Bio UT1
Bio UT1
Uploaded by
Jes RenCopyright:
Available Formats
Bio UT1
Bio UT1
Uploaded by
Jes RenCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Bio UT1
Bio UT1
Uploaded by
Jes RenCopyright:
Available Formats
I.
TRUE or FALSE
1. TRUE
2. FALSE
3. TRUE
4. FALSE
5. FALSE
6. FALSE
7. FALSE
8. FALSE
9. TRUE
10. FALSE
II. IDENTIFICATION
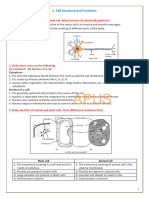
CELL MEMBRANE 1. The Part of the cell that regulates entry and exit of substances in and out of
the cell.
NUCLEUS 3. It is considered as the control center of the cell.
MITOCHONDDRIA 4. It is considered as the powerhouse of the cell.
CELL 5. The basic unit of life.
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM6. It synthesized secretory proteins and membrane proteins.
GOLGI BODY 7. It modifies, sorts and packs materials synthesized in the cell.
LYSOSOMES 8. It helps in digesting large molecules.
ROUGH ER 9. It is an Endoplasmic Reticulum with ribosomes attached into it.
VACUOLES 10.It stores substances including waste products.
III. ESSAY
1. Explain the Postulates of the Cell Theory.
The Unified Cell Theory was proposed by both Theodor Schwann and Matthias Schleiden. There are
three postulates in Cell theory. The first postulate states that all living things are made up of cells. The
second postulate states that cells are the most basic unit of cell. And the third, and last, postulate states
that All organisms are made up of one or more cells.
2. Differentiate Animal and Plant Cell.
There are many different nuances between animal and plant cells. Some difference can be found in the
organelles. Plant cells have a cell wall, vacuole and chloroplast, whilst animal cells have a centrosome. A
difference can also be perceived on the shape of the cell. Plant cells have a rectangular structure and
animal cells have a circular shape. Plant cells also rely on the chloroplast for energy but animal cells
don’t.
3. What is the contribution of Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in the Cell theory?
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek was a Dutch microscopist that was born in October 24, 1632 and died in Delft
on August 26, 1723. He was the first man to observe bacteria and protozoa. While using a microscope
to examine pond water in 1674, he observed dozens of protists, which he called 'animalcules,'
as well as spirogyra, or green algae. he discovery of the cell was made possible by the invention
of the microscope, which was made possible by improved lens-grinding techniques.
4. What is the function of Ribosomes in our cell?
A ribosome is a small organelle that can be found in cells. Ribosomes are composed of special
proteins and nucleic acids. It functions as a micro-machine for making proteins. It is also the
translator of information in the cell. The translation of information and the Linking of amino acids
are at the heart of the protein production process.
5. Explain the hierarchy of biological organization of living things.
Biological organization is the hierarchy of complex biological structures and systems that define life
using a reductionistic approach. There are seven levels of organizational structure in hierarchy.
The biological levels of organization of living things arranged from the simplest to most complex are:
organelle, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms, populations, communities, ecosystem, and
biosphere. The simplest level of organization for living things is a single organelle, which is composed of
aggregates of macromolecules. The highest level of organization for living things is the biosphere; it
encompasses all other levels.
You might also like
- BIOLOGY Lesson Note SS 2Document6 pagesBIOLOGY Lesson Note SS 2jonahorji100% (1)
- Cell TheoryDocument32 pagesCell TheorySumana BasuNo ratings yet
- Stemazing Contest Guidelines: Component Area: Grade Level: Event Package: No. of ParticipantsDocument1 pageStemazing Contest Guidelines: Component Area: Grade Level: Event Package: No. of Participantsmark joseph cometa100% (6)
- Cell Structure and Function3Document15 pagesCell Structure and Function3marklexter.b.bardelosaNo ratings yet
- General Biology Modules 1 3Document36 pagesGeneral Biology Modules 1 3Glen MillarNo ratings yet
- HO1 - 8 - Biology April 23-24 PDFDocument10 pagesHO1 - 8 - Biology April 23-24 PDFSaghana SaravanakarthikNo ratings yet
- CellDocument4 pagesCellgitansh2010gauravNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document3 pagesChapter 6chunnushankyNo ratings yet
- Copy of ANSWERS To 1.1 and Part of 1.2 STUDY GUIDEDocument4 pagesCopy of ANSWERS To 1.1 and Part of 1.2 STUDY GUIDE326anievesNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Cell Structure and Function - NotesDocument8 pagesUnit 2 - Cell Structure and Function - Notesronel.jnmsNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet in Biology 1: Quarter 1 Week 1Document10 pagesLearning Activity Sheet in Biology 1: Quarter 1 Week 1Ryan Negad100% (1)
- Gen Bio 1 Quarter 1Document46 pagesGen Bio 1 Quarter 1Ac BelenNo ratings yet
- plant-and-animal-cellsDocument60 pagesplant-and-animal-cellstyronetercenio712No ratings yet
- 1st ClassDocument8 pages1st ClassSamson AdewaleNo ratings yet
- 01 Cell TheoryDocument9 pages01 Cell TheoryRay NavarroNo ratings yet
- STB 121 Theory-1Document93 pagesSTB 121 Theory-1ahmfroshkidNo ratings yet
- General Biology-Stem DDocument5 pagesGeneral Biology-Stem Digotugirlalways143No ratings yet
- Senior High School - STEMDocument93 pagesSenior High School - STEMMaam Elle CruzNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory and Cell OrganellesDocument1 pageCell Theory and Cell OrganellesB09 Hernandez, Sean Matthew F.No ratings yet
- Bio1 Lesson 1 NotesDocument7 pagesBio1 Lesson 1 Notesykanemoto81No ratings yet
- Alpah Term Scheme of Work of S.S. TwoDocument39 pagesAlpah Term Scheme of Work of S.S. Twojeremiah oseniNo ratings yet
- Biology REVIEW FOR CMDocument12 pagesBiology REVIEW FOR CMyangyang804574No ratings yet
- Parasitology ReviewDocument2 pagesParasitology ReviewKalana maduwanthaNo ratings yet
- Types of Cell PDFDocument20 pagesTypes of Cell PDFDave Billona100% (1)
- Biology SS2 First TermDocument51 pagesBiology SS2 First Termoyussuf2008No ratings yet
- Ranging From 10-100 M: Blood Cells Are Rounded DisksDocument9 pagesRanging From 10-100 M: Blood Cells Are Rounded DisksJanine LimjucoNo ratings yet
- Gen BioDocument21 pagesGen Biosadangalvin16No ratings yet
- Cell ProjectDocument15 pagesCell ProjectCandiceNo ratings yet
- Cell Classix Session3 Made by Purnima Sharma 1Document7 pagesCell Classix Session3 Made by Purnima Sharma 1jeetjyoti787No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and OrganizationDocument13 pagesCell Structure and Organizationomololabalogun676No ratings yet
- MST chapter 4 for midtermDocument4 pagesMST chapter 4 for midtermAbdul macaampaoNo ratings yet
- CellDocument21 pagesCellMychelle HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Senior High School - STEMDocument85 pagesSenior High School - STEMMary Grace MacadiniNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument45 pagesBIOLOGYBenmashour BiaoNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 3-4Document6 pagesGen Bio 3-4Honey Joy Leopando SabadoNo ratings yet
- Biotech Session 1Document18 pagesBiotech Session 1j_ngetich_k7375No ratings yet
- Alpah Term ss2 Biology e - NoteDocument39 pagesAlpah Term ss2 Biology e - NoteSamuel BiyamaNo ratings yet
- 9th Unit 1Document17 pages9th Unit 1[36] IX-B P.Vishnu Vardhan ReddyNo ratings yet
- LookbookDocument23 pagesLookbooksresshanthgNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School, Bangalore - East Biology Notes Cell:Structure and FunctionDocument4 pagesDelhi Public School, Bangalore - East Biology Notes Cell:Structure and FunctionSaket TNo ratings yet
- Bio 101 General BiologyDocument7 pagesBio 101 General BiologyMohammed kashimNo ratings yet
- Cell - Structure & Functions: VSA Type QuestionsDocument5 pagesCell - Structure & Functions: VSA Type Questionsbhatsajid6731No ratings yet
- SummaryDocument19 pagesSummaryAntenehMarelignNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Cell, Cell Theory, and Cell TypesDocument34 pagesLesson 1 Cell, Cell Theory, and Cell TypesAbubakar DucaysaneNo ratings yet
- What Makes Animal Cells DifferentDocument14 pagesWhat Makes Animal Cells DifferentGian Carlo Angon100% (1)
- BiologyDocument39 pagesBiologyRizzuya UrakuwaNo ratings yet
- The Science of Cytology Cell Theory: The Principle Core of BiologyDocument6 pagesThe Science of Cytology Cell Theory: The Principle Core of Biologyhendrix obciana100% (1)
- General Biology 1 - Q1 - Week 1Document16 pagesGeneral Biology 1 - Q1 - Week 1Rb Atienza EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Biological SystemDocument131 pagesFundamentals of Biological Systempon_parivendanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Human BodyDocument51 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Human BodyEight AlykNo ratings yet
- Cells Are The Basic Units of LifeDocument5 pagesCells Are The Basic Units of LifeBRAYAN ALEXIS DE SOUSA LORANo ratings yet
- 8th Biology NotesDocument23 pages8th Biology NotesDarling VenkiNo ratings yet
- Jilbert B. Gumaru, LPTDocument85 pagesJilbert B. Gumaru, LPTJulius MacaballugNo ratings yet
- AS Biology - Module 1 Chapter 1: Structure and Function of The Cell Introduction To The CellDocument11 pagesAS Biology - Module 1 Chapter 1: Structure and Function of The Cell Introduction To The CellJosebeth CairoNo ratings yet
- Earth Life Science Module 5Document15 pagesEarth Life Science Module 5Rosalyn Pagatpatan BarolaNo ratings yet
- PlantDocument6 pagesPlantjarifalhadi29No ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument104 pagesCell BiologyADARSH RNo ratings yet
- Miller & Levine Biology Chapter 7 SummaryDocument6 pagesMiller & Levine Biology Chapter 7 Summarybob0% (1)
- The Fundamental Unit of Life - CW Copy Notes Class 9 PDFDocument5 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of Life - CW Copy Notes Class 9 PDFmanoharrish3No ratings yet
- The Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandThe Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Villavicencio GenPhys q4w3Document1 pageVillavicencio GenPhys q4w3Jes RenNo ratings yet
- Capstone ResearchDocument2 pagesCapstone ResearchJes RenNo ratings yet
- Bio q4w1Document1 pageBio q4w1Jes RenNo ratings yet
- Bio q2w1Document2 pagesBio q2w1Jes RenNo ratings yet
- Bio Final2Document2 pagesBio Final2Jes RenNo ratings yet
- Need and Demand of Education For SocialDocument18 pagesNeed and Demand of Education For SocialsidraNo ratings yet
- Ungamudii Mwari Wangu Session 3Document466 pagesUngamudii Mwari Wangu Session 3pmugova004No ratings yet
- Strategies in Organizing and Delivering An Impromptu SpeechDocument5 pagesStrategies in Organizing and Delivering An Impromptu SpeechSherannie Abalo100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in MapehDocument5 pagesLesson Plan in MapehSandra EladNo ratings yet
- Bio UT1Document2 pagesBio UT1Jes RenNo ratings yet
- Cell Division SEDocument3 pagesCell Division SEQueso BadotaNo ratings yet
- Case ConceptualizationDocument4 pagesCase ConceptualizationrochelledgcNo ratings yet
- Unit 20: How Do You Like To Learn?Document2 pagesUnit 20: How Do You Like To Learn?đang lơ lửng Hana là cục bôngNo ratings yet
- Cover Letter ADHDocument2 pagesCover Letter ADHAlbert Domaboc HisolerNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) in Science 7 Topic/ Lesson Name Time Allotment Teacher Content StandardsDocument2 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) in Science 7 Topic/ Lesson Name Time Allotment Teacher Content StandardsGeneva macahiaNo ratings yet
- 考虑需求侧响应的综合能源系统可靠性评估 邱红桦Document6 pages考虑需求侧响应的综合能源系统可靠性评估 邱红桦方亮No ratings yet
- TRDC ProfileDocument6 pagesTRDC ProfilePrespective innovationNo ratings yet
- E3 ESOL Writing Candidate Paper PPADocument10 pagesE3 ESOL Writing Candidate Paper PPALisa NormanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 5Document51 pagesChapter 1 5Julius HipolNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 Vocabulary Part IDocument5 pagesExercise 1 Vocabulary Part IDintya Andari Risty23No ratings yet
- LISTENING TEST 2024 - KopiDocument4 pagesLISTENING TEST 2024 - KopidangertubetvNo ratings yet
- Poetry On Death and LossDocument13 pagesPoetry On Death and LossGeraldine QuirogaNo ratings yet
- A Survey of IEEE 802.11p MAC ProtocolDocument7 pagesA Survey of IEEE 802.11p MAC ProtocolHUYDONGBKNo ratings yet
- Escorpizo Vs University of BaguioDocument3 pagesEscorpizo Vs University of BaguioChristelle Ayn BaldosNo ratings yet
- Form 1 Reading Assessment RubricDocument1 pageForm 1 Reading Assessment RubricNest PunoNo ratings yet
- FRONTIERS Krakow GDCDocument65 pagesFRONTIERS Krakow GDCGordana Dodig-CrnkovicNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mapeh 3 - Q1 - W3Document5 pagesDLL - Mapeh 3 - Q1 - W3Daffodil Rona CedenioNo ratings yet
- Netherlands Experience (Nancy Matos)Document2 pagesNetherlands Experience (Nancy Matos)Jônathas SilveiraNo ratings yet
- Converting What You Read Into Personal RealizationDocument6 pagesConverting What You Read Into Personal RealizationAshirbad SahooNo ratings yet
- Support LetterDocument2 pagesSupport LetterkjkullaNo ratings yet
- Bedanking ThesisDocument6 pagesBedanking Thesisafkodkedr100% (2)
- World History B Syllabus 1Document2 pagesWorld History B Syllabus 1api-272160407No ratings yet
- EhetheatththDocument111 pagesEhetheatththOmer FarooqNo ratings yet
- كتاب المرونة النفسيةDocument33 pagesكتاب المرونة النفسيةMarwa KhaledNo ratings yet