Thread Inspection
Thread Inspection
Uploaded by
Ahmed MushtaqCopyright:
Available Formats
Thread Inspection
Thread Inspection
Uploaded by
Ahmed MushtaqOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Thread Inspection
Thread Inspection
Uploaded by
Ahmed MushtaqCopyright:
Available Formats
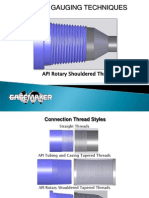
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 1
Thread Inspection
Casing:
•The terms Casing applies to pipe that is used to line the drilled hole to protect the
well from formation fluid flow or formation collapse.
Tubing:
•The term Tubing applies to the innermost pipe in a well. Well fluids are brought to
the surface through the tubing.
Threading
A machining process to form root and crest on the component to enable it to form
long gas tight string
Coupling
Component with Thread use to connect two part.
Thread inspection
Evaluation of Threading process to comply with API 5 B and API 5 B1
specification
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 2
Thread Inspection
Specifications and reference:
API 5 CT
Casing Size range 4½” to 20”
Tubing size range 1” to 4½”
Coupling for all product
API 5 B
•Specification for Threading, Gauging and Thread Inspection
of Casing, Tubing, and Line Pipe Threads.
API 5 B1
• Gauging and Inspection of Casing, Tubing, and Line Pipe Threads
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 3
Thread Inspection
Elements of Thread
Chamfer: The beveled surface, beginning at the end of the pipe or coupling, in
which the thread form starts
Crest: The top of the thread.
Root: The bottom of the thread.
Effective thread length: Designated as L2 for round thread This is the theoretical
point at which the vanish cone angle begins.
Full-crest thread length: The length measured parallel to the thread axis from the
end of the pipe to the first non full-crested thread.
Perfect thread length: The last perfect thread location on external threads.
Imperfect thread length: The buttress threads located beyond the L7 plane (away
from the pipe ends).
Standoff: A distance from coupling face to pipe thread vanish point
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 4
Thread Inspection
Elements of Thread
Height of thread: The distance between the root and crest of the thread measured
normal (perpendicular) to the thread axis.
Lead: The distance from a point on a thread to a corresponding point on the next
thread turn, measured parallel to the thread axis.
Pitch diameter: On a taper thread, the pitch diameter at a given position on the
thread axis is the diameter of the pitch cone at that position. On buttress threads, this
is midway between the major and minor diameter
Torque: A force that tends to produce rotation—the force causing a threaded
connection to makeup
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 5
Thread Inspection
Types of Threads
External Upset Tubing
Non Upset Tubing
Short Thread Casing
Long Thread Casing
Buttress Thread Casing
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 6
Thread Inspection
Elements of Thread - Round Tread Casing Tubing 8 RD LC
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 7
Thread Inspection
Elements of Thread - Round Tread Casing Tubing 8 RD LC
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 8
Thread Inspection
Elements of Thread – Buttress Tread Configuration up to 13 3/8 “ OD 5 TPI BC
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 9
Thread Inspection
Elements of Thread – Buttress Tread Configuration up to 13 3/8 “ OD 5 TPI BC
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 10
Thread Inspection
To Start With
•Request the product thread drawing or details of Threading parameter Production
order document is having all this information .
•Verify Required Measuring Gauges are available
•Verify inspection reports are available
•List all the gage serial numbers used to inspect the part
•Verify the ball contact sizes are correct
•Set the gages to a zero on a calibrated standard
•Clean thread with air remove any loose particle and burr on the thread profile
•Verify the thread form is correct
•Start the inspection
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 11
Thread Inspection
Ring and Plug Gauges to Measure Stand off
Deviation from Basic value is measured .
Ring gauge is used for External thread –
Casing and Tubing
Plug Gauge is used for Internal Threading -
Coupling
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 12
Thread Inspection
Thread Height Gauge
Align the gage base parallel to the
thread axis and tilt the base back and
Gauge setting ensure Zero on forth to obtain the lowest reading
master reference gauge by moving
backward and forward
•8 Round thread height = .072125”
•10 Round thread height = .05560”
•Buttress ¾”TPF thread height = .0620”
•Buttress 1”TPF thread height = .0620”
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 13
Thread Inspection
Thread Height Gauge
• Set Height Gauge using a setting Gauge Number TH-3002
standard
• Double check zero setting 1. Measure only within the perfect
• Start Measurement thread length. Perfect thread
length is labeled “L2” on the
product drawing.
2. Align the gage base parallel to
the thread axis and tilt the base
back and forth to obtain the
lowest reading.
8 Round thread height = .072125”
10 Round thread height = .05560”
Buttress ¾”TPF thread height = .0620”
Buttress 1”TPF thread height = .0620”
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 14
Thread Inspection
Thread Lead Gauge
Ensure Zero on master reference gauge by moving
gauge left/right in fixed distance 1inch or 2 inch
Place the fixed ball contact in the first full
depth thread. try to find out zero reading
record deviation
• Lead per inch +/-0.003”
•Cumulative Lead +/- 0.006”
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 15
Thread Inspection
Thread Lead Gauge
Measuring the part
Gauge Number LG-5002
Set using a Standard 1. Place the fixed ball contact in the first full depth
thread.
Double-check your zero setting
2. Move the fixed ball back one thread and check
Measure the part
again.
Compare the standard to the machined lead
3. Try to find out Zero or Deviation
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 16
Thread Inspection
Thread Taper Gauge
Set Zero reading at first thread Take
first reading at 5 or 8 TPI as per Thread
parameter by moving the dial pin in
thread root finding out gauge return
point repeat process two- three times
in same plan
There are two cone angles or tapers
Taper Per Foot -TPF
•All 8-round threads are ¾”
•Buttress sizes 4½”- 13⅜” are 1” TPF
•Buttress sizes 16”- 20” are 1” TPF
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 17
Thread Inspection
Thread Taper Gauge
Zero the dial on the first thread.
Do not lock the bezel clamp!
To inspect, move the gage up the taper 1”
(8-round = 8 threads, Buttress = 5 threads)
After moving back 1” up the taper, double-check
your radial position of the gage to the part or chuck
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 18
Thread Inspection
Thread MRP Gauge
Engage the fixed point in
starting thread try to find out
zero reading record deviation
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 19
Thread Inspection
Thread MRP Gauge
While holding
MRP-2001 the gage
is preset to sizeagainst the of
by the use part
“A”
face,
& “B”sweep left and right to find the
Rod Standards
largest indicator value. Then, rotate the “B”
gage 90° and repeat Standard
The MRP Shoe makes contact with the crest cone
“A” Standard
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 20
Thread Inspection
What we do with MRP Gauge
Largest and smallest indicator readings provide data for calculating Average Cone Diameter
(ACD) and Thread Ovality. They both use the same data but calculate the readings in
different ways.
Average Cone Diameter Ovality
The diameter of the part would be, How egg-shaped or out of round
if it were round LARGE
the pipe is
READING
(Largest Diameter - Smallest Diameter) = ACD Largest Diameter - Smallest Diameter = Ovality
2 SMALL
READING
Largest Smallest Averaged Largest Smallest
Ovality
Diameter Diameter Diameter Diameter Diameter
+.005 -.010 -.0025 +.005 -.010 .015
Largest Smallest Averaged Largest Smallest
Ovality
Diameter Diameter Diameter Diameter Diameter
-.005 -.010 -.0075 -.005 -.010 .005
Largest Smallest Averaged Largest Smallest
Ovality
Diameter Diameter Diameter Diameter Diameter
-.015 +.001 -.007 -.015 +.001 .016
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 21
Thread Inspection
Average Cone Diameter
Average Cone Diameter is the distance across the face of the pipe or coupling.
Determining the “round” diameter of a connector requires locating the largest and the smallest diameter
readings on the part and taking the average of these two readings.
LARGE
READING
SMALL
READING
Largest Smallest Averaged Largest Smallest Averaged
Diameter Diameter Diameter Diameter Diameter Diameter
+.005 -.010 -.0025 +.005 -.005 .000
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 22
Thread Inspection
Thread Ovality
Thread Ovality is the amount of out-of-roundness in a piece of pipe or a coupling. Determining
ovality requires locating the largest and the smallest diameter readings on the part and adding the
smallest reading to the largest reading. The ovality is the difference between these values. Ovality
readings are always positive (no sign attached).
LARGE
READING
SMALL
READING
Largest Smallest Total
Largest Smallest Total
Diameter Diameter Ovality
Diameter Diameter Ovality
+.005 -.010 .015 +.005 -.005 .010
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 23
Thread Inspection
Pin Length Inspection
Always keep the scale parallel to
the pipe axis.
L2=Perfect thread length. Crest of thread
L2 must have a full radius top.
L4
L4=Last scratch length.
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 24
Thread Inspection
Thread Form Inspection
TP-8R Profile inspecting pin and coupling thread. Always check the first starting thread.
Remember: When debarring the thread with a flapper wheel, burrs can be rolled into the thread groove. When the
connections are made up on the rig, burrs will cause galling Ensure
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 25
Thread Inspection
Coupling Thread Lead Inspection
Gauge number LG-5002
• Set Gauge to zero using a standard 1. Place the fixed ball contact in the first full
• Double check your zero setting depth thread.
2. Move the fixed ball back one thread and
check again.
3. Record measurement .
Remember: Each different taper requires a different lead setting standard
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 26
Thread Inspection
Coupling Thread Height Inspection
Set to zero using a standard
Double check your zero setting
Gauge number TH-3006
Thread Heights:
8-Round = .0721” 1. Align the gage parallel to the thread axis.
Buttress = .0620” 2. Lift up and down to obtain the lowest reading.
3. Record your measurement.
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 27
Thread Inspection
Coupling Taper Inspection
Gauge Number IT 6000
Zero the dial on the first thread.
Do not lock the bezel clamp!
Note the radial location of the gage to
the part or chuck.
(6 or 12 o’clock is best)
To inspect, move the gage down
the taper 1” or:
8 threads for 8-round
5 threads for Buttress
After moving 1” down the taper,
double check your radial position of
the gage to the part or chuck.
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 28
Thread Inspection
Coupling PD Inspection with an MRP-2002
(Crest Cone Diameter Inspection)
“B”
Standard
Gauge Number MRP-2002 is preset to size with the
use of “A” & “B” Rod Standards
While holding the gage against the part face,
sweep left & right to find the largest indicator
value
Rotate the gage 90° and repeat
“A”
Standard
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 29
Thread Inspection
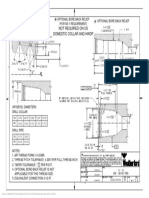
Coupling Length Inspection
Q
“Q” is measured from the coupling face
to the start of the 35° chamfer.
Always keep the scale parallel to the
coupling axis.
NL/2 = ½ the coupling length.
NL/2
NL = Length of coupling.
Coupling Length (NL)
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 30
Thread Inspection
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 31
Thread Inspection
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 32
Thread Inspection
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 33
Thread Inspection
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 34
Thread Inspection
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 35
Thread Inspection
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 36
Thread Inspection
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 37
Thread Inspection
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 38
Thread Inspection
MRP Gauge Tolerance
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 39
Thread Inspection
MRP Gauge Tolerance
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 40
Thread Inspection
18-Jul-23 Threading Inspection 41
You might also like
- API Spec 7-2 Threading Ang Gauging of Rotary Shouldered Connections100% (1)API Spec 7-2 Threading Ang Gauging of Rotary Shouldered Connections124 pages
- Testing & Commissioning of Fan Coil Units FCU'sNo ratings yetTesting & Commissioning of Fan Coil Units FCU's3 pages
- Turbotorque™: Lightning Fast Torque On DemandNo ratings yetTurbotorque™: Lightning Fast Torque On Demand16 pages
- TenarisHydril Wedge 563 RunningGuidelinesNo ratings yetTenarisHydril Wedge 563 RunningGuidelines16 pages
- Field Inspection Procedure For Used GPDS Connections Revision 03 PDF0% (1)Field Inspection Procedure For Used GPDS Connections Revision 03 PDF3 pages
- Tapered Thread Inspection - Tubing, Casing, &: Required EquipmentNo ratings yetTapered Thread Inspection - Tubing, Casing, &: Required Equipment1 page
- Pitch Diameter and Ovality Gages Tapered Threads MRP-1000 Series MRP-2000 Series MRP-3000 SeriesNo ratings yetPitch Diameter and Ovality Gages Tapered Threads MRP-1000 Series MRP-2000 Series MRP-3000 Series2 pages
- Running Procedure: Voestalpine Tubulars GMBH & Co KG Voestalpine Tubulars GMBH & Co KGNo ratings yetRunning Procedure: Voestalpine Tubulars GMBH & Co KG Voestalpine Tubulars GMBH & Co KG16 pages
- BVM Corporation Maintenance Manual: "C", "T", & "MP" Series Safety Clamps100% (1)BVM Corporation Maintenance Manual: "C", "T", & "MP" Series Safety Clamps8 pages
- BDS VAM®+TOP+Casing Regular 7.000 29.00 RegularNo ratings yetBDS VAM®+TOP+Casing Regular 7.000 29.00 Regular1 page
- Tubing & Casing Thread Inspection-Thread LeadNo ratings yetTubing & Casing Thread Inspection-Thread Lead1 page
- ACS800 Single Drive Technical Catalogue REV E EN PDFNo ratings yetACS800 Single Drive Technical Catalogue REV E EN PDF56 pages
- Installation Guide: Directed Digital SolutionsNo ratings yetInstallation Guide: Directed Digital Solutions22 pages
- Starting Systems - Application & Installation Guide - Lebw4980No ratings yetStarting Systems - Application & Installation Guide - Lebw498032 pages
- Preventive Maintenance For The Max CR System Formerly The CR 975 System (PM1883-1)No ratings yetPreventive Maintenance For The Max CR System Formerly The CR 975 System (PM1883-1)30 pages
- Technical Information Sound Shell Installation Instructions For COPELAND SCROLL™ CompressorsNo ratings yetTechnical Information Sound Shell Installation Instructions For COPELAND SCROLL™ Compressors5 pages
- Study of Single Plate Clutch: Presented by:-PANKAJ SHARMANo ratings yetStudy of Single Plate Clutch: Presented by:-PANKAJ SHARMA16 pages
- SET-111. RFID Based Prepaid Card For Petrol StationNo ratings yetSET-111. RFID Based Prepaid Card For Petrol Station3 pages
- Operation Manual Plastic Extrusion WelderNo ratings yetOperation Manual Plastic Extrusion Welder20 pages
- Wolaita Sodo University School of Informatics: Department of Information TechnologyNo ratings yetWolaita Sodo University School of Informatics: Department of Information Technology4 pages
- API Spec 7-2 Threading Ang Gauging of Rotary Shouldered ConnectionsAPI Spec 7-2 Threading Ang Gauging of Rotary Shouldered Connections
- Field Inspection Procedure For Used GPDS Connections Revision 03 PDFField Inspection Procedure For Used GPDS Connections Revision 03 PDF
- Tapered Thread Inspection - Tubing, Casing, &: Required EquipmentTapered Thread Inspection - Tubing, Casing, &: Required Equipment
- Pitch Diameter and Ovality Gages Tapered Threads MRP-1000 Series MRP-2000 Series MRP-3000 SeriesPitch Diameter and Ovality Gages Tapered Threads MRP-1000 Series MRP-2000 Series MRP-3000 Series
- Running Procedure: Voestalpine Tubulars GMBH & Co KG Voestalpine Tubulars GMBH & Co KGRunning Procedure: Voestalpine Tubulars GMBH & Co KG Voestalpine Tubulars GMBH & Co KG
- BVM Corporation Maintenance Manual: "C", "T", & "MP" Series Safety ClampsBVM Corporation Maintenance Manual: "C", "T", & "MP" Series Safety Clamps
- ACS800 Single Drive Technical Catalogue REV E EN PDFACS800 Single Drive Technical Catalogue REV E EN PDF
- Starting Systems - Application & Installation Guide - Lebw4980Starting Systems - Application & Installation Guide - Lebw4980
- Preventive Maintenance For The Max CR System Formerly The CR 975 System (PM1883-1)Preventive Maintenance For The Max CR System Formerly The CR 975 System (PM1883-1)
- Technical Information Sound Shell Installation Instructions For COPELAND SCROLL™ CompressorsTechnical Information Sound Shell Installation Instructions For COPELAND SCROLL™ Compressors
- Study of Single Plate Clutch: Presented by:-PANKAJ SHARMAStudy of Single Plate Clutch: Presented by:-PANKAJ SHARMA
- SET-111. RFID Based Prepaid Card For Petrol StationSET-111. RFID Based Prepaid Card For Petrol Station
- Wolaita Sodo University School of Informatics: Department of Information TechnologyWolaita Sodo University School of Informatics: Department of Information Technology