Problem 1 Problem 3
Problem 1 Problem 3
Uploaded by
John Larry CorpuzCopyright:
Available Formats
Problem 1 Problem 3
Problem 1 Problem 3
Uploaded by
John Larry CorpuzOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Problem 1 Problem 3
Problem 1 Problem 3
Uploaded by
John Larry CorpuzCopyright:
Available Formats
Corpuz, John Larry
20-0710-436
GEN0107
Problem 1 Problem 3
𝑏 (𝑥 − ℎ)2 + (𝑦 − 𝑘)2 = 𝑟 2
𝑚 = 𝑥 − 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑐𝑒𝑝𝑡 = −
𝑚
(ℎ, 𝑘) = (0,0)
𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 − 𝑚2
𝑥 2 + 𝑦2 = 𝑟 2
𝑦′ = 𝑚
2𝑥𝑑𝑥 + 2𝑦𝑑𝑦 = 0
𝒚 = 𝒚′ 𝒙 − 𝒚′𝟐
2𝑥 + 2𝑦𝑦 ′ = 0
2𝑥𝑑𝑥 + 2𝑦𝑑𝑦 = 0
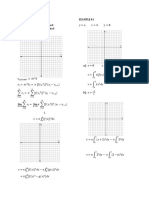
Figure 1. Graph of the equation
Figure 3. Graph of the equation
Problem 2
−𝑏
𝑥 − 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑐𝑒𝑝𝑡 = = −2
𝑚 Problem 4
𝑏 = 2𝑚 (𝑥 − ℎ)2 + (𝑦 − 𝑘)2 = 𝑟 2
𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 + 2𝑚 = 𝑚(𝑥 + 2) (𝑥 − ℎ)2 + 𝑦 2 − 2𝑦𝑘 = 0
𝑦′ = 𝑚 2(𝑥 − ℎ) + 2(𝑦 − 𝑘) = 0
′ (𝒙
𝒚=𝒚 + 𝟐) 𝑥 − ℎ = −(𝑦 − 𝑘)𝑦 ′ : 𝑝𝑙𝑢𝑔𝑔𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑖𝑛𝑡𝑜 𝑓𝑖𝑟𝑠𝑡 𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛
(𝑦 − 𝑘)2 𝑦′2 + (𝑦 − 𝑘)2 = 𝑟 2
(𝑦 − 𝑘)2 𝑦′2 + 𝑦 − 2𝑦𝑘 = 0
3
2(𝑦 − 𝑘)𝑦 ′ + 2(𝑦 − 𝑘)2 𝑦 ′ 𝑦 ′′ + 2(𝑦 − 𝑘)𝑦′ = 0
2
𝑦 ′ + (𝑦 − 𝑏)𝑦 ′′ + 1 = 0
(𝑦 − 𝑏)𝑦 ′′ = −1 − 𝑦 ′ 2
𝟐 𝟐 𝟐
𝒚𝟐 𝒚′′𝟐 + 𝟐𝒚(𝟏 + 𝒚′ )𝒚′′ − (𝟏 + 𝒚′ ) (𝒚′ )𝟐 = 𝟎
Figure 2. Graph of the equation
Corpuz, John Larry
20-0710-436
GEN0107
∓2𝑎𝑦′
𝑦 ′′ =
∓2𝑎
( ′ )2
𝑦
2𝑎𝑦 ′′ = ∓(𝑦 ′ )3
±(𝒚′ )𝟑 + 𝟐𝒂𝒚′′ = 𝟎
Figure 4. Graph of the equation
Problem 5
(𝑥 − ℎ)2 = ±4𝑎(𝑦 − 𝑘)
2(𝑥 − ℎ)2 = ±4𝑎𝑦′
2 = ±4𝑎𝑦′′
𝟏
𝒚′′ = ±
𝟐𝒂
Figure 6. Graph of the equation
Figure 5. Graph of the equation
Problem 6
(𝑦 − 𝑘)2 = ±4𝑎(𝑥 − ℎ)
2(𝑦 − 𝑘)𝑦 ′ = ±4𝑎
±2𝑎
𝑦′ =
𝑦−𝑘
∓2𝑎
𝑦−𝑘 =
𝑦′
∓2𝑎𝑦′
𝑦 ′′ =
(𝑦 − 𝑘)2
You might also like
- Iec TR 62278-3-2010Document70 pagesIec TR 62278-3-2010Joanne W100% (2)
- THE RING by Bernard SmithDocument4 pagesTHE RING by Bernard SmithFlor Hay Day0% (2)
- Reuben Swinburne Clymer - Soul Consciousness 1 Ebook - PDF PDFDocument112 pagesReuben Swinburne Clymer - Soul Consciousness 1 Ebook - PDF PDFAlfa1100% (1)
- Exercise 2 - Answer KeyDocument4 pagesExercise 2 - Answer Keyaljonjuls.lanzagaritaNo ratings yet
- Laplace 2Document12 pagesLaplace 2bananaboooooootNo ratings yet
- Seminar 4Document4 pagesSeminar 4x59rbhdkxhNo ratings yet
- Calculo 3: Ecuaciones DiferencialesDocument6 pagesCalculo 3: Ecuaciones DiferencialesJOSUÉ G. USQUIZA COLÁNNo ratings yet
- Factor Deintegracion8Document7 pagesFactor Deintegracion8pepe2002hu12No ratings yet
- EVA3Document7 pagesEVA3pepe2002hu12No ratings yet
- INTEGRACIONDocument7 pagesINTEGRACIONpepe2002hu12No ratings yet
- EVA3Document7 pagesEVA3José Luis GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Trayectorias OrtogonalesDocument6 pagesTrayectorias OrtogonalesShelly Stefhany Laban SeminarioNo ratings yet
- Kevin 7Document5 pagesKevin 7edwin franklinNo ratings yet
- Boundary Value Problem NumecDocument17 pagesBoundary Value Problem NumecshakiruNo ratings yet
- QUISPE OCHOA Johan David 2018-119016Document3 pagesQUISPE OCHOA Johan David 2018-119016David 8ANo ratings yet
- Solid of RevolutionDocument4 pagesSolid of RevolutionNicole TiancoNo ratings yet
- Medi1 U2 A3Document6 pagesMedi1 U2 A3Magally Conde ArandaNo ratings yet
- Lineal Bryan VenturaDocument5 pagesLineal Bryan VenturaBryan VenturaNo ratings yet
- Tgs 9 Kalkulus 2Document2 pagesTgs 9 Kalkulus 2kuro inuNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 8 - Higher Order Derivatives - With SamplesDocument16 pagesLECTURE 8 - Higher Order Derivatives - With SamplesJulius CodiamatNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument39 pagesUntitledMiguel GomezNo ratings yet
- Upto Mid-TermDocument39 pagesUpto Mid-TermSourav DeNo ratings yet
- الفصل الرابع المحاضرة السابع مع الحلDocument6 pagesالفصل الرابع المحاضرة السابع مع الحلابراهيم المهندسNo ratings yet
- De Midterms ReviewerDocument3 pagesDe Midterms ReviewerDENISE RIEL DINGLASANNo ratings yet
- Problemset AnswerkeyDocument7 pagesProblemset AnswerkeyDaille Wroble GrayNo ratings yet
- Nama: Zerry Ramadhan Nim:03171076: Tugas MatrekDocument6 pagesNama: Zerry Ramadhan Nim:03171076: Tugas MatrekAhmad GrabNo ratings yet
- Tutorial EUM ODEDocument7 pagesTutorial EUM ODENurul HanisNo ratings yet
- Assignment 14Document3 pagesAssignment 14kennethreyeschan100% (1)
- gr10t2 Functions Parabola Function MemoDocument8 pagesgr10t2 Functions Parabola Function MemoaaronmaburutseNo ratings yet
- Calculo Iv 4Document5 pagesCalculo Iv 4Thati MendozaNo ratings yet
- Apartats B I C - SOLUCIONS DerivadesDocument8 pagesApartats B I C - SOLUCIONS Derivadesayamaqmaf2007No ratings yet
- Unit I Part CDocument28 pagesUnit I Part CMahalakshmiNo ratings yet
- ED 2 ParcialDocument2 pagesED 2 ParcialVanessaVargasNo ratings yet
- Practica S01 - 2022-II-MAIIDocument2 pagesPractica S01 - 2022-II-MAIICASTILLO MONZON BRAYAN ALDAIRNo ratings yet
- Internal Assignment: Name Sneha SankhlaDocument10 pagesInternal Assignment: Name Sneha SankhlaSneha SankhlaNo ratings yet
- Práctica 9Document1 pagePráctica 9CARLOS EDUARDO CARDENAS GUEVARANo ratings yet
- Kalkulus 2Document3 pagesKalkulus 2Nur AstryantyNo ratings yet
- MA1511 Tut 1 Basic Q SolnsDocument5 pagesMA1511 Tut 1 Basic Q Solnsjoelteng2309No ratings yet
- Practica S01 - 2024-I-MPIDocument2 pagesPractica S01 - 2024-I-MPIMaria FernandaNo ratings yet
- QUIZ #1 (Basic Calculus) PDFDocument8 pagesQUIZ #1 (Basic Calculus) PDFAbigail CostalesNo ratings yet
- Solution To Extra Problem Set 7: Alternative Solution: Since Is Symmetric About The Plane 0, We HaveDocument11 pagesSolution To Extra Problem Set 7: Alternative Solution: Since Is Symmetric About The Plane 0, We Have物理系小薯No ratings yet
- Instant Download for First Course in Differential Equations Modeling and Simulation 2nd Smith Solution Manual 2024 Full Chapters in PDFDocument67 pagesInstant Download for First Course in Differential Equations Modeling and Simulation 2nd Smith Solution Manual 2024 Full Chapters in PDFsilvesllukan0No ratings yet
- TaylorDocument2 pagesTaylorMeraz Virgilio EduardoNo ratings yet
- Topic 5Document16 pagesTopic 5Jenny Rose DangalanNo ratings yet
- Mg. Miguel Perez GonzalesDocument3 pagesMg. Miguel Perez Gonzalesestudio de tiempo UCVNo ratings yet
- Lect 3 Nonlin ODEDocument13 pagesLect 3 Nonlin ODEZahra AlamNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus SolutionsDocument4 pagesVector Calculus SolutionsGEMMA REGALADONo ratings yet
- Signals Final Exam 2023 - Model AnswerDocument16 pagesSignals Final Exam 2023 - Model AnswerAhmed SamiNo ratings yet
- A-Level H2 Maths 2010 - Paper 2: Mathematics (Higher 2) 9740/02Document11 pagesA-Level H2 Maths 2010 - Paper 2: Mathematics (Higher 2) 9740/02Lawrence Lim Ah KowNo ratings yet
- TAREA 8 Derivada ImplícitaDocument4 pagesTAREA 8 Derivada ImplícitaTatyNo ratings yet
- Taller1 Ecuaciones PDFDocument2 pagesTaller1 Ecuaciones PDFJoseth RamirezNo ratings yet
- TAREA 3 Rosas Perez ErikaDocument12 pagesTAREA 3 Rosas Perez ErikaRosas Pérez Erika ArlethNo ratings yet
- Universidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos: Facultad de Ingenieria Industrial Calculo Iii Práctica 2Document3 pagesUniversidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos: Facultad de Ingenieria Industrial Calculo Iii Práctica 2Liliana QGNo ratings yet
- Parcial #1Document22 pagesParcial #1gloriaNo ratings yet
- TD2 Additional Exo Diff EqsDocument1 pageTD2 Additional Exo Diff EqsZaki KaminskyNo ratings yet
- Expansions - WorksheetDocument11 pagesExpansions - Worksheetst10858No ratings yet
- SPH410 Y2S2 2024 CAT 2 Marking SchemeDocument4 pagesSPH410 Y2S2 2024 CAT 2 Marking SchemeligawacalvinceNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Pure Mathematics Seminarfont 14Document40 pagesSolutions To Pure Mathematics Seminarfont 14muwanguziebenezarNo ratings yet
- Pauta 3°Prueba AntiguaDocument4 pagesPauta 3°Prueba AntiguaJoaquin Prieto GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Tutoría de Cálculo Diferencial - 101223Document6 pagesTutoría de Cálculo Diferencial - 101223Sebastián Rugeles ChacónNo ratings yet
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Ee Mapping 2Document6 pagesEe Mapping 2John Larry CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Family of Curves: - Joel R. PalacolDocument12 pagesFamily of Curves: - Joel R. PalacolJohn Larry Corpuz100% (1)
- Gen 0107 Differential EquationsDocument11 pagesGen 0107 Differential EquationsJohn Larry CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations: - Engr. Joel R. PalacolDocument16 pagesDifferential Equations: - Engr. Joel R. PalacolJohn Larry CorpuzNo ratings yet
- 1mtech Ee PCDDocument89 pages1mtech Ee PCDJohn Larry CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Last Week: Analysis of Pinion-Rack W Velocity Feedback: e ( ) (For K 100)Document14 pagesLast Week: Analysis of Pinion-Rack W Velocity Feedback: e ( ) (For K 100)John Larry CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Bs Instrumentation Engineering CurriculumDocument2 pagesBs Instrumentation Engineering CurriculumJohn Larry CorpuzNo ratings yet
- StatDocument9 pagesStatJohn Larry CorpuzNo ratings yet
- SANI0115bp 012615Document1 pageSANI0115bp 012615John Larry CorpuzNo ratings yet
- 5.tube VS PipeDocument4 pages5.tube VS PipeJohn Larry CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Runner Blade Profile of Francis Turbine To Minimize Sediment ErosionDocument12 pagesOptimizing Runner Blade Profile of Francis Turbine To Minimize Sediment ErosionJohn Larry CorpuzNo ratings yet
- 0.COVER PAGE Process Piping Design & EngineeringDocument2 pages0.COVER PAGE Process Piping Design & EngineeringJohn Larry CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Contextualized GrammarDocument23 pagesContextualized GrammarQuinie AsperinNo ratings yet
- Mst112 Final Reviewer Part 1Document5 pagesMst112 Final Reviewer Part 1John MichaelNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: 1 IdentificationDocument10 pagesSafety Data Sheet: 1 IdentificationKara WhiteNo ratings yet
- 9157 - Part-4 - 5ed - 2020 VISUAL AIDSDocument243 pages9157 - Part-4 - 5ed - 2020 VISUAL AIDSFaraz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Villa Taman Firdaus (English Presentation)Document38 pagesVilla Taman Firdaus (English Presentation)Albert LutanoNo ratings yet
- Beriberi: An Ailment of AfricaDocument3 pagesBeriberi: An Ailment of AfricaSachin BalajiNo ratings yet
- Fuels and CombustionDocument28 pagesFuels and CombustionDrupad PatelNo ratings yet
- Quiz-1,2,3,4,5 Competency AppraisalDocument20 pagesQuiz-1,2,3,4,5 Competency AppraisalDANIELA DALISAYNo ratings yet
- Siemon Tera E6 Cable Spec SheetDocument2 pagesSiemon Tera E6 Cable Spec SheetAdrian Gamboa MarcellanaNo ratings yet
- Sartorius A 200 S Analytic Balance Service Manual PDFDocument45 pagesSartorius A 200 S Analytic Balance Service Manual PDFpawnammalNo ratings yet
- Menu Good Folks - Baru - Set Night Menu - Jempol Foto N Text Menu N Favorite TagDocument13 pagesMenu Good Folks - Baru - Set Night Menu - Jempol Foto N Text Menu N Favorite TagIvan Christian SaputraNo ratings yet
- Santos Training2Document27 pagesSantos Training2AjatNo ratings yet
- Radiation UnitsDocument2 pagesRadiation UnitsYudhaPrawiraNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2: Accepted AnswersDocument10 pagesAssignment 2: Accepted AnswersxlntyogeshNo ratings yet
- Isolated Footing Design (Square Footing)Document5 pagesIsolated Footing Design (Square Footing)Santosh BasnetNo ratings yet
- Perrier - Assignment 4Document6 pagesPerrier - Assignment 4Marylou BasmadjianNo ratings yet
- Brockhampton - Rex Orange County - Billie Eilish: Spring 2019Document28 pagesBrockhampton - Rex Orange County - Billie Eilish: Spring 2019Felice Cabral0% (1)
- Pengaruh Kepemimpinan Dan Motivasi Kerja Terhadap Kinerja Perawat Di Rs TK Ii Putri Hijau Dengan Sikap Kerja Sebagai Variabel ModeratingDocument15 pagesPengaruh Kepemimpinan Dan Motivasi Kerja Terhadap Kinerja Perawat Di Rs TK Ii Putri Hijau Dengan Sikap Kerja Sebagai Variabel ModeratingciskaNo ratings yet
- Statement of Purpose (Ashok)Document2 pagesStatement of Purpose (Ashok)Sagar AryalNo ratings yet
- Hull Modelling Using Max SurfDocument249 pagesHull Modelling Using Max Surfദേവ ദേവൻNo ratings yet
- Outline For Module2Document13 pagesOutline For Module2Angelica NicholeNo ratings yet
- Ese 570 Mos Inverters: Static CharacteristicsDocument42 pagesEse 570 Mos Inverters: Static CharacteristicsVipul MistryNo ratings yet
- 懷孕用藥速查表 - 懷孕分級Document39 pages懷孕用藥速查表 - 懷孕分級virtus0202No ratings yet
- Butler Frames of WarDocument16 pagesButler Frames of WarRaghav PuriNo ratings yet
- Producing A Pharmaceutical or Biopharmaceutical: The Manufacturing ProcessDocument27 pagesProducing A Pharmaceutical or Biopharmaceutical: The Manufacturing Processhamna farooqiNo ratings yet
- Washing Machine Beko WTIK72151Document40 pagesWashing Machine Beko WTIK72151Jalil BouhdidNo ratings yet
- A Number Theoretic Approach To Music Theory: N X 0 H (X N) X N 1 H (X N)Document12 pagesA Number Theoretic Approach To Music Theory: N X 0 H (X N) X N 1 H (X N)Lrac DleiFrapNo ratings yet