Intestinal Obstruction: Borborygmi Bacterial Activity
Intestinal Obstruction: Borborygmi Bacterial Activity
Uploaded by
Shiella Heart MalanaCopyright:
Available Formats
Intestinal Obstruction: Borborygmi Bacterial Activity
Intestinal Obstruction: Borborygmi Bacterial Activity
Uploaded by
Shiella Heart MalanaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Intestinal Obstruction: Borborygmi Bacterial Activity
Intestinal Obstruction: Borborygmi Bacterial Activity
Uploaded by
Shiella Heart MalanaCopyright:
Available Formats
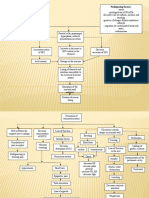
Intestinal Obstruction
Adhesion due to abdominal
surgery
Cessation of peristalsis
Increased contractions of Borborygmi Gases and fluids Bacterial
proximal intestine accumulate in the area Activity
Distention of intestine
Persistent
Severe Increased intraluminal pressure vomiting
colicky
abdominal
pain
Increased secretions into the intestine Loss of hydrogen,
ions, potassium
Compression of veins
Metabolic
alkalosis
Increased venous pressure
Decreased absorption
Edema of the intestine
Dec arterial blood supply Compression of
terminal branches of
mesenteric artery
Ischemia, Anoxia
Necrosis Perforation Bacteria or toxins leak into:
of necrotic
segments
Gangrenous
intestinal wall Peritoneal
Blood supply
cavity
Dec bowel Cessation of
sounds Peritonitis Bacteremia
peristalsis
Septicemia
Diagnostic Examination Medical Management Nursing Management
Computed Tomography (CT) scan - It detects
A nasogastric tube is placed and inserted for the Fluid resuscitation with electrolyte replenishment is
inflammation, edema, and bleeding. Examine the soft
tissue and organs of the abdomen for cysts and gastrointestinal contents to be aspirated and prevent necessary to maintain proper volume status.
malignancies. aspiration to the patient. Patients should be placed on NPO and stomach
s
Ultrasonography - It helps screen for kidney stones, liver Other resuscitative measures to be placed and inserted decompression using a nasogastric tube and flatus tube
illness, malignancies, and various other abdominal are intravenous fluid’s commencement and to reduce discomfort, vomiting, and distension.
problems. Examine the source of your stomach ache or replacement of electrolytes to correct imbalances. Determine the usual range for urea and electrolyte
bloating. An appropriate dose of Opiate Analgesia is findings to recognize dehydration and the danger of
Fluoroscopy - To assess the existence of arterial administered based on the tolerance of the patient. deterioration and intervene effectively.
obstructions, see the transit of contrast via the For symptomatic management, it should be noted that The use of a nasogastric tube allows for intestinal
gastrointestinal system and the flow of blood through the though it does not aggravate surgical results, if there are decompression, which relieves discomfort around the
coronary arteries. any, some of the medications can make obstructive blockage. Also, to aid in the management of emesis,
Air or barium enema - It allows for more accurate colon
dysmotility worse. These medications include opioids provide correct intake and output data, and reduce the
imaging. During the surgery, the doctor will inject air or
and anti-spasmodic danger of aspiration.
liquid barium into the colon through the rectum.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) - It aids in site For patients considered terminal, it is significant to If the patient is unstable or sick, use a Foley catheter to
identification and etiology estimate. MRI might enable involve them early in palliative care to avoid refusal and monitor the patient's urine.
more precise and faster identification of patients for promote continuity of care. If the pain is severe, the nurse may provide analgesics.
operative intervention without exposing them to radiation. Patients with problems or recurring blockage should be
closely monitored.
You might also like
- Concept Map Liver CirrhosisssDocument2 pagesConcept Map Liver CirrhosisssAsniah Hadjiadatu Abdullah92% (12)
- 70791658786Document3 pages70791658786gulcherrudisney259No ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Guide To Managing AutismDocument89 pagesA Comprehensive Guide To Managing Autismapi-3696876100% (4)
- Adtech Week 7&8Document17 pagesAdtech Week 7&8Shiella Heart MalanaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating Factorsgodwinkent888No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Pernicious AnemiaDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Pernicious AnemiaMikhael Anthony Medina50% (4)
- Gastrointestinal DisordersDocument27 pagesGastrointestinal DisordersRI NA100% (5)
- DIGESTIVE SYSTEM of VERTEBRATE-COMPARATIVE ANATOMYDocument58 pagesDIGESTIVE SYSTEM of VERTEBRATE-COMPARATIVE ANATOMYpratiwi kusuma64% (11)
- 1940 FoodScienceBodyDocument378 pages1940 FoodScienceBodyXian-li100% (4)
- Chapter-7-Pathophysiology Nephrotic SyndromeDocument3 pagesChapter-7-Pathophysiology Nephrotic SyndromeCxarina RamirezNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Appendicitis: Vague, Dull, Diffuse Pain in The Midabdomen or EpigastriumDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Appendicitis: Vague, Dull, Diffuse Pain in The Midabdomen or EpigastriumGinoTevesNo ratings yet
- B. I. Pathophysiology: Book-Based A. HerniaDocument10 pagesB. I. Pathophysiology: Book-Based A. HerniaSiena PlacinoNo ratings yet
- PathyDocument3 pagesPathyTRIXY MAE HORTILLANO100% (1)
- Payhway IleusDocument1 pagePayhway IleusLarasparkyu ElfNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology-AppendicitisDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology-AppendicitisMaria Socorro Sismundo DavidNo ratings yet
- IV PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesIV PathophysiologyJanedear Pasal100% (1)
- VC Obstruction, Heart Failure (Post-Hepatic) Portal Vein Thrombosis (Pre-Hepatic) Excessive Vomiting/retchingDocument1 pageVC Obstruction, Heart Failure (Post-Hepatic) Portal Vein Thrombosis (Pre-Hepatic) Excessive Vomiting/retchingNenita Gayo FrondaNo ratings yet
- PPK Prost atDocument2 pagesPPK Prost atlisarahmaasrilNo ratings yet
- 5th Year General Surgery Notes - Upper GIT SurgeryDocument4 pages5th Year General Surgery Notes - Upper GIT SurgeryJason Harry100% (2)
- Cholelithiasis CholecystitisDocument1 pageCholelithiasis Cholecystitissamliebareng77No ratings yet
- Disruption of Nerves Coordinating Bowel Peristalsis Lab FindingsDocument1 pageDisruption of Nerves Coordinating Bowel Peristalsis Lab FindingsmiallyannaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Pancreatitis: Causes ComplicationsDocument1 pageChronic Pancreatitis: Causes ComplicationsNikey LimNo ratings yet
- Clinicopharmacological ConferenceDocument7 pagesClinicopharmacological ConferenceNestley TiongsonNo ratings yet
- Woc CBDDocument4 pagesWoc CBDcahyaNo ratings yet
- Bpud, PathoDocument2 pagesBpud, PathoSheng GosepNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Esophagus.Document3 pagesDiseases of Esophagus.Isabel Castillo100% (2)
- Mind Map GallstonesDocument1 pageMind Map GallstonesMuhamad MaxumNo ratings yet
- November 10 2021 Tumor BoardsDocument5 pagesNovember 10 2021 Tumor BoardsJorge De VeraNo ratings yet
- PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesPathophysiologyMoises Clerick BalloguingNo ratings yet
- Hepato BiliaryDocument47 pagesHepato BiliaryMikaela Ysabel CañaNo ratings yet
- Pathway GGKDocument2 pagesPathway GGKzakaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute AppendicitisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Acute AppendicitissiarahNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CholeDocument3 pagesPathophysiology CholeClyde AleczandreNo ratings yet
- Mind Map GallstonesDocument2 pagesMind Map GallstonesMuhamad MaxumNo ratings yet
- 12 - 34 - 35 EsophagusDocument54 pages12 - 34 - 35 EsophagusdrhydrogenNo ratings yet
- Pancreatitis Aguda FlashCardDocument1 pagePancreatitis Aguda FlashCardKarina AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Causes of Upper GI Bleeding - UpToDateDocument8 pagesCauses of Upper GI Bleeding - UpToDateAra ThalianaNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Acute AppendicitisDocument1 pagePa Tho Physiology of Acute Appendicitisromeo rivera100% (4)
- UlcerdiseaseDocument1 pageUlcerdiseaseJulia TarlacNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CholelithiasisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology CholelithiasisLovely Darole100% (1)
- Stomach Disorders: Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument2 pagesStomach Disorders: Peptic Ulcer Diseasekilladim992No ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of PIHDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology of PIHCarren_Louise__8090No ratings yet
- Pathophy Nov 22 2017Document2 pagesPathophy Nov 22 2017Jeanette Ðimalanta ÐumagasNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Obstruction in Pediatric PatientsDocument25 pagesIntestinal Obstruction in Pediatric PatientsHaryo Priambodo100% (1)
- PatophysiologyDocument1 pagePatophysiologyMj GanioNo ratings yet
- The Abdominal OrgansDocument56 pagesThe Abdominal OrgansAjeng FikihNo ratings yet
- Liver Cirrhosis PathophysiologyDocument1 pageLiver Cirrhosis PathophysiologyAlliah OrdanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysio 2Document3 pagesPathophysio 2Jewel YapNo ratings yet
- Path o Physio 123Document2 pagesPath o Physio 123rjalavazo1989No ratings yet
- Exam 2Document15 pagesExam 2srjones340No ratings yet
- Urolithiasis NP: Deficit of KnowledgeDocument2 pagesUrolithiasis NP: Deficit of Knowledgevictor zhefaNo ratings yet
- Acute PancreatitisDocument19 pagesAcute PancreatitisMaaz MansoorNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology-Ng Hirschsprung DiseaseDocument3 pagesPathophysiology-Ng Hirschsprung DiseaseJan Rae Barnatia AtienzaNo ratings yet
- FlukeDocument12 pagesFlukeNJ TamayoNo ratings yet
- Digestive System GlossaryDocument3 pagesDigestive System GlossaryHASSAM KHANNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology EclampsiaDocument5 pagesPathophysiology EclampsiaYael EzraNo ratings yet
- Dr. Astried Indrasari - Capd 12 SepDocument18 pagesDr. Astried Indrasari - Capd 12 SepArnelia GumantiNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology - AppendicitisDocument5 pagesPathophysiology - AppendicitisAzielle Joyce RosquetaNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of Acute GastroenteritisDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology of Acute Gastroenteritisromeo rivera100% (16)
- Forensic 2 - Personal Identification TechniquesDocument25 pagesForensic 2 - Personal Identification TechniquesShiella Heart MalanaNo ratings yet
- Case Study GordonsDocument2 pagesCase Study GordonsShiella Heart MalanaNo ratings yet
- Soclit WK 1Document42 pagesSoclit WK 1Shiella Heart MalanaNo ratings yet
- Lesson: Job Application: WEEK 10: MidtermDocument6 pagesLesson: Job Application: WEEK 10: MidtermShiella Heart MalanaNo ratings yet
- Adtech Week 9Document13 pagesAdtech Week 9Shiella Heart MalanaNo ratings yet
- Narrative ReportDocument4 pagesNarrative ReportShiella Heart MalanaNo ratings yet
- CP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesCP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanShiella Heart MalanaNo ratings yet
- Skills:: Romulo M. Agustin Jr. Bagumbayan, Lal-Lo, Cagayan Mobile Number: 09054836922Document1 pageSkills:: Romulo M. Agustin Jr. Bagumbayan, Lal-Lo, Cagayan Mobile Number: 09054836922Shiella Heart MalanaNo ratings yet
- Week-5. Learning Resources and Assessments-Prelim: Introduction To Lesson 5Document9 pagesWeek-5. Learning Resources and Assessments-Prelim: Introduction To Lesson 5Shiella Heart MalanaNo ratings yet
- Cheryl Tatano Beck1 For MergeDocument14 pagesCheryl Tatano Beck1 For MergeShiella Heart MalanaNo ratings yet
- Enumerate at Least 15 Violation Under Republic Act 4136 and Give The Old and New PenaltyDocument5 pagesEnumerate at Least 15 Violation Under Republic Act 4136 and Give The Old and New PenaltyShiella Heart MalanaNo ratings yet
- Number 2 Na ThemeDocument1 pageNumber 2 Na ThemeShiella Heart MalanaNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument9 pagesScienceCristina MaquintoNo ratings yet
- Simulated Body Fluids CompositionDocument14 pagesSimulated Body Fluids CompositionAnuj Sharma100% (1)
- Case Study of AmoebiasisDocument7 pagesCase Study of Amoebiasisbuzz Q75% (4)
- Understanding and Controlling The Irritable BowelDocument95 pagesUnderstanding and Controlling The Irritable BowelketiNo ratings yet
- Some of The Life Processes in The Living Beings Are Described BelowDocument21 pagesSome of The Life Processes in The Living Beings Are Described BelowTECH CORNERNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology For Nursing and Healthcare Students, 2nd Edition PDFDocument39 pagesFundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology For Nursing and Healthcare Students, 2nd Edition PDFtadon92475No ratings yet
- Frog Dissection Internal Anatomy FinalsDocument4 pagesFrog Dissection Internal Anatomy FinalsAlma LibangNo ratings yet
- Rinhs Science 8 4th Activity 2 Digestive System Crossword Puzzle For MondayDocument1 pageRinhs Science 8 4th Activity 2 Digestive System Crossword Puzzle For MondayRyan BersaminNo ratings yet
- Short Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs) - Mediated Gut Epithelial and Immune Regulation and Its Relevance For Inflammatory Bowel DiseasesDocument16 pagesShort Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs) - Mediated Gut Epithelial and Immune Regulation and Its Relevance For Inflammatory Bowel DiseasesLevente BalázsNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument74 pagesDigestive SystemJohn BethanyNo ratings yet
- Poultry Health ManagementDocument32 pagesPoultry Health Managementdawn100% (2)
- Unit 5 ReviewDocument2 pagesUnit 5 Reviewdty2257202010031No ratings yet
- Papaya: Q. Choose The Correct AlternativesDocument2 pagesPapaya: Q. Choose The Correct AlternativesSai Soham PradhanNo ratings yet
- Gut Rebuilding Protocol : Standard Process Supplements Lunch DinnerDocument1 pageGut Rebuilding Protocol : Standard Process Supplements Lunch DinnerSteve KellerNo ratings yet
- Grodner and Escott-Stump: Nutritional Foundations and Clinical Application: A Nursing Approach, 6th Edition Chapter 3Document10 pagesGrodner and Escott-Stump: Nutritional Foundations and Clinical Application: A Nursing Approach, 6th Edition Chapter 3Izzie JeanNo ratings yet
- Grade-6 Edited RTPDocument32 pagesGrade-6 Edited RTPDanah Jamille AbadillaNo ratings yet
- CH-2 (Nutrition in Animals) NotesDocument9 pagesCH-2 (Nutrition in Animals) NotespranavNo ratings yet
- Abdominal X RayDocument64 pagesAbdominal X RayabhishekbmcNo ratings yet
- 4-HLS SLIDE, SplinaDocument153 pages4-HLS SLIDE, Splinaapi-3804539No ratings yet
- Health Book For TeachersDocument281 pagesHealth Book For TeachersRene H. Framcisco, MD100% (2)
- Jason Prall Ultimate Gut Repair BlueprintDocument7 pagesJason Prall Ultimate Gut Repair BlueprintDraganescu Violeta100% (3)
- AIS2 DR Daniel Nuzum Hormoneclass Detox ProtocolDocument24 pagesAIS2 DR Daniel Nuzum Hormoneclass Detox ProtocolPanther Prime50% (2)
- Final Demo Lp a Detailed Lesson Plan About Digestive SystemDocument12 pagesFinal Demo Lp a Detailed Lesson Plan About Digestive SystemjalangairaNo ratings yet
- "Just One Bottle Won't Hurt" - or Will It?: Supplementation of The Breastfed Baby Marsha WalkerDocument4 pages"Just One Bottle Won't Hurt" - or Will It?: Supplementation of The Breastfed Baby Marsha WalkerRamona BunescuNo ratings yet
- Animal Structure and Function Answer KeyDocument2 pagesAnimal Structure and Function Answer KeykpenalesNo ratings yet