DOAC Chart
DOAC Chart
Uploaded by
Rawan ZayedCopyright:
Available Formats
DOAC Chart
DOAC Chart
Uploaded by
Rawan ZayedOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
DOAC Chart
DOAC Chart
Uploaded by
Rawan ZayedCopyright:
Available Formats
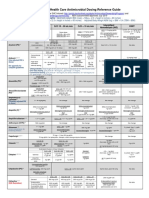
Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs)
Dabigatran Rivaroxaban Apixaban Edoxaban
(Pradaxa) (Xarelto) (Eliquis) (Savaysa)
Drug Classification Selective thrombin inhibitor Selective direct Xa inhibitor Selective direct Xa inhibitor Selective direct Xa inhibitor
FDA Approved - Nonvalvular AF - Nonvalvular AF - Nonvalvular AF - Nonvalvular AF
Indications - Treatment of VTE - Treatment of VTE - Treatment of VTE - Treatment of VTE
- Reduce risk of recurrent VTE - Reduce risk of recurrent VTE - Reduce risk of recurrent VTE
- VTE prophylaxis (hip) - VTE prophylaxis (hip & knee) - VTE prophylaxis (hip & knee)
Half-life 12-17 hrs 5-9 hrs 8-15 hrs 10-14 hrs
14-17 hrs (elderly) 9-12 hrs (elderly)
Time to max effect 2 hrs 2-4 hrs 3 hrs 1-2 hrs
Renal Clearance 80% renal 66% renal 25% renal 50% renal
20% biliary 33% biliary 75% biliary 50% biliary
Dosage AF: AF: AF: AF:
150 mg BID 20 mg DAILY with PM meal 5 mg BID 60 mg DAILY
VTE treatment & Recurrent VTE: VTE treatment: VTE treatment: VTE treatment:
150 mg BID after 5-10 days of 15 mg BID x 21 days, then 20 10 mg BID x 7 days, then 5 60 mg daily after 5-10 days of
parenteral anticoagulant mg DAILY with PM meal mg BID parenteral anticoagulant
VTE Prophylaxis: Recurrent VTE: Recurrent VTE: 2.5 mg BID
110 mg 1-4 hrs post hip 20 mg daily with PM meal
surgery then 220 mg daily x VTE prophylaxis:
35 days VTE prophylaxis: Hip surgery: 2.5 mg BID x 35
Hip surgery: 10 mg daily x 35 days
days Knee surgery: 2.5 mg BID x
Knee surgery: 10 mg daily x 12 12 days
days
Dosing Adjustments and AF: CrCl 15-30: 75 mg BID AF: CrCl 15-50: 15 mg daily AF: if 2 of 3 criteria met then AF: CrCl > 95: avoid use
Considerations CrCl < 15: avoid use CrCl < 15: avoid use decrease to 2.5 mg BID: CrCl 15 – 30: 30 mg daily
Age > 80 CrCl < 15: avoid use
VTE: CrCl < 30: avoid use VTE Treatment and Prophylaxis: Wt < 60 kg
CrCl < 30: avoid use Creatinine > 1.5 VTE: CrCl 15 – 30: 30 mg daily
CrCl < 15: avoid use
Hemodialysis: 5 mg BID (reduce
dose if 2 of 3 criteria above met)
VTE Treatment and Prophylaxis:
CrCl < 15: avoid use
Contraindications - Avoid in pregnancy, breastfeeding or in severe liver disease
Monitoring No lab testing available. All DOACs affect the INR. Measuring INRs during co-administration may not be useful for determining an appropriate
dose of warfarin.
Peri-procedure Pre- - Standard bleed risk procedure - Standard bleed risk procedure - Standard bleed risk procedure - Standard bleed risk procedure
use op CrCl ≥ 50: stop 1-2 days prior CrCl > 30: stop 24 hrs prior Scr ≥ 50: stop 24 hrs prior CrCl ≥ 50: stop 24 hrs prior
(see U-Connect CrCl < 50: stop 3-5 days prior CrCl < 30: stop 48 hrs prior Scr < 50: stop 48 hrs prior CrCl < 50: stop 48 hrs prior
Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs)
for UW guidelines)
- High bleed risk procedure: - High bleed risk procedure: - High bleed risk procedure: - High bleed risk procedure:
CrCl ≥ 50: stop 2-4 days prior CrCl > 30: stop 48 hrs prior CrCl ≥ 50: stop 48 hrs prior CrCl ≥ 50: stop 48 hrs prior
CrCl < 50: stop > 5 days prior CrCl < 30: stop 72 hrs prior CrCl < 50: stop 72 hrs prior CrCl < 50: stop 72 hrs prior
Post- - For low bleed risk surgery restart within 24 hrs post-op if ok with surgeon
op - For high bleed risk surgery restart within 72 hrs post-op if ok with surgeon
Switching from DOAC to - If CrCl > 50: start warfarin 3 days Initiate warfarin & a parenteral If continuous anticoagulation is - If taking 60 mg, reduce to 30 mg
warfarin prior to stopping dabigatran anticoagulant 24 hrs after necessary, stop apixaban & and begin warfarin
- If CrCl 31-50: start warfarin 2 stopping rivaroxaban begin both a parenteral - If taking 30 mg, reduce to 15 mg
days prior to stopping dabigatran anticoagulant & warfarin when and begin warfarin
- If CrCl 15-30: start warfarin 1 day next dose is due; stop parenteral - measure INR at least weekly and
prior to stopping dabigatran anticoagulant when INR at goal just prior to the use of edoxaban
- when INR > 2.0 stop edoxaban
Switching from DOAC to - If CrCl >30, start UFH or - If CrCl >30, start UFH or Start UFH or enoxaparin 12 hrs D/c edoxaban and start parenteral
IV UFH or enoxaparin enoxaparin 12 hrs after last dose enoxaparin 12 hrs after last dose after the last apixaban dose AC at the time of next dose of
- If CrCl <30, consider starting - If CrCl <30, consider starting edoxaban
UFH or enoxaparin 24 hrs after last UFH or enoxaparin 24 hrs after
dose last dose
Switching from warfarin Allow INR to drop to < 2.0 before Allow INR to drop to < 3.0 before Allow INR to drop to < 2.0 before Start when INR is < 2.5
to DOAC initiating initiating initiating
Switching from Start DOAC 2 hrs before the time to next subcutaneous anticoagulant dose Discontinue LMWH and start
parenteral AC to DOAC Start DOAC at the time of IV heparin discontinuation edoxaban at the time of next
schedule dose LMWH
- Discontinue heparin drip and
start edoxaban 4 hrs later
Recommendations for - Only DOAC with antidote: - For all DOACs hemostasis expected within 12-24 hrs after last dose
bleeding besides blood Idarucizumab - Oral activated charcoal given within 2 hrs may decrease plasma concentrations
products (see UW - Only DOAC that can be
guidelines on U-Connect) moderately reversed by dialysis
Missed Dose - Take missed dose ASAP, but if - If taking 15 mg BID: Take - Take missed dose ASAP on same day
next dose is < 6 hrs away, skip ASAP to ensure 30 mg daily - The dose should not be doubled to make up for a missed dose
the missed dose - For daily dose: Take missed
- Do not take 2 doses at the same dose immediately
time
Drug Interactions - P-gp & strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (amiodarone, cyclosporine, ketoconazole, quinidine, verapamil, azole antifungals, nicardipine, ritonavir), may
serum concentration
- P-gp & strong CYP3A4 inducers (carbamazepine, dexamethasone, phenytoin, prazosin, rifampin, nafcillin, rifampin) may decrease the serum
concentration
Use for electrical Demonstrated to be effective anti-coagulant in the setting of cardioversion with guidelines similar to warfarin
cardioversion
Nonbleeding Side Dyspepsia (5-10%) None
Effects
Advantages - Fixed dose
- No bridging
- No INR monitoring required
- No food restrictions & fewer drug interactions
Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs)
Disadvantages - Cost
- Lack of antidote & difficult to manage bleeding
- Difficult to determine compliance
- Missed dose may place pt at increased risk of thromboembolic event
- Renal monitoring and dose adjustment required
Lab Frequency follow- Yearly: Hgb, renal and liver function
up 6 monthly: Renal function if CrCl 30-60 ml/min, or if on dabigatran and > 75 years or fragile
3 monthly: If co-morbidity or condition that may impact renal or hepatic function
References:
European Heart Rhythm Association Practical Guide on the use of new oral anticoagulants in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation (2013) 15, 625-651.
Chest Supplement, Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th edition, ACCP.
RE-LY trial: NEJM 2009; 361:1139
ROCKET-AF trial: NEJM 2011: 365:883.
ARISTOTLE trial: NEJM 2011: 365:981.
Package inserts from Pradaxa, Xarelto, Eliquis, Savaysa
Developed by Kathy Wackerle, APRN-BC
Reviewed by Dr. Craig January
October 2015
You might also like
- Dosage Calculation Practice WorkbookDocument35 pagesDosage Calculation Practice Workbookcrazy crazy crazy100% (1)
- NEONATOLOGYDocument8 pagesNEONATOLOGYmymamym100% (1)
- VTE Risk AssessmentDocument2 pagesVTE Risk AssessmentpriyopanjiNo ratings yet
- Route of AdministrationDocument48 pagesRoute of AdministrationFranchesca LugoNo ratings yet
- Venous Thromboembolism With Blanks ResidentsDocument9 pagesVenous Thromboembolism With Blanks Residentsapi-648714317No ratings yet
- Mild Moderate Severe Clinical Criteria: Covid ProtocolDocument4 pagesMild Moderate Severe Clinical Criteria: Covid ProtocolSiaNo ratings yet
- (April 2020) : Is The Indication Appropriate For A Doac?Document1 page(April 2020) : Is The Indication Appropriate For A Doac?SNo ratings yet
- ABVD-v1.1Document5 pagesABVD-v1.1hapnt79No ratings yet
- SHC ABX Dosing GuideDocument7 pagesSHC ABX Dosing GuideDanielVillaNo ratings yet
- Antiplatelet Drug Comparison Chart (Asa-Clopi-Prasu-Tica)Document1 pageAntiplatelet Drug Comparison Chart (Asa-Clopi-Prasu-Tica)Ponpimol Odee BongkeawNo ratings yet
- Acid Supressive TherapyDocument89 pagesAcid Supressive TherapyWahyu Agung DewaandikaNo ratings yet
- Thrombosis Risk Factor Assessment (Choose All That Apply) : Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Prophylaxis OrdersDocument2 pagesThrombosis Risk Factor Assessment (Choose All That Apply) : Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Prophylaxis OrdersPutu Gizha Satrya GautamaNo ratings yet
- Stanford Health Care Antimicrobial Dosing Reference GuideDocument7 pagesStanford Health Care Antimicrobial Dosing Reference GuideKarl Martin PinedaNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Dosing GuideDocument7 pagesAntimicrobial Dosing GuideMuhammad RawasNo ratings yet
- SHC ABX Dosing GuideDocument7 pagesSHC ABX Dosing GuideDeena AlJawamisNo ratings yet
- NOAC ChartDocument2 pagesNOAC Chartsgod34No ratings yet
- 2014 SHC ABX Dosing GuideDocument4 pages2014 SHC ABX Dosing GuideisnaeniNo ratings yet
- Revised COVID 19 SARS-COV2 Treatment Protocol - FinalDocument6 pagesRevised COVID 19 SARS-COV2 Treatment Protocol - FinalupsahuNo ratings yet
- Protocolo Covid 19 Ihss HRN PDFDocument5 pagesProtocolo Covid 19 Ihss HRN PDFJennifer CarcamoNo ratings yet
- (R) Choep: IndicationDocument5 pages(R) Choep: IndicationAlina CrissNo ratings yet
- NH Protocol For Covid Management FinalDocument7 pagesNH Protocol For Covid Management FinalhoneyworksNo ratings yet
- SHC Antimicrobial Dosing GuideDocument7 pagesSHC Antimicrobial Dosing GuideHelder LopesNo ratings yet
- Anticoagulation 2024Document11 pagesAnticoagulation 2024V NNo ratings yet
- Drugrenaladjustment 12052565Document18 pagesDrugrenaladjustment 12052565jirat iyarapongNo ratings yet
- BMC COVID Anticoagulation Algorithm Update 5 1 20Document1 pageBMC COVID Anticoagulation Algorithm Update 5 1 20Avinash KumbharNo ratings yet
- SHC Vancomycin Dosing GuideDocument8 pagesSHC Vancomycin Dosing GuidePitchya WangmeesriNo ratings yet
- FAQ - DOAC in CKD Update - FinalDocument4 pagesFAQ - DOAC in CKD Update - Finalraea.dobsonNo ratings yet
- STEMI NotesDocument8 pagesSTEMI NotesIzzul HafiyNo ratings yet
- PTO DM 2 Rev Akhir FikkDocument30 pagesPTO DM 2 Rev Akhir FikkDhani WiganiNo ratings yet
- Renal Dosage Adjustment Guidelines For Antimicrobials: WWW - Unmc.edu/aspDocument34 pagesRenal Dosage Adjustment Guidelines For Antimicrobials: WWW - Unmc.edu/aspعبدالواسع نعمانNo ratings yet
- XARELTODocument4 pagesXARELTOMohammed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Stanford Dosing AntibioticsDocument6 pagesStanford Dosing AntibioticsSayeerah MamaNo ratings yet
- Management of Convulsion in PaediatricsDocument21 pagesManagement of Convulsion in PaediatricsjuwelukgNo ratings yet
- 38054 台北市聯合醫院抗生素商品名對照表 PDFDocument99 pages38054 台北市聯合醫院抗生素商品名對照表 PDFka timNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Drug Dosing GuidelinesDocument182 pagesPediatric Drug Dosing GuidelinesamiratolanNo ratings yet
- Frequent Asking & QuestionDocument18 pagesFrequent Asking & QuestionLhynda Priarti LatifNo ratings yet
- R Mini CHOPDocument5 pagesR Mini CHOPgrethelvalencialaurelNo ratings yet
- Sample Obstetrics Orders: By: Mitra Ahmad SoltaniDocument62 pagesSample Obstetrics Orders: By: Mitra Ahmad Soltanialmslmani9524100% (2)
- 3 - Ob Orders, or Tech, MaterialsDocument14 pages3 - Ob Orders, or Tech, MaterialsJC GoodLifeNo ratings yet
- Stanford Hospital & Clinics Antimicrobial Dosing Reference Guide 2013Document3 pagesStanford Hospital & Clinics Antimicrobial Dosing Reference Guide 2013SANCHOSKYNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Dosing Guidelines For Renal ImpairmentDocument6 pagesAntibiotic Dosing Guidelines For Renal ImpairmentvitauxianaNo ratings yet
- SHC Vancomycin Dosing Guide PDFDocument6 pagesSHC Vancomycin Dosing Guide PDFAbu Hammoud AlyazeediNo ratings yet
- Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs) For Treatment of DVTDocument11 pagesDirect Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs) For Treatment of DVTLuana MNo ratings yet
- GP AEC DVT Talk FinalDocument57 pagesGP AEC DVT Talk FinalTuan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Stanford Health Care Antimicrobial Dosing Reference GuideDocument6 pagesStanford Health Care Antimicrobial Dosing Reference GuidePaan SuthahathaiNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 Resource PackDocument22 pagesPaper 1 Resource PackHaw Feng ChanNo ratings yet
- Stress Related Mucosal Injury (SRMI) - FinalDocument36 pagesStress Related Mucosal Injury (SRMI) - Finalvadivel kumaran sivasankaranNo ratings yet
- Doacs For VteDocument10 pagesDoacs For VteAhmed MohammedNo ratings yet
- Antiretroviral Therapy: Pharmacology: Cristina Gruta, PharmdDocument47 pagesAntiretroviral Therapy: Pharmacology: Cristina Gruta, PharmdMalueth AnguiNo ratings yet
- Lipids Topic DiscussionDocument10 pagesLipids Topic Discussionapi-665372449No ratings yet
- Antibiotik For Renal FailureDocument6 pagesAntibiotik For Renal FailureWidhy Joss BangetzNo ratings yet
- White Chodosh Appendix VI HSV FINALDocument5 pagesWhite Chodosh Appendix VI HSV FINALSuzana VoiculescuNo ratings yet
- SHC Vancomycin Dosing GuideDocument9 pagesSHC Vancomycin Dosing GuideDanielVillaNo ratings yet
- Renal PharmacologyDocument52 pagesRenal Pharmacologyashraf0% (1)
- Guide To AnticoagulantsDocument6 pagesGuide To AnticoagulantssargentsilerNo ratings yet
- Olaparib BRCA Mutated HER2 Negative Early Breast CancerDocument8 pagesOlaparib BRCA Mutated HER2 Negative Early Breast CancersmokkerNo ratings yet
- Abvd Hem HLDocument6 pagesAbvd Hem HLTowhidulIslamNo ratings yet
- Acs 2023 Part 4 Presentation VersionDocument38 pagesAcs 2023 Part 4 Presentation Versionapi-668470097No ratings yet
- VancomycinDocument6 pagesVancomycinMohammed SaifanNo ratings yet
- 2016 01 M.R. Antibiotic Renal Dosing PDFDocument5 pages2016 01 M.R. Antibiotic Renal Dosing PDFMardari Bogdan CatalinNo ratings yet
- Simplifying Psychiatric Documentation: Time-Saving Templates for Medication RecommendationsFrom EverandSimplifying Psychiatric Documentation: Time-Saving Templates for Medication RecommendationsNo ratings yet
- Financialmanagement 1Document3 pagesFinancialmanagement 1Sujatha J Jayabal100% (2)
- Evaluasi Penggunaan Antibiotika Berdasarkan Metode: Defined Daily Dose (DDD) Pada Pasien Ulkus DiabetikumDocument9 pagesEvaluasi Penggunaan Antibiotika Berdasarkan Metode: Defined Daily Dose (DDD) Pada Pasien Ulkus DiabetikumAzahrah Mawaddah IINo ratings yet
- Notices For The Application of Plant Master FileDocument7 pagesNotices For The Application of Plant Master FileAnandharaj AsaithambiNo ratings yet
- Advanced Cosmetic Sciences Admission Procedure 21-22 English AbstractDocument9 pagesAdvanced Cosmetic Sciences Admission Procedure 21-22 English AbstractTinotenda GambaraNo ratings yet
- Kansas Pharmaceutical Collaborative - 2006 CSG Innovations Award WinngerDocument6 pagesKansas Pharmaceutical Collaborative - 2006 CSG Innovations Award Winngerbvoit1895No ratings yet
- Technician Manual PDFDocument35 pagesTechnician Manual PDFMohamed RageNo ratings yet
- Bpharm 5 Sem Industrial Pharmacy 1 bp502t 2022Document1 pageBpharm 5 Sem Industrial Pharmacy 1 bp502t 2022Shaan MohammadNo ratings yet
- Sambungan Data Persediaan Obat PuskesmasDocument7 pagesSambungan Data Persediaan Obat PuskesmasMerry OctafiaNo ratings yet
- Formatting, Assembling, and Submitting The New Drug ApplicationDocument25 pagesFormatting, Assembling, and Submitting The New Drug ApplicationAgnimitra Dinda100% (1)
- 02-2 A History of Pharmacy in PicturesDocument39 pages02-2 A History of Pharmacy in Picturesnimona berhanuNo ratings yet
- 08-12-2022Document26 pages08-12-2022Hendy Kilat BuanaNo ratings yet
- Herbs, Laboratories, and RevolDocument15 pagesHerbs, Laboratories, and Revolhung tsung jenNo ratings yet
- Daftar Obat UgdDocument5 pagesDaftar Obat Ugddedi darmawanNo ratings yet
- Quick Review On All The Aphorisms of Organon of Medicine 6 EditionDocument11 pagesQuick Review On All The Aphorisms of Organon of Medicine 6 EditionVishalNo ratings yet
- Rational Use of MedicineDocument18 pagesRational Use of MedicineSteven A'Baqr EgiliNo ratings yet
- Dr. G Praveen KumarDocument36 pagesDr. G Praveen KumarMuhammad Riaz BhattiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Multiple Choice Questions: InstructionsDocument16 pagesChapter 4: Multiple Choice Questions: InstructionsDavidNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis in Preclinical DevelopementDocument26 pagesData Analysis in Preclinical DevelopementOmkar KaleNo ratings yet
- Hospital Pharmacy Practice in Saudi Arabia: Dispensing and Administration in The Riyadh RegionDocument9 pagesHospital Pharmacy Practice in Saudi Arabia: Dispensing and Administration in The Riyadh RegionNisa SundariNo ratings yet
- MEDICAMENTOSDocument8 pagesMEDICAMENTOSPakinn ShadoowNo ratings yet
- List of Predator JournalsDocument31 pagesList of Predator JournalsVicko SuswidiantoroNo ratings yet
- Daily Activities of A Clinical PharmacistDocument20 pagesDaily Activities of A Clinical PharmacistAnoop Tandur0% (1)
- Perspectives of Hospital Administration in Geriatrics Care: Miguel A. Ramos JR., MD, PHDDocument4 pagesPerspectives of Hospital Administration in Geriatrics Care: Miguel A. Ramos JR., MD, PHDrnrmmanphdNo ratings yet
- Pre-Import Permit: CommodityDocument3 pagesPre-Import Permit: Commoditychristina tetemkeNo ratings yet
- Hospital Functions and Support Functions AssignmentDocument7 pagesHospital Functions and Support Functions AssignmentPrasoon BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- ECTD Tech Guide v1.1Document26 pagesECTD Tech Guide v1.1DontYou KnowMeNo ratings yet
- FDA EUA Covid-19 TestsDocument3 pagesFDA EUA Covid-19 TestsActionNewsJaxNo ratings yet
- AUC and Clearance-Drug CalculationsDocument6 pagesAUC and Clearance-Drug CalculationsManikanta GupthaNo ratings yet