DNA polymerase
Histone proteins help in DNA packaging and folding.
adds nucleotides to the primers to synthesise the new DNA strands.
Chromatin is the uncoiled form of chromosome.
* RNA primers are needed because DNA polymerase can’t add nucleotides if
Chromosomes are classified into 4 according to there is no existing nucleotides.
their shapes;
One of the new DNA strands is synthesized continuously (leading strand) and
Metacentric; both chromosome arms have the other one is synthesized non-continuously (lagging strand) as short pieces of
same length DNA called Okazaki fragments. This is because DNA polymerase can form DNA
Submetacentric: lower arm is longer only in 5’ to 3’ direction.
Telocentric; upper arm is not present
Acrocentric; upper arm is very short
B. NUCLEIC ACIDS
Large molecules, made of nucleotides which are joined by phosphodiester
bonds
2 types; DNA and RNA.
Functions:
Storing genetic information
Regulating metabolic activities of cells
Maintaining genetic continuity between generations.
Each nucleotides consists of;
a 5-carbon sugar, (deoxyribose or ribose)
a nitrogenous base (adenine, guanine, Then, RNA primers are replaced with DNA nucleotides by DNA polymerase.
cytosine, thymine and uracil). Finally ligase enzyme joins the DNA pieces together.
{A and G are called purines, C,T and U are
(Study picture 3.16; page 117, erlangga book)
called pyrimidines.]
a phosphate 3. DNA to Protein
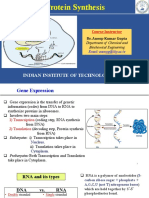
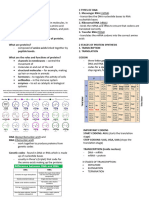
1. DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) vs RNA (Ribonucleic acid) DNA controls protein synthesis in two steps; transcription (DNA to mRNA) and
translation (mRNA to protein)
Characteristics DNA RNA
Type of sugar Deoxyribose Ribose In transcription, RNA polymerase binds to promoter region of DNA and starts
Bases ACGT ACGU
forming mRNA in 5’ to 3’ direction. The first 3 letters (start codon) of mRNA is
Double or single stranded Double Single
always AUG. RNA polymerase copies the DNA until one of the stop codons (UAA,
How is it produced? Replicates itself by Sythesised for DNA by
UAG and UGA). Product of transcription in eukaryotes is pre-mRNA with introns
DNA polymerase. RNA polymerase.
Functions Storing information Transferring and exons. Exons are coding segments while introns are non-coding.
and regulating information and
In mRNA processing, pre-mRNA is modified by removing introns. Then it is called
metabolic activities protein synthesis
mRNA and it moves into cytoplasm.
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology In translation, ribosome reads mRNA starting with the 5’ end and synthesise a
chain of amino acids (protein/polypeptide).
tRNAs bring amino acids to ribosomes. For each amino acid there is a different t
RNA.
When a ribosome reads the start codon (AUG), the tRNA with matching anti-
codon (UAC) brings methionine amino acid into ribosome. Then for each one of
the following codons, tRNAs with matching anticodons bring amino acid. When
ribosome reads the stop codon, no more amino acids are added and protein
synthesis is completed.
rRNA is found in the structure of ribosomes.
(Study diagrams 3.22,23,24,25; page 125-127, erlangga book)
You might also like
- Hourglass Workout Program by Luisagiuliet 276% (21)Hourglass Workout Program by Luisagiuliet 251 pages
- The Hold Me Tight Workbook - Dr. Sue Johnson100% (16)The Hold Me Tight Workbook - Dr. Sue Johnson187 pages
- Read People Like A Book by Patrick King-Edited62% (66)Read People Like A Book by Patrick King-Edited12 pages
- Livingood, Blake - Livingood Daily Your 21-Day Guide To Experience Real Health77% (13)Livingood, Blake - Livingood Daily Your 21-Day Guide To Experience Real Health260 pages
- COSMIC CONSCIOUSNESS OF HUMANITY - PROBLEMS OF NEW COSMOGONY (V.P.Kaznacheev,. Л. V. Trofimov.)94% (212)COSMIC CONSCIOUSNESS OF HUMANITY - PROBLEMS OF NEW COSMOGONY (V.P.Kaznacheev,. Л. V. Trofimov.)212 pages
- Donald Trump & Jeffrey Epstein Rape Lawsuit and Affidavits83% (1016)Donald Trump & Jeffrey Epstein Rape Lawsuit and Affidavits13 pages
- The 36 Questions That Lead To Love - The New York Times94% (34)The 36 Questions That Lead To Love - The New York Times3 pages
- The 36 Questions That Lead To Love - The New York Times95% (21)The 36 Questions That Lead To Love - The New York Times3 pages
- Jeffrey Epstein39s Little Black Book Unredacted PDF75% (12)Jeffrey Epstein39s Little Black Book Unredacted PDF95 pages
- The 4 Hour Workweek, Expanded and Updated by Timothy Ferriss - Excerpt23% (954)The 4 Hour Workweek, Expanded and Updated by Timothy Ferriss - Excerpt38 pages
- AQA-A-Level-Biology-Lecture-28_-Transcription-and-TranslationNo ratings yetAQA-A-Level-Biology-Lecture-28_-Transcription-and-Translation16 pages
- Lesson Check Answer Key_ DNA, RNA, and ProteinNo ratings yetLesson Check Answer Key_ DNA, RNA, and Protein1 page
- PDF-LESSON-13-NUCLEIC-ACID-CENTRAL-DOGMANo ratings yetPDF-LESSON-13-NUCLEIC-ACID-CENTRAL-DOGMA18 pages
- Genetic Code, DNA, RNA, Protein SynthesisNo ratings yetGenetic Code, DNA, RNA, Protein Synthesis46 pages
- DNA-Replication-and-Protein-Synthesis-The-Machinery-of-LifeNo ratings yetDNA-Replication-and-Protein-Synthesis-The-Machinery-of-Life22 pages
- Heredity - How A Protein Is Made Using DNA InformationNo ratings yetHeredity - How A Protein Is Made Using DNA Information45 pages
- Protein Synthesis: Indian Institute of Technology PatnaNo ratings yetProtein Synthesis: Indian Institute of Technology Patna29 pages
- Protein Synthesis - DNA Transcription and Translation-2No ratings yetProtein Synthesis - DNA Transcription and Translation-251 pages
- Central Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas YarsiNo ratings yetCentral Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Yarsi27 pages
- IB Diploma Biology: Essential Idea: Transcription and Translation Allow The GeneticNo ratings yetIB Diploma Biology: Essential Idea: Transcription and Translation Allow The Genetic37 pages
- Bacterial Genetics: Genetic Elements Such As Plasmids or Bacteriophages (BacterialNo ratings yetBacterial Genetics: Genetic Elements Such As Plasmids or Bacteriophages (Bacterial14 pages
- Heredity Inheritance and Variation LectNo ratings yetHeredity Inheritance and Variation Lect33 pages
- Central Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Yarsi100% (1)Central Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Yarsi27 pages
- RNA and Protein Synthesis: By: Anne Russell, Madelyn Stroder, Hannah Black, and Bailey MillsNo ratings yetRNA and Protein Synthesis: By: Anne Russell, Madelyn Stroder, Hannah Black, and Bailey Mills12 pages
- Molecular Structure of DNA, RNA, and Proteins DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis (Cenabre, Fortun, Ibal)No ratings yetMolecular Structure of DNA, RNA, and Proteins DNA Replication and Protein Synthesis (Cenabre, Fortun, Ibal)2 pages
- 4.9 Chapter 4 - Protein Synthesis - TranscriptionNo ratings yet4.9 Chapter 4 - Protein Synthesis - Transcription19 pages
- Controlled Substances: - Alphabetical OrderNo ratings yetControlled Substances: - Alphabetical Order11 pages
- LT 2662a Brochure Design Guide For Bonding Rubber and Thermoplastic Elastomers Volume 3 2011No ratings yetLT 2662a Brochure Design Guide For Bonding Rubber and Thermoplastic Elastomers Volume 3 201182 pages
- Vacuum Relief Valve: Product Literature & Maintenance GuidelinesNo ratings yetVacuum Relief Valve: Product Literature & Maintenance Guidelines17 pages
- How Plastics Have Changed The World, Both Socially and EconomicallyISC Chemistry ProjectBiswajit DasNo ratings yetHow Plastics Have Changed The World, Both Socially and EconomicallyISC Chemistry ProjectBiswajit Das1 page
- A Review Paper On Emulsion Polymerization of Vinyl Acetate: Sandeeptripathi, Shahida Anjum, Ashwini SoodNo ratings yetA Review Paper On Emulsion Polymerization of Vinyl Acetate: Sandeeptripathi, Shahida Anjum, Ashwini Sood26 pages
- Recent Advances in Modeling and Experiments of Kevlar Ballistic Fibrils, Fibers, Yarns and Flexible Woven Textile Fabrics - A ReviewNo ratings yetRecent Advances in Modeling and Experiments of Kevlar Ballistic Fibrils, Fibers, Yarns and Flexible Woven Textile Fabrics - A Review27 pages
- Extraction and characterization of a novel tropical fibre Megaphrynium macrostachyum as a biosourced reinforcement for gypsum-based biocomposites (2)No ratings yetExtraction and characterization of a novel tropical fibre Megaphrynium macrostachyum as a biosourced reinforcement for gypsum-based biocomposites (2)5 pages
- Berflex: Description Method of ApplicationNo ratings yetBerflex: Description Method of Application2 pages