Force & Motion - I: PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems
Force & Motion - I: PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems
Uploaded by
Romou AlsaaqCopyright:
Available Formats
Force & Motion - I: PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems
Force & Motion - I: PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems
Uploaded by
Romou AlsaaqOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Force & Motion - I: PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems
Force & Motion - I: PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems
Uploaded by
Romou AlsaaqCopyright:
Available Formats
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems –
CHAPTER
Force & Motion – I
5 Newton’s Laws
Vertical motion
Horizontal motion
Mixed forces
Contact forces
Inclines
General problems
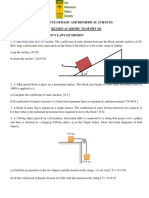
1. A 5.0-kg block is lowered with a downward acceleration of 2.8 m/s2 by means of a rope. What is the force
of the block on the rope? (Ans: 35 N, down)
2. An elevator of mass 480 kg is designed to carry a maximum load of 3000 N. What is the tension in the
elevator cable at the maximum load when the elevator moves down accelerating at 9.8 m/s2? (Ans: 0)
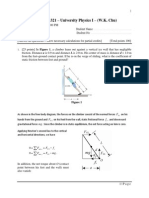
3. A 2.00-kg mass is hanging from the ceiling of an elevator accelerating upward at a = 2.50 m/s2 (see figure
1). What is the tension T in the string? (Ans: 24.6 N)
4. An object is hung from a spring balance attached to the ceiling of an elevator. The balance reads 70 N when
the elevator is at rest. What is the reading of the spring balance when the elevator is moving upward with an
acceleration of 4.9 m/s2? (Ans: 105 N)
5. A 70-kg man stands on a spring scale in an elevator that has a downward acceleration of 2.8 m/s2. What
will the scale read? (Ans: 490 N)
6. A monkey hangs vertically from a rope in a descending elevator that decelerates at 2.4 m/s2. If the tension
in the rope is 400 N, find the mass of the monkey. (Ans: 33 kg)
7. Two students are dragging a box (m = 100 kg) across a horizontal frozen lake. The first student pulls with
force F 1 = 50.0 N, while the second one pulls with force F 2 . The box is moving in the x direction with
acceleration a (see figure 2). Assuming that friction is negligible, what is F 2 ? (Ans: 86.6 N)
8. Only two forces act upon a 5.0-kg box. One of the forces is F 1 = 6.0 î + 8.0 ĵ (N). If the box moves with a
constant velocity of v = 1.6 î +1.2 ĵ (m/s), what is the magnitude of the second force? (Ans: 10 N)
9. An object of mass M = 10 kg, moving on a frictionless horizontal surface, is subjected to two applied
forces as shown in figure 3. In which situation is the object accelerating to the right? (Ans: d)
10. A car of mass 1000 kg is initially at rest. It moves along a straight road for 20 s and then comes to rest
again. The velocity – time graph for the movement is given in figure 4. What is the magnitude of the net force
that acts on the car while it is slowing down to stop from t = 15 s to t = 20 s? (Ans: 2000N)
11. A 20.0-kg block is resting on a frictionless horizontal table. A horizontal string pulls the block. If the
tension in the string is 20.0 N, what is the speed of the block after moving 2.0 m? (Ans: 2.0 m/s)
Dr. M. F. Al-Kuhaili – PHYS 101 – Chapter 5 Page 1
12. A block of mass 2.0 kg is being pushed by a force parallel to the ground, as shown in figure 5. The block
is observed to have an acceleration of 1.0 m/s2 down the incline. Assume the incline is frictionless. Calculate the
magnitude of the force. (Ans: 9.0 N)
13. In figure 6, a 25-kg box is pushed across a frictionless horizontal floor with a force of 20 N, directed at an
angle of 20o below the horizontal. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the box? (Ans: 0.75 m/s2)
14. A 2.0-kg box slides down a frictionless vertical wall while you push on it with a force F at a 30o angle
with the vertical (see figure 7). What is the magnitude of the normal force of the wall on the box if it is to slide
down at constant speed? (Ans: 11.3 N)
15. A 2.3-N weight is suspended by a string from a ceiling and held at an angle θ from the vertical by a 4.0-N
horizontal force F, as shown in figure 8. What is the magnitude of the tension in the string? (Ans: 4.6 N)
16. The weight of an astronaut on Earth is 800 N. What is his weight on planet Mars, where g = 3.76 m/s2?
(Ans: 307 N)
17. A constant force F of magnitude 20 N is applied to block A of mass m = 4.0 kg, which pushes block B, as
shown in figure 9. The block slides over a frictionless flat surface with an acceleration of 2.0 m/s2. What is the
net force on block B? (Ans:12 N, to the right)
18. Three equal mass blocks each of mass 2.0 kg move together over a horizontal frictionless surface. Two
forces, F 1 = 40 î (N) and F 2 = –10 î (N) are applied on the three-mass system (see figure 10). What is the net
force on the middle mass? (Ans: 10 î N)
19. Figure 11 shows block A of mass 6.0 kg and block B of mass 8.0 kg connected by a rigid rod of negligible
mass. Force F a = 16 î (N) acts on block A and force F b = –30 î (N) acts on block B. What is the tension in the
rod? (Neglect friction) (Ans: 22 N)
20. Two blocks are in contact on a frictionless table. A horizontal force is applied to block m 2 , as shown in
figure 12. If m 1 = 3 kg, m 2 = 2 kg, and F = 5 N, find the magnitude of the force between the two blocks.
(Ans: 3 N)
21. Two blocks of masses m 1 = 2.0 kg and m 2 = 3.0 kg are connected as shown in figure 13. Find the tension
T 2 if T 1 = 50 N. (Ans: 30 N)
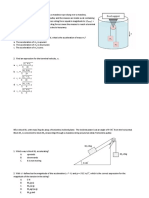
22. In the system shown in figure 14, a horizontal force F acts on the 8.0-kg object. The horizontal surface is
frictionless. What is the magnitude of F if the 5.0-kg object has a downward acceleration of 1.0 m/s2?
(Ans: 54 N)
23. A 2.0-kg mass has a velocity of (2.0 î + 2.0 ĵ ) m/s at one instant. Four seconds later, its velocity is
(2.0 î +14 ĵ ) m/s. Assuming that the object is under the influence of a single constant force, find this force.
(Ans: 6.0 ĵ N)
24. Three books (X, Y, and Z) rest on a table as shown in figure 16. The weight of each book is also indicated
in the figure. What is the magnitude of the force of book Z on book Y? (Ans: 9 N)
25. A 4.0-kg block is pushed up a 30° inclined frictionless plane with a constant horizontal force F (figure
17). If the block moves with constant speed, find the magnitude of the force F. (Ans: 23 N)
26. A 3.0-kg block slides on a frictionless 37° incline plane. A vertical force of 15 N is applied to the block
(see figure 18). What is the acceleration of the block? (Ans: 2.9 m/s2 down the incline)
Dr. M. F. Al-Kuhaili – PHYS 101 – Chapter 5 Page 2
27. A block with m 1 = 5.7 kg on a frictionless 30° inclined plane is connected by a cord over a massless
frictionless pulley to a second block with m 2 = 3.5 kg hanging vertically as shown in figure 19. What is the
acceleration of m 2 ? (Ans: 0.69 m/s2 downward)
28. When a 40-N force, parallel to an incline and directed up the incline, is applied to a crate on a frictionless
incline that is 30o above the horizontal, the acceleration of the crate is 2.0 m/s2, down the incline. Find the mass
of the crate. (Ans: 14 kg)
29. Two boxes, one of mass m = 5.00 kg and the other with an unknown mass M, are connected with a string
passing over a massless frictionless pulley and are placed on frictionless planes, as shown in figure 20.What
must be the mass M, if it goes down the plane with an acceleration of a = 2.45 m/s2? (Ans: 19.1 kg)
30. Two equal-mass blocks rest on frictionless surfaces, as in figure 21. Assuming the pulleys to be light and
frictionless, find the time required for block A to move 0.5 m down the incline, starting from rest. (Ans: 0.64 s)
31. Two blocks of masses m 1 = 4.00 kg and m 2 = 2.00 kg are connected by a string passing over a massless
and frictionless pulley and placed on a frictionless horizontal table, as shown in figure 22. A force of F = 10.0 N
at an angle of 60.0° with the horizontal is applied to m 1 . What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the
system? (Ans: 2.43 m/s2)
32. Two blocks of masses m 1 = 5.0 kg and m 2 = 10 kg are connected by a massless rod and slide on a
frictionless 30° incline as shown in figure 23. What is the tension in the rod? (Ans: zero)
33. Two masses m 1 = 2 kg and m 2 = 4 kg are connected by a light string that passes over a frictionless and
massless pulley (see figure 24). Find the magnitude of the acceleration of the masses. (Ans: 3.27 m/s2)
34. Two forces, F 1 and F 2 , are acting on a 3.0-kg box in the xy plane. Figure 25 shows only F 1 and the
acceleration a of the box. Find F 2 . (Ans: -72 î +24 ĵ N)
◦ below
35. A 25.0-kg crate is pushed across a frictionless horizontal floor with a force of 200 N, directed 20
the horizontal. What is the magnitude of the normal force of the floor on the crate? (Ans: 313 N)
36. Figure 27 shows the force versus time graph of a force acting on a 5.0-kg object moving in the x direction
along a frictionless one-dimensional track. At t = 0, the object is moving in the negative direction of the x axis
with a speed of 2.0 m/s. What are the speed and direction of the object at t = 7.0 s?
(Ans: 7.0 m/s in the positive x direction)
37. A force F = 10 N is applied to block 1, as shown in figure 29. The masses of blocks 1, 2, and 3 are 5 kg, 3
kg, and 2 kg, respectively. What is the magnitude of the force exerted by block 2 on block 1? Assume the
surface is frictionless. (Ans: 5 N)
38. A mass is suspended by a string from the ceiling of a train accelerating horizontally at 2.5 m/s2. What is
the angle that the string makes with the vertical? (Ans: 14o)
40. Two horizontal forces perpendicular to each other act at the same time on a 5.0-kg box on a horizontal
frictionless floor. One force is 6.0 N and the other is 8.0 N in magnitude. What is the magnitude of the
acceleration of the box? (Ans: 2.0 m/s2)
Dr. M. F. Al-Kuhaili – PHYS 101 – Chapter 5 Page 3
ABCDE Conceptual Problems
1. Three blocks, (A,B,C), each having mass M, are connected by strings, as shown in figure 15. Block C is
pulled to the right by a force F that causes the entire system to accelerate. Neglecting friction, what is the
tension T 1 between blocks B and C?
A. 2F/3
B. F/2
C. F/3
D. F
E. 4F/3
2. Acceleration is always in the direction:
A. of the net force.
B. of the initial velocity.
C. of the final velocity.
D. of the displacement.
E. opposite to the frictional force.
3. Consider a particle in motion while the net external force on it is zero. Which of the following statements
is correct in this case?
A. The particle must be moving at a constant velocity.
B. The particle must be moving at a constant speed in a circle.
C. The particle will come to rest after some time.
D. The velocity of the particle is always perpendicular to
the direction of the motion.
E. The particle has an acceleration of 9.8 m/s2.
4. To measure your weight, you stand on a spring scale on the floor of an elevator. Among the following
situations, select the one that gives the highest reading on the scale:
A. The elevator moves upward with increasing speed.
B. The elevator moves upward with decreasing speed.
C. The elevator remains stationary.
D. The elevator moves downward with increasing speed.
E. The elevator moves downward at constant speed.
5. Two boxes A and B (m A = 3.0 kg, and m B =1.0 kg) are in contact on a horizontal frictionless surface, and
move along the x axis (see figure 26). A horizontal force F = 10.0 î (N) is applied on box A. The net force acting
on A is F 1 and on B is F 2 . Which one of the following statements is correct?
6. Which of the following is NOT an example of accelerated motion?
A. The horizontal component of a projectile motion.
B. The vertical component of a projectile motion.
C. A circular motion at constant speed.
D. A swinging pendulum.
E. The Earth's rotation about the sun.
Dr. M. F. Al-Kuhaili – PHYS 101 – Chapter 5 Page 4
7. A 1000-kg airplane moves in straight horizontal flight at constant speed. The force of air resistance is 1800
N. The net force on the plane is:
A. zero
B. 11800 N
C. 1800 N
D. 9800 N
E. none of these
8. An object is being accelerated in the absence of friction by a 100-N force. A second force of 100-N is then
applied to the object in a direction opposite to the direction of motion. The object with these two forces acting
on it will
A. Move at a constant velocity
B. Slow down
C. Move in a circle
D. Stop rapidly
E. Move backward
9. Figure 28 shows four possible choices for the direction of ONE force of magnitude F to be applied to a
◦. The directions are either horizontal or vertical. (for all choices, we
block on an inclined plane of angle 30
assume that the block remains on the inclined plane). Rank the choices according to the magnitude of the
normal force on the block from the plane, greatest first.
A. choice 4, choice 3, choice 1, choice 2
B. choice 3, choice 4, choice 1, choice 2
C. choice 1, choice 3, choice 4, choice 2
D. choice 2, choice 3, choice 1, choice 4
E. (choice 3 and choice 4) tie, (choice 1 and choice 2) tie
10. A 13-N weight and a 12-N weight are connected by a massless string over a massless, frictionless pulley.
The 13-N weight has a downward acceleration equal to:
A. g/25
B. g/12
C. g/13
D. g
E. (13/25)g
11. A 100-kg man standing on a scale in a moving elevator reads his weight as 490 N. The acceleration of the
elevator is:
A. 4.9 m/s2 downward
B. 4.9 m/s2 upward
C. 9.8 m/s2 upward
D. 9.8 m/s2 downward
E. zero
Dr. M. F. Al-Kuhaili – PHYS 101 – Chapter 5 Page 5
Dr. M. F. Al-Kuhaili – PHYS 101 – Chapter 5 Page 6
Dr. M. F. Al-Kuhaili – PHYS 101 – Chapter 5 Page 7
You might also like
- TB Chapter7 PDFDocument24 pagesTB Chapter7 PDFAsmaa AhmedNo ratings yet
- Tie Requirements For RC Columns Bresler Gilbert ACI SJ 1961Document16 pagesTie Requirements For RC Columns Bresler Gilbert ACI SJ 1961oggy1844No ratings yet
- 081 CH 5Document5 pages081 CH 5Andrew James ReadNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Newton's Law of MotionDocument12 pagesTutorial - Newton's Law of MotionNURUL NAJIHAH KHAIRUDDINNo ratings yet
- Exercise: Chapter 4Document2 pagesExercise: Chapter 4Lorenzo YapNo ratings yet
- JR Iit StarDocument18 pagesJR Iit Star2pwxanqt8aNo ratings yet
- 2.4 2.6 Newtons Laws and Momentum PDFDocument10 pages2.4 2.6 Newtons Laws and Momentum PDFAZTonseNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion - Tutorial 5 - April 2022Document11 pagesLaws of Motion - Tutorial 5 - April 2022ngwenyanjabulo007No ratings yet
- Unit 3 ExercisesDocument6 pagesUnit 3 Exercises张书No ratings yet
- Easy ProblemsDocument15 pagesEasy ProblemsChennaiSuperkingsNo ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument5 pagesLaws of MotionAnaya PatelNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document4 pagesTutorial 4Cheryl LowNo ratings yet
- Sheet 3 (Exercise)Document5 pagesSheet 3 (Exercise)Mohamed MagedNo ratings yet
- 3.1 ForceDocument80 pages3.1 ForceMuhd AfifNo ratings yet
- USTH B1 Exercise Part3 QuestionDocument7 pagesUSTH B1 Exercise Part3 Questionbình minh trầnNo ratings yet
- Physics Sheet 3Document5 pagesPhysics Sheet 3MariamNo ratings yet
- PHYF 115 Tutorial 5Document2 pagesPHYF 115 Tutorial 5Azri RahimiNo ratings yet
- Chap2 Q USTH Exercise B1 QuestionOnlyDocument7 pagesChap2 Q USTH Exercise B1 QuestionOnlyTrần Hoàng Việt100% (1)
- UP HW CH 5 SDocument5 pagesUP HW CH 5 SCarlo DomanaisNo ratings yet
- Physics 4A Chapter 5 HW ProblemsDocument3 pagesPhysics 4A Chapter 5 HW Problemstannguyen8No ratings yet
- TUTORIAL DAS 14103 - Chapter 4 PDFDocument4 pagesTUTORIAL DAS 14103 - Chapter 4 PDFNajiha Sufian100% (1)
- Newton's 2nd Law of MotionDocument14 pagesNewton's 2nd Law of MotionGarrey BrionesNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document5 pagesTutorial 4Winni Tan100% (1)
- Tutorial 5 Force and MotionDocument4 pagesTutorial 5 Force and MotionNadhirah Kaspol AnuarNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet G9 Unit 3&4Document2 pagesWork Sheet G9 Unit 3&4Amarch BahiluNo ratings yet
- General Physics Worksheet For Freshman UnityDocument3 pagesGeneral Physics Worksheet For Freshman UnityZiyad MohammedNo ratings yet
- 081 CH 6Document5 pages081 CH 6Harpreet BolaNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2024-01-26 at 1.11.22 at NightDocument2 pagesScreenshot 2024-01-26 at 1.11.22 at NightMerwan AKNo ratings yet
- Basic Dynamics NumericalsDocument7 pagesBasic Dynamics Numericalsashok royNo ratings yet
- Additional Tension Practice PDFDocument2 pagesAdditional Tension Practice PDFSri KannanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - ReviewPackage Multiple ChoiceSolutionDocument16 pagesUnit 2 - ReviewPackage Multiple ChoiceSolutionThuran NathanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 - Newton's Laws - 093239Document2 pagesTutorial 5 - Newton's Laws - 093239musamugabazi68No ratings yet
- NLM Subjective Problems-SP-NPJC 1-June 13Document19 pagesNLM Subjective Problems-SP-NPJC 1-June 13Mohit GargNo ratings yet
- Ch8 Review Problems NewDocument6 pagesCh8 Review Problems NewVic VanceNo ratings yet
- 50Document22 pages50rockingjoeNo ratings yet
- HSC Y11 Physics 3 Dynamics and Equilibrium RevisionDocument10 pagesHSC Y11 Physics 3 Dynamics and Equilibrium RevisiondarrellsunglinNo ratings yet
- WORK POWER ENERGY - ASSIGNMENTyDocument3 pagesWORK POWER ENERGY - ASSIGNMENTysaiprittNo ratings yet
- Force and Friction WorksheetDocument2 pagesForce and Friction WorksheetAdil AliNo ratings yet
- Lom AssDocument17 pagesLom AssvinodwarriorNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM - SOLVING - Friction and 2nd Law UstDocument34 pagesPROBLEM - SOLVING - Friction and 2nd Law UstMarj Ladica MangaNo ratings yet
- USTH B1 ExerciseMechanics Part3 SolutionDocument10 pagesUSTH B1 ExerciseMechanics Part3 Solutionabcvn67No ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document5 pagesTutorial 4love sunwooNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 Solution PDFDocument10 pagesAssignment 3 Solution PDFAhmed AttallaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - 2 - Chap - 2Document8 pagesWorksheet - 2 - Chap - 2midasasfaw100% (1)
- Tut2 2Document4 pagesTut2 2indrachapa.325No ratings yet
- FRICTION Class Notes Free Full SyllabusDocument2 pagesFRICTION Class Notes Free Full Syllabuskrahul39896666No ratings yet
- Cavendish University Zambia: School of MedicneDocument2 pagesCavendish University Zambia: School of MedicneMuhau ZvikomboreroNo ratings yet
- Latihan UTSDocument13 pagesLatihan UTSAyu Patresia NababanNo ratings yet
- Tut Test 6 MemoDocument8 pagesTut Test 6 MemoVogelNo ratings yet
- 4.laws of MotionDocument7 pages4.laws of Motionmoheed.akmalNo ratings yet
- Padilla Karl Aaron D. EN1 4STEMDocument25 pagesPadilla Karl Aaron D. EN1 4STEMKurt Allen PadillaNo ratings yet
- Uploads563856384743unit 3 Work Energy Power Practice Questions 2019 PDFDocument6 pagesUploads563856384743unit 3 Work Energy Power Practice Questions 2019 PDFRolando TorresNo ratings yet
- PHY1103 Tutorial 01Document2 pagesPHY1103 Tutorial 01siriwardanashashanka098No ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 3Document3 pagesTutorial Sheet 3fracksonbanda311No ratings yet
- Problemas Re SueltosDocument7 pagesProblemas Re SueltosFanny Méndez100% (1)
- Topik2 1 (Forceandmotion 1) 20240604080133Document5 pagesTopik2 1 (Forceandmotion 1) 20240604080133Vania ParamithaNo ratings yet
- Problems MechanicsDocument28 pagesProblems MechanicsdebasijNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Work Energy Power Practice Questions v2 2016 AnswersDocument6 pagesUnit 3 Work Energy Power Practice Questions v2 2016 AnswersJane CongaoNo ratings yet
- 2a-Dynamics MC Practice ProblemsDocument26 pages2a-Dynamics MC Practice Problemsruuki25No ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Vectors: PHYS 101 Previous Exam ProblemsDocument4 pagesVectors: PHYS 101 Previous Exam ProblemsRomou AlsaaqNo ratings yet
- Motion in Two & Three Dimensions: PHYS 101 Previous Exam ProblemsDocument7 pagesMotion in Two & Three Dimensions: PHYS 101 Previous Exam ProblemsRomou AlsaaqNo ratings yet
- Measurement: PHYS 101 Previous Exam ProblemsDocument2 pagesMeasurement: PHYS 101 Previous Exam ProblemsRomou AlsaaqNo ratings yet
- Motion Along A Straight Line: PHYS 101 Previous Exam ProblemsDocument5 pagesMotion Along A Straight Line: PHYS 101 Previous Exam ProblemsRomou AlsaaqNo ratings yet
- A-Z in HVAC DesignDocument93 pagesA-Z in HVAC DesignRomou AlsaaqNo ratings yet
- متابعة صيانة التكييف المركزيDocument52 pagesمتابعة صيانة التكييف المركزيRomou Alsaaq100% (1)
- Fish Body Sizes Change With Temperature But Not All Species Shrink With Warming - OADocument33 pagesFish Body Sizes Change With Temperature But Not All Species Shrink With Warming - OApy5rqjsw7yNo ratings yet
- VHDL Implemenation of Cordic AlgorithmDocument39 pagesVHDL Implemenation of Cordic Algorithm1234sharada50% (2)
- Lab 9 NC GGDocument5 pagesLab 9 NC GGFahad SikandriNo ratings yet
- 2018 Papers: Isbn: 978-1-64353-065-9Document1 page2018 Papers: Isbn: 978-1-64353-065-9gioNo ratings yet
- CBSE Clas 7 Maths Worksheet - Exponents & Powers PDFDocument4 pagesCBSE Clas 7 Maths Worksheet - Exponents & Powers PDFIhtesham HussainNo ratings yet
- Chapitre 2Document44 pagesChapitre 2Eya FakhfekhNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 - Overlapping Generations PDFDocument53 pagesLecture 8 - Overlapping Generations PDFutsoreeNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 2: Q. Write A Shell Script To Swap Two Numbers Without Using 3rd VariableDocument14 pagesExperiment - 2: Q. Write A Shell Script To Swap Two Numbers Without Using 3rd VariableDevam ShethNo ratings yet
- Expansion and Factorization: Q.1. Using The Standard Formulae, Expand Each of The Following (I) (Ii)Document20 pagesExpansion and Factorization: Q.1. Using The Standard Formulae, Expand Each of The Following (I) (Ii)Pravat Tiadi100% (1)
- Caps Textbook Physical Science Grade11 PDFDocument525 pagesCaps Textbook Physical Science Grade11 PDFNeil Joseph AlcalaNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Project FileDocument21 pagesComputer Science Project FileVidya SajitNo ratings yet
- Mesl Elements 3Document227 pagesMesl Elements 3Jay Mark CayonteNo ratings yet
- Advance Concept in Data Bases Unit-1 by Arun Pratap SinghDocument71 pagesAdvance Concept in Data Bases Unit-1 by Arun Pratap SinghArunPratapSingh100% (2)
- Fanuc 0i-M ManualDocument58 pagesFanuc 0i-M Manualrastaegg75% (4)
- Image Clustering: Prof. Dr. Rafiqul Islam Department of CSEDocument26 pagesImage Clustering: Prof. Dr. Rafiqul Islam Department of CSEMainul IslamNo ratings yet
- OACC Data Analysis SAC 2019 FinalDocument9 pagesOACC Data Analysis SAC 2019 FinallokieNo ratings yet
- Standard Deviation (Ungrouped Data)Document6 pagesStandard Deviation (Ungrouped Data)Arielle T. TanNo ratings yet
- Controls Engineering in FRCDocument236 pagesControls Engineering in FRCDFGNo ratings yet
- Relevance Trees and Morphologic Analysis (Relevance Trees)Document4 pagesRelevance Trees and Morphologic Analysis (Relevance Trees)Muteeb KhanNo ratings yet
- Toc Project ReportDocument17 pagesToc Project ReportKrishna ReddyNo ratings yet
- Chapter (1) Heet SDocument7 pagesChapter (1) Heet SsaadNo ratings yet
- Elastic Analysis of Load Distribution in Wide Faced Spur GearsDocument208 pagesElastic Analysis of Load Distribution in Wide Faced Spur GearsJulian Steward100% (1)
- Research and Applications of The Fuzzy Control Used in The Wireless Illumination Measurement and Control System of The GreenhouseDocument5 pagesResearch and Applications of The Fuzzy Control Used in The Wireless Illumination Measurement and Control System of The GreenhouseyopisukitaNo ratings yet
- PSY Lecture 4Document1 pagePSY Lecture 4nataliejunk2No ratings yet
- Topic - 17 TransformationsDocument88 pagesTopic - 17 TransformationsJorifNo ratings yet
- Maths Class X Chapter 10 Circles Practice Paper 09 AnswersDocument11 pagesMaths Class X Chapter 10 Circles Practice Paper 09 AnswersPaarvathy RamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- UNIT 7 Number System and Bases: CSEC Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument4 pagesUNIT 7 Number System and Bases: CSEC Multiple Choice QuestionsAFRO TVNo ratings yet
- A BUSINESS RESEARCH METHODS-Assignment UBISDocument3 pagesA BUSINESS RESEARCH METHODS-Assignment UBISnàvàz_enzêêNo ratings yet