Hyperthermia NCP
Hyperthermia NCP
Uploaded by
maeca101Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hyperthermia NCP
Hyperthermia NCP
Uploaded by
maeca101Copyright:
Available Formats
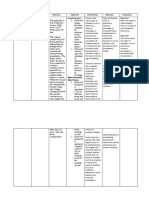
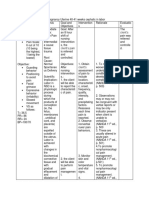
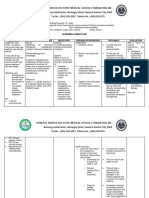
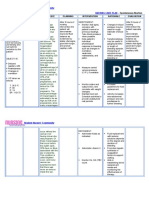
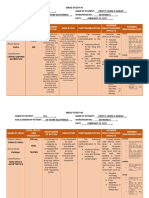
Caberte, Mae Lyn M.
BSN 3-F Group 20
Patient’s Name: AJG
Medical Diagnosis: acute gastritis t/c UTI
Nursing Diagnosis: hyperthermia r/t present infection as evidenced by increased WBC in CBC result
Short Term Goal: At the end of shift, the patient’s temperature will lower to 37 °
Long Term Goal: At the end of hospitalization, the patient’s core temperature will be in normal range.
Cues Problem Scientific Rationale Nsg. Interventions Rationale Evaluation
O> received pt. awake Hyperthermia A fever occurs when the -provide surface cooling by -to promote heat loss by Goal met. Patient’s body
>not in cardiopulmonary body sets the core means of undressing, cool radiation, conduction, temperature lowered to
distress temperature to a higher environment, tepid sponge convection and 36.8° C. No reoccurrence
>skin warm to touch temperature, through the bath, local ice packs evaporation, especially in of fever was noted.
>febrile action of the pre-optic especially in groin and areas of high blood flow
region of the anterior axillae
hypothalamus. For
>temp: 38.1 example, in response to a -administer medication -to treat underlying cause
HR: 139 bacterial or viral infection, such as antibiotics as
RR 29 the body will raise its ordered
temperature, much like
raising the temperature -administer replacement -to support circulating
setting on a thermostat. fluids and electrolytes volume and tissue
perfusion
SOURCE: Wikipedia.org
-note sweating as body -evaporation is decreased
attempts to increase heat by environmental factors
loss of high humidity and high
ambient temperature
-maintain in bed rest -to reduce metabolic
demands/ oxygen
consumption
You might also like
- Clinical Reasoning Questions - CollaborationDocument4 pagesClinical Reasoning Questions - CollaborationMohammad OmarNo ratings yet
- Assesment Diagnosis Inference Objective Intervention Raionale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: Long Term Goal: Goal MetDocument2 pagesAssesment Diagnosis Inference Objective Intervention Raionale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: Long Term Goal: Goal MetChaeL90No ratings yet
- Normal Spontaneous DeliveryDocument64 pagesNormal Spontaneous DeliveryMichellin Andres MarianoNo ratings yet
- NCP - Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisDocument12 pagesNCP - Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisAya BolinasNo ratings yet
- Rhetorical Analysis Final 1Document5 pagesRhetorical Analysis Final 1api-507725488No ratings yet
- NCP Fever: Read Books, Audiobooks, and More Scribd, IncDocument10 pagesNCP Fever: Read Books, Audiobooks, and More Scribd, IncEricsonMitraNo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia: A Nursing Care Plan Presented To Maria Catherine Belarma, RN, MNDocument6 pagesHyperthermia: A Nursing Care Plan Presented To Maria Catherine Belarma, RN, MNJanelle NarcisoNo ratings yet
- NCP Gastric CancerDocument6 pagesNCP Gastric Cancerhayascent hilarioNo ratings yet
- NCP ProperDocument5 pagesNCP ProperRustan FrozenNo ratings yet
- DS LosartanDocument1 pageDS LosartanYuuki Chitose (tai-kun)No ratings yet
- NCP PainDocument5 pagesNCP PainChloe Crystal DorojaNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage, Route & Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side-Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesName of Drug Dosage, Route & Frequency Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Side-Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDivine Grace Arreglo AbingNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument10 pagesDrug AnalysisChanel BalinbinNo ratings yet
- SDL3Document2 pagesSDL3Margaux BaynosaNo ratings yet
- NCP RHDDocument4 pagesNCP RHDlouie john abilaNo ratings yet
- NCP NSD 2Document3 pagesNCP NSD 2Warren Bilog OleaNo ratings yet
- School of Health and Allied Health Sciences Nursing Department Self-Directed Learning (Nur 146 - Clinical Area)Document3 pagesSchool of Health and Allied Health Sciences Nursing Department Self-Directed Learning (Nur 146 - Clinical Area)Duchess Juliane Jose MirambelNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute Pain OB WardDocument2 pagesNCP Acute Pain OB WardJACOB AQUINTEYNo ratings yet
- Postoperative Nursing Care Plan For Cesarian Section Patient Case Pres orDocument6 pagesPostoperative Nursing Care Plan For Cesarian Section Patient Case Pres orLoren EstefanNo ratings yet
- NCP AgeDocument1 pageNCP AgecaressmeNo ratings yet
- AspirinDocument1 pageAspirinAmanda CoadNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Evaluation Nsg. Action RationaleDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Evaluation Nsg. Action RationaleRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Domperidone CompressDocument1 pageDrug Study Domperidone CompressAngelica TolledoNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis-FdarDocument1 pageCase Analysis-FdarDyanne BautistaNo ratings yet
- ALMOETE Bullous ImpetigoDocument4 pagesALMOETE Bullous ImpetigoGail NamangdanNo ratings yet
- TrimetazidineDocument2 pagesTrimetazidinemasheennavirgoNo ratings yet
- NCP Readiness UTI 1Document5 pagesNCP Readiness UTI 1Mary Grace AgataNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PantoprazoleDocument3 pagesDrug Study PantoprazoleIRISH CACAYANNo ratings yet
- Scientific Analysis Goal: Goal:: Subjective CuesDocument2 pagesScientific Analysis Goal: Goal:: Subjective CuesChloie Marie RosalejosNo ratings yet
- NCP For Swine FluDocument3 pagesNCP For Swine FluGiana CalloNo ratings yet
- Discharge Plan Methods InstructionsDocument5 pagesDischarge Plan Methods InstructionsKirk CabasaNo ratings yet
- Labor Nursing Care PlansDocument58 pagesLabor Nursing Care PlansMuhamad AriNo ratings yet
- Post Cesarean Section DeliveryDocument5 pagesPost Cesarean Section Deliveryᒙᕧᖇᕦᙏᖻ ᗴᔛᓦᗩᖆᗩNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument5 pagesNCPMcmc Ryan Ferdinand GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Revised NCP (Baiae)Document9 pagesRevised NCP (Baiae)Jennifer BactatNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan. HypertensionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan. HypertensionKiara Shanelle Posadas AbrioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - HYPERTENSIONDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan - HYPERTENSIONJas Slk0% (1)
- NCP For Cough 1Document3 pagesNCP For Cough 1Ro VinNo ratings yet
- SAS - Session-24-Research 1Document5 pagesSAS - Session-24-Research 1ella retizaNo ratings yet
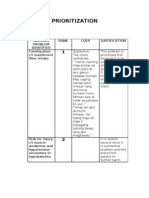
- PrioritizationDocument1 pagePrioritizationJLAZRONo ratings yet
- Tramadol Drug StudyDocument4 pagesTramadol Drug StudyJust A Nsg StudentNo ratings yet
- AmbroxolDocument1 pageAmbroxolPrecious CarmelaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Silliman UniveristyDocument17 pagesNursing Care Plan: Silliman UniveristyKassandra LabeNo ratings yet
- NCP Abdominal PainDocument3 pagesNCP Abdominal PainShaina Rica TayagNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY OmeprazoleDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY OmeprazoleBRYCE WILLIAM GONo ratings yet
- Case Analysis For FNCPDocument6 pagesCase Analysis For FNCPOfficially RandomNo ratings yet
- BSN 215 Reflection Essay - LagoDocument2 pagesBSN 215 Reflection Essay - LagoAlliahkherzteen LagoNo ratings yet
- Ncp. HyperDocument2 pagesNcp. HyperZmiaNo ratings yet
- Burn - Daily Physical AssessmentDocument8 pagesBurn - Daily Physical AssessmentkrishcelNo ratings yet
- NCP and Drug Study For Ob WardDocument7 pagesNCP and Drug Study For Ob WardAce Fabrigas100% (1)
- NCP LupusDocument5 pagesNCP LupusMarwin OditaNo ratings yet
- 01 NGT Procedure With RationaleDocument4 pages01 NGT Procedure With RationaleAryaj SulitNo ratings yet
- Ortho NCPDocument3 pagesOrtho NCPMarshin Thea CelociaNo ratings yet
- NCP Cough PneumoniaDocument2 pagesNCP Cough PneumoniaAirme Raz AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Primaxin (Imipenem - Cilistatin)Document2 pagesPrimaxin (Imipenem - Cilistatin)ENo ratings yet
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument1 pageImpaired Physical MobilitySheena Yen de Pano-PagdalianNo ratings yet
- Nursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Spontaneous AbortionDocument2 pagesNursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Spontaneous AbortionMina RacadioNo ratings yet
- SNU49Document2 pagesSNU49Nora BacolNo ratings yet
- Rafin NCP and Drug StudyDocument7 pagesRafin NCP and Drug StudyCezanne CruzNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Date, Shift & Time Assessment Need Nursing Diagnosis Plan Intervention EvaluationDocument6 pagesDate, Shift & Time Assessment Need Nursing Diagnosis Plan Intervention EvaluationAubrey Unique EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: ER DrugsDocument5 pagesDrug Study: ER Drugsmaeca101No ratings yet
- Insulin Insulin Is A Hormone Central To Regulating Carbohydrate and Fat MetabolismDocument4 pagesInsulin Insulin Is A Hormone Central To Regulating Carbohydrate and Fat Metabolismmaeca101No ratings yet
- Drug Study: ER DrugsDocument5 pagesDrug Study: ER Drugsmaeca101No ratings yet
- Therapeutic Communication Techniques PresentationDocument17 pagesTherapeutic Communication Techniques Presentationmaeca101100% (2)
- Lesson PlanDocument1 pageLesson Planmaeca101No ratings yet
- Hypertension Mini Case StudyDocument5 pagesHypertension Mini Case Studymaeca101100% (1)
- Laboratory Exam Normal Value Details and IndicationsDocument5 pagesLaboratory Exam Normal Value Details and Indicationsmaeca101No ratings yet
- Name: Section: Group Number: Patient's InitialsDocument4 pagesName: Section: Group Number: Patient's Initialsmaeca101No ratings yet
- Broadsheet Internet EditionDocument12 pagesBroadsheet Internet Editionmaeca101No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug Studymaeca101No ratings yet
- Grade 8 Health (Performance Output)Document2 pagesGrade 8 Health (Performance Output)MARLON MARTINEZNo ratings yet
- Hi V and Hemophilia Addressing Stigma and DiscriminationDocument21 pagesHi V and Hemophilia Addressing Stigma and DiscriminationKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNo ratings yet
- Seminar Case Study FinalDocument36 pagesSeminar Case Study FinalshahadNo ratings yet
- Abo Incompatible Stem Cell Transplant - Laboratory Side BDocument28 pagesAbo Incompatible Stem Cell Transplant - Laboratory Side BAlita PalpialyNo ratings yet
- Agencies Related To Welfare Services To The ChildrenDocument68 pagesAgencies Related To Welfare Services To The ChildrenArchana89% (19)
- Clove Oil AnalgesicDocument6 pagesClove Oil AnalgesicyesiNo ratings yet
- Qafe Green Coffee-Power Point Presentation-FinalDocument11 pagesQafe Green Coffee-Power Point Presentation-FinalPrem MathewNo ratings yet
- Cue and Clue PL Idx PDX PTX Pmo&Ed: Mr. T/86Yo/ Ward 26 Subjective Non PharmacologyDocument8 pagesCue and Clue PL Idx PDX PTX Pmo&Ed: Mr. T/86Yo/ Ward 26 Subjective Non PharmacologyIka AyuNo ratings yet
- 4 Drug Study (Opd)Document4 pages4 Drug Study (Opd)Cristyl Shine BariaoNo ratings yet
- Yoga MatDocument13 pagesYoga MatAnanthNo ratings yet
- Chemical Hazards MT......Document32 pagesChemical Hazards MT......mayuri zanwarNo ratings yet
- Manuel Richards - Nasal Polyps Treatment Miracle EbookDocument23 pagesManuel Richards - Nasal Polyps Treatment Miracle EbookshandoshNo ratings yet
- Drug Interaction Report - Acetylsalicylic Acid, Atorvastatin, Carbamazepine, Enoxaparin, Escitalopram, Fluconazole, Losartan..Document7 pagesDrug Interaction Report - Acetylsalicylic Acid, Atorvastatin, Carbamazepine, Enoxaparin, Escitalopram, Fluconazole, Losartan..mariaclarasfreitas2No ratings yet
- Aagamanam - Final 28.4.2020 PDFDocument52 pagesAagamanam - Final 28.4.2020 PDFAnwar SalimNo ratings yet
- Immunology QuestionsDocument186 pagesImmunology QuestionsMoush AbdiNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts On Laboratory Biosafety-Converted - 1040766564Document49 pagesBasic Concepts On Laboratory Biosafety-Converted - 1040766564johaylie porrasNo ratings yet
- MastitisDocument2 pagesMastitisJuviely PremacioNo ratings yet
- HA RLE WS 24 Assessing Female Genitalia and RectumDocument9 pagesHA RLE WS 24 Assessing Female Genitalia and RectumANA DelafuenteNo ratings yet
- StoryDocument14 pagesStorynaitiksharma877No ratings yet
- (Ebook PDF) Health Psychology 10th Edition Download PDFDocument43 pages(Ebook PDF) Health Psychology 10th Edition Download PDFkyansrenker100% (6)
- MERCK MANUAL-Electrical InjuriesDocument6 pagesMERCK MANUAL-Electrical InjuriesJOSE LUIS FALCON CHAVEZNo ratings yet
- Semi-Lesson Plan OfficeDocument6 pagesSemi-Lesson Plan OfficeJezzamine SantosNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology UpdateDocument2 pagesOphthalmology UpdateskNo ratings yet
- SOP - Post Lockdown 150420 - Revised Final VersionDocument26 pagesSOP - Post Lockdown 150420 - Revised Final VersionKuls Kuls100% (1)
- Health EducationDocument5 pagesHealth EducationMichellin Lara VergaraNo ratings yet
- SEMINAR On HyperthyroidismDocument17 pagesSEMINAR On HyperthyroidismAmit RanjanNo ratings yet
- Anggraini & Pusspasari 2019Document8 pagesAnggraini & Pusspasari 2019Berlianti Citra MaulidyaNo ratings yet
- Cysts of The Oral CavityDocument270 pagesCysts of The Oral CavitySally Mahfouz100% (6)
- Evaluation of Sanitation Management at Bassajabalaba Secondary School in Bushenyi District Ishaka Municipality.Document9 pagesEvaluation of Sanitation Management at Bassajabalaba Secondary School in Bushenyi District Ishaka Municipality.KIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONNo ratings yet