Worksheet 17
Worksheet 17
Uploaded by
JunLi CaiCopyright:
Available Formats
Worksheet 17
Worksheet 17
Uploaded by
JunLi CaiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Worksheet 17
Worksheet 17
Uploaded by
JunLi CaiCopyright:
Available Formats
17 Worksheet (AS)
206
1 The nuclide decays by emitting α-particles and β-particles in a series of decays to form 82
Pb. Eight α-particles are emitted in the sequence. How many β-particles are emitted? [1]
A 6
B 8
C 10
D 12
2 An isotope of uranium, with proton number 92 and nucleon number 235, emits a series of
-particles and β-particles. What is the proton number and nucleon number after five
-particles and two β-particles are emitted? [1]
Proton number Nucleon number
A 80 215
B 82 213
C 84 215
D 86 226
3 What can be assumed to be the maximum range of an -particle in air? [1]
A a few millimetres
B a few centimetres
C a few metres
D a few kilometres
4 In an α-particle scattering experiment a very thin gold film is bombarded with α-particles.
What is observed? [1]
A A few α-particles are deflected through an angle greater than 90º.
B Most α-particles are deflected through angles greater than 90º.
C No α-particle continues on its original path.
D No α-particle is deflected through an angle greater than 90º.
5 What can be concluded about a gold nucleus when α-particles are scattered by a thin gold foil? [1]
A The nucleus contains protons.
B The nucleus contains neutrons.
C The nucleus is much smaller than the size of the atom.
D The nucleus is surrounded by electrons.
6 a Give the name of each of the following ionising radiations:
i [1]
ii [1]
iii γ [1]
b Which radiation is the most ionising? [1]
c What is wrong with the statement below written by a student in his notes?
Beta-particles emitted from a radioactive material are electrons that have been ejected
from their orbits around the atoms. [1]
7 State two of the properties of γ-radiation. [2]
AS and A Level Physics Original material © Cambridge University Press 2010 1
17 Worksheet (AS)
8 a In each case below, write a nuclear decay equation.
i The polonium isotope emits an α-particle and changes into an isotope of
lead (Pb). [2]
ii The strontium isotope emits a β-particle and changes into an isotope of
yttrium (Y). [2]
b Explain why the nucleon number in your answer to a ii does not change. [2]
9 During the transformation of the thorium isotope into an isotope of radon (Rn),
a total of three α-particles and two β-particles are emitted. Determine the nucleon number
and proton number of the isotope of radon. [4]
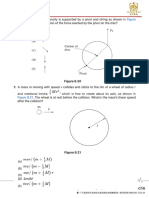
10 In an α-particle scattering experiment, α-particles are fired towards a thin gold foil.
a The diagram shows three α-particles approaching a gold nucleus in the foil.
i Copy the diagram and on your copy complete the paths of the α-particles. [3]
gold
nucleus
ii Add to your diagram a dotted line to show the path taken by slower α-particles
travelling initially along each of the same three lines. Label each of these dotted lines
‘slow’. [2]
iii Explain why the α-particle comes closer to the gold nucleus when the α-particle is
initially faster. [2]
b Explain why this scattering experiment leads to the conclusion that an atom is mainly
composed of empty space, with a very small nucleus. [2]
c Suggest an approximate value for:
i the diameter of a gold nucleus
ii the diameter of a gold atom. [2]
11 a Distinguish between the random and the spontaneous nature of radioactive decay. [4]
b Explain why the evaporation of water molecules from water is faster at higher temperatures
but the emission of radioactive particles is unchanged as the temperature is raised. [2]
c List α, β and γ-radiation, of similar energy, in ascending order of:
i ionising ability (ion pairs created per mm in air) [1]
ii range in air [1]
iii mass [1]
iv speed. [1]
Total: Score: %
AS and A Level Physics Original material © Cambridge University Press 2010 2
You might also like
- MATHS Grade 10 TESTS 2024Document62 pagesMATHS Grade 10 TESTS 2024chrisnambinga8100% (1)
- Icru 16 PDFDocument59 pagesIcru 16 PDFMardeyNo ratings yet
- The Velocity-Time Graphs Represent The Motion of Two Cars, Car A and Car B. Justify AllDocument5 pagesThe Velocity-Time Graphs Represent The Motion of Two Cars, Car A and Car B. Justify AllJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- 6243-02 Jan 2009 MS (Unit 3 Old Syllabus)Document11 pages6243-02 Jan 2009 MS (Unit 3 Old Syllabus)Ibrahim Bt50% (2)
- Uncertainty ReviewDocument5 pagesUncertainty ReviewAmelia RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- 2.1 and 2.2 Misc and Data AnalysisanswersDocument15 pages2.1 and 2.2 Misc and Data AnalysisanswersMalak Alqaidoom100% (1)
- International Accounting & Multinational Enterprises: Lee H. Radebaugh Sidney J. Gray Ervin L. BlackDocument26 pagesInternational Accounting & Multinational Enterprises: Lee H. Radebaugh Sidney J. Gray Ervin L. BlackNidhi Mittal100% (1)
- A2 Physics DefinitionsDocument5 pagesA2 Physics DefinitionsEjaz YounisNo ratings yet
- M1 VectorsDocument2 pagesM1 Vectorszohrabian0% (1)
- Proton Emission: Page IssuesDocument6 pagesProton Emission: Page IssuesAnonymous gUjimJKNo ratings yet
- Safe Transport of Radioactive Materials, Philosophy & OverviewDocument14 pagesSafe Transport of Radioactive Materials, Philosophy & OverviewalkhiatNo ratings yet
- M Schemes 17Document2 pagesM Schemes 17Md. Rakibul Islam RanaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 14Document4 pagesWorksheet 14JunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- MARK SCHEME For The June 2005 Question Paper: University of Cambridge International Examinations GCE Advanced LevelDocument6 pagesMARK SCHEME For The June 2005 Question Paper: University of Cambridge International Examinations GCE Advanced LevelCaterina De LucaNo ratings yet
- Hookes Law QuestionsDocument1 pageHookes Law QuestionsSharuvindan NairNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 10Document3 pagesWorksheet 10JunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Anxiety and Resistance Training PDFDocument12 pagesAnxiety and Resistance Training PDFPaulo AfonsoNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning Averages From A Frequency Table GCSE WorksheetDocument14 pagesThird Space Learning Averages From A Frequency Table GCSE WorksheettrishNo ratings yet
- 9 Worksheet (AS) : Data Needed To Answer Questions Can Be Found in The Data, Formulae and Relationships Sheet.Document3 pages9 Worksheet (AS) : Data Needed To Answer Questions Can Be Found in The Data, Formulae and Relationships Sheet.Ruby ChongNo ratings yet
- Topic - 1 Measurement and UncertaintiesDocument11 pagesTopic - 1 Measurement and UncertaintiesKevin OktaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Questions KinematicsDocument7 pagesChapter Questions KinematicsJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity (Multiple Choice) QPDocument20 pagesRadioactivity (Multiple Choice) QPKimNo ratings yet
- Series and Parallel Circuits Practical - KS3Document2 pagesSeries and Parallel Circuits Practical - KS3Dominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- Check Point Notes - ElectricityDocument70 pagesCheck Point Notes - ElectricityaghayousufproNo ratings yet
- A'level Modern Physics NotesDocument64 pagesA'level Modern Physics NotesLubangula UthumanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/42Document24 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: PHYSICS 9702/42Công Phạm BáNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/22Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Physics 0625/22jad obaidNo ratings yet
- CH - 20 Magnetism WorksheetDocument7 pagesCH - 20 Magnetism WorksheetAna BegovacNo ratings yet
- 21 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (A2) : E E E EDocument3 pages21 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (A2) : E E E EvinuyeNo ratings yet
- How To Calculate Maintenance Calories - JC Fitness PDFDocument7 pagesHow To Calculate Maintenance Calories - JC Fitness PDFmustabeenasadNo ratings yet
- Neltas Topper JiteshDocument7 pagesNeltas Topper Jiteshnishayadav05052012100% (1)
- H2 Jun Holiday Assignment 2013 AnswersDocument12 pagesH2 Jun Holiday Assignment 2013 AnswersKaitlyn HoNo ratings yet
- Sample - Physics Form 5yearly Lesson Plan 2010Document20 pagesSample - Physics Form 5yearly Lesson Plan 2010Mohd Khairul AnuarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet IGCSEDocument6 pagesWorksheet IGCSEsiennaNo ratings yet
- 5054 s20 QP 11 PDFDocument16 pages5054 s20 QP 11 PDFJack KowmanNo ratings yet
- R2019 49P1MSDocument29 pagesR2019 49P1MSSkruzdelyte MielaNo ratings yet
- 6A Capacitors Worksheet 2016Document8 pages6A Capacitors Worksheet 2016Leighton ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Particles and Atoms MCQ TestDocument5 pagesParticles and Atoms MCQ TestVgyggNo ratings yet
- C A 1 M G: NsscoDocument7 pagesC A 1 M G: NsscoNamasiku MuyundaNo ratings yet
- Moments Exam QuestionsDocument11 pagesMoments Exam Questionsbooboo100% (1)
- A Level Physic 2 2017 PDFDocument324 pagesA Level Physic 2 2017 PDFAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Independent Study Booklet Part DDocument13 pagesMechanics Independent Study Booklet Part DnavNo ratings yet
- Phys 1121 Kinematic NotesDocument17 pagesPhys 1121 Kinematic NoteshardkntNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Methods in Physics (Part I)Document72 pagesMathematical Methods in Physics (Part I)Correos WebNo ratings yet
- Business Studies MsceDocument65 pagesBusiness Studies MsceajchiutsiNo ratings yet
- Name: - : Temperature Conversion WorksheetDocument1 pageName: - : Temperature Conversion WorksheetChristian DelapazNo ratings yet
- Work With FunDocument8 pagesWork With FunnooriNo ratings yet
- IFY Physics EoS1 Test 2223 V5 MSDocument10 pagesIFY Physics EoS1 Test 2223 V5 MSthecoolace9No ratings yet
- Light & WaveDocument11 pagesLight & WaveDewan Olin ChotepadaeNo ratings yet
- Wave Phenomena PracticeDocument63 pagesWave Phenomena PracticeDeepak SinghNo ratings yet
- Daltons Law WorksheetDocument2 pagesDaltons Law WorksheetMary ruth DavidNo ratings yet
- 14 - 15 - H2 - EMI - Notes TeacherDocument21 pages14 - 15 - H2 - EMI - Notes TeacherAgus LeonardiNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Revision Practice TestDocument19 pagesCH 7 Revision Practice Testpedro pascalNo ratings yet
- 5.1.2 Worksheet 2Document3 pages5.1.2 Worksheet 2Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- CAPE Unit 2 Paper 2 2013Document14 pagesCAPE Unit 2 Paper 2 2013CAPE Past PapersNo ratings yet
- General Wave Properties 2 QPDocument11 pagesGeneral Wave Properties 2 QPshadybitxhespamNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper 1 TZ1 SLDocument14 pagesPhysics Paper 1 TZ1 SLSurendraNo ratings yet
- Malam Doc Chemistry Form 5: Chapter 2: Name: . ClassDocument7 pagesMalam Doc Chemistry Form 5: Chapter 2: Name: . ClassAzie Nurul AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet States of MatterDocument6 pagesWorksheet States of MatterPRUTHIVI BEHRANo ratings yet
- 17 Worksheet (AS) Nuclear PhysicsDocument2 pages17 Worksheet (AS) Nuclear PhysicsMahad AsimNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 17Document2 pagesWorksheet 17Md. Rakibul Islam RanaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 17 PDFDocument2 pagesWorksheet 17 PDFVijay Bhaskar0% (1)
- Nuclear atom (1)Document8 pagesNuclear atom (1)Enock SemweziNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Choices for the Twenty-First Century: A Citizen's GuideFrom EverandNuclear Choices for the Twenty-First Century: A Citizen's GuideNo ratings yet
- Unit Lesson Plan - Electric Potential and CapacitanceDocument4 pagesUnit Lesson Plan - Electric Potential and CapacitanceJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- A Level Physics 9702 P4 Questions - Extract - 1Document2 pagesA Level Physics 9702 P4 Questions - Extract - 1JunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS and A Level Physics Students Book 3rd Edition (Sang, D, Jones, G, Woodside, R and Chadha, G) (Z-Lib - Org) - ExtractDocument1 pageCambridge International AS and A Level Physics Students Book 3rd Edition (Sang, D, Jones, G, Woodside, R and Chadha, G) (Z-Lib - Org) - ExtractJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- CH15 Oscillatory Motion and WavesDocument5 pagesCH15 Oscillatory Motion and WavesJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- May 2021 3Document2 pagesMay 2021 3JunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Unit Lesson Plan-Sources of Magnetic FieldDocument3 pagesUnit Lesson Plan-Sources of Magnetic FieldJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Ap Physc M - Kinematics 1 Dimension Presentation - 2018 05 01Document113 pagesAp Physc M - Kinematics 1 Dimension Presentation - 2018 05 01JunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 13Document4 pagesWorksheet 13JunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 12Document3 pagesWorksheet 12JunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 11Document4 pagesWorksheet 11JunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 09Document3 pagesWorksheet 09JunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Laws of GravitationDocument3 pagesLaws of GravitationJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- 作业 1.30Document1 page作业 1.30JunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 15Document5 pagesWorksheet 15JunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Questions Work Energy and PowerDocument6 pagesChapter Questions Work Energy and PowerJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Questions Newton S LawsDocument8 pagesChapter Questions Newton S LawsJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Quiz 4-SolutionsDocument2 pagesQuiz 4-SolutionsJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic InductionJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- 2 1作业Document2 pages2 1作业JunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Direct Current CircuitsDocument4 pagesDirect Current CircuitsJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy, and PowerDocument5 pagesWork, Energy, and PowerJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Newton's LawsDocument5 pagesNewton's LawsJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument4 pagesKinematicsJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Linear MomentumDocument4 pagesLinear MomentumJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Rotational MotionDocument5 pagesRotational MotionJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Questions VectorsDocument5 pagesChapter Questions VectorsJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Questions Linear MomentumDocument6 pagesChapter Questions Linear MomentumJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- Protection Against Radiation Exposure: Medical Imaging DepartmentDocument14 pagesProtection Against Radiation Exposure: Medical Imaging Departmentrashdi ShahadNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS Form 5: Unit 5: RadioactivityDocument27 pagesPHYSICS Form 5: Unit 5: RadioactivityDahliza KamatNo ratings yet
- 1 RT08 Occupational Exposure WEBDocument87 pages1 RT08 Occupational Exposure WEBRichar Pinedo CadilloNo ratings yet
- Absolute Dating ActivityDocument5 pagesAbsolute Dating Activityapi-164191091No ratings yet
- Binding Energy Worksheet - 3Document4 pagesBinding Energy Worksheet - 3Ysabela BernardoNo ratings yet
- Nuclear ChemistryDocument32 pagesNuclear ChemistryJingWeybzNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Engineering and Design: J. Washington, J. KingDocument14 pagesNuclear Engineering and Design: J. Washington, J. KingWalid BadrNo ratings yet
- AT6101DR Spectrometer: Radiation Background Measurement and No-Sampling RadiometryDocument2 pagesAT6101DR Spectrometer: Radiation Background Measurement and No-Sampling RadiometryNabila Qurrota AiniNo ratings yet
- 1 - Nuclear Chemistry PDFDocument51 pages1 - Nuclear Chemistry PDFSangga Buana Komara100% (1)
- SPECT/CT Radiation DosimetryDocument13 pagesSPECT/CT Radiation DosimetryMohamed Abd ElazizNo ratings yet
- Fanr Reg 24 EngDocument53 pagesFanr Reg 24 EngRads53No ratings yet
- Physics WB - Section 5 AnswersDocument7 pagesPhysics WB - Section 5 AnswersRamNo ratings yet
- Radiation Dose Limits: Appendix BDocument6 pagesRadiation Dose Limits: Appendix BVaradha Rajan100% (2)
- Radioactivity: Name: Muhammad Dzul Ammar Bin Aslan Class: 5 Ibnu Haitham Teacher: Miss Maisara Binti Mad YonDocument16 pagesRadioactivity: Name: Muhammad Dzul Ammar Bin Aslan Class: 5 Ibnu Haitham Teacher: Miss Maisara Binti Mad YonDzul AmmarNo ratings yet
- PAG 07.3 - Determine Half-Life Using An Ionisation ChamberDocument3 pagesPAG 07.3 - Determine Half-Life Using An Ionisation ChamberjmsonlNo ratings yet
- Safety Feature of RNPPDocument29 pagesSafety Feature of RNPPAmit PaulNo ratings yet
- Radioactive Material Safety Data SheetDocument8 pagesRadioactive Material Safety Data SheetSofi Anna Nur PitasariNo ratings yet
- WP 1: Identification of Improved Safety Features of Lw-SmrsDocument51 pagesWP 1: Identification of Improved Safety Features of Lw-SmrspriteshNo ratings yet
- Attomic Accident by James MahaffeyDocument9 pagesAttomic Accident by James MahaffeyAbdul basitNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance in BrachytherapyDocument13 pagesQuality Assurance in BrachytherapypawanNo ratings yet
- Mục 143. Tiêu Bản Mẫu NhômDocument1 pageMục 143. Tiêu Bản Mẫu NhômDo HungNo ratings yet
- 5 2 Radioactivity 6Tm4aTipbO9YbgShDocument40 pages5 2 Radioactivity 6Tm4aTipbO9YbgSharshmaanranaarshmaanranaNo ratings yet
- Oppenheimer PhysicsDocument3 pagesOppenheimer PhysicsAditya SthaNo ratings yet
- Icru 50 (Tele)Document81 pagesIcru 50 (Tele)Moisés Escobar Jiménez100% (1)
- 4 TUV DR Rev14 - Luis Tirso M Rivilla General Hospital (Apr-July 2015) SignedDocument2 pages4 TUV DR Rev14 - Luis Tirso M Rivilla General Hospital (Apr-July 2015) SignedAndy MolinaNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Stability and RadioactivityDocument35 pagesNuclear Stability and RadioactivityAmirHakimRusliNo ratings yet
- Questions Usage 1Document6 pagesQuestions Usage 1mangalraj900No ratings yet