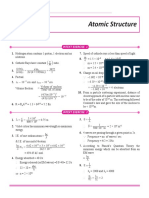
5.1 Electron Drift Questions I = Naqv: R A = Π A = 7 N = 1 Aqv I = N
5.1 Electron Drift Questions I = Naqv: R A = Π A = 7 N = 1 Aqv I = N
Uploaded by
wjdoCopyright:
Available Formats
5.1 Electron Drift Questions I = Naqv: R A = Π A = 7 N = 1 Aqv I = N
5.1 Electron Drift Questions I = Naqv: R A = Π A = 7 N = 1 Aqv I = N
Uploaded by
wjdoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
5.1 Electron Drift Questions I = Naqv: R A = Π A = 7 N = 1 Aqv I = N
5.1 Electron Drift Questions I = Naqv: R A = Π A = 7 N = 1 Aqv I = N
Uploaded by
wjdoCopyright:
Available Formats
Sierra Estep
Pd 2
5.1 Electron drift questions
I = nAqv
1. Iron has 1.7 ◊ 1029 electrons per cubic metre. Estimate the size of current produced if electrons in
an iron wire of diameter 1 mm drift at about 10−4 m s−1. The magnitude of the charge of an electron
is 1.60 × 10−19 C.
A = π r2 = π (0.0005)2
A = 7.85 x 107 m2 , n = 1.7x 1029 , q = 1.6 x 1019 , v = 104
I = nAqv = (7.85 x 107 )(1.7x 1029 )(1.6 x 1019 )(104 ) = 2.14 A
2.Use the formula above to decide if the following statements are true or false;
a. The drift velocity of electrons in a wire is proportional to the current that flows in a wire.
True: can be rearranged as v=I/nAq, I and v are proportional.
b. For a material such as copper, which has a high concentration of free electrons, the drift velocity
is less than for a material with a lower concentration.
True: Because there are more electrons in copper, there is less space to move and the electrons
move more slowly.
c. If a current flows from a thick copper wire into a thinner copper wire, the electrons will slow
down (their drift speed will decrease).
ngI
False: The variables are inversely proportional, because it can be rewritten as A =v, so they will
speed up in the thinner wire.
3. Calculate the drift velocity of electrons in a copper wire of cross-sectional area 1 mm2 when a current
of 2.5 A flows through it (for copper n = 8.5 x 1028 m-3)
A = 0.001 , n = 8.5 x 1028 , q = 1.6 x 1019 , I = 2.5
I = nAqv
2.5 = (8.5 x 1028 )(0.001)(1.6 x 1019 )v
v = 1.84 x 107 m/s
Sierra Estep
Pd 2
4. An electron is accelerated by a potential difference of 500 V. The work done on the electron is
converted to kinetic energy as the electron accelerates. Calculate the speed reached by the accelerated
electron.
√
2qV
v= m
2(1.6 x 1019 )(500)
v =
√ 9.12 x 1024
= 4.18 x 105 m/s
5. A proton is also accelerated by a potential difference of 500V. Calculate the speed it reaches.
√
2qV
v= m
2(1.6 x 1019 )(500)
v=
√ 1.64 x 1024
= 9.79 x 103 m/s
6. An electron is accelerated by a potential difference of 4000 V. What energy does it gain in eV? How
many Joules is that?
V=W/q, 4000=W/ 1.6 x 1019 , W = 6.4 x 1016 eV
1 eV = 1.6 × 10 19
, so (6.4 × 10
16
)(1.6 × 10
19
) , 1.02 × 10
34
j
You might also like
- Solutions To Levi Applied Quantum Mechanics 2nd EdDocument73 pagesSolutions To Levi Applied Quantum Mechanics 2nd EdSam Johnson67% (3)
- Final Exam SolutionsDocument4 pagesFinal Exam Solutionsdredg0661No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Physics Solutions - Chapter 26Document76 pagesFundamentals of Physics Solutions - Chapter 26maddmagg100% (1)
- Solutions PDFDocument161 pagesSolutions PDFSmriti Rai50% (2)
- Student Exploration: Photoelectric Effect: JosephDocument6 pagesStudent Exploration: Photoelectric Effect: JosephJoey Minogue100% (1)
- Chapter 8Document11 pagesChapter 8SalvadoRaulJr.No ratings yet
- Solid State NumericalsDocument4 pagesSolid State NumericalsharshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21Document1 pageChapter 21physicsolaNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor DevicesDocument7 pagesSemiconductor DevicesgamingpubgteamNo ratings yet
- 02 - 09atomic Physics - 232-262Document14 pages02 - 09atomic Physics - 232-262eamcetmaterialsNo ratings yet
- M.Engg in Electronics Engineering Semester-1: Lecturer-In-Charge: Dr. Joe O'MahoneyDocument8 pagesM.Engg in Electronics Engineering Semester-1: Lecturer-In-Charge: Dr. Joe O'Mahoneyjomongeorge001No ratings yet
- 2-Atomic Structure PDFDocument16 pages2-Atomic Structure PDFYash BhalekarNo ratings yet
- 3 - ch-4 XII - ANSDocument5 pages3 - ch-4 XII - ANSaugustyadwarikavsiNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials 2 - Chapter 18Document4 pagesEngineering Materials 2 - Chapter 18Andres PerezNo ratings yet
- EE130 Discussion 2 NotesDocument4 pagesEE130 Discussion 2 NotesSaied Aly SalamahNo ratings yet
- PK Solution Set3&4 MergedDocument16 pagesPK Solution Set3&4 Merged23je0819No ratings yet
- Razavi - HW 1Document6 pagesRazavi - HW 1Shubham GuptaNo ratings yet
- Physics-12-Ch 11 & 12 & 13-Solns PDFDocument134 pagesPhysics-12-Ch 11 & 12 & 13-Solns PDFax1leNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Solutions (Global Edition) : Prob. 8.1Document11 pagesChapter 8 Solutions (Global Edition) : Prob. 8.1성민김No ratings yet
- BETutorial 1Document3 pagesBETutorial 1lifecrazy657No ratings yet
- VL2022230501086 DaDocument2 pagesVL2022230501086 DabihbugvNo ratings yet
- Problem Set SemiconductorDocument1 pageProblem Set SemiconductorTushaarKumarNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document15 pagesChap 2Vatsal ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Physics 2075Document5 pagesPhysics 2075sujeet.jha.311No ratings yet
- HW 3solution PDFDocument6 pagesHW 3solution PDFanna.heeohNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT 2 (Subjective) Carrier TransportDocument3 pagesASSIGNMENT 2 (Subjective) Carrier TransportAniket SinghNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16Document6 pagesLecture 16Suraj sssNo ratings yet
- Preview Question PaperDocument12 pagesPreview Question PaperChirag BansalNo ratings yet
- Assignment2 SolDocument4 pagesAssignment2 SolSrea11No ratings yet
- 13 Current ElectricityDocument19 pages13 Current ElectricityApplicable AppleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Carrier Transport PhenomenaDocument56 pagesChapter 2 Carrier Transport PhenomenaMamapaiya HaariNo ratings yet
- Solutions For The Homework 2Document4 pagesSolutions For The Homework 2arsalanNo ratings yet
- Q Mechanics Tutorial IIIDocument5 pagesQ Mechanics Tutorial IIIsalonipriya3545No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument9 pagesUntitledعسم ساماNo ratings yet
- Hw5soln 2006Document7 pagesHw5soln 2006DeepikaNo ratings yet
- Additional Solved Problems For TextDocument58 pagesAdditional Solved Problems For TextKIMBERLY ANNE DIAZNo ratings yet
- ModernDocument19 pagesModernAbhinandan KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Carrier Transport PhenomenaDocument54 pagesChapter 2 - Carrier Transport PhenomenaDesmond Kuek100% (2)
- 802x 05 Sol11Document2 pages802x 05 Sol11Mamadou kaNo ratings yet
- 7 - EMI - Solved Exam. Module-4Document5 pages7 - EMI - Solved Exam. Module-4Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Carrier Transport PhenomenaDocument48 pagesChapter 2 - Carrier Transport PhenomenaYew Keong Ng100% (3)
- Numericals On Band Theory of SolidsDocument9 pagesNumericals On Band Theory of SolidsAdityaraj JadhavNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument9 pagesElectrostaticsTaerg SemajNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity NotesDocument26 pagesCurrent Electricity NotesSourav SahaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Semiconductor Devices Module 1Document4 pagesAssignment Semiconductor Devices Module 1Shivam Kumar0% (1)
- 802x 05 Sol8Document2 pages802x 05 Sol8Mamadou kaNo ratings yet
- Electron Physics AssignmentsDocument4 pagesElectron Physics Assignmentssandeshregmi189No ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument11 pagesElectricityi919647No ratings yet
- PdfjoinerDocument7 pagesPdfjoinermdilshadshigri1000No ratings yet
- Arthur Bieser Solution Chap 2Document21 pagesArthur Bieser Solution Chap 2Sma Shamsi45% (20)
- 3428825Document23 pages3428825Ghubaida HassaniNo ratings yet
- Home AssignmentDocument2 pagesHome AssignmentEffecure HealthcareNo ratings yet
- Atomic PhysicsDocument14 pagesAtomic PhysicssmeenaNo ratings yet
- Photo Bohr Xray NumericalsDocument17 pagesPhoto Bohr Xray NumericalsSaroj PoudelNo ratings yet
- Tutorial4 SolutionsDocument9 pagesTutorial4 SolutionsAditya JabadeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Ncert XIIDocument16 pagesChapter 1 Ncert XIIaaditya160807No ratings yet
- EEE118 Problem SheetsDocument6 pagesEEE118 Problem Sheetsالأردني JordanianNo ratings yet
- Question No. 01: Assignment No. 01 Modern PhysicsDocument11 pagesQuestion No. 01: Assignment No. 01 Modern PhysicsUMAR DRAZNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Problems in Quantum Mechanics: Third EditionFrom EverandProblems in Quantum Mechanics: Third EditionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- 2023 Final Paper Grade 10-1Document13 pages2023 Final Paper Grade 10-1jqm2hxqnrdNo ratings yet
- Greentek Catalogue - 14.10.2016 PDFDocument69 pagesGreentek Catalogue - 14.10.2016 PDFDan PopescuNo ratings yet
- ACS 2000AD APPL SW Troubleshooting ManualDocument70 pagesACS 2000AD APPL SW Troubleshooting Manualadrianahouki75% (4)
- Determining The (In-Plane) Flow Rate Per Unit Width and Hydraulic Transmissivity of A Geosynthetic Using A Constant HeadDocument10 pagesDetermining The (In-Plane) Flow Rate Per Unit Width and Hydraulic Transmissivity of A Geosynthetic Using A Constant HeadLeudy UtriaNo ratings yet
- LAS Electronics 10 Q2 Week 1 2 1Document11 pagesLAS Electronics 10 Q2 Week 1 2 1samanthaNo ratings yet
- PM Model Exam Set-VI - 2079!5!18 - SolDocument8 pagesPM Model Exam Set-VI - 2079!5!18 - SolDarpan AdhikariNo ratings yet
- On CFDDocument22 pagesOn CFDDivyansh TiwariNo ratings yet
- QP Latest Vendor List QFM-DT-017-05 Rev 0 2010-02-23 PVL List ApprovedDocument78 pagesQP Latest Vendor List QFM-DT-017-05 Rev 0 2010-02-23 PVL List Approvedavivekprasath40% (5)
- SD840S PDF, SD840S Description, SD840S Datasheets, SD840S View - ALLDATASHEET - PDFDocument2 pagesSD840S PDF, SD840S Description, SD840S Datasheets, SD840S View - ALLDATASHEET - PDFOralia MendezNo ratings yet
- MRMD MRSO MRSE Examination Content Syllabus Jan 13 2021Document8 pagesMRMD MRSO MRSE Examination Content Syllabus Jan 13 2021William WongNo ratings yet
- Atmos Ent WorkstationDocument40 pagesAtmos Ent WorkstationbiomedicalNo ratings yet
- WHB PERHITUNGAN Coba 1Document24 pagesWHB PERHITUNGAN Coba 1Ayu permata sariNo ratings yet
- Presentation On "Wireless Power Transmission"Document31 pagesPresentation On "Wireless Power Transmission"Vanitha GowdaNo ratings yet
- User Manual AC-DCDocument3 pagesUser Manual AC-DCdurgesh choudharyNo ratings yet
- QL 110 Series Area Lighting Spec Sheet 1984Document2 pagesQL 110 Series Area Lighting Spec Sheet 1984Alan MastersNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Engineering GATE 2020 SolutionsDocument33 pagesPetroleum Engineering GATE 2020 SolutionsGate Aiots Petroleum AdminNo ratings yet
- GIL-NGR - Technical Document-01Document6 pagesGIL-NGR - Technical Document-01jitendra prasadNo ratings yet
- Subiecte ETTIDocument3 pagesSubiecte ETTIValentin VntNo ratings yet
- Wearable Robotic Glove Design Using Surface-Mounted ActuatorsDocument12 pagesWearable Robotic Glove Design Using Surface-Mounted ActuatorsSky SantanderNo ratings yet
- G9 G) Energy, Work and Power - EfficiencyDocument12 pagesG9 G) Energy, Work and Power - EfficiencyAlhasan AlmoaqalehNo ratings yet
- Introduction-Design-Guide 2Document16 pagesIntroduction-Design-Guide 2Sutha100% (1)
- Integration As The Limit of A SumDocument2 pagesIntegration As The Limit of A SumIm rich lolNo ratings yet
- Catalyst Deactivation 1Document3 pagesCatalyst Deactivation 1davidolalere7No ratings yet
- 2907 Chemistry Paper With Solution MorningDocument8 pages2907 Chemistry Paper With Solution MorninghelioNo ratings yet
- Wall Chart SEDEX Filters EngDocument1 pageWall Chart SEDEX Filters EngGermano BissonNo ratings yet
- Service Manual TCL Inverter Wall MountedDocument58 pagesService Manual TCL Inverter Wall MountedNanang Edy cahyonoNo ratings yet
- Quest Book Icse 9 ChemistryDocument24 pagesQuest Book Icse 9 ChemistryjapneetfirstNo ratings yet
- Cri 178Document11 pagesCri 178Regie SalidagaNo ratings yet
- 2024-2025 Std9 PCMB - CT+Weekly Test Schdule - MLPDocument2 pages2024-2025 Std9 PCMB - CT+Weekly Test Schdule - MLPThomas GomesNo ratings yet