PR Closed System 2
PR Closed System 2
Uploaded by
Mareta DanarCopyright:
Available Formats
PR Closed System 2
PR Closed System 2
Uploaded by
Mareta DanarCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
PR Closed System 2
PR Closed System 2
Uploaded by
Mareta DanarCopyright:
Available Formats
Exercises of Closed System 1.
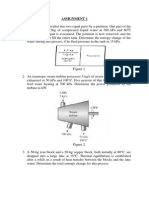
A piston-cylinder device with a set of stops on the top contains 5 kg of saturated liquid water at 200 kPa. Heat is now transferred to the water, causing some of the liquid to evaporate and move the piston up. When the piston reaches the stops, the enclosed volume is 100 L. More heat is added until the pressure is doubled. Show the process on a P-v diagram with respect to saturation lines, and determine (a) the amount of liquid at the final state, in any, (b) the final temperature, and (c) the total work and heat transfer. 2. Is the energy required to heat from 295 to 315 K the same as the energy required to heat it (a) from 340 to 360 K, (b) from 1200 to 1220 K? Assume the pressure remains constant in both cases. 3. Determine the enthalpy change h of nitrogen in kJ/kg, as it is heated from 400 to 600 K, using (a) the empirical data for h from the nitrogen table (Table A-18), (b) the empirical specific heat equation as a function of temperature (Table A-2c), (c) the cp value at the average temperature (Table A-2b), and (d) the the cp value at room temperature (Table A-2a). 4. A 4x5x7 m3 room is heated by the radiator of a steam-heating steam. The steam radiator transfers heat at a rate 10,000 kJ/h, and a 100 W fan is used to distribute the warm air in the room. The rate of heat loss from the room is estimated to be about 5,000 kJ/h. If the initial temperature of the room air is 10 C, determine how long it will take for the air temperature to rise to 20 C. Assume constant specific heats at room temperature. 5. A student living in a 4x6x6 m3 dormitory room turns on her 200W fan before she leaves the room on a summer day, hoping that the room will be cooler when she comes back in the evening. Assuming all the doors and windows are tightly closed and disregarding any heat transfer through the walls and the windows, determine the temperature in the room when she comes back 8 hours later. Use specific heat values at room temperature, and assume the room to be at 100 kPa and 15 C in the morning when she leaves 6. An insulated rigid tank is divided into two equal parts by a partition. Initially, one part contains 2 kg of an ideal gas at 500 kPa and 70 C, an the other part is evacuated. The partition is now removed, and the gas expands into the entire tank. Determine the final temperature and pressure in the tank. 7. A mass of 5 kg of saturated water vapor at 300 kPa is heated at constant pressure until the temperature reaches 200C. Calculate the work done by the steam during this process. Answer: 165.9 kJ 8. A mass of 2.4 kg of air at 150 kPa and 12C is contained in a gas-tight, frictionless piston cylinder device. The air is now compressed to a final pressure of 600 kPa. During the process, heat is transferred from the air such that the temperature inside the cylinder remains constant. Calculate the work input during this process. Answer: 272 kJ 9. A pistoncylinder device contains 50 kg of water at 250 kPa and 25C. The cross-sectional area of the piston is 0.1 m2. Heat is now transferred to the water, causing part of it to evaporate and expand. When the volume reaches 0.2 m3, the piston reaches a linear spring whose spring constant is 100 kN/m. More heat is transferred to the water until the piston rises 20 cm more. Determine (a) the final pressure and temperature and (b) the work done during this process. Also, show the process on a P-V diagram.
Answers: (a) 450 kPa, 147.9C, (b) 44.5 kJ
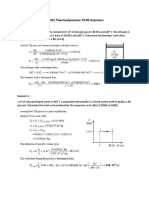
10. A pistoncylinder device contains 0.15 kg of air initially at 2 MPa and 350C. The air is first expanded isothermally to 500 kPa, then compressed polytropically with a polytropic exponent of 1.2 to the initial pressure, and finally compressed at the constant pressure to the initial state. Determine the boundary work for each process and the net work of the cycle. 11. A well-insulated rigid tank contains 5 kg of a saturated liquidvapor mixture of water at l00 kPa. Initially, three-quarters of the mass is in the liquid phase. An electric resistor placed in the tank is connected to a 110-V source, and a current of 8 A flows through the resistor when the switch is turned on. Determine how long it will take to vaporize all the liquid in the tank. Also, show the process on a T-v diagram with respect to saturation lines.
12. A pistoncylinder device contains steam initially at 1 MPa, 450C, and 2.5 m3. Steam is allowed to cool at constant pressure until it first starts condensing. Show the process on a T-v diagram with respect to saturation lines and determine (a) the mass of the steam, (b) the final temperature, and (c) the amount of heat transfer. 13. A pistoncylinder device initially contains 0.8 m3 of saturated water vapor at 250 kPa. At this state, the piston is resting on a set of stops, and the mass of the piston is such that a pressure of 300 kPa is required to move it. Heat is now slowly transferred to the steam until the volume doubles. Show the process on a P-v diagram with respect to saturation lines and determine (a) the final temperature, (b) the work done during this process, and (c) the total heat transfer. Answers: (a) 662C, (b) 240 kJ, (c) 1213 kJ
You might also like
- Thermodynamics An Engineering Approach: Thermo 1 (MEP 261)Document22 pagesThermodynamics An Engineering Approach: Thermo 1 (MEP 261)cwidiNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of Oil & Gas WellsDocument71 pagesLife Cycle of Oil & Gas WellsSorin100% (3)
- T 2Document1 pageT 2jfl2096No ratings yet
- Ned University of Engineering & Technology Department of Food Engineering Thermodynamics - Assignment SPRING SEMESTER 2020-2021Document4 pagesNed University of Engineering & Technology Department of Food Engineering Thermodynamics - Assignment SPRING SEMESTER 2020-2021Sahar Batool QaziNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems On First Law For Closed SystemDocument3 pagesPractice Problems On First Law For Closed SystemNetra PujarNo ratings yet
- ThermoDocument4 pagesThermowong zhi chengNo ratings yet
- ChE 204 HW-4 and HW-5 Together, Spring 2014, See Changes!Document5 pagesChE 204 HW-4 and HW-5 Together, Spring 2014, See Changes!Irene Kaye AceroNo ratings yet
- Taller 2 2023-1Document8 pagesTaller 2 2023-1anderson ortizNo ratings yet
- TD Worksheet 1Document6 pagesTD Worksheet 1murtessaahmed9No ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document2 pagesTutorial 2Nayli SorfinaNo ratings yet
- ME 63 Prob Set 2Document2 pagesME 63 Prob Set 2RamonVannCleffRaroNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 PDFDocument3 pagesTutorial 5 PDFAnonymous hxyDxxcoJNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 First Law 2016Document8 pagesAssignment 1 First Law 2016PabitraBadhuk0% (1)
- Assignment EntropyDocument2 pagesAssignment Entropyme22b009No ratings yet
- Kkpk1223 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics I Tutorial Iv SEMESTER II 2023/2024Document2 pagesKkpk1223 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics I Tutorial Iv SEMESTER II 2023/2024catrineNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 5 ExamplesDocument26 pagesLecture - 5 ExamplesDimas Angga100% (7)
- Work Sheet 1Document3 pagesWork Sheet 1TMedhin MisganawNo ratings yet
- 2022 Tut 5Document2 pages2022 Tut 5Kethavath Sunil ch21b047No ratings yet
- Sheet #7Document4 pagesSheet #7AHMED BAKRNo ratings yet
- Sheet 3 - ME 211TDocument4 pagesSheet 3 - ME 211Tsophia haniNo ratings yet
- ThermoDocument5 pagesThermoTerry Clarice DecatoriaNo ratings yet
- More Problems in Pure SubstanceDocument3 pagesMore Problems in Pure SubstancedeyhritamNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 3Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet 3Syed YousufuddinNo ratings yet
- Kkpk1223 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics I Tutorial Vi SEMESTER II 2023/2024Document2 pagesKkpk1223 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics I Tutorial Vi SEMESTER II 2023/2024catrineNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics QuestionsDocument4 pagesThermodynamics Questionsprateek vyasNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document6 pagesAssignment 1Roshan ShanmughanNo ratings yet
- ME331 Thermodynamics: PS #3 Solutions: Numeric 1Document14 pagesME331 Thermodynamics: PS #3 Solutions: Numeric 1Crimson MorangeNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 4 (Chapter 5) Due 3:00 PM of February 07, 2008 1Document2 pagesAssignment # 4 (Chapter 5) Due 3:00 PM of February 07, 2008 1Adam SchellNo ratings yet
- Assignment ProblemsDocument2 pagesAssignment ProblemsRam SharmaNo ratings yet
- 1 Lista 1 2021Document4 pages1 Lista 1 2021Tiago OliveiraNo ratings yet
- 23mee202et Questionbooklet-2-1Document9 pages23mee202et Questionbooklet-2-1rethinagiriswaransheshanthNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Thermo I PDF 1Document13 pagesWorksheet Thermo I PDF 1roba angasuNo ratings yet
- Tutorial ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesTutorial Thermodynamics23f3001728No ratings yet
- T 5Document2 pagesT 5jfl2096No ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Tutorial ProblemsDocument20 pagesThermodynamics Tutorial ProblemsRishabh Sharma100% (1)
- 5.1 Prob - Sheet.entropyDocument2 pages5.1 Prob - Sheet.entropyShrinivas Subhash HulsureNo ratings yet
- Group Quiz ME 63 THYZ - WFWX EntropyDocument2 pagesGroup Quiz ME 63 THYZ - WFWX Entropyluvieduffy_13No ratings yet
- CHE 220-FALL23-Homework VDocument2 pagesCHE 220-FALL23-Homework Vsemikonino35No ratings yet
- Problem Sheet-03 ME201 1st LawDocument2 pagesProblem Sheet-03 ME201 1st LawPratyusha SatpathyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 10Document7 pagesAssignment 10Mohamed RaafatNo ratings yet
- ChE 122 LE1 Samplex 2Document3 pagesChE 122 LE1 Samplex 2googley71No ratings yet
- 11me201 Thermodynamics QuestionsDocument12 pages11me201 Thermodynamics QuestionsramsastryNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 01Document2 pagesAssignment # 01Zafarullah HakroNo ratings yet
- Problemas TermoDocument3 pagesProblemas TermocleonardoeNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Review ProblemsDocument3 pagesThermodynamics Review ProblemssayanNo ratings yet
- Sheet #7Document4 pagesSheet #7Iam A gnoomNo ratings yet
- 2020S ME211 HW2correctedDocument2 pages2020S ME211 HW2corrected박천우No ratings yet
- AssignDocument2 pagesAssignHabtamu Tkubet EbuyNo ratings yet
- More Thermo Problems..Document3 pagesMore Thermo Problems..bmz00000No ratings yet
- 11me201 Thermodynamics QuestionsDocument12 pages11me201 Thermodynamics QuestionsJustin Cox0% (2)
- Practice Problem (Chap # 03)Document4 pagesPractice Problem (Chap # 03)nandlalwarsoorNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Questions On Thermo 1Document1 pageTutorial Questions On Thermo 1MuhammadAizatNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems On EntropyDocument1 pagePractice Problems On EntropyNetra PujarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document25 pagesChapter 7Nabeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document2 pagesTutorial 4tehpohkee50% (2)
- Exercise PyeqDocument2 pagesExercise PyeqNaufal SyafiqNo ratings yet
- ME211 Sheet 3A Properties of Pure SubstanceDocument3 pagesME211 Sheet 3A Properties of Pure SubstanceTito HeshamNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Assignment SheetDocument3 pagesThermodynamics Assignment SheetSatwikMohantyNo ratings yet
- QB Unit 1Document6 pagesQB Unit 1Gaurav GadhesariaNo ratings yet
- Pdms Syntax Library v1.1 2012Document35 pagesPdms Syntax Library v1.1 2012seenu189100% (1)
- Method and Model Development For Manufacturing Cost Estimation During The Early Design Phase Related To The Complexity of The Machining ProcessesDocument10 pagesMethod and Model Development For Manufacturing Cost Estimation During The Early Design Phase Related To The Complexity of The Machining ProcessesMareta DanarNo ratings yet
- CD7725Document24 pagesCD7725Mareta DanarNo ratings yet
- Py Rig HT: Design and Measurement of Losses in Ac Induction Motor With Different Rotor Bar MaterialDocument24 pagesPy Rig HT: Design and Measurement of Losses in Ac Induction Motor With Different Rotor Bar MaterialMareta DanarNo ratings yet
- Cico 200Document2 pagesCico 200Bis ChemNo ratings yet
- Maquina de Soldar MillerDocument40 pagesMaquina de Soldar MillerCarlo Andreé Egúsquiza RamosNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet (Atomic Spectroscopy - I) : School of Chemistry and Biochemistry, TIET, Patiala Applied Chemistry (UCB008)Document4 pagesTutorial Sheet (Atomic Spectroscopy - I) : School of Chemistry and Biochemistry, TIET, Patiala Applied Chemistry (UCB008)Yuvraj SinghNo ratings yet
- 9.7 PaintingDocument62 pages9.7 PaintingAnbu AlagupandianNo ratings yet
- Cat Ultra Synthetic Generator Grease: Long Life, Extreme PressureDocument2 pagesCat Ultra Synthetic Generator Grease: Long Life, Extreme PressureEslam MahfouzNo ratings yet
- Elemental Analysis of Different Floral Honeys of East Godvari Dist., Andhra Pradesh, IndiaDocument5 pagesElemental Analysis of Different Floral Honeys of East Godvari Dist., Andhra Pradesh, IndiaIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Bioactive LiquidDocument8 pagesBioactive LiquidArdyas Wisnu BaskoroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Solid State PrinciplesDocument65 pagesChapter 1 Solid State PrinciplesPeter YekNo ratings yet
- Why Use Silicones in Personal Care Part 1Document8 pagesWhy Use Silicones in Personal Care Part 1JulioNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 - KC DeterminationDocument12 pagesExperiment 7 - KC DeterminationDan Chen0% (1)
- Dr. Umar Jan Pandit: Personal DetailsDocument6 pagesDr. Umar Jan Pandit: Personal Detailsumar panditNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual LG 8 KGDocument36 pagesInstruction Manual LG 8 KGmanojganewattaNo ratings yet
- Photobioreactor Design and Parameters Essential For Algal Cultivation Using Industrial Wastewater - A ReviewDocument13 pagesPhotobioreactor Design and Parameters Essential For Algal Cultivation Using Industrial Wastewater - A ReviewSolidarioNo ratings yet
- Final Assessment of Mass Transfer: Ismail Idris AbdulazizDocument23 pagesFinal Assessment of Mass Transfer: Ismail Idris Abdulazizاسماعیل ادریس عبدالعزیزNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Thermal Expansion Coefficient of Glasses 1976 Journal of Non Crystalline SolidsDocument9 pagesCalculation of Thermal Expansion Coefficient of Glasses 1976 Journal of Non Crystalline SolidsGarlapati Srinivasa RaoNo ratings yet
- 721, 721TC / ST: HydraulicDocument1 page721, 721TC / ST: HydraulicEdu ZamalloaNo ratings yet
- Amylase Activity of Starch Degrading BacDocument13 pagesAmylase Activity of Starch Degrading BacRaisya RagilNo ratings yet
- Threaded Insert Systems: Edition 05 2013Document48 pagesThreaded Insert Systems: Edition 05 2013Shanil BussooaNo ratings yet
- Penthouse Summer 1996Document2 pagesPenthouse Summer 1996John M. CavoteNo ratings yet
- Ce 8381som Lab ManualDocument31 pagesCe 8381som Lab ManualAERO JPR50% (2)
- Principle of Open Channel FlowDocument39 pagesPrinciple of Open Channel FlowEugene Acuin Jaraplasan100% (2)
- Amicon Ultra 4 ML GuideDocument12 pagesAmicon Ultra 4 ML Guidemohit16ukNo ratings yet
- Journal of Global Pharma Technology Purification, Beneficiation and Activation of Iraqi Attapulgite Clay MineralDocument9 pagesJournal of Global Pharma Technology Purification, Beneficiation and Activation of Iraqi Attapulgite Clay MineralKomang VeraNo ratings yet
- Metronelec Ionic Contamination Tester CT1000Document2 pagesMetronelec Ionic Contamination Tester CT1000Lee HitchensNo ratings yet
- UserManual Biolyzer-300 PDFDocument331 pagesUserManual Biolyzer-300 PDFJames PiauNo ratings yet
- Mini ThesisDocument22 pagesMini Thesisnraliasy channelNo ratings yet
- Antigen Preparation Form BacteriaDocument17 pagesAntigen Preparation Form BacteriaProvince Public Health Laboratory JanakpurNo ratings yet
- Phy Chem Math Eng Timetable - DTW Tutorials Jamb 2024Document7 pagesPhy Chem Math Eng Timetable - DTW Tutorials Jamb 2024ggold0934No ratings yet
- GE - 200802 - Technical Specs Jenbacher Type 6 PDFDocument2 pagesGE - 200802 - Technical Specs Jenbacher Type 6 PDFsakthivelNo ratings yet