0% found this document useful (0 votes)
50 views7 pagesUnderstanding Senses and Body Response
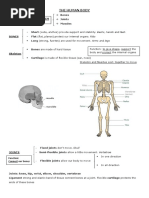
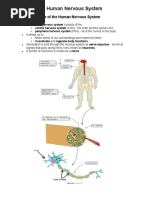
The document summarizes how the human senses of sight, hearing, smell, taste and touch work to receive information from the environment. It describes how sensory neurons transmit this information to the brain through the nervous system, which is divided into the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and peripheral nervous system. The brain processes the sensory information and sends motor neuron signals to the musculoskeletal system (skeleton, joints and muscles) to coordinate the body's responses.
Uploaded by
Patricia Perez AbrilCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
50 views7 pagesUnderstanding Senses and Body Response
The document summarizes how the human senses of sight, hearing, smell, taste and touch work to receive information from the environment. It describes how sensory neurons transmit this information to the brain through the nervous system, which is divided into the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and peripheral nervous system. The brain processes the sensory information and sends motor neuron signals to the musculoskeletal system (skeleton, joints and muscles) to coordinate the body's responses.
Uploaded by
Patricia Perez AbrilCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd