MLC f42
MLC f42
Uploaded by
harry stamperCopyright:
Available Formats
MLC f42
MLC f42
Uploaded by
harry stamperOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
MLC f42
MLC f42
Uploaded by
harry stamperCopyright:
Available Formats
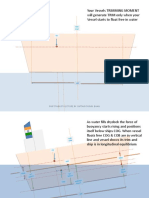
- defines longitudinal centre of gravity (LCG) and longitudinal centre of buoyancy (LCB)
LCB is the longitudinal centre of buoyancy. This is the longitudinal centre of the
underwater volume, and is the point through which all the buoyancy can be said to act
vertically upwards. LCG is the longitudinal centre of gravity. This is the point through
which all of the weight of the vessel can be said to act vertically downwards. Usually,
the reference point for locating the LCG is either of the forward or aft perpendiculars.
- states that a ship trims about the centre of flotation until LCG and LCB are in the same vertical line
The ship trims about the centre of flotation. At the same time the position of
the LCB moves and the ship must trim until G and B are again in a vertical line. When
LCG and LCB are in the same vertical line, the rotation will stop, the vessel will be
trimmed by the stern. If the vessel had started with LCB aft of LCG, then the rotation
would cause a trim by the bow.
- states that the distance of the LOB from amidships or from the after perpendicular is given in a ship‘s
hydrostatic data for the ship on an even keel
A ship’s hydrostatic data includes A series of graphs drawn to a vertical scale of
draught and a base of length, which gives values such as the centre
of buoyancy, displacement, moment causing unit trim, and centre of flotation. In practice
tables with hydrostatic parameters calculated for different draughts are used. However,
only having traditional graphs it is possible to observe character of hydrostatic curves
and understand ship behavior.
- explains that the LCG must be at the same distance from amidships as LCB when the ship floats on an
even keel
It must be remembered that LCB and LCG are in exactly the same position as the transverse
centre of buoyancy and the transverse centre of gravity of the vessel.
- shows on a diagram of a ship constrained to an even keel the couple that is formed by the weight and
buoyancy forces when LCG is not the same distance from amidships as LCB
- states that the trimming moment = displacement x the horizontal distance between LCB (tabulated)
and LCG
- (actual) = Δ x GG1
- where GG1 is the horizontal distance between the position of LCG for the even- keel condition and the
actual LCG
- states that trim = (Δ x GG1) / MCT 1cm
- states that if the actual LCG is abaft the tabulated position of LCB, then the trim will be by the stern,
and vice versa
- given the initial displacement, initial position of LCG, masses loaded or discharged and their LCGs,
calculates the final position of LCG
- using a ship‘s hydrostatic data and a given disposition of cargo, fuel, water and stores, determines the
trim, the mean draught and the draughts at each end
- calculates the mass to move between given positions to produce a required trim or draught at one end
You might also like
- Astm C125 PDFDocument5 pagesAstm C125 PDFZEC LIMITED100% (2)
- Test Stabillity 1 2009Document6 pagesTest Stabillity 1 2009Yuriy Kakaranze0% (1)
- Basic StabilityDocument124 pagesBasic StabilityReynante P. Consul86% (7)
- Seam 4 ADocument4 pagesSeam 4 ARoy CamajalanNo ratings yet
- The Stability Book: DisplacementDocument5 pagesThe Stability Book: DisplacementAsif Siddiqui100% (1)
- f0lc 35 Ship Stability - Theory App - Outcome 3 - Cover Sections 1-3Document33 pagesf0lc 35 Ship Stability - Theory App - Outcome 3 - Cover Sections 1-3Amit Chahande100% (1)
- A General Discussion On Ship StabilityDocument6 pagesA General Discussion On Ship StabilityAnonymous UCveMQNo ratings yet
- SHIP B - Data-Booklet-MCA-SQA-Chief-Mate-Stability-Book-B-V1.2-January-2022Document69 pagesSHIP B - Data-Booklet-MCA-SQA-Chief-Mate-Stability-Book-B-V1.2-January-2022ShanilNo ratings yet
- Intact Stability For All ShipsDocument1 pageIntact Stability For All ShipsAnil PatidarNo ratings yet
- Initial Transverse Metacenter CugalDocument19 pagesInitial Transverse Metacenter CugalPete KatipunanNo ratings yet
- HR0L 35 LO 3 S2 (Shear Forces and Bending Moments) - 464458981Document21 pagesHR0L 35 LO 3 S2 (Shear Forces and Bending Moments) - 464458981noczviviNo ratings yet
- List of GZ Curves To Be Looked Upon For Stability Exam SqaDocument2 pagesList of GZ Curves To Be Looked Upon For Stability Exam SqaithankjesusNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Movement of GDocument398 pages1.0 Movement of GГенна ФелексовNo ratings yet
- Floatation and Its Laws PDFDocument2 pagesFloatation and Its Laws PDFtarak das0% (1)
- LISTDocument5 pagesLISTBharatiyulamNo ratings yet
- Stability BDocument16 pagesStability BVineet KumarNo ratings yet
- Stability Theory IIIDocument32 pagesStability Theory IIISergio RuedaNo ratings yet
- Práctico 3Document2 pagesPráctico 3Andres Caribaldi0% (1)
- 2R SquatDocument11 pages2R SquatInsan Ahammad100% (1)
- Your Vessels Trimming Moment Will Generate TRIM Only When Your Vessel Starts To Float Free in WaterDocument3 pagesYour Vessels Trimming Moment Will Generate TRIM Only When Your Vessel Starts To Float Free in WaterSushil BhanNo ratings yet
- Ship Stability Course Part 5Document119 pagesShip Stability Course Part 5Gilles MathieuNo ratings yet
- 1539055397phase 2 Subra CH 8 Solved by KS ChadhaDocument17 pages1539055397phase 2 Subra CH 8 Solved by KS ChadhaSaurav NaskarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To TSSDocument11 pagesIntroduction To TSSnoczviviNo ratings yet
- Adverse Stability: Check You Progress NameDocument3 pagesAdverse Stability: Check You Progress NameArun Ketu SethNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument24 pagesUnit IsomasundaramNo ratings yet
- Cargo Work: Gross Vulume Occupied by Cargo Weight of CargoDocument2 pagesCargo Work: Gross Vulume Occupied by Cargo Weight of CargoAbu Syeed Md. Aurangzeb Al MasumNo ratings yet
- 2 - Compass NotesDocument30 pages2 - Compass NotesAeshwarya AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Ship Theory - Longitudinal StabilityDocument15 pagesShip Theory - Longitudinal StabilityAji Putra PNo ratings yet
- Questions For Ship Stability - DokmarDocument43 pagesQuestions For Ship Stability - Dokmarajrocha1107No ratings yet
- Basic StabilityDocument79 pagesBasic StabilityRoneil BaculioNo ratings yet
- E04-Ship Geometry & Hydrostatic CalculationsDocument2 pagesE04-Ship Geometry & Hydrostatic Calculationsarise tettehNo ratings yet
- Stability CriteriaDocument7 pagesStability CriteriaSuperducksNo ratings yet
- Metacentre & Metacentric Height of A Ship (02042020)Document3 pagesMetacentre & Metacentric Height of A Ship (02042020)Xahid HasanNo ratings yet
- Deck CargoDocument29 pagesDeck CargoKaede xNo ratings yet
- Section 23 Intact and Damage Stability: I - Part 6 GL 2010 Page 23-1Document8 pagesSection 23 Intact and Damage Stability: I - Part 6 GL 2010 Page 23-1JAAK2005No ratings yet
- OOW SQA Stability March 2005 JULY 16Document147 pagesOOW SQA Stability March 2005 JULY 16Christiana SukhuNo ratings yet
- Producing A Curve of Statical StabilityDocument8 pagesProducing A Curve of Statical Stabilityrsinha06089411No ratings yet
- 06 NAC Free Surface Effect (160213)Document10 pages06 NAC Free Surface Effect (160213)Gilles MathieuNo ratings yet
- Transverse Stability of ShipDocument12 pagesTransverse Stability of ShipIrakli ShavishviliNo ratings yet
- Rule 35 - Sound Signals inDocument31 pagesRule 35 - Sound Signals inMitch Speeder100% (1)
- 02.04b Ch4 PPT SlidesDocument114 pages02.04b Ch4 PPT Slidespothiraj100% (2)
- B1b StabilityDocument17 pagesB1b StabilityDarwin Neil MoranoNo ratings yet
- Lesson-1 Introduction To Stability: BM KMDocument75 pagesLesson-1 Introduction To Stability: BM KMPulung WNo ratings yet
- 1 Seam 2 LM PrelimDocument64 pages1 Seam 2 LM PrelimTrestan TenegraNo ratings yet
- Good Stability NotesDocument51 pagesGood Stability Notesdarrelsilva100% (1)
- 1i Cot Due To DensityDocument2 pages1i Cot Due To DensityShankar SinghNo ratings yet
- BilgingDocument10 pagesBilgingImanNo ratings yet
- Assign No 3 GZ CurveDocument3 pagesAssign No 3 GZ CurveShikhar SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Stability Theory With Ques and AnsDocument25 pagesStability Theory With Ques and AnsAnkit BatraNo ratings yet
- Describe and Illustrate Standard Steel SectionsDocument11 pagesDescribe and Illustrate Standard Steel SectionsNull NullNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4.1 Introduction To Stability: BM KMDocument66 pagesLesson 4.1 Introduction To Stability: BM KMDrago Dragic100% (1)
- Ship Stability Course Part 4Document118 pagesShip Stability Course Part 4Gilles MathieuNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Solutions 2009-2010Document9 pagesFinal Exam Solutions 2009-2010engnavaljoaoNo ratings yet
- Trim HandoutDocument1 pageTrim Handoutjwaters3No ratings yet
- Ship Stability: Damaged Stability of ShipsDocument11 pagesShip Stability: Damaged Stability of ShipsgeorgesagunaNo ratings yet
- 95SCS-4 Sr. No. EMR Examination of Marine Engineer OfficerDocument5 pages95SCS-4 Sr. No. EMR Examination of Marine Engineer OfficerThapliyal SanjayNo ratings yet
- BilgingDocument104 pagesBilginggeminiansailor100% (2)
- 01-NAC-Introduction To Ship Stability (160419)Document40 pages01-NAC-Introduction To Ship Stability (160419)MuhammadIlhamNugroho100% (1)
- Seam6-Midterms NotesDocument5 pagesSeam6-Midterms NotesOrewa madamada daneNo ratings yet
- Draft Survey TheoryDocument7 pagesDraft Survey Theoryarshit sharmaNo ratings yet
- DC-DC Converter, Relay Drive and Motor Drive Applications: Absolute Maximum RatingsDocument6 pagesDC-DC Converter, Relay Drive and Motor Drive Applications: Absolute Maximum RatingsEka Hikmah PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Co Po Mapping (Example)Document2 pagesCo Po Mapping (Example)selva_raj215414No ratings yet
- Video Cap XDocument94 pagesVideo Cap XsunsrinivasNo ratings yet
- Title:: To Make A Slot by Shaper MachineDocument4 pagesTitle:: To Make A Slot by Shaper MachineMD Mahmudul Hasan MasudNo ratings yet
- G. Tuttle - 2022 Voltage/current Dividers - 1Document13 pagesG. Tuttle - 2022 Voltage/current Dividers - 1SkyNo ratings yet
- Aircraft HardwareDocument26 pagesAircraft Hardwaregueting_overNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Analysis of An Offshore Ship-Mounted Crane Subject To Sea Wave DisturbancesDocument6 pagesDynamics Analysis of An Offshore Ship-Mounted Crane Subject To Sea Wave DisturbancesEhab WilsonNo ratings yet
- A Simple Model For Analyzing P2P StreamingDocument10 pagesA Simple Model For Analyzing P2P StreamingIvanIvanovichIvanovNo ratings yet
- 552 Notes 9Document19 pages552 Notes 9Ishita AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Control of A Lightweight Flexible Robotic Arm Using Sliding ModesDocument8 pagesControl of A Lightweight Flexible Robotic Arm Using Sliding ModesLarbi ElbakkaliNo ratings yet
- Purchase Order: VK Portable Cabins Subha ElanDocument2 pagesPurchase Order: VK Portable Cabins Subha Elanelan subhaNo ratings yet
- 13 HorticultureDocument1 page13 Horticulturenitin guptaNo ratings yet
- Cat Catalouge Print MachineDocument451 pagesCat Catalouge Print MachineAndreea Boacara100% (6)
- 6043 122 4300 Split Coupled Vertical in Line Parts ListDocument15 pages6043 122 4300 Split Coupled Vertical in Line Parts Listspeedy712No ratings yet
- Voltage Drop in Transmission LinesDocument1 pageVoltage Drop in Transmission LinesPradeep SinghNo ratings yet
- OTTVDocument54 pagesOTTVSonia Radix PatriaNo ratings yet
- Elastic Modulus RelationshipsDocument2 pagesElastic Modulus Relationshipsaishwarya25singhNo ratings yet
- Unitrac 80WDocument1 pageUnitrac 80WprogramacionavanzadaNo ratings yet
- Net Ready-Strategies For Success in The E-Conomy: by Amir Hartman and John Sifonis, With John KadorDocument7 pagesNet Ready-Strategies For Success in The E-Conomy: by Amir Hartman and John Sifonis, With John Kadorjohannamac2No ratings yet
- Manual MAH 80-3 ACDocument41 pagesManual MAH 80-3 ACkrp857349No ratings yet
- Equnix PostgreSQL Query TuningDocument45 pagesEqunix PostgreSQL Query TuningPutri Herdiyani100% (1)
- CoCubes Test PatternDocument3 pagesCoCubes Test PatternMallikarjun AradhyaNo ratings yet
- Acoustics - Laboratory Tests On Noise Emission From Appliances and Equipment Used in Water Supply InstallationsDocument24 pagesAcoustics - Laboratory Tests On Noise Emission From Appliances and Equipment Used in Water Supply Installationsgs.phamngochaoNo ratings yet
- PR Closed System 2Document2 pagesPR Closed System 2Mareta DanarNo ratings yet
- Azot Refinery BelarusDocument36 pagesAzot Refinery BelarusThiwakkaran Muagan100% (1)
- UT Testing-Study NotesDocument1,224 pagesUT Testing-Study NotesCharlie Chong94% (18)
- Dhis2 Developer ManualDocument291 pagesDhis2 Developer ManualnisheednairNo ratings yet
- Elem BCD For PostingDocument40 pagesElem BCD For PostingPRC BoardNo ratings yet
- KTM 690rally Parts List 2007-2008Document65 pagesKTM 690rally Parts List 2007-2008s11159100% (1)