Experiment 5 Aim::-Diagnosis of Ignition System Faults Apparatus Required
Experiment 5 Aim::-Diagnosis of Ignition System Faults Apparatus Required
Uploaded by
bansalmohit01Copyright:
Available Formats
Experiment 5 Aim::-Diagnosis of Ignition System Faults Apparatus Required
Experiment 5 Aim::-Diagnosis of Ignition System Faults Apparatus Required
Uploaded by
bansalmohit01Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Experiment 5 Aim::-Diagnosis of Ignition System Faults Apparatus Required
Experiment 5 Aim::-Diagnosis of Ignition System Faults Apparatus Required
Uploaded by
bansalmohit01Copyright:
Available Formats
Experiment 5 Aim:- Diagnosis of ignition system faults
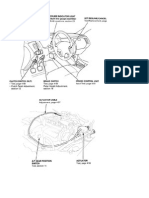
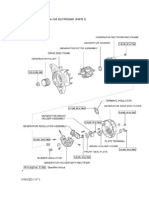
APPARATUS REQUIRED: 1. Multimeter 2. Feeler gauge 3. Battery 4. Lamp 5. Screw Driver 6. Spark plug tester and ignition coil tester. PROCEDURE: If the engine does not start after cranking, check for fuel in the fuel system and its faults. If the fuel system is found to be correct, then check the ignition system. TO CHECK PRIMARY CIRCUIT: Remove the distributor cap and take out the rotor. See that the contact breaker points are opening and closing freely. Check the contact breaker gap with a feeler gauge and it should be around 0.35 -0.40 mm.Adjust the gap if necessary. TO CHECK THE SECONDARY CIRCUIT: The major defects in the secondary circuit are likely to occur in spark plug distributor cap and rotor, H.T leads and ignition coil. 1. To spot the fault, remove the H.T lead from one of the spark plug. Place its ends about 10 mm from the engine block. With the ignition on, crank the engine. If the spark jumps across the gap regularly and with good intensity, then the entire secondary circuit up to and including the distributor is working alright and any fault could lie in the spark plug. 2. To check if there is any problem in the spark plug, remove one spark plug from engine and check for any carbon deposit between the electrode gap. If there is any carbon deposit, clean the plug and adjust the electrode gap before using. 3. If there is no carbon deposits, connect H.T lead from the distributor to this spark plug and place the plug on the cylinder block. Now crank the engine and notice the spark from plug. If the plug produces a blue spark of high intensity, the pug is alright and if not, check the plug for correct electrode gap or fit a new plug and check it. If the spark occurs, then the fault is with spark plug. 4. When even placing the H.T lead about 5 mm from the cylinder, if a spark of good intensity is not obtained, then the fault must be either in the distributor or in the coil.
5. Remove the distributor gap and check for corrosion in the rotor tip and condition of carbon brushes. If there is any fault, change it. If it is alright, then the fault might be with ignition coil. 6. To check the ignition coil, remove it from the vehicle. Connect the positive and negative terminals of ignition coil to an ignition coil tester and the H.T lead is connected to the spark plug. On pressing the cut-off button in the tester, if a blue spark of good intensity jumps across the spark plug, then the coil is in good condition. If not, replace the coil with a new one. OPERATING PROCEDURE: 1. Give connections as detailed in the assembly of parts. Check all the connections are given properly. 2. Using the knob in D.C controller unit, set the rpm to the idle (800 rpm) by adjusting the knob and rpm can be measured in the display provided in the timing light. 3. Measure the timing angle (Mark on the disc must match with the pointer on the cabinet) by adjusting knob provided in the timing light. Press the MODE switch to measure the dwell angle and note the values in the tabular column. (A sample tabular column is attached). 4. Increase the rpm with an increment of 100 every time and measure the timing angle and dwell angle using the step-3. 5. Using the same procedure using the vacuum pump connected, measure the dwell and timing angle. Testing at 800, 900, 1000, 1500 RPMs are good speed to test the distributor and always run the test From slower to higher RPM to get the better results. CAUTION: Hold the secondary cable with insulated pliers made up of non conductive material. Do not metal pliers with insulated handles. . RESULT: Thus the fault in the ignition system is diagnosed and the engine is started.
Without Vacuum Engine RPM Dwell angle Timing angle
With Vacuum Engine RPM Dwell angle Timing angle
Spark plug and contact breaker point test: Color of spark Spark plug gap Contact breaker point gap : : :
You might also like
- GM Automatic Overdrive Transmission Builder's and Swapper's GuideFrom EverandGM Automatic Overdrive Transmission Builder's and Swapper's GuideRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Tune-Up Guide For Geo Metro 1.0 Liter CarsDocument8 pagesTune-Up Guide For Geo Metro 1.0 Liter CarsDerek JewettNo ratings yet
- Ford Tempo Topaz 1984-1994 Repair GuideDocument11 pagesFord Tempo Topaz 1984-1994 Repair GuideFer VN100% (2)
- 1987 RAM 50 2.6L Carburetor AdjustmentsDocument5 pages1987 RAM 50 2.6L Carburetor AdjustmentsMetalAnon100% (1)
- MC Gregor Crane and 501-MOB-boat-davit - CARGOTEC - Manual SP2423-1-15 UMDocument193 pagesMC Gregor Crane and 501-MOB-boat-davit - CARGOTEC - Manual SP2423-1-15 UMHristo75% (4)
- 816C1 Instruction ManualDocument10 pages816C1 Instruction Manualmaheshaeee_796422500100% (1)
- Repair Guides - Carbureted Fuel System - Rochester 2se - E2se CarburetorDocument5 pagesRepair Guides - Carbureted Fuel System - Rochester 2se - E2se CarburetoreducsalNo ratings yet
- E15 CarburetorDocument16 pagesE15 CarburetorPriyantha Galgepitiya100% (5)
- Weber ManualDocument28 pagesWeber ManualMedardo SilvaNo ratings yet
- Diesel Generator TroubleshootingDocument7 pagesDiesel Generator TroubleshootingChandra Vinoth Senthilnathan100% (4)
- Carb Turbo Kit InstructionsDocument11 pagesCarb Turbo Kit InstructionsKevin ShankleNo ratings yet
- Chevelle Performance Projects: 1964-1972From EverandChevelle Performance Projects: 1964-1972Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- EX8000 Kse487Document12 pagesEX8000 Kse487azry_alqadryNo ratings yet
- NSCHE Presentation - GAS LIFTDocument15 pagesNSCHE Presentation - GAS LIFTiyandaseun8846No ratings yet
- Astm D 1816-04Document5 pagesAstm D 1816-04Jonathan LayedraNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Testing BlazerDocument308 pagesDiagnosis and Testing BlazerAli Castillo100% (2)
- Engine MechanicDocument631 pagesEngine Mechanicgeorge100% (1)
- Engine Tune-Up: Ii. Tools and MaterialsDocument6 pagesEngine Tune-Up: Ii. Tools and MaterialsdrakuleeNo ratings yet
- Lesson - Check and Test Starting SystemDocument138 pagesLesson - Check and Test Starting SystemMarcel Baring ImperialNo ratings yet
- Exp 5Document6 pagesExp 5Aryan KumarNo ratings yet
- How - To Engine Tune-Up BasicsDocument6 pagesHow - To Engine Tune-Up Basicsimplode32No ratings yet
- Service & Maintenance of Jaguar & Land Rover CarsDocument76 pagesService & Maintenance of Jaguar & Land Rover CarsPrakashRaiNo ratings yet
- How To Test and Repair Small Engine Ignition System ProblemsDocument5 pagesHow To Test and Repair Small Engine Ignition System ProblemsAlfred E. Newman100% (1)
- Engine Test EquipmentDocument63 pagesEngine Test Equipmentalipotjoshua2003No ratings yet
- BlueDriver Compression Test Results SheetDocument3 pagesBlueDriver Compression Test Results SheeteelturkiNo ratings yet
- Routin 1Document32 pagesRoutin 1beshoybeshoo51No ratings yet
- Installing The Hot-Spark SVDA 034 Distributor With 3BOS4U1 Electronic IgnitionDocument4 pagesInstalling The Hot-Spark SVDA 034 Distributor With 3BOS4U1 Electronic IgnitionIsaias PrestesNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: Labplant Sd-05 Spray DryerDocument14 pagesService Manual: Labplant Sd-05 Spray Dryerfacu_falaNo ratings yet
- Dodge 5.9!03!07 Diagnostic Rail 2Document5 pagesDodge 5.9!03!07 Diagnostic Rail 2Ovidio RiosNo ratings yet
- Ignition HTMDocument7 pagesIgnition HTMjorge Angel LopeNo ratings yet
- Dis Ix DistributorlesDocument8 pagesDis Ix DistributorlespedroaraoztNo ratings yet
- CBLM S Ignition SystemDocument17 pagesCBLM S Ignition Systemace ebradoNo ratings yet
- Cruise ControlDocument14 pagesCruise Controlposlovni2No ratings yet
- Mallory Points Ignition Conversion ModuleDocument4 pagesMallory Points Ignition Conversion Modulepaul_a_rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Removal & Installation: PrintDocument8 pagesRemoval & Installation: PrintElliAbatziNo ratings yet
- P0304-Cylinder 4 Misfire: 1. Cylinder Mis-Fire Condition ActiveDocument6 pagesP0304-Cylinder 4 Misfire: 1. Cylinder Mis-Fire Condition ActiveNguyễn Văn AnNo ratings yet
- ZT2560 Repair ManualDocument16 pagesZT2560 Repair ManualwmbuckstonNo ratings yet
- Operation 1Document9 pagesOperation 1Wbamlak AshebrNo ratings yet
- Documento Anexo Guia 2 de Electric Id Ad (Parte 2)Document12 pagesDocumento Anexo Guia 2 de Electric Id Ad (Parte 2)David MendozaNo ratings yet
- Iso 14224 2016 EspanolDocument21 pagesIso 14224 2016 EspanolpicottoNo ratings yet
- Bottom Feed Port Fuel InjectorsDocument6 pagesBottom Feed Port Fuel InjectorsdarherreraNo ratings yet
- Kip or Troubleshooting GuideDocument10 pagesKip or Troubleshooting Guideweber888100% (1)
- I08-0740 Instructions 2022 v1.5 WebDocument1 pageI08-0740 Instructions 2022 v1.5 WebLeandro CaraccioliNo ratings yet
- 14 CUX Cold Start UpdateDocument16 pages14 CUX Cold Start UpdateAldous Cosmo GitlesNo ratings yet
- Sisweb Sisweb Techdoc Techdoc Print Pag - pdf1Document91 pagesSisweb Sisweb Techdoc Techdoc Print Pag - pdf1MatiussChesteerNo ratings yet
- Scooter Troubleshooting &tuning GuideDocument7 pagesScooter Troubleshooting &tuning Guidestuhoug100% (1)
- Maintenance Manual Engine XinchaiDocument14 pagesMaintenance Manual Engine XinchaiМаксимNo ratings yet
- Diesel Air Heater Fault FindingDocument6 pagesDiesel Air Heater Fault FindingIlieNo ratings yet
- Power Sunroof: Calibration & Timing NoteDocument23 pagesPower Sunroof: Calibration & Timing NoteEngine Tuning UPNo ratings yet
- Chương 3 Kiểm traDocument45 pagesChương 3 Kiểm tra20145391studentNo ratings yet
- Dellorto Carb Install Instructions For 13bDocument7 pagesDellorto Carb Install Instructions For 13bBrent Z. BaileyNo ratings yet
- Volvo 740 SolutionDocument26 pagesVolvo 740 SolutionPaulo MandingaNo ratings yet
- Instructions: Things You'llDocument15 pagesInstructions: Things You'llMuhrif MaharoffNo ratings yet
- 05-244 Common Rail Diag Kit Instructions 091205Document14 pages05-244 Common Rail Diag Kit Instructions 091205Luis Segovia Cortes100% (1)
- Testing and Adjusting: Cerrar SISDocument33 pagesTesting and Adjusting: Cerrar SISJose Luis Garcia Blanco100% (2)
- Ignition System Chevrolet TrailBlazerDocument9 pagesIgnition System Chevrolet TrailBlazerjulio diazNo ratings yet
- The Book of the Singer Junior - Written by an Owner-Driver for Owners and Prospective Owners of the Car - Including the 1931 SupplementFrom EverandThe Book of the Singer Junior - Written by an Owner-Driver for Owners and Prospective Owners of the Car - Including the 1931 SupplementNo ratings yet
- Installation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitFrom EverandInstallation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitNo ratings yet
- Land Rover Series I-III: Your expert guide to common problems & how to fix themFrom EverandLand Rover Series I-III: Your expert guide to common problems & how to fix themNo ratings yet
- Stories from the Road 2: An Automotive Case Studies SeriesFrom EverandStories from the Road 2: An Automotive Case Studies SeriesNo ratings yet
- How to Build & Power Tune Distributor-type Ignition Systems: New 3rd Edition!From EverandHow to Build & Power Tune Distributor-type Ignition Systems: New 3rd Edition!No ratings yet
- Delco Radio Owner's Manual Model 633; Delcotron Generator InstallationFrom EverandDelco Radio Owner's Manual Model 633; Delcotron Generator InstallationNo ratings yet
- Diesel Engine Care and Repair: A Captain's Quick GuideFrom EverandDiesel Engine Care and Repair: A Captain's Quick GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- ARMY TM 9-2320-280-20-2 HMMWV Unit Mantainance Vol 2 JUL04Document953 pagesARMY TM 9-2320-280-20-2 HMMWV Unit Mantainance Vol 2 JUL04RockWagonNo ratings yet
- Basin of PetroleumDocument23 pagesBasin of PetroleumRodrigoQueirozNo ratings yet
- Crude Oil Properties (Laboratory)Document15 pagesCrude Oil Properties (Laboratory)gshdavid100% (1)
- Pipe Bending Machine Manual SmallDocument99 pagesPipe Bending Machine Manual SmallRajesh Kannan100% (2)
- CMR-MDT: Cost-Effective SolutionsDocument3 pagesCMR-MDT: Cost-Effective Solutionshamed1725No ratings yet
- Abbreviations Oil and GasDocument2 pagesAbbreviations Oil and GasSavannah MarieNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Rate of EvaporationDocument22 pagesFactors Affecting Rate of EvaporationShimnu MoneNo ratings yet
- Compressor ExhausterDocument4 pagesCompressor ExhausterJeeva RajNo ratings yet
- CQ Petroleum ProductsDocument15 pagesCQ Petroleum Productsapi-3826629No ratings yet
- Topic: Mathematical Modelling of Liquid Loading in Natural Gas ReservoirDocument14 pagesTopic: Mathematical Modelling of Liquid Loading in Natural Gas ReservoirAkashShuklaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: Cambridge O Level Chemistry 5070Document39 pagesSyllabus: Cambridge O Level Chemistry 5070Abdur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Motorcycle Engine Cooling SystemDocument9 pagesMotorcycle Engine Cooling SystemGODNo ratings yet
- Chery QQ6 - Manual de Servicio CompletoDocument511 pagesChery QQ6 - Manual de Servicio CompletoClaudio Bravo100% (3)
- Turbinas de PerforacionDocument21 pagesTurbinas de Perforacionjairaso2950No ratings yet
- MS3XV357 Hardware 1.3Document214 pagesMS3XV357 Hardware 1.3Lucas VitorNo ratings yet
- FRAMODocument128 pagesFRAMOFanisKountouris100% (5)
- Jobs Safety Plan - TemplateDocument16 pagesJobs Safety Plan - TemplateFairus Md Yusof100% (2)
- Ravinder Singh - Pathetic - 4% Avg Core Infrastructure Growth in Last 3 YearsDocument2 pagesRavinder Singh - Pathetic - 4% Avg Core Infrastructure Growth in Last 3 YearsSurendera M. BhanotNo ratings yet
- LindeDocument28 pagesLindenadjib62100% (1)
- Gas Chromatograph GC PDFDocument68 pagesGas Chromatograph GC PDFEdwin Titirico ApazaNo ratings yet
- Pramac GSW110IDocument10 pagesPramac GSW110IJanko GardaševićNo ratings yet
- Indian Raiilway - BS-105 With A&c 2Document17 pagesIndian Raiilway - BS-105 With A&c 2paimpilly100% (1)
- 628Document4 pages628sdiamanNo ratings yet
- Valves & Pumps For Use With Willett®/Videojet® PrintersDocument11 pagesValves & Pumps For Use With Willett®/Videojet® Printersdiegosc2200No ratings yet
- Unimog U 400: Technical DataDocument2 pagesUnimog U 400: Technical DataUsNdaomanuNo ratings yet
- Line Identification Line Size Pipe Line No. (In.) Spec ServiceDocument20 pagesLine Identification Line Size Pipe Line No. (In.) Spec Servicesamer8saifNo ratings yet