100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
689 viewsPharmacologic Class: Therapeutic Class: Atypical: Dibenzothiazepine Derivative Antipsychotic
Pharmacologic Class: Therapeutic Class: Atypical: Dibenzothiazepine Derivative Antipsychotic
Uploaded by
Bianca Nicole Gacad FernandezQuetiapine fumarate (Seroquel, Seroquel XR) is an atypical antipsychotic used to treat schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive episodes associated with bipolar disorder. It works by increasing acetylcholine levels in the brain. Common side effects include headache, drowsiness, dizziness, constipation, and dry mouth. Rare but serious side effects include neuroleptic malignant syndrome and prolonged QT interval. Nurses monitor patients for side effects and adverse drug reactions, provide education on proper administration, and assess for signs of tardive dyskinesia or suicidal ideation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Pharmacologic Class: Therapeutic Class: Atypical: Dibenzothiazepine Derivative Antipsychotic
Pharmacologic Class: Therapeutic Class: Atypical: Dibenzothiazepine Derivative Antipsychotic
Uploaded by
Bianca Nicole Gacad Fernandez100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
689 views2 pagesQuetiapine fumarate (Seroquel, Seroquel XR) is an atypical antipsychotic used to treat schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive episodes associated with bipolar disorder. It works by increasing acetylcholine levels in the brain. Common side effects include headache, drowsiness, dizziness, constipation, and dry mouth. Rare but serious side effects include neuroleptic malignant syndrome and prolonged QT interval. Nurses monitor patients for side effects and adverse drug reactions, provide education on proper administration, and assess for signs of tardive dyskinesia or suicidal ideation.
Original Title
quetiapine fumarate
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Quetiapine fumarate (Seroquel, Seroquel XR) is an atypical antipsychotic used to treat schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive episodes associated with bipolar disorder. It works by increasing acetylcholine levels in the brain. Common side effects include headache, drowsiness, dizziness, constipation, and dry mouth. Rare but serious side effects include neuroleptic malignant syndrome and prolonged QT interval. Nurses monitor patients for side effects and adverse drug reactions, provide education on proper administration, and assess for signs of tardive dyskinesia or suicidal ideation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
689 views2 pagesPharmacologic Class: Therapeutic Class: Atypical: Dibenzothiazepine Derivative Antipsychotic
Pharmacologic Class: Therapeutic Class: Atypical: Dibenzothiazepine Derivative Antipsychotic
Uploaded by
Bianca Nicole Gacad FernandezQuetiapine fumarate (Seroquel, Seroquel XR) is an atypical antipsychotic used to treat schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive episodes associated with bipolar disorder. It works by increasing acetylcholine levels in the brain. Common side effects include headache, drowsiness, dizziness, constipation, and dry mouth. Rare but serious side effects include neuroleptic malignant syndrome and prolonged QT interval. Nurses monitor patients for side effects and adverse drug reactions, provide education on proper administration, and assess for signs of tardive dyskinesia or suicidal ideation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Fernandez, Bianca Nicole G.
February 22-24, 2020
BSN 3B-2a CI: Ma’am Ruth Abigail Valdez
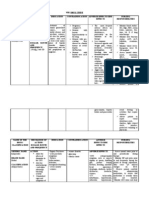
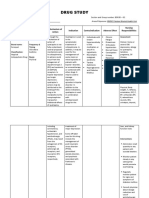
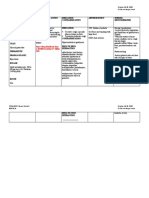
Generic Name / Brand Name Mode of Action Side effects and Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility
Drug Classification
Generic Name May slow the decline of cognitive Side Effects Administration
function in patients with Alzheimer’s Monitor fasting blood lipids
quetiapine fumarate Frequent (19%–10%): Headache, before treatment.
disease by increasing acetylcholine
drowsiness, dizziness. Give immediate-release tablets
Brand Name concentration at cholinergic
transmission sites. This action Occasional (9%–3%): Constipation, with or without food; give
Seroquel, Seroquel XR prolongs and exaggerates the effects extended-release tablets without
orthostatic hypotension, tachycardia,
of acetylcholine that are otherwise food or with a light meal.
Drug Classification dry mouth, dyspepsia, rash, asthenia,
blocked by toxic levels of Don’t confuse Seroquel with
abdominal pain, rhinitis.
Pharmacologic class: Serzon (an antidepressant).
anticholinergics.
Dibenzothiazepine derivative Rare (2%): Back pain, fever, weight
Uses gain.Adverse reactions Patient monitoring
Therapeutic class: Atypical Monitor neurologic status,
antipsychotic Treatment of schizophrenia. CNS: dizziness, sedation, cognitive especially for signs and
Treatment of acute manic episodes impairment, extrapyramidal symptoms of tardive dyskinesia,
associated with bipolar disorder symptoms, suicidal ideation, or neuroleptic
(alone or in combination with lithium tardive dyskinesia, neuroleptic malignant syndrome.
or valproate). Maintenance treatment malignant syndrome, seizures, Be aware that patient should
of bipolar disorder as an adjunct to suicide undergo lens examination when
lithium or valproic acid. Treatment of CV: tachycardia, palpitations, starting treatment and at 6-month
acute depressive episodes associated intervals during long-term
peripheral edema, orthostatic
with bipolar disorder. treatment.
hypotension, hypertension, QT-
Monitor blood pressure for
interval prolongation
orthostatic hypotension.
EENT: cataracts, ear pain, rhinitis, Monitor patient closely for
pharyngitis prolonged QT interval.
GI: constipation, dyspepsia, dry Monitor fasting blood lipids
mouth, anorexia periodicall during treatment.
Hematologic: leukopenia
Metabolic: hypothyroidism Patient teaching
Respiratory: cough, dyspnea Tell patient to take immediate-
Skin: diaphoresis release tablets with or without
Other: weight gain, flulike food and to take extended-release
symptoms, acute withdrawal form preferably in the evening,
symptoms with abrupt cessation swallowed whole, without food or
with a light meal.
Instruct patient not to crush,
Fernandez, Bianca Nicole G. February 22-24, 2020
BSN 3B-2a CI: Ma’am Ruth Abigail Valdez
break, or chew extended-release
tablets.
Teach patient to recognize and
immediately report signs and
symptoms of neuroleptic
malignant syndrome (such as high
fever, sweating, unstable blood
pressure, stupor, muscle rigidity,
changes in mood or behavior and
tardive dyskinesia) and prolonged
QT interval.
You might also like
- WALC 4 Functional ReadingDocument184 pagesWALC 4 Functional ReadingAngela100% (7)
- Risperidone Drug StudyDocument2 pagesRisperidone Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- (Medical Psychiatry 29) Borwin Bandelow, Dan J. Stein - Social Anxiety Disorder-Marcel Dekker (2004) PDFDocument347 pages(Medical Psychiatry 29) Borwin Bandelow, Dan J. Stein - Social Anxiety Disorder-Marcel Dekker (2004) PDFmaria100% (1)
- Drug Study ClozapineDocument2 pagesDrug Study ClozapineRobert Martin Rivera PuertaNo ratings yet
- ZopicloneDocument2 pagesZopicloneMichael KuzbytNo ratings yet
- AlprazolamDocument2 pagesAlprazolamRenggaSuhardijantoNo ratings yet
- Lithium Carbonate Drug StudyDocument3 pagesLithium Carbonate Drug Studynot your medz duranNo ratings yet
- HOSPRules Chapter 133Document318 pagesHOSPRules Chapter 133kazooedNo ratings yet
- Quetiapine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesQuetiapine Drug StudyEula Angelica Oco100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyYasminGianneDeOcampoBarizoNo ratings yet
- Haloperidol DRUG STUDYDocument2 pagesHaloperidol DRUG STUDYaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- QuetiapineDocument1 pageQuetiapineHanna Se100% (1)
- Biperiden (C)Document2 pagesBiperiden (C)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- GENERIC NAME: Clonazepam BRAND NAME: RivotrilDocument2 pagesGENERIC NAME: Clonazepam BRAND NAME: RivotrildanaNo ratings yet
- Ritalin LA: Initial, 20 MG PO qAM May Adjust Dose in Weekly 10-mg Incremen TS, Not To Exceed 60 Mg/day (Patients Requiring A Lower InitialDocument2 pagesRitalin LA: Initial, 20 MG PO qAM May Adjust Dose in Weekly 10-mg Incremen TS, Not To Exceed 60 Mg/day (Patients Requiring A Lower InitialKwin SaludaresNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CLOZAPINEDocument6 pagesDrug Study CLOZAPINESandra ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Name of Drug Action Indication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilityDocument4 pagesDrug Study: Name of Drug Action Indication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilityBel CortezNo ratings yet
- PrimidoneDocument6 pagesPrimidoneKim SunooNo ratings yet
- Librium ChlordiazepoxideDocument2 pagesLibrium ChlordiazepoxideENo ratings yet
- Citalopramhydrobromide CelexaDocument3 pagesCitalopramhydrobromide CelexaKristi Wray100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyRej Gallien PontalbaNo ratings yet
- DRUG StudyDocument3 pagesDRUG StudyArfe BaquinquitoNo ratings yet
- ClonazepamDocument2 pagesClonazepamjhezelle05100% (2)
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilityDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilityJezzy Ann F. SarrozaNo ratings yet
- Perphenazine Drug StudyDocument4 pagesPerphenazine Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Generic Name: Chlorpromazine BrandDocument1 pageName of Drug Generic Name: Chlorpromazine BrandkarenmichellelecarozNo ratings yet
- Drug Study For Thiothixene and OlanzapineDocument3 pagesDrug Study For Thiothixene and OlanzapineHARVEY SELIMNo ratings yet
- DroperidolDocument1 pageDroperidolIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FluvoxamineDocument2 pagesDrug Study FluvoxamineAngeline de Gala0% (1)
- Buspar (Buspirone)Document1 pageBuspar (Buspirone)ENo ratings yet
- Prozac FluoxetineDocument2 pagesProzac FluoxetineENo ratings yet
- FlupentixolDocument1 pageFlupentixolArnzz AgbulosNo ratings yet
- MirtazapineDocument4 pagesMirtazapineJEn ValentosNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness Indicated by A Reduction in Psychotic BehaviorDocument4 pagesEffectiveness Indicated by A Reduction in Psychotic BehaviorGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Amitriptyline Hydro ChlorideDocument4 pagesAmitriptyline Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941100% (1)
- ChlorpromazineDocument2 pagesChlorpromazineFay Dominguez100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CCMHDocument35 pagesDrug Study CCMHJose Mari F. EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study About Carbamazepine Used For Down Syndrome Patients With Seizure PDFDocument4 pagesDrug Study About Carbamazepine Used For Down Syndrome Patients With Seizure PDFAlexander Miguel M. AbasNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- Paxil: Generic Name: Paroxetine HydrochlorideDocument3 pagesPaxil: Generic Name: Paroxetine Hydrochloridenasir khanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - ClozapineDocument5 pagesDrug Study - ClozapinecutemaibearNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY ClonazepamDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY ClonazepamP BNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyKeanu ArcillaNo ratings yet
- CCMH Drug StudyDocument5 pagesCCMH Drug StudyJoy JarinNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyzenNo ratings yet
- Biperiden Drug StudyDocument1 pageBiperiden Drug StudyMill Jan CruzNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyPao HinojosaNo ratings yet
- School of Nursing and Midwifery: Emilio Aguinaldo CollegeDocument3 pagesSchool of Nursing and Midwifery: Emilio Aguinaldo CollegeMiggsNo ratings yet
- Lithium CarbonateDocument2 pagesLithium CarbonateArnzz AgbulosNo ratings yet
- Lithium DrugstudyDocument2 pagesLithium DrugstudyJezzy Ann F. SarrozaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study 1 (Done)Document3 pagesDrug Study 1 (Done)Otaku MiyoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic ClassDocument4 pagesPharmacologic ClassBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Librium Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLibrium Drug StudyCherry BangsilanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyTeZza_Enano_2209100% (1)
- DiazepamDocument1 pageDiazepamStephanie PeNo ratings yet
- Antidepressants, Antihistamines, General Anesthetics, MAO Inhibitors, OpioidsDocument3 pagesAntidepressants, Antihistamines, General Anesthetics, MAO Inhibitors, Opioidskaycelyn jimenezNo ratings yet
- Quetiapine - Drug Study - BSN3D BantayDocument4 pagesQuetiapine - Drug Study - BSN3D BantayJAN FEDERICK BANTAYNo ratings yet
- Atropine Sulfate Indications: Adverse Effects: CNS: Headache, Ataxia, Contraindication: Assessment & Drug EffectsDocument4 pagesAtropine Sulfate Indications: Adverse Effects: CNS: Headache, Ataxia, Contraindication: Assessment & Drug EffectsMarie Kris Chua AbelleraNo ratings yet
- NCP DS NCM114 RleDocument12 pagesNCP DS NCM114 RleAllysa Kyle AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Intervention Generic Name: Haloperidol (Haldol) Brand NameDocument2 pagesDrug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Intervention Generic Name: Haloperidol (Haldol) Brand Namemyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- Psych Duty All Drug StudyDocument45 pagesPsych Duty All Drug Studysnowmudag2No ratings yet
- Drug Analysis in PsychDocument3 pagesDrug Analysis in PsychBryan Andrew GonzalesNo ratings yet
- 12 Cranial Nerves: FERNANDEZ, Bianca Nicole GDocument1 page12 Cranial Nerves: FERNANDEZ, Bianca Nicole GBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- BSN3B 2A Research ManuscriptDocument99 pagesBSN3B 2A Research ManuscriptBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Side Effects Frequent: Insomnia, Heartburn, Patient MonitoringDocument2 pagesGeneric Name Side Effects Frequent: Insomnia, Heartburn, Patient MonitoringBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Health Care: Biopsychosocial BeingDocument17 pagesHealth Care: Biopsychosocial BeingBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- BSN 3b-2a Sample Survey QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesBSN 3b-2a Sample Survey QuestionnaireBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Side Effects Frequent (7%) : Headache. Occasional (3%-2%) : Diarrhea, Patient MonitoringDocument2 pagesGeneric Name Side Effects Frequent (7%) : Headache. Occasional (3%-2%) : Diarrhea, Patient MonitoringBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Valproic Acid: Pharmacologic Class: CarboxylicDocument2 pagesValproic Acid: Pharmacologic Class: CarboxylicBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism 1. DefinitionDocument2 pagesHyperthyroidism 1. DefinitionBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- PNSSDocument2 pagesPNSSBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic ClassDocument4 pagesPharmacologic ClassBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication / Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication / Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Risk Factors and Common Test of Genetic DisordersDocument29 pagesRisk Factors and Common Test of Genetic DisordersBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Milestones of Fetal Growth and Development: Gracy EspinoDocument18 pagesMilestones of Fetal Growth and Development: Gracy EspinoBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Vitamin Function Food SourcesDocument2 pagesVitamin Function Food SourcesBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- 5 Drugs 1 IVDocument10 pages5 Drugs 1 IVBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Functions and Effects of VitaminsDocument2 pagesFunctions and Effects of VitaminsBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Diesel-Engine Exhaust Filter Reduces Harmful Particles by 98 PercentDocument4 pagesDiesel-Engine Exhaust Filter Reduces Harmful Particles by 98 PercentBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Diesel-Engine Exhaust Filter Reduces Harmful Particles by 98 PercentDocument3 pagesDiesel-Engine Exhaust Filter Reduces Harmful Particles by 98 PercentBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Stool Collection Guidelines: You Will NeedDocument5 pagesStool Collection Guidelines: You Will NeedBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Absorption and Storage VITAMINSDocument2 pagesAbsorption and Storage VITAMINSBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Maternal Health Program - Intro and Micronutrient SupplDocument55 pagesMaternal Health Program - Intro and Micronutrient SupplBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis Via FoleyDocument2 pagesUrinalysis Via FoleyBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Performing Surgical Scrubbing, Gowning, Gloving and Serving Gown and GlovesDocument3 pagesPerforming Surgical Scrubbing, Gowning, Gloving and Serving Gown and GlovesBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Disorders in PregnancyDocument93 pagesPsychiatric Disorders in Pregnancyjinijinu100% (4)
- How Alois Alzheimer Redefined DementiaDocument4 pagesHow Alois Alzheimer Redefined DementiaElaineWilliamsNo ratings yet
- William Glasser Choice Theory-1Document13 pagesWilliam Glasser Choice Theory-1greg lucasNo ratings yet
- Clinical Counseling Psychology: Art TherapistDocument8 pagesClinical Counseling Psychology: Art TherapistElvedin KahrovicNo ratings yet
- Autism Spectrum Disorders Etiology and PDocument7 pagesAutism Spectrum Disorders Etiology and PGabriela Lala100% (1)
- Assignment (Pharmacology 1)Document7 pagesAssignment (Pharmacology 1)Ashaduzzaman suvoNo ratings yet
- Sweat It Out? The Effects of Physical Exercise On Cognition and Behavior in Children and Adults With ADHD: A Systematic Literature ReviewDocument24 pagesSweat It Out? The Effects of Physical Exercise On Cognition and Behavior in Children and Adults With ADHD: A Systematic Literature Reviewditza sharfina adaniNo ratings yet
- Family Health Disease BookDocument125 pagesFamily Health Disease Bookmahadabrata21No ratings yet
- Psy Disorder 1Document4 pagesPsy Disorder 1dariosumandeNo ratings yet
- Selective Mutism-For SchoolDocument4 pagesSelective Mutism-For SchoolJeanrose Alavata100% (1)
- DBT For Adolescents With Repeated Suicidal and Self-Harming BehaviorDocument10 pagesDBT For Adolescents With Repeated Suicidal and Self-Harming BehaviorSarahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Schizophrenia and Psychotic DisordersDocument3 pagesChapter 13 Schizophrenia and Psychotic DisordersHaylle ThomasNo ratings yet
- Schiz BrochureDocument2 pagesSchiz Brochureapi-344064794No ratings yet
- Cognitive Rigidity - The 8-Ball From HellDocument3 pagesCognitive Rigidity - The 8-Ball From HellNicasio AquinoNo ratings yet
- TCL PsychologyDocument15 pagesTCL PsychologyYachira2009No ratings yet
- Labelling in Special Education: Where Do The Benefits Lie?Document17 pagesLabelling in Special Education: Where Do The Benefits Lie?Sai smitaNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Slides - Chapter5Document25 pagesPowerpoint Slides - Chapter5amarjit singh khadwalNo ratings yet
- Methods in CounselingDocument25 pagesMethods in CounselingMaryJoyceRamosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Clinical and Counselling Psychology 03Document30 pagesIntroduction To Clinical and Counselling Psychology 03Ram Lifschitz100% (1)
- Logbook 2018Document10 pagesLogbook 2018TuwilikaNafukaNo ratings yet
- The Autism Observation Scale For Infants Scale DevDocument9 pagesThe Autism Observation Scale For Infants Scale DevPAULA LUCASNo ratings yet
- Run Down 5th ICPHDocument5 pagesRun Down 5th ICPHYulia Afrina NstNo ratings yet
- Why We All Need To Practice Emotional First AidDocument2 pagesWhy We All Need To Practice Emotional First AidGlennNo ratings yet
- Repetition Compulsion PDFDocument5 pagesRepetition Compulsion PDFJJNo ratings yet
- DSM 4 ADHD and EEFFDocument5 pagesDSM 4 ADHD and EEFFManuel PasteneNo ratings yet
- Republic of The PhilippinesDocument8 pagesRepublic of The PhilippinesRolando MintalNo ratings yet
- Brief Interventions and Brief Therapy For Substance AbuseDocument254 pagesBrief Interventions and Brief Therapy For Substance AbuseSasu Nicoleta100% (6)