General Physics 1
General Physics 1
Uploaded by
John Ahron BalinoCopyright:
Available Formats
General Physics 1
General Physics 1
Uploaded by
John Ahron BalinoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
General Physics 1
General Physics 1
Uploaded by
John Ahron BalinoCopyright:
Available Formats
General Physics 2 most precise value of the magnitude of the charge of
an electron or a proton, which is denoted by e, is
COULOMB’S LAW 1.60217653(14) x 10-19 Coulomb, C. The numbers in
Electric Charge parentheses are the uncertainties in the last two digits.
Note that the masses of the proton and neutron are
• electricity came from the Greek work elektron, or nearly equal and are roughly 2000 times the mass of
amber. It is given the name electricity by Sir the electron. Over 99.9% of the mass of any atom is
Wilhelm Gilbert because amber had been the first concentrated in its nucleus. Normally, atoms have zero
substance known by the ancients to exhibit net charge. They are electrically neutral because they
electrification by rubbing. Im gonna show you a have an equal number of protons and electrons. But
short clip ok showing the electric charge produced electrons do not always stay in the atoms, instead they
by rubbing amber with cloth. can be removed by rubbing.
• It was known that when amber was rubbed with
dry cloth--producing what now one would call Law of Charges
static electricity--it could attract light objects, such
• Charles-Augustin de Coulomb
as bits of paper. This attractive force is known as
electrostatic force. Electrification was called "the “Two positive charges or two negative charges repel
most important engineering achievement of the each other. A positive charge and a negative charge
20th century”. Actually it paved the way for second attract each other.”
industrial revolution.
● Benjamin Franklin (1706-1790) suggested calling
• Steam power and metal production first industrial
these two kinds of charge negative and positive,
revolution/ automation and digitization through
respectively, and these names are still used.
the use of electronics and computers, the
invention of the Internet, and the discovery of ● When the Van de Graaff generator starts charging,
nuclear energy. it transfers the charge to the person who is
• artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, the Internet of touching it. Since the person's hair follicles are
Things (IoT), genetic engineering, quantum getting charged to the same potential, they try to
computing, repel each other. This is why the hair actually stands
• basic property of matter carried by some up. It would not make a difference if the polarity of
elementary particles that governs how the the Van de Graaff generator were reversed. As long
particles are affected by an electric or magnetic as the person is insulated, the charge will build up
field.
Atomic Model
Electric Charge is Conserved
• “The algebraic sum of all electric charges in any
closed system is constant.”
• “The magnitude of charge of the electron or proton
is a natural unit of charge.”
● If we rub together a plastic rod and a piece of fur,
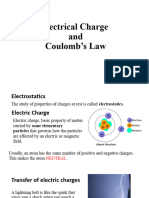
● Atoms have electric charges inside them. In the center both initially uncharged, the rod acquires a
of each atom is the nucleus. This is made up of protons negative charge (since it takes electrons from the
(carriers of positive charges) and neutrons (uncharged fur) and the fur acquires a positive charge of the
particles). In the outer part of the atom are found the same magnitude (since it has lost as many
orbiting electrons (carriers of negative charges). The electrons as the rod has gained). Hence the total
most precise value of the mass of proton is electric charge on the two bodies together does
1.67262171(29) x 10-27 kg, while that of the electron is not change. In any charging process, charge is not
9.1093826(16) x 10-31 kg. The most precise value of created nor destroyed; it is merely transferred
the mass of neutron is 1.67492728(29) x 10-27 kg. The from one body to another.
Conductors and Insulators Coulomb’s Law
• Some materials let electricity pass through them • In 1784, Charles Agustin de Coulomb (1736-1806), a
easily. These materials are known as electrical French physicist, discovered the nature of electrical
conductors. forces exerted by bodies upon one another.
• Many metals, such as copper, iron and steel, are • “The magnitude of the electric force between two
good electrical conductors. That is why the parts of point charges is directly proportional to the product
electrical objects that need to let electricity pass of the charges and inversely proportional to the
through are always made of metal. square of the distance between them.”
• Metal is used in plugs to allow electricity to
● Matter is made up of atoms containing electrically
transfer from the wall socket, through the plug,
charged particles. Many properties of matter result
and into a device such as a radio or TV.
from the electrical forces of attraction and
• In a light bulb, the metal filament conducts
repulsion among the particles. Among these
electricity and causes the light bulb to light up.
properties are the formation of molecules,
● https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/topics/z2882hv/art cohesion, and adhesion.
icles/zxv482p
● Coulomb's torsion balance charles-augustin de
● Electric charges are more easily moved in some Coulomb measured the magnitudes of the electric
materials. This characteristic led to the classification forces between charged objects using the torsion
of materials into two groups – conductors and balance which he invented.
insulators. Materials whose
● Coulomb's torsion balance is an instrument that
● electric charges are free to move within are called enables us to verify experimentally the quantitative
conductors. In some materials, electric charges are law of interaction between electrical charges.
not free to move within. Such materials are called
● Charles Augustin de Coulomb measured the
insulators.
magnitudes of the electric forces between charged
Conductors and Insulators objects using the torsion balance, which he
invented.
• Some materials do not allow electricity to pass
through them. These materials are known ● Coulombs torsion balance is an instrument that
as electrical insulators. enable us to verify experimentally the quantitative
• Plastic, wood, glass and rubber are good electrical law of interaction between electrical charges.
insulators. That is why they are used to cover
● Cylindrical glass case, lid, glass tube, torsion head,
materials that carry electricity.
torsion fibre, needle, brass disc, and sphere
• The plastic covering that surrounds wires is an
electrical insulator. It stops you from getting an ● Scale is used to measure the torsion produced, or
electrical shock the intensity of
• https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/topics/z2882hv/art
icles/zxv482p
● Electric charges are more easily moved in some
materials. This characteristic led to the classification
of materials into two groups – conductors and
insulators. Materials whose
● electric charges are free to move within are called
conductors. In some materials, electric charges are
not free to move within. Such materials are called
insulators.
● Some materials called semiconductors are
intermediate in their properties between good
conductors and good insulators. Certain materials
known as superconductors become perfect
conductors at very low temperatures.
● silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and
elements near the so-called "metalloid staircase"
on the periodic table. Usually ginagamit sa
electronics technology sa computer
● =electric force=Coulomb
constant=charges=distance of separation
● 8.9875517923(14)×109 kg⋅m3⋅s−2⋅C−2
● 9.0 x 109 N∙m2/C2
● Coulomb’s law calculates the magnitude of the
force F between two point charges, q1 and q2,
separated by a distance r. In SI units, the
constant k is equal to
● k=8.988×109N⋅m2C2≈8.99×109N⋅m2C2
● In mathematical terms, the magnitude F of the
force that each of two point charges q1 and q2 a
distance r apart exerts on the other can be
expressed as
● Colomb's law states that the magnitude of the
electrostatic force of attraction or repulsion
between two electrically charged bodies is directly
proportional to the product of the charge of the
charged bodies and inversely proportional to the
square of the distance between the center of the
charged bodies
You might also like
- B.SC - Physics Complete Notes of Electricity and Magnetism100% (1)B.SC - Physics Complete Notes of Electricity and Magnetism134 pages
- Lesson 1 Electric Charge Coulombs Law Electric Fields and Electric Flux2 PDF100% (1)Lesson 1 Electric Charge Coulombs Law Electric Fields and Electric Flux2 PDF10 pages
- Electric Charge, Coulomb'S Law, Electric Fields, and Electric FluxNo ratings yetElectric Charge, Coulomb'S Law, Electric Fields, and Electric Flux80 pages
- Genius Physics ..Pradeep Kshetrapal Electrostatics100% (1)Genius Physics ..Pradeep Kshetrapal Electrostatics24 pages
- Module 1 Basic Electrical Ideas and UnitsNo ratings yetModule 1 Basic Electrical Ideas and Units12 pages
- Electric Charge AND Field: PHY 334 Fundamental of Physics, Electricity, Magnetism and OpticsNo ratings yetElectric Charge AND Field: PHY 334 Fundamental of Physics, Electricity, Magnetism and Optics108 pages
- Universal Concept Classes:-Daksh Pandey ElectrostaticsNo ratings yetUniversal Concept Classes:-Daksh Pandey Electrostatics42 pages
- Chapter 1 - Electric Charges - Fields (Student Copy)No ratings yetChapter 1 - Electric Charges - Fields (Student Copy)34 pages
- LECTURE 01 (NOTE) - Module 01 - Coulomb's LawNo ratings yetLECTURE 01 (NOTE) - Module 01 - Coulomb's Law8 pages
- electricity_1811b78f-67c6-4aa6-b9ee-70d48d9e44cfNo ratings yetelectricity_1811b78f-67c6-4aa6-b9ee-70d48d9e44cf22 pages
- Physics Ii: Elektron, or Amber. It Is Given The NameNo ratings yetPhysics Ii: Elektron, or Amber. It Is Given The Name13 pages
- Lecture-1-Electric Charge and Coulomb's LawNo ratings yetLecture-1-Electric Charge and Coulomb's Law29 pages
- Applied Physics: Electric Charge Coulomb's LawNo ratings yetApplied Physics: Electric Charge Coulomb's Law19 pages
- UCSP Q1 MODULE 1 INTRO Nature Goals and Perspectives in Anthropology Sociology Political ScienceNo ratings yetUCSP Q1 MODULE 1 INTRO Nature Goals and Perspectives in Anthropology Sociology Political Science13 pages
- 2.1.4 Notes (Chapter 4) 4.2 The Structure of An Atom (P. 108)No ratings yet2.1.4 Notes (Chapter 4) 4.2 The Structure of An Atom (P. 108)9 pages
- Lecture No.7: Capacitance and Dielectric MaterialsNo ratings yetLecture No.7: Capacitance and Dielectric Materials10 pages
- Flow Separation Control Utilizing Plasma Actuators: Stefan NilssonNo ratings yetFlow Separation Control Utilizing Plasma Actuators: Stefan Nilsson70 pages
- Electrolysers Fuel Cells and Batteries V1 1No ratings yetElectrolysers Fuel Cells and Batteries V1 1223 pages
- Full Lab Report Charges and Fields Phy 150100% (1)Full Lab Report Charges and Fields Phy 15011 pages
- Chittagong University of Engineering and TechnologyNo ratings yetChittagong University of Engineering and Technology4 pages
- Multiple Choice Question Bank (MCQ) Term - I: Class - XII100% (1)Multiple Choice Question Bank (MCQ) Term - I: Class - XII55 pages
- Science8 q3 Mod3 Week5-6 Subatomic-Particles v5100% (1)Science8 q3 Mod3 Week5-6 Subatomic-Particles v528 pages
- 5 Targeted Individuals Expose Shocking Electronic Harassment and Torture - Stillness in The StormNo ratings yet5 Targeted Individuals Expose Shocking Electronic Harassment and Torture - Stillness in The Storm29 pages
- Dps Rubypark Kolkata STUDY MATERIAL (2020-2021) Sub-Physics Class 7 Topic: ElectricityNo ratings yetDps Rubypark Kolkata STUDY MATERIAL (2020-2021) Sub-Physics Class 7 Topic: Electricity12 pages
- Current Electricity NCERT Notes + PYQ'sNo ratings yetCurrent Electricity NCERT Notes + PYQ's22 pages
- EM-I-Ch 2-Coulomb's Law and Electric Field IntensityNo ratings yetEM-I-Ch 2-Coulomb's Law and Electric Field Intensity23 pages