Hematology Pathology - 004) Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (AML) (Illustrations - Key)
Hematology Pathology - 004) Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (AML) (Illustrations - Key)
Uploaded by
hasanatiya41Copyright:
Available Formats
Hematology Pathology - 004) Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (AML) (Illustrations - Key)
Hematology Pathology - 004) Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (AML) (Illustrations - Key)
Uploaded by
hasanatiya41Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Hematology Pathology - 004) Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (AML) (Illustrations - Key)
Hematology Pathology - 004) Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (AML) (Illustrations - Key)
Uploaded by
hasanatiya41Copyright:
Available Formats
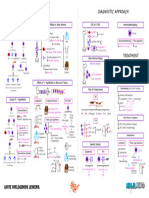
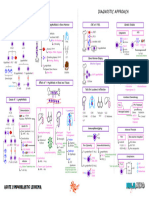
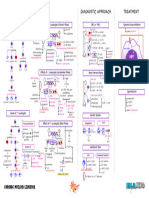
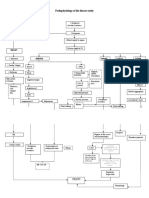
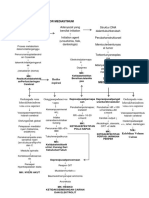
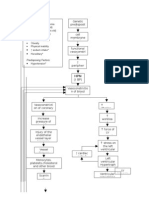
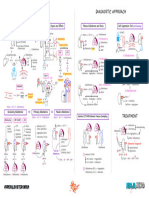
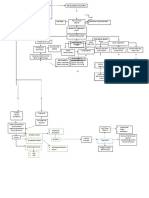
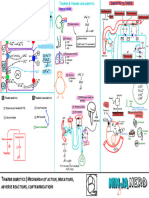
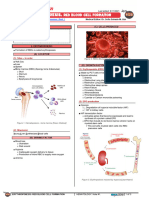
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DIAGNOSTIC APPROACH
Hematopoiesis Pathway Effects of ↑↑ Myeloblasts in Bone Marrow CBC w/ P.B.S. Immunophenotyping
↓↓RBC’s Myeloperoxidase
↑↑ Myeloblasts (2/2 ↓Space) M.P.O.
Hemocytoblast ↓↓PLTs
↓↓Functional WBC’s
↑↑Risk of Infections ↑ Immunohistochemistry Flow Cytometry
PNA pneumonia Variable WBC’s
myeloid lymphoid ↓
stem cells stem cells ↑↑Mortality
M.S.C. L.S.C.
RBC
↑↑Myeloblasts M.P.O. (+) → AML N/A
↓↓ Anemia (↓Space)
↑↑↑
↑↑↑
P.B.S. Auer rods (APL)
Fatigue, Pallor, Dyspnea
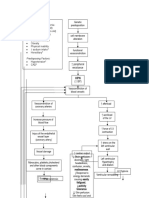
TREATMENT
peripheral blood smear
PLT
↓↓ Thrombocytopenia (↓Space) UTI
RBC PLT Myeloblast ↑↑ Lymphoblast Bone Marrow Biopsy
Bruising, Bleeding
Definitive Diagnosis Chemotherapy: AML (non APL Subtype)
promyelocyte ↑↑Myeloblasts
Expands Bone Marrow
P.M.C. B-lymphocytes Induction → Consolidation → Maintenance
T-lymphocytes Bone Pain Cellulitis
>20% Myeloblasts Agents
Auer rods (APL) Cytarabine
Ida/daunorubicin
Neutrophils Eosinophils Basophils
Effects of ↑↑ Myeloblasts in Blood and Tissues
Tests of Complications Chemotherapy: AML (APL Subtype)
Granulocytes
Promote Differentiation
(≥100K) Disseminated intravascular coagulation DIC
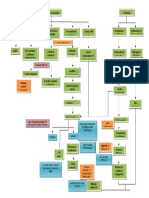
Causes of ↑↑ Myeloblasts Myeloblast → P.M.C. → Granulocyte
Leukostasis Cutaneous/Mucosal DIC (APL)
Agents
ATRA
1 AML ALL Leukemia Cutis
Chemoradiation (M/C) Tissue ± Arsenic Trioxide
H.C.B. Gingival Hyperplasia plasminogen
activator ↑PIT ↑INR ↓Fibrinogen ↑D-Dimer ↓PLTs ↓RBC’s
↑↑DNA H/A ↑TPA ↑Tissue
Factor Bone Marrow Transplant
Mutation Replication TIA Tumor Lysis Syndrome
↑↑Fibrinolysis (III) T.L.S.
CVA ↑↑K+ AML (Poor prognostic findings)
M.S.C. L.S.C.
2 AKI
M/C ↑↑Bleeding ↑↑Clotting
Genetic Dx
3-
↑↑PO4 + Ca2+ ↑Cr AML (Failed chemotherapy)
• 2/2 Chemotherapy Risk Crystals
↓↓Clotting ↑↑Uric Acid ↑BUN
Down Syndrome Dyspnea L/C
(Trisomy 21) • Spontaneous Factors ↓↓Ca 2+ Complications
Myeloblast ↑↑
acute promyelocytic leukemia Hypoxemia 2/2 ↑↑ Tumor Burden
(2/2 Consumption)
AML Subtype (APL)
(↑↑Myeloblasts )
15;17 translocation Leukostasis Tumor Lysis Syndrome
PML-RAR-α
Genetic Studies
ICH inter cerbral
P.M.C. Vision Ca2+ Cytoreduction
hemorrhage
Changes ↑K+
3 Cytogenetics PCR
3 IVF
Bone Marrow Disorder ↑PO
3- Hydroxyurea
Vision Loss 4
↑Uric Acid Crystals Pulmonary Leukapheresis * ↑Purines 1
MDS →→→ AML Hemorrhage
AKI Allopurinol
Chemotherapy
acute kidney injury
CML →→→ 15;17 ↓Uric Acid
↓UOP ↓AKI
Granulocytes chronic myeloid 2 (toxic)
leukemia ↑Cr Bruising Rasburicase
Bleeding 15;17 translocation (+) PML-RAR-α (+)
↑BUN ↑Allantoin
myelodysplastic syndrome (non-toxic)
APL APL
ACUT E MYELOGENOUS LEUKEMIA
You might also like
- Pathophys BURNDocument2 pagesPathophys BURNpaupaulala83% (6)
- Pathophysiology CVADocument2 pagesPathophysiology CVASewyel Garburi100% (6)
- Acute Myelogenous LeukemiaDocument1 pageAcute Myelogenous LeukemiadevendraNo ratings yet
- Hematology Pathology - 003) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) (Illustrations - Key)Document1 pageHematology Pathology - 003) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) (Illustrations - Key)hasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Hematology Pathology - 005) Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) (Illustrations - Key)Document1 pageHematology Pathology - 005) Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) (Illustrations - Key)hasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Hematology Pathology - 006) Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) (Illustrations - Key)Document1 pageHematology Pathology - 006) Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) (Illustrations - Key)hasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Case Study - PathophysiologyDocument1 pageCase Study - Pathophysiologychristelleannebabon196No ratings yet
- Anemia Differential Diagnosis : Microcytic Normocytic MacrocyticDocument1 pageAnemia Differential Diagnosis : Microcytic Normocytic Macrocyticمحمد عقيلي100% (1)
- EMD1 Pc1 PATOFISIOLOGI SEPSISDocument5 pagesEMD1 Pc1 PATOFISIOLOGI SEPSISRasyid RidhaNo ratings yet
- Plasma ProteinsDocument24 pagesPlasma Proteinsarka paramanikNo ratings yet
- Over Weight / Obesity Stress Smoking Cocaine Use / Abuse Sedentary Lifestyle Diet in Fats, Na, CholesterolDocument4 pagesOver Weight / Obesity Stress Smoking Cocaine Use / Abuse Sedentary Lifestyle Diet in Fats, Na, Cholesterollouije_mombael2000No ratings yet
- Pa ToDocument2 pagesPa Tokz392No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology 08 10 24Document7 pagesPathophysiology 08 10 24Abbie NunezNo ratings yet
- Hytension For 16 Years Men (64 Years Old) Cigarette Smoking (32 Pack Years) Alcoholic Drinker For 32 Years Fond of Eating Fatty Foods Physical Inability Sodium Intake HereditaryDocument3 pagesHytension For 16 Years Men (64 Years Old) Cigarette Smoking (32 Pack Years) Alcoholic Drinker For 32 Years Fond of Eating Fatty Foods Physical Inability Sodium Intake HereditaryJohn Paulo CatacutanNo ratings yet
- Anemia DX TXDocument2 pagesAnemia DX TXProsanjit MajumderNo ratings yet
- Patofisiologi Tumor Mediastinum Faktor Hormonal: Ketidakefektifan Perfusi Jaringan PeriferDocument1 pagePatofisiologi Tumor Mediastinum Faktor Hormonal: Ketidakefektifan Perfusi Jaringan PeriferZuvita TahtaNo ratings yet
- Anemia Workup - Approach Considerations, Investigation For Pathogenesis, Evaluation For Blood LossDocument14 pagesAnemia Workup - Approach Considerations, Investigation For Pathogenesis, Evaluation For Blood LossRahul SahadevanNo ratings yet
- Sec2 G8Document2 pagesSec2 G8อัมพกา ทองแท้No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 pagesPathophysiology Diagram of Congestive Heart Failurea_samiane64% (11)
- Pharmacology Drug ChartDocument40 pagesPharmacology Drug Chart8zcjft96dgNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CHFDocument3 pagesPathophysiology CHFKit LaraNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 & 2 Pathophysiology DiagramDocument1 pageDiabetes Mellitus Type 1 & 2 Pathophysiology DiagramJaica TambisNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology - Drug ChartsDocument39 pagesPharmacology - Drug ChartsAsim Ishaq100% (5)
- HepatocellularDocument1 pageHepatocellularJoevet T. TadlasNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram of the Control of Circulatory SystemDocument1 pageBlock Diagram of the Control of Circulatory Systemwaelmansour25No ratings yet
- Disease PatternsDocument1 pageDisease PatternsSean KeenanNo ratings yet
- Anemias - XLSX - Sheet1Document2 pagesAnemias - XLSX - Sheet1scri66960No ratings yet
- Basic HematologyDocument69 pagesBasic HematologyDimas Bayu FirdausNo ratings yet
- HTN PathoDocument1 pageHTN PathoShelley Jade MenorNo ratings yet
- Multisystem ProblemsDocument90 pagesMultisystem ProblemsAlexander Blanche PajelaNo ratings yet
- Mitral Valve Stenosis: Peripheral OrgansDocument1 pageMitral Valve Stenosis: Peripheral OrgansPäw YusophNo ratings yet
- Conditions That Cause Interference On Most Hematology AnalyzersDocument2 pagesConditions That Cause Interference On Most Hematology AnalyzersSamantha IsabelNo ratings yet
- Pharmacodynamics of Inhalational AnestheticsDocument2 pagesPharmacodynamics of Inhalational Anestheticsmadeha goharNo ratings yet
- Anemia: Myelodysplastic SyndromeDocument1 pageAnemia: Myelodysplastic SyndromeFidesha Nurganiah SiregarNo ratings yet
- SOCA B3 CASE 3 - Iron Deficiency AnemiaDocument10 pagesSOCA B3 CASE 3 - Iron Deficiency AnemiaVaness ViendryNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Pathology - 008) Hyperaldosteronism (Illustrations - Key)Document1 pageEndocrinology Pathology - 008) Hyperaldosteronism (Illustrations - Key)hasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Classification of AnaemiaDocument1 pageClassification of Anaemianmyza89No ratings yet
- Pathway Gagal JantungDocument1 pagePathway Gagal Jantungmarlinapsik14No ratings yet
- X.0Y Control of Peripheral Circulation: OutlineDocument4 pagesX.0Y Control of Peripheral Circulation: OutlineAya ARNo ratings yet
- Blood and PlasmaDocument19 pagesBlood and Plasmaarka paramanikNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Pathology - 007) Cushing's Syndrome (Illustrations - Key)Document1 pageEndocrinology Pathology - 007) Cushing's Syndrome (Illustrations - Key)hasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Anemia PathoDocument1 pageAnemia PathoKathleen EvizaNo ratings yet
- 10heart Failure Pathophysiology and Forms (3094)Document32 pages10heart Failure Pathophysiology and Forms (3094)Fatima MaazNo ratings yet
- 6.22 Urinary SystemDocument9 pages6.22 Urinary SystemGhianx Carlox PioquintoxNo ratings yet
- Khaled Khalilia: Normocytic Microcytic Macrocytic HemolyticDocument12 pagesKhaled Khalilia: Normocytic Microcytic Macrocytic HemolyticrupNo ratings yet
- RBC DisordersDocument8 pagesRBC DisordersDavid JohnNo ratings yet
- HEMATOLOGIDocument1 pageHEMATOLOGICholis Nur AiniNo ratings yet
- 1 Cell Injury KSMADocument40 pages1 Cell Injury KSMASumeet UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Preeclampsia Eclampsia PathophyDocument2 pagesPreeclampsia Eclampsia PathophyLesther Alba Dela Cruz50% (2)
- Hematology Lab DiagnosisDocument2 pagesHematology Lab Diagnosisbaratniloy1No ratings yet
- Regulation of ErythropoiesisDocument3 pagesRegulation of ErythropoiesisFlowerNo ratings yet
- Case AnalisisDocument1 pageCase AnalisisHeather BrownNo ratings yet
- Anemia ApproachDocument1 pageAnemia ApproachLanaNo ratings yet
- Hematology Oncology - Anemia ApproachDocument1 pageHematology Oncology - Anemia ApproachEugen MNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure Regulation Hypertension AtfDocument4 pagesBlood Pressure Regulation Hypertension AtfMariaNo ratings yet
- Systolic and Diastolic DysfunctionDocument1 pageSystolic and Diastolic DysfunctionAhmad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Pathology - 007) Cushing's Syndrome (Notes)Document7 pagesEndocrinology Pathology - 007) Cushing's Syndrome (Notes)hasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Endocrine Physiology) 15. Adrenal Medulla - Catecholamines - KeyDocument1 pageEndocrine Physiology) 15. Adrenal Medulla - Catecholamines - Keyhasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Orthopedic DisordersDocument15 pagesOrthopedic Disordershasanatiya41100% (1)
- Reumato and EndocrineDocument106 pagesReumato and Endocrinehasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Endocrinology Pathology - 009) Pheochromocytoma (Illustrations - Key)Document1 pageEndocrinology Pathology - 009) Pheochromocytoma (Illustrations - Key)hasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Development & Growth Nutrition & Behavioral DisordersDocument27 pagesDevelopment & Growth Nutrition & Behavioral Disordershasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Hematology& Onco LectureDocument66 pagesHematology& Onco Lecturehasanatiya41No ratings yet
- 010 - Cardiovascular Physiology) Cardiovascular Cardiac CycleDocument3 pages010 - Cardiovascular Physiology) Cardiovascular Cardiac Cyclehasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Neurology LectureDocument48 pagesNeurology Lecturehasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Pharmacology Basics - 016) Drugs For Heart Failure (Notes - Q&A)Document3 pagesPharmacology Basics - 016) Drugs For Heart Failure (Notes - Q&A)hasanatiya41No ratings yet
- CardiologyDocument43 pagesCardiologyhasanatiya41No ratings yet
- 057 - Endocrinology Physiology) OvulationDocument4 pages057 - Endocrinology Physiology) Ovulationhasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Pharmacology) 09 Thiazide Diuretics - KeyDocument1 pageCardiovascular Pharmacology) 09 Thiazide Diuretics - Keyhasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Pharmacology Basics - 016) Drugs For Heart Failure (Notes)Document25 pagesPharmacology Basics - 016) Drugs For Heart Failure (Notes)hasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Pharmacology) 03 Heparin - KeyDocument1 pageCardiovascular Pharmacology) 03 Heparin - Keyhasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Pharmacology) 07 Calcium Channel Blockers - KeyDocument1 pageCardiovascular Pharmacology) 07 Calcium Channel Blockers - Keyhasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Hematology Pathology - 003) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) (Notes)Document11 pagesHematology Pathology - 003) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) (Notes)hasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Malabsorption Conditions Notes - Diagrams & Illustrations - OsmosisDocument7 pagesMalabsorption Conditions Notes - Diagrams & Illustrations - Osmosishasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Inflammatory Arthritis Notes - Diagrams & Illustrations - OsmosisDocument15 pagesInflammatory Arthritis Notes - Diagrams & Illustrations - Osmosishasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Hematologic Infections Notes - Diagrams & Illustrations - OsmosisDocument6 pagesHematologic Infections Notes - Diagrams & Illustrations - Osmosishasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Plasma Cell Dyscrasias Notes - Diagrams & Illustrations - OsmosisDocument6 pagesPlasma Cell Dyscrasias Notes - Diagrams & Illustrations - Osmosishasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Hematology Pathology - 006) Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) (Notes)Document8 pagesHematology Pathology - 006) Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) (Notes)hasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Vasculitis PPT NotesDocument14 pagesVasculitis PPT Noteshasanatiya41No ratings yet
- 342 - Hematology Physiology) Erythropoiesis Red Blood Cell FormationDocument6 pages342 - Hematology Physiology) Erythropoiesis Red Blood Cell Formationhasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Hematology Pathology - 005) Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) (Notes)Document8 pagesHematology Pathology - 005) Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) (Notes)hasanatiya41No ratings yet
- 347 - Hematology Physiology) Hemostasis Coagulation CascadeDocument6 pages347 - Hematology Physiology) Hemostasis Coagulation Cascadehasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Meeting1 Lec1Document73 pagesMeeting1 Lec1hasanatiya41No ratings yet
- Doosan Enerbility NPP Construction - Leaflet - EnglishDocument4 pagesDoosan Enerbility NPP Construction - Leaflet - EnglishTotoroNo ratings yet
- MainDocument32 pagesMainHoang Minh AnhNo ratings yet
- Kgaf 2020 Stall FormDocument7 pagesKgaf 2020 Stall FormAmit JainNo ratings yet
- Ghaus-ul-Azam, The Greatest Saint of All TimeDocument7 pagesGhaus-ul-Azam, The Greatest Saint of All TimeSyed Mujtaba QuaderNo ratings yet
- Walter Lewin LEC8Document29 pagesWalter Lewin LEC8Legalli AmcaNo ratings yet
- OSI Model Reference Chart PDFDocument1 pageOSI Model Reference Chart PDFKulbir SinghNo ratings yet
- DLL Environmentl IssueDocument5 pagesDLL Environmentl IssueRose Ann TuburanNo ratings yet
- Price List 13.10.21Document3 pagesPrice List 13.10.21prince kumarNo ratings yet
- Data Analytics FileDocument139 pagesData Analytics FileROHITH S 2227951No ratings yet
- It Service Mindset - For Website 0Document61 pagesIt Service Mindset - For Website 0Pagemaker DigitalNo ratings yet
- Asmamaw Module Edit 11 FontDocument155 pagesAsmamaw Module Edit 11 FontEdlamu AlemieNo ratings yet
- Concept Sa Et EmpowermentDocument3 pagesConcept Sa Et EmpowermentRoens ArdemilNo ratings yet
- Resourcing and Talent ManagementDocument76 pagesResourcing and Talent Managementdr.svr13No ratings yet
- Set de Copias 5th YearDocument36 pagesSet de Copias 5th Yearnanu grafica100% (2)
- The Wall Streetjournal 4 November 2023Document52 pagesThe Wall Streetjournal 4 November 2023Prashant SiwachNo ratings yet
- Identity TheftDocument2 pagesIdentity TheftRamil dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Ancient Egyptian Lamps & Lighting, Magic and The Hebrew Menorah (Author Mogg Morgan)Document13 pagesAncient Egyptian Lamps & Lighting, Magic and The Hebrew Menorah (Author Mogg Morgan)Dan SimpsonNo ratings yet
- Metadel BeleteDocument22 pagesMetadel BeleteKalicha DoyoNo ratings yet
- Early Trade ContactsDocument10 pagesEarly Trade ContactsLorraine Alunday Ngao-iNo ratings yet
- Books ListDocument3 pagesBooks ListSebin C SNo ratings yet
- Learning Module Design For Grade 7 - EclipsesDocument4 pagesLearning Module Design For Grade 7 - EclipsesAndrew Bondad50% (2)
- Goldilocks and The Three DinosaursDocument5 pagesGoldilocks and The Three DinosaursalexandrechausenNo ratings yet
- Okinawan Strength: Developing The "Iron Body" Stuart Mcgill PHDDocument4 pagesOkinawan Strength: Developing The "Iron Body" Stuart Mcgill PHDthieranitaNo ratings yet
- HR KPIsDocument151 pagesHR KPIstaapNo ratings yet
- ISO Certificate For Shri Sai Baba Temple'Thane, MaharashtraDocument5 pagesISO Certificate For Shri Sai Baba Temple'Thane, MaharashtrarOhit beHaLNo ratings yet
- Postal Code in The Dominican RepublicDocument21 pagesPostal Code in The Dominican RepublicTITAN GODNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Audio 1Document30 pagesReviewer in Audio 1renz daveNo ratings yet
- Florida Voter Suppression LawsuitDocument69 pagesFlorida Voter Suppression LawsuitDaniel Uhlfelder100% (1)
- Techniques and Principles in Language Teaching: The Grammar-Translation MethodDocument32 pagesTechniques and Principles in Language Teaching: The Grammar-Translation MethodChristina SanchezNo ratings yet
- Proctor Forms and Analysis: Department of Information TechnologyDocument7 pagesProctor Forms and Analysis: Department of Information TechnologyIT79 Yash SamantNo ratings yet