Notes For Metallic Bonding
Notes For Metallic Bonding
Uploaded by
いい子Copyright:
Available Formats
Notes For Metallic Bonding
Notes For Metallic Bonding
Uploaded by
いい子Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Notes For Metallic Bonding
Notes For Metallic Bonding
Uploaded by
いい子Copyright:
Available Formats
Anglo-Chinese School (Independent) The Physical Setting Structure of Matter: What Lies Beneath
Objectives: Section A: Review of Metallic Bonding Section B: Physical Properties of Metals Section C: Overall Review of Chemical Bonding
Section A Review of Metallic Bonding
Zoom In
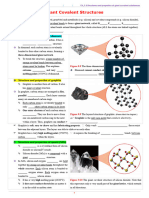
Figure 1: Diagram of a metallic lattice. Atoms in metals are packed very closely in an orderly arrangement. Each atom loses its valence electrons to become a positive ion. Metals are described as having a regular arrangement of positive ions in a sea of delocalized electrons. The electrons are free to move about within the structure and are said to form a sea of electrons around the metal ions. There are strong forces between the positive ions and electrons metallic bonding
Section B: Physical Properties of Metals
Property 1: High Melting Point and Boiling Point What do you understand by the term melting point? Melting Process: When a pure solid is heated, the particles in it gain energy and the vibration of the particles increases until eventually the particles are able to overcome the forces that hold them in their fixed positions. Hence, the melting point is the fixed temperature at which a pure solid turns into a liquid at atmospheric pressure. What do you understand by the term boiling point? Boiling process: When a pure liquid is heated, the particles in it gains energy and move more quickly. Eventually, the particles have enough energy to completely break the forces holding them together. The particles are now able to move freely and far apart. Hence, the boiling point is the temperature at which a pure liquid turns into a gas at atmospheric pressure.
Why do metals generally have a high melting point and high boiling point? Reason: As the forces of attraction between the sea of delocalized electrons and positive ions (cations) is very strong, a large amount of heat is required to break up the giant lattice. Hence, metals have a high melting point and boiling point. List some metals that have a high melting and boiling point.
Magnesium, Iron, Copper and Tungsten List some metals that have a low melting and boiling point.
Mercury and the Group I elements Application/Uses: Tungsten is used to make the filaments of light bulbs due to its high melting point. It does not melt even when glowing white-hot inside a bulb.
Welding is the most economical and efficient way to join metals permanently. It is the only way of joining two or more pieces of metals to make them act as a single piece.
Property 2: High Density Why do metals generally have a high density? Reason: As the ions in metals are closely packed in the lattice, they generally have high densities.
Property 3: Malleable and Ductile What do you understand by the term malleable? A substance is said to be malleable when it can be beaten into sheets. What do you understand by the term ductile? A substance is said to be ductile when it can be pulled out into wires.
metal ion
+ +
free electron
+ + +
applied force
+ + +
(a) Before a force is applied, the metal atoms form an orderly and rigid arrangement.
(b) When a force is applied, one layer of metal ions slides over the other.
Figure 2: Sliding of one layer of metal ions over others when a force is applied. If a small stress is put onto the metal, the layers of atoms will start to roll
over each other. If the stress is released again, they will fall back to their original positions. Under these circumstances, the metal is said to be elastic.
slip plane
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
+ +
Figure 3: Sliding of one layer of metal ions over others when a small stress is applied.
Figure 4: Sliding of one layer of metal ions over others when a large stress is applied. Why are pure metals generally malleable and ductile? Reason: Though the attraction between the sea of electrons and the metal ions is strong, it is not rigid. Combined with the regular arrangement of the ions in layers, the layers of ions can slip over each other into new positions when a force is applied to the metal, without breaking the metallic bond. Hence, metals are malleable and ductile. List some examples of metals that are malleable and ductile.
Aluminum Application/Uses: Aluminum is used to make foil for wrapping purposes due to its high malleability. Property 4: Thermal Conductivity
Why are metals usually good conductors of heat? When one end of a piece of metal is heated, the positive ions vibrate more vigorously. The vibrating ions transfer energy to the mobile electrons. These mobile electrons move to other parts of the metal and transmit this energy to other positive ions. In this way, heat is transferred quickly throughout the metal. List some examples of metals that are good conductors of heat.
Copper and aluminum Application/Uses: Copper is used to make kitchen utensils such as kettles, steam pipes, boilers, etc., due to its heat conductivity.
Aluminum is used to make kitchen utensils such as kettles, pots and pans due to its heat conductivity.
Property 5: Electrical Conductivity Why are metals good conductors of electricity?
e+ -
e-
Ammeter
e
-
e e
-
Free electrons leave the metal and moves towards the positive terminal
e e
-
e
-
e-
Metal
More electrons enter the metal from the negative terminal
The positive ions remain in position while the transfer of electrons takes place.
Figure 5: Mobile electrons in a metal connected to an electrical circuit. List some examples of metals that are good conductors of electricity.
Copper and aluminum Application/Uses: Large amounts of copper are used to make electrical wires and cables due to its good electrical conductivity.
Aluminum or its alloys are widely used in making overhead lines and energy cables due to its good electrical conductivity.
Characteristic
Ionic Compound
Covalent Compounds Simple Molecule Macromolecule Non-metals only Atoms
Metal
Bonding between: Particles present: State at r.t.p: Melting point & Boiling point:
Metal and non-metal Ions (Cations & Anions) Solid High Strong electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions. A lot of energy is required to break them. Conducts electricity only in molten and aqueous state but not in solid state. In molten and aqueous state, ions are mobile and able to conduct electrical
Non metals only Molecules
Metals only Fixed positive ions in a sea of delocalized electrons Solid High *Exception: Hg Strong metallic bond between ions and delocalized electrons.
Gas or volatile liquid Low Weak Van der Waals forces between molecules. Little energy is required to break them. Does not conduct electricity in any state.
Solid High Exist as macromolecule with strong covalent bonds between atoms. A lot of energy is required to break them. Does not conduct electricity in any state. *Exception: Graphite is a
Electrical Conductivity:
Conducts electricity in solid and molten state.
Exist as molecules. particles.
conductor in solid state. Absence of mobile charged Presence of mobile electron cloud which are able to carry electrical silicon and silica.
Absence of mobile charged particles in diamond,
charges. In solid state, ions are held rigidly in fixed positions and are unable to move thus unable to conduct Solubility: electricity. Soluble in polar solvents like water. Soluble in non-polar / organic solvents like chloroform and benzene. Examples: Diagram: Sodium Chloride Insoluble in water. Iodine
Graphite can conduct electricity due to the presence of mobile electrons which can carry electrical charges. Insoluble in water and almost all solvents.
charges.
Insoluble in water.
Diamond
Graphite
Magnesium
BONDING
Ionic (Electrovalent) define as Transfer of electron (s) from metals to non-metals forms ions 1e2e3emacromolecules diamond, graphite, silicon and silicon dioxide Properties (1) High m.p. and b.p. (2) Non-conductors of electricity *exception: graphite (3) Insoluble in all solvents (4) Exist as a solid at r.t.p.
Covalent define as Sharing of electron (s) from non-metals and non-metals forms simple molecules
Metallic define as Lattice of positive fixed ions in a sea of electrons from metals only forms Properties (1) High m.p. and b.p. (2) High density (3) Malleable and ductile (4) Conductors of heat (5) Conductors of electricity (6) Solids at r.t.p.
elements H2, O2, N2, Cl2
compounds HCl, H2O, NH3 can have
NaCl
NaCl 2 MgCl
AlCl3 AlCl3
lattice structure Properties (1) High m.p. and b.p. (2) Conducts electricity in molten or aqueous state (3) Dissolves in polar solvents (4) Usu. solid at r.t.p.
single bonds H-H
double bonds O=O
triple bonds NN
Properties (1) Low m.p. and b.p. (2) Non-conductors of electricity (3) Dissolves in non-polar solvents (4) Usu. exists as liquids and gases at r.t.p.
Section C Overall Review of Chemical Bonding
Substance Formula sodium chloride NaCl Bonding diagram Structure type ionic
methane
CH4
simple molecular
carbon dioxide diamond
CO2
simple molecular
giant molecular
copper
Cu
metallic
You might also like
- Chemistry Notes (The Particulate Nature of Matter)Document5 pagesChemistry Notes (The Particulate Nature of Matter)Teo Jia Ming Nickolas100% (3)
- Topic 2 Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument19 pagesTopic 2 Kinetic Particle TheoryKaixin HuangNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Electrolysis With Instructional LessonDocument15 pagesLesson Plan Electrolysis With Instructional LessonMichael Harris100% (1)
- IGCSE Chemistry DefinitionsDocument5 pagesIGCSE Chemistry DefinitionsTanmay Karur100% (1)
- Reactivity Series ExperimentDocument3 pagesReactivity Series ExperimentSourabh DasNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Worksheet 17.1Document1 pageIGCSE Physics Worksheet 17.1Alex DatsyukNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Transport In HumansFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Transport In HumansNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument26 pagesMetallic BondingAlaa HafizNo ratings yet
- Ch3 - Chemical Bonding (IGCSE Study Notes)Document11 pagesCh3 - Chemical Bonding (IGCSE Study Notes)Amal HassanNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Chemical BondsDocument7 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Chemical BondsdanielmahsaNo ratings yet
- Lattice EnergyDocument14 pagesLattice Energyvita iftitahiyahNo ratings yet
- Igcse Chemistry NotesDocument46 pagesIgcse Chemistry Notesapi-1811760180% (1)
- O Level Chemistry Complete Notes PDFDocument192 pagesO Level Chemistry Complete Notes PDFMian zainNo ratings yet
- Elements Compounds and Mixtures HW For AssessmentDocument9 pagesElements Compounds and Mixtures HW For Assessmentsmic3904No ratings yet
- 1 Lattice Energy and Born-Haber Cycle 1Document31 pages1 Lattice Energy and Born-Haber Cycle 1ashleyjap123No ratings yet
- Chap 8 Class 9 Physics NotesDocument16 pagesChap 8 Class 9 Physics NotesMustafa Bin AmarNo ratings yet
- Practice Worksheet of Chemical BondingDocument2 pagesPractice Worksheet of Chemical Bondingch khakanNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab ReportDocument3 pagesPhysics Lab ReportRey Malvin SG PallominaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 The Particulate Nature of Matter NotesDocument7 pagesTopic 1 The Particulate Nature of Matter Notessteve KingNo ratings yet
- Addu High School Hithadhoo/Addu C TOPIC: ENTROPY-Enthalpy of Solution Worksheet 2Document8 pagesAddu High School Hithadhoo/Addu C TOPIC: ENTROPY-Enthalpy of Solution Worksheet 2Neen NaazNo ratings yet
- IBDP Chemistry Bonding Questions MSDocument10 pagesIBDP Chemistry Bonding Questions MSsquailgeNo ratings yet
- Chap5 IGCSE Chemistry NotesDocument13 pagesChap5 IGCSE Chemistry NotesMisbah Kamran0% (1)
- IGCSE 22 ElectricChargeDocument21 pagesIGCSE 22 ElectricChargeSam JordanNo ratings yet
- Elements and Compounds For MYP 3Document18 pagesElements and Compounds For MYP 3Maira ButtNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 (Electrolysis) Form 4Document9 pagesChapter 6 (Electrolysis) Form 4AliahYusriNo ratings yet
- Chemical Energetics: Igcse ChemistryDocument12 pagesChemical Energetics: Igcse ChemistrySherly LeticiaNo ratings yet
- C10 Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument55 pagesC10 Acids, Bases and SaltsKris DookharanNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules & IonsDocument5 pagesAtoms, Molecules & IonsSalman ZubaerNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: CHEMISTRY 9701/42Document24 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: CHEMISTRY 9701/42Ahmed NaserNo ratings yet
- Static Electricity: Cambridge IGCSE PhysicsDocument27 pagesStatic Electricity: Cambridge IGCSE PhysicsSajayanKSNo ratings yet
- O Levels Cehimstry-Atomic Structure - Chemical BondingDocument16 pagesO Levels Cehimstry-Atomic Structure - Chemical Bondingjave_yeongNo ratings yet
- Writing and Balancing Chemical EquationsDocument31 pagesWriting and Balancing Chemical EquationsEthan-Dale BrownNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 17 Static ElectricityDocument54 pagesChapter - 17 Static ElectricityNayeem Hakim100% (1)
- Chemical Bonding NotesDocument9 pagesChemical Bonding NotesLouisiana SollestreNo ratings yet
- Reactivity SeriesDocument19 pagesReactivity SeriesZheng JoeyNo ratings yet
- Definitions - Electricity - Edexcel Physics IGCSEDocument3 pagesDefinitions - Electricity - Edexcel Physics IGCSESyed Moinul HoqueNo ratings yet
- EDEXCEL MODEL PHYSICS ANSWERS 1995-2001 (04-Oct-10)Document265 pagesEDEXCEL MODEL PHYSICS ANSWERS 1995-2001 (04-Oct-10)Radiant ree100% (1)
- The Particulate Nature of Matter: IGCSE ChemistryDocument8 pagesThe Particulate Nature of Matter: IGCSE ChemistryVibinraj K Nileshwar100% (1)
- IGCSE Chemistry Section 2 Lesson 1Document66 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Section 2 Lesson 1Antonia Putri Sri Nova YolandhaNo ratings yet
- Ib Chemistry: Topic 3 PeriodicityDocument90 pagesIb Chemistry: Topic 3 Periodicitynoob masterNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Simple Magnetism and Magnetic FieldsDocument9 pages4.1 Simple Magnetism and Magnetic FieldsIshraque MahmudNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Periodic TableDocument0 pagesIntroduction To The Periodic TableAdnan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class 7 Science Question PaperDocument3 pagesCbse Class 7 Science Question PaperSunaina RawatNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Physics - Oup - Com.pk Download (252 Pages - Free)Document2 pagesFundamental Physics - Oup - Com.pk Download (252 Pages - Free)patrick shulaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding 1Document81 pagesChemical Bonding 1RIMMY AUGUSTINE 2138110No ratings yet
- List of Definition in Chemistry F4Document7 pagesList of Definition in Chemistry F4Lil' Nyeh100% (1)
- 9.3 Giant Covalent StructuresDocument2 pages9.3 Giant Covalent StructureshadenluiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument24 pagesChapter 11 Acids, Bases and SaltsSook JeanNo ratings yet
- A Level Physic 2 2017 PDFDocument324 pagesA Level Physic 2 2017 PDFAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- AS Level Chemistry - Unit 1 Revision GuideDocument16 pagesAS Level Chemistry - Unit 1 Revision GuideJoel Biffin100% (1)
- Caie A2 Chemistry 9701 Theory v3Document33 pagesCaie A2 Chemistry 9701 Theory v3Aditya Drolia100% (1)
- Complete Chemistry Revision Guide IGCSEDocument290 pagesComplete Chemistry Revision Guide IGCSEsakibsultan_308No ratings yet
- Light NotesDocument13 pagesLight NoteskenixtanNo ratings yet
- Space Physics Question Sheet (SOLVED)Document24 pagesSpace Physics Question Sheet (SOLVED)AHMED100% (1)
- What Is A Mole SummativeDocument8 pagesWhat Is A Mole Summativeapi-291560513No ratings yet
- Year 10 - iGCSE - Topic 1 - Bonding - Metallic BondingDocument32 pagesYear 10 - iGCSE - Topic 1 - Bonding - Metallic BondingAdithyaNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 2Document15 pagesAssignment - 2padhiyararpitaNo ratings yet
- Nso Science Olympiad Sample Question Paper 1 Class 7Document31 pagesNso Science Olympiad Sample Question Paper 1 Class 7Himanshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- TestDocument6 pagesTestvergereNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Physical Science Course of StudyDocument3 pagesGrade 11 Physical Science Course of StudyJobeth Presto AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Chapterwise Important QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapterwise Important Questionsrl3559980No ratings yet
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology Organic Chemistry 5.13Document2 pagesMassachusetts Institute of Technology Organic Chemistry 5.13Mauricio Andrés Gutiérrez BravoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding - Study NotesDocument15 pagesChemical Bonding - Study NotesTamoghna DeyNo ratings yet
- Dipole Moments in Organic ChemistryDocument294 pagesDipole Moments in Organic Chemistrysankar RNo ratings yet
- Class IX Chemistry Chapter 05Document10 pagesClass IX Chemistry Chapter 05Sam FisherNo ratings yet
- Jose P. Laurel Sr. High SchoolDocument8 pagesJose P. Laurel Sr. High SchoolEricha Solomon0% (1)
- Project Work Chem.Document48 pagesProject Work Chem.kabiraazthakur01No ratings yet
- Lec 2Document43 pagesLec 2SaadFarooqNo ratings yet
- Roni - Matter ProbsDocument11 pagesRoni - Matter ProbsMoses Junior100% (1)
- Everyday Science Mcqs by Pakmcqs FullDocument82 pagesEveryday Science Mcqs by Pakmcqs FullJiskani Nawaz100% (2)
- Lesson 1.2 Intermolecular Forces of Attraction (Study Guide)Document22 pagesLesson 1.2 Intermolecular Forces of Attraction (Study Guide)Wilmark Rivera Official100% (2)
- Formal Charge WorksheetDocument3 pagesFormal Charge WorksheethbjvghcgNo ratings yet
- Rubber PhysicsDocument140 pagesRubber Physicssvk_ntNo ratings yet
- Zbornik Radova Sa OTEH 2014Document883 pagesZbornik Radova Sa OTEH 2014Aerokosmonautika100% (1)
- Laboratory Technician Chemistry Group SyllabusDocument4 pagesLaboratory Technician Chemistry Group SyllabusMayursinh SolankiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry HydrocarbonsDocument144 pagesChemistry HydrocarbonsRudens100% (2)
- Chemistry Question Bank 1 - FinalDocument27 pagesChemistry Question Bank 1 - FinalKim LeeNo ratings yet
- ICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper - 2018 Time: 2 Hrs. Max. Marks: 80Document6 pagesICSE Board Class X Chemistry Board Paper - 2018 Time: 2 Hrs. Max. Marks: 80King YashasNo ratings yet
- Molecular Spectra-1Document17 pagesMolecular Spectra-1maldeansh.pvtNo ratings yet
- Sat TestDocument14 pagesSat TestDuy Khang Bui100% (1)
- Experiment 12Document7 pagesExperiment 12Hugo Andrei Zambrano IglesiasNo ratings yet
- MEC 353 Fluid Mechanics: Lecture NotesDocument470 pagesMEC 353 Fluid Mechanics: Lecture NotesbaderNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding - Important Qs - Important Questions - 2021-22 - ICSE 9th Atomic Structure and Chemical BondingDocument3 pagesAtomic Structure and Chemical Bonding - Important Qs - Important Questions - 2021-22 - ICSE 9th Atomic Structure and Chemical BondingVivaan Gandhi100% (2)
- Chemistry Syllabus & Question Bank Course Title: Chemistry, Course Code: CHEM-111 (Credit: 3)Document17 pagesChemistry Syllabus & Question Bank Course Title: Chemistry, Course Code: CHEM-111 (Credit: 3)saifNo ratings yet
- Timetable Channel 15 Engineering Sciences, IIT MADRASDocument3 pagesTimetable Channel 15 Engineering Sciences, IIT MADRASumashankaryaligarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8.5 Bond Order and LengthDocument7 pagesLesson 8.5 Bond Order and LengthNewshaSajadiNo ratings yet
- UdkdfhvkdhfnfDocument12 pagesUdkdfhvkdhfnfG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet