0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 viewsWeek 07 Sequential Circuits Sec A
Week 07 Sequential Circuits Sec A
Uploaded by
Muhammad RafayThis document discusses sequential logic circuits and storage elements. It covers:
1) Sequential circuits contain feedback paths through storage elements like latches and flip-flops that allow the circuit to have a memory of past states.
2) There are two types of sequential circuits - synchronous use a global clock while asynchronous update individually without synchronization.
3) Latches and flip-flops are described as the basic storage elements, with latches being level sensitive and flip-flops edge sensitive due to using clock transitions.
4) Common latch and flip-flop circuits like the SR latch, D latch, and JK flip-flop are illustrated and their operations explained.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Week 07 Sequential Circuits Sec A
Week 07 Sequential Circuits Sec A
Uploaded by
Muhammad Rafay0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views25 pagesThis document discusses sequential logic circuits and storage elements. It covers:
1) Sequential circuits contain feedback paths through storage elements like latches and flip-flops that allow the circuit to have a memory of past states.
2) There are two types of sequential circuits - synchronous use a global clock while asynchronous update individually without synchronization.
3) Latches and flip-flops are described as the basic storage elements, with latches being level sensitive and flip-flops edge sensitive due to using clock transitions.
4) Common latch and flip-flop circuits like the SR latch, D latch, and JK flip-flop are illustrated and their operations explained.
Original Description:
dld
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
This document discusses sequential logic circuits and storage elements. It covers:
1) Sequential circuits contain feedback paths through storage elements like latches and flip-flops that allow the circuit to have a memory of past states.
2) There are two types of sequential circuits - synchronous use a global clock while asynchronous update individually without synchronization.
3) Latches and flip-flops are described as the basic storage elements, with latches being level sensitive and flip-flops edge sensitive due to using clock transitions.
4) Common latch and flip-flop circuits like the SR latch, D latch, and JK flip-flop are illustrated and their operations explained.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views25 pagesWeek 07 Sequential Circuits Sec A
Week 07 Sequential Circuits Sec A
Uploaded by
Muhammad RafayThis document discusses sequential logic circuits and storage elements. It covers:
1) Sequential circuits contain feedback paths through storage elements like latches and flip-flops that allow the circuit to have a memory of past states.
2) There are two types of sequential circuits - synchronous use a global clock while asynchronous update individually without synchronization.
3) Latches and flip-flops are described as the basic storage elements, with latches being level sensitive and flip-flops edge sensitive due to using clock transitions.
4) Common latch and flip-flop circuits like the SR latch, D latch, and JK flip-flop are illustrated and their operations explained.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 25
Week 07
Digital Logic Design [MCT-241]
Sequential Logic
• It consists of a combinational circuit to which storage
elements are connected to form a feedback path.
• The storage elements are devices capable of storing
binary information.
• The binary information stored in these elements at
any given time defines the state of the sequential
circuit at that time.
SEQUENTIAL • The block diagram demonstrates that the outputs in a
CIRCUITS sequential circuit are a function not only of the inputs,
but also of the present state of the storage elements
Types of Sequential Circuits
• There are two main types of sequential circuits, and their
classification is a function of the timing of their signals:
• Synchronous Sequential Circuits
All Sequential components get updated at the same time. The
time is usually provided as the Clock. All components have
the same Clock and get updated simultaneously.
The Clock is provided by a Clock Generator which provides a
clock signal having the form of a periodic train of clock pulses.
• Asynchronous Sequential Circuits
The sequential components get updated individually without
any synchronization.
Synchronous
clocked
sequential
circuit
Latches
Storage Element
Latch : A Storage Element
• A storage element in a digital circuit can maintain a
binary state indefinitely (as long as power is
delivered to the circuit), until directed by an input
signal to switch states.
• Storage elements that operate with signal levels
(rather than signal transitions) are referred to as
latches; those controlled by a clock transition are
flip-flops.
• Latches are said to be level sensitive devices; flip-
flops are edge-sensitive devices.
• The two types of storage elements are related
because latches are the basic circuits from which all
flip-flops are constructed.
SR Latch
SR Latch
SR Latch with NAND Gate
SR Latch with Control Input
D Latch
(Transparent Latch)
D Latch (Transparent Latch)
One way to eliminate the
undesirable condition of the
Instead of S and R input this
indeterminate state in the
Latch has just one Input (D),
SR latch is to ensure that
other than Enable.
inputs S and R are never
equal to 1 at the same time
D Latch (Transparent Latch)
Graphic symbols for latches
17/10/2022
• 24
• 35
Flip Flop
Flip Flop
• The D latch with pulses in its control input is essentially a flip-flop that is triggered every time the
pulse goes to the logic-1 level.
• As long as the pulse input remains at this level, any changes in the data input will change the
output and the state of the latch.
• When latches are used for the storage elements, a serious difficulty arises.
• The state transitions of the latches start as soon as the clock pulse changes to the logic-1
level.
• The new state of a latch appears at the output while the pulse is still active.
• This output is connected to the inputs of the latches through the combinational circuit.
• If the inputs applied to the latches change while the clock pulse is still at the logic-1 level, the
latches will respond to new values and a new output state may occur.
• The result is an unpredictable situation, since the state of the latches may keep changing for
as long as the clock pulse stays at the active level.
Latch vs Flip Flop
• The problem with the
latch is that it responds to
a change in the level of a
clock pulse.
• The key to the proper
operation of a flip-flop is
to trigger it only during a
signal transition.
There are two ways to convert a Latch to
a Flip Flop
One way is to employ two Another way is to produce a
latches in a special flip-flop that triggers only
configuration that isolates the during a signal transition (from
output of the flip-flop and 0 to 1 or from 1 to 0) of the
prevents it from being affected synchronizing signal (clock) and
while the input to the flip-flop is is disabled during the rest of
changing. the clock pulse
Method-1 for D
Flip Flop
Method-2
for D Flip
Flop
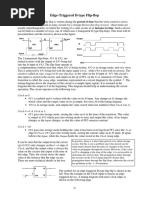
The timing of the response of a flip-flop to input data
and to the clock must be taken into consideration when
one is using edge-triggered flip-flops.
There is a minimum time called the setup time during
which the D input must be maintained at a constant
value prior to the occurrence of the clock transition.
Flip flop and
Delays Similarly, there is a minimum time called the hold time
during which the D input must not change after the
application of the positive transition of the clock.
The propagation delay time of the flip-flop is defined
as the interval between the trigger edge and the
stabilization of the output to a new state
19/10/2022
• 16
• 21
• 24
• 28
• 20-14
• 20-32
You might also like
- COEN 3103 Lesson 11 - Introduction To Sequential Logic CircuitsDocument32 pagesCOEN 3103 Lesson 11 - Introduction To Sequential Logic CircuitsJohnloyd TalagtagNo ratings yet
- State Reduction and AssignmentDocument49 pagesState Reduction and AssignmentJames Francis100% (4)
- Digital Electronics Unit VDocument36 pagesDigital Electronics Unit VtalkwithgamersNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Sequential CKT - L10Document45 pagesIntroduction To Sequential CKT - L10dandalerushi20No ratings yet
- STLD TestDocument136 pagesSTLD TestganeshNo ratings yet
- Digital Lesson 5 Part 1Document50 pagesDigital Lesson 5 Part 1DAVIE MATIASNo ratings yet
- 8. Sequential CircuitsDocument36 pages8. Sequential Circuits2305a21050No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document123 pagesChapter 5mominmohi1No ratings yet
- Chapter 4-SequentialCircuitsDocument36 pagesChapter 4-SequentialCircuitsnhi.phanngoc.cit21No ratings yet
- Synchronous Sequential LogicDocument97 pagesSynchronous Sequential LogicHassnainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Sequential Logics (EEEg4302) 2Document31 pagesChapter 6 - Sequential Logics (EEEg4302) 2Toli fiqeeNo ratings yet
- DCFMOD4Document44 pagesDCFMOD4nonsharedsecretNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Lecture 3Document69 pagesUNIT 1 Lecture 3Peaceful SoulNo ratings yet
- Linear Integrated Circuits Lab Manual For Flip Flops and Logic GatesDocument14 pagesLinear Integrated Circuits Lab Manual For Flip Flops and Logic GatesTimoth DevNo ratings yet
- DLD ch4Document57 pagesDLD ch4Senay MehariNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic Design (ES216) Lec 22-24Document45 pagesDigital Logic Design (ES216) Lec 22-24rodili8762No ratings yet
- Synchronous Sequential LogicDocument69 pagesSynchronous Sequential Logic魏延任No ratings yet
- Chpater 1 - FFs and CountersDocument38 pagesChpater 1 - FFs and Countersplayer1855.01No ratings yet
- EET206 M4 Ktunotes - inDocument195 pagesEET206 M4 Ktunotes - inKhaled AlshurmanNo ratings yet
- Prez1 PDFDocument49 pagesPrez1 PDFDusan SimijonovicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document107 pagesChapter 5pororo20030807No ratings yet
- Unit 4-dld Notes (Pranalini)Document42 pagesUnit 4-dld Notes (Pranalini)Sariki SantoshNo ratings yet
- LCD Module 4ADocument38 pagesLCD Module 4ANijil JosephNo ratings yet
- Flip-Flops, Registers, Counters, and A Simple ProcessorDocument33 pagesFlip-Flops, Registers, Counters, and A Simple ProcessorsupriantoNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3: Sequential Logic CircuitDocument15 pagesChapter-3: Sequential Logic CircuitPRABHAKAR MORENo ratings yet
- Chapter-3: Sequential Logic CircuitDocument15 pagesChapter-3: Sequential Logic CircuitPRABHAKAR MORENo ratings yet
- Logic Design Presentation - Latches & Flip FlopsDocument16 pagesLogic Design Presentation - Latches & Flip FlopsKudzai Russell MutanhaurwaNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iii Sequential Logic CircuitsDocument104 pagesUnit-Iii Sequential Logic CircuitsAswin ThangarajuNo ratings yet
- Sequential Circuits Design: Digital ElectronicsDocument14 pagesSequential Circuits Design: Digital Electronicsعباس محمد عباس عبدالحسينNo ratings yet
- Flip FlopDocument15 pagesFlip Flopinboxinsta0987No ratings yet
- Combinational ReviewDocument42 pagesCombinational Reviewyousefazam120No ratings yet
- co lab practical viva questionsDocument4 pagesco lab practical viva questionsrsaraswat530No ratings yet
- Unit II DpcoDocument41 pagesUnit II DpcoSunil Anandh ITNo ratings yet
- Edge-Triggered D-Type Flip-Flop: 0 TransitionDocument5 pagesEdge-Triggered D-Type Flip-Flop: 0 TransitionUsNo ratings yet
- Tan NNDocument10 pagesTan NNIT'S MAXX GAMINGNo ratings yet
- 26 Sequential Logic Circuit Introduction 18-02-2023Document14 pages26 Sequential Logic Circuit Introduction 18-02-2023Back upNo ratings yet
- Flip FlopDocument35 pagesFlip Flopநட்ராஜ் நாதன்No ratings yet
- Digital Electronics 16-10-24Document63 pagesDigital Electronics 16-10-24kuntham tcr20No ratings yet
- EE-221 Chap07 Part-01Document42 pagesEE-221 Chap07 Part-01AliNo ratings yet
- Lecture #32 Registers, Counters EtcDocument21 pagesLecture #32 Registers, Counters EtcRajan GoyalNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 Important QuestionsDocument21 pagesUnit-3 Important Questions16 lily Gagan deepNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document33 pagesPresentation 1Satyajit GantayatNo ratings yet
- Sequential CircuitsDocument19 pagesSequential CircuitsSalil TimalsinaNo ratings yet
- Flip Flops: Digital Logic Design LabDocument23 pagesFlip Flops: Digital Logic Design LabAstitav chauhanNo ratings yet
- Basic Structure: What Is Latch ? Explain Its Operation in DetailDocument4 pagesBasic Structure: What Is Latch ? Explain Its Operation in Detailrehman65456jhdyw23798No ratings yet
- Unit 4Document27 pagesUnit 4Nikhil H RajuNo ratings yet
- Sequential Circuits: Cpe 443/L Advanced Logic CircuitsDocument35 pagesSequential Circuits: Cpe 443/L Advanced Logic CircuitsKent Genzen Corpus100% (1)
- Mini Project DigitDocument7 pagesMini Project DigitMUHAMMAD IZZAT BIN ZULKIFLI STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Digital Electronics NotesDocument191 pagesDigital Electronics NotesSatyam ShivamNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic Design Sequential CircuitsDocument35 pagesDigital Logic Design Sequential CircuitsV Iv Ek ParekhNo ratings yet
- Chapter5: Synchronous Sequential Logic: Lecture2-Study Problems in Latches and Design D Flip-FlopsDocument20 pagesChapter5: Synchronous Sequential Logic: Lecture2-Study Problems in Latches and Design D Flip-FlopsHamza RiazNo ratings yet
- Ddco Mod 2Document28 pagesDdco Mod 2pradeepkshettar77No ratings yet
- Digital Electronics: CT 304N Unit-4 (Part:1) Flip Flops & Sequential Logic and CircuitsDocument39 pagesDigital Electronics: CT 304N Unit-4 (Part:1) Flip Flops & Sequential Logic and CircuitsLiyanshu patelNo ratings yet
- Latch and Flip-FlopDocument58 pagesLatch and Flip-FlopDalila Nadia RazaliNo ratings yet
- DCD Unit - 3Document33 pagesDCD Unit - 3Prathap VuyyuruNo ratings yet
- Two MarksDocument17 pagesTwo MarksGodwin CNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Analog Dialogue, Volume 48, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #13From EverandAnalog Dialogue, Volume 48, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #13Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- 20 Nov 2024Document1 page20 Nov 2024Muhammad RafayNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Work Shop Note BookDocument46 pagesMechanical Work Shop Note BookMuhammad RafayNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Machine WithoutDocument1 pageAssignment of Machine WithoutMuhammad RafayNo ratings yet
- Mit18 05 s22 ProbabilityDocument112 pagesMit18 05 s22 ProbabilityMuhammad RafayNo ratings yet
- DLD Lab 04-BCD To Seven SegmentDocument6 pagesDLD Lab 04-BCD To Seven SegmentMuhammad RafayNo ratings yet
- Mit18 05 s22 StatisticsDocument173 pagesMit18 05 s22 StatisticsMuhammad RafayNo ratings yet
- Lab No 6 - Coordinated Control - Signal OverlapDocument5 pagesLab No 6 - Coordinated Control - Signal OverlapMuhammad RafayNo ratings yet
- DLD Lab 01-Number SystemDocument7 pagesDLD Lab 01-Number SystemMuhammad RafayNo ratings yet
- Update 80 DR List With PMDC NumDocument311 pagesUpdate 80 DR List With PMDC NumMuhammad RafayNo ratings yet
- DLD Lab 03-Combinational LogicDocument6 pagesDLD Lab 03-Combinational LogicMuhammad RafayNo ratings yet
- PivotDocument16 pagesPivotMuhammad RafayNo ratings yet
- FasoresDocument18 pagesFasoresjuniorotavioNo ratings yet
- Electricity PracticeDocument108 pagesElectricity PracticeVarshLokNo ratings yet
- Manual CaladoraDocument32 pagesManual CaladoraMiguel Angel Vega TrejoNo ratings yet
- Astm E1312Document3 pagesAstm E1312David Francisco Plata DuranNo ratings yet
- UC900 SS23 Cat.7 LSH-FR C S1d1a1Document3 pagesUC900 SS23 Cat.7 LSH-FR C S1d1a1acastanopadilla4100No ratings yet
- Unit Iv Coa - PPTDocument99 pagesUnit Iv Coa - PPTfreeid5899No ratings yet
- LSLL-105: Asme B16.5 Raised FaceDocument1 pageLSLL-105: Asme B16.5 Raised FacegusbecNo ratings yet
- Hb2637l-Evk-301 DPT HSDocument10 pagesHb2637l-Evk-301 DPT HSAlec NanetteNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgment: Mr. Girish M, Assistant Professor, and Also My Guide MR - Guruprasad K N, AssistantDocument5 pagesAcknowledgment: Mr. Girish M, Assistant Professor, and Also My Guide MR - Guruprasad K N, AssistantChandra PrakashNo ratings yet
- Hardware Manual of The Easy Servo Drives: ES-DH SeriesDocument28 pagesHardware Manual of The Easy Servo Drives: ES-DH Serieshuutan12345No ratings yet
- qp2620 20 Dfu DeuDocument292 pagesqp2620 20 Dfu DeudjokanomcaNo ratings yet
- 1 Magnetism New Aug 2022Document19 pages1 Magnetism New Aug 2022WaleedNo ratings yet
- Bhitar Gaon PDFDocument1 pageBhitar Gaon PDFNeha SinghNo ratings yet
- Minebea Stepper Motor InformationDocument5 pagesMinebea Stepper Motor InformationreynosodiNo ratings yet
- P220 Lab KirchhoffDocument4 pagesP220 Lab KirchhoffAndualem MokonenNo ratings yet
- Ecooler2400 (12V) Service ManualDocument17 pagesEcooler2400 (12V) Service ManualTim SanzNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: Champion™ 30 DSPDocument16 pagesService Manual: Champion™ 30 DSPmariopilar100% (1)
- Envelope Tracking in Power Amplifiers: A Presentation OnDocument75 pagesEnvelope Tracking in Power Amplifiers: A Presentation OnAnurag Vijay AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Molded Case Circuit Breaker Application and Maintenance Guide - Revision 2Document268 pagesMolded Case Circuit Breaker Application and Maintenance Guide - Revision 2Sebastião Jorge dos SantosNo ratings yet
- Qorivva Simple Cookbook: "Hello World" Programs To Exercise Common Features On MPC5500 & MPC5600 MicrocontrollersDocument248 pagesQorivva Simple Cookbook: "Hello World" Programs To Exercise Common Features On MPC5500 & MPC5600 MicrocontrollersAjaya HsNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE Physics by Tom Duncan and Heather KennettDocument2 pagesCambridge IGCSE Physics by Tom Duncan and Heather KennettMOKHOBONo ratings yet
- II1-0801 Rev 1.0Document4 pagesII1-0801 Rev 1.0Llorenç Alomar LlompartNo ratings yet
- Exyte Malaysia - Energized Electrical Work (EEW) TrainingDocument35 pagesExyte Malaysia - Energized Electrical Work (EEW) TrainingThirumaran MuthusamyNo ratings yet
- GSM Based Home Security System Project Using Microcontroller 8051Document2 pagesGSM Based Home Security System Project Using Microcontroller 8051Debebe TsedekeNo ratings yet
- Diagramas Demag ChinoDocument188 pagesDiagramas Demag ChinoLeninNo ratings yet
- Tripoli University Department of Electrical & Electronic EngineeringDocument44 pagesTripoli University Department of Electrical & Electronic EngineeringtojogofirNo ratings yet
- 7 MV Switchgear Mar 24 25 PDFDocument230 pages7 MV Switchgear Mar 24 25 PDFAyerNo ratings yet
- Ee Obj 3Document35 pagesEe Obj 3Shaira Sto TomasNo ratings yet
- Catalogue Mcf88Document18 pagesCatalogue Mcf88Frank ZampaNo ratings yet
- T5L DGUSII Application Development Guide V2.5Document219 pagesT5L DGUSII Application Development Guide V2.5ZillaIllozNo ratings yet