Year 11 Biology TIME: 2 Hours
Year 11 Biology TIME: 2 Hours
Uploaded by
AdrianHedleyCopyright:
Available Formats
Year 11 Biology TIME: 2 Hours
Year 11 Biology TIME: 2 Hours
Uploaded by
AdrianHedleyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Year 11 Biology TIME: 2 Hours
Year 11 Biology TIME: 2 Hours
Uploaded by
AdrianHedleyCopyright:
Available Formats
DEPARTMENT FOR CURRICULUM,
LIFELONG LEARNING AND EMPLOYABILITY
Directorate for Learning and Assessment Programmes Track 3
Educational Assessment Unit
Annual Examinations for Secondary Schools 2023
YEAR 11 BIOLOGY TIME: 2 hours
Name: _____________________________________ Class: _______________
Section A Section B
Question
No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 5
Max.
10 11 8 11 7 8 15 15 15 15 15
mark
TOTAL MARK
Actual
mark
85% Theory Paper 15% Practical Final Score
Section A: Answer all questions in this section.
1. Figure 1 shows a cross-section of a kidney.
Figure 1: Cross-section of a kidney
Source: Science Diagrams
a. Identify the section of the kidney that: (3)
contains loop of Henle and collecting ducts
collects urine as it is produced
opens into afferent arterioles
b. The kidney filters urea, a nitrogenous waste product.
i) Name where and describe when urea is produced. (2)
____________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________
ii) Name one other function of the kidney other than filtering urea out of the
blood. (1)
____________________________________________________________
c. Explain the role of Anti-Diuretic Hormone (ADH) on the kidneys on a hot day if
you do not drink. (4)
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
Total: 10 marks
Page 2 of 12 Biology – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2023
2. Figure 2 shows nine common invertebrates found in soil. The title in the bracket
gives the taxonomical group of the organism.
Figure 2: Common soil invertebrates
Source: Advanced Biology, C J Clegg with D G Mackean
a. Name one invertebrate from the figure that is not an arthropod. (1)
________________________________________________________________
b. i) The insect group has two larvae, that of the fly and the beetle. Describe
how larvae develop into adults. (3)
____________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________
ii) From the figure, give one distinguishing feature that identifies the
woodlouse from the mite. (1)
____________________________________________________________
c. In an investigation on the total numbers of invertebrates in soil, a group of
students used a soil sampler to obtain soil cores 5 cms wide down to a depth of
20 cms. The soil was taken from an abandoned field.
The results obtained were the following:
Depth/cm 2.5 5.0 7.5 10.0 12.5 15.0 17.5 20.0
Average no. of
animals per 5 85 160 44 49 20 12 7 9
cm core
i) On the following page, using the graph paper provided, plot a histogram of
the average no. of animals per 5 cm core (y-axis) against depth in cms (x-
axis). (4)
ii) Describe the general trend of this graph. (2)
____________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________
Total: 11 marks
Biology – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2023 Page 3 of 12
Page 4 of 12 Biology – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2023
3. Figure 3 shows the label of a bottle of orange juice.
a. Explain why:
i) drinking this drink will provide strong bones and teeth.
(3)
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
ii) it is best that obese people do not drink this drink. (2)
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
_________________________________________________
Figure 3
Source: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Images-of-
the-juice-bottles-with-different-sugar-labels-or-no-label_fig1_350768927
b. Benedict’s solution can be used to test the presence of reducing sugar in this
drink.
i) Give the initial colour of the Benedict’s solution. (1)
____________________________________________________________
ii) State the end result if a reducing sugar is present. (1)
____________________________________________________________
iii) Explain why identifying the result may be difficult when testing the above
orange juice. (1)
____________________________________________________________
Total: 8 marks
4a. Use your biological knowledge to explain the following:
The ozone hole above the Antarctic is slowly decreasing in size. (3)
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
Biology – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2023 Page 5 of 12
b. In 2019, Malta had the second highest nitrate levels in ground water in Europe,
over 50mg per litre.
i) Outline two causes that lead to the high nitrate levels in ground water. (2)
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
ii) Propose one way to reduce these nitrate levels. (1)
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
c. The following is a paragraph on a non-native species of crab in the
Mediterranean Sea.
“The Mediterranean is changing, and our only solution is to adapt" says Ben Souissi.
Climate change means it will likely be impossible to stop the continued spread of
destructive invaders (Blue crabs) across the Mediterranean. But in a region where
so much depends on healthy ecosystems, there is an urgent need to act.
Source: https://www.bbc.com/future/article/20220809-how-the-mediterranean-became-the-worlds-
most-invaded-sea
i) Define the term ecosystem. (2)
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
ii) Why is the increase in the Mediterranean Sea temperature bringing about a rapid
invasion of the crabs? (1)
________________________________________________________________
iii) Give two reasons why the countries around the Mediterranean need a ‘healthy
ecosystem’. (2)
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
Total: 11 marks
5. Figure 4 shows the rate of photosynthesis at different temperatures.
Figure 4: Graph of rate of photosynthesis against temperature
Source: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/
Page 6 of 12 Biology – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2023
a. What is the importance of carbon dioxide in photosynthesis? (1)
________________________________________________________________
b. i) Describe the trend from Point A to Point B. (1)
________________________________________________________________
ii) Explain why the rate of photosynthesis decreases from Point B to Point C.
(3)
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
c. A farmer growing tomatoes sets the temperature of the tomato greenhouse to
37˚C. Explain why the farmer chooses this temperature. (2)
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
Total: 7 marks
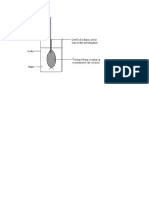
6. Figure 5 shows an apparatus used to demonstrate anaerobic respiration.
Figure 5: Apparatus for anaerobic respiration
Source: https://qsstudy.com/experiment-of-anaerobic-respiration/
a. Write an equation to show the substrate/s and products of anaerobic respiration
in yeast cells. (1)
________________________________________________________________
b. Explain why a layer of oil was put on top of the glucose and yeast suspension. (2)
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
c. Explain the presence of lime water in the test-tube. (1)
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
Biology – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2023 Page 7 of 12
d. Human muscle cells can also respire anaerobically. What causes muscle fatigue?
Use the terms anaerobic respiration and oxygen debt in your answer. (4)
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
Total: 8 marks
Section B: Attempt Question 1 and any two other questions.
1. Read the following article and answer the questions that follow.
Climate change is making plants more vulnerable to disease
When heat waves hit, they don't just take a toll on people - the plants we depend on
for food suffer too. That's because when temperatures get too high, certain plant
defences, such as the defence hormone salicylic acid, don't work as well leaving them
more susceptible to attacks from microbes and insect pests. Scientists say they have
identified a specific protein in plant cells that explains why immunity falters as the
mercury rises. They've also figured out a way to reverse the loss and bolster plant
defences against the heat.
The findings, were found in a spindly plant with white flowers called Arabidopsis
thaliana that is the ‘lab rat’ of plant research. Heat waves can have a dramatic effect
on hormone defences in Arabidopsis plants, leaving them more prone to infection by a
bacterium called Pseudomonas syringae.
Normally when this microbe attacks, the levels of salicylic acid in a plant's leaves
increase to keep bacteria from spreading. But when temperatures rise above 30˚ C
for just two days, plants can no longer make enough defence hormone to keep
infection from taking hold. Through experiments, the authors found that many genes
that were suppressed at elevated temperatures were regulated by the same gene.
This gene acts like a master switch that controls other genes, so anything that
downregulates or ‘turns off’ the gene means lots of other genes are turned off, too -
they don't make the proteins that enable a plant cell to build up salicylic acid.
Further experiments revealed that the cellular machinery needed to start reading out
the genetic instructions in the CBP60g gene doesn't assemble properly when it gets
too hot, and that's why the plant's immune system can't do its job anymore.
The team was able to show that mutant Arabidopsis plants that had their CBP60g
gene constantly ‘switched on’ were able to keep their defence hormone levels up and
bacteria at bay, even under heat stress. Next, the researchers found a way to
engineer heat-resilient plants that turned on the CBP60g master switch only when
under attack, and without stunting their growth - which is critical if the findings are
going to help protect plant defences without negatively impacting crop yields.
The findings could be good news for food supplies made insecure by climate change.
The team found that elevated temperatures didn't just impair salicylic acid defences in
Arabidopsis plants - it had a similar effect on crop plants such as tomato, rapeseed
and rice. The team stated: "We were able to make the whole plant immune system
more robust at warm temperatures. If this is true for crop plants as well, that's a
really big deal because then we have a very powerful weapon."
Adapted from https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2022/06/220629121138.htm
Page 8 of 12 Biology – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2023
a. From the text, identify the terms that signify the following: (1, 1, 1)
i) a nitrogenous organic compound composed of long chains of amino acids.
ii) a sequence of DNA considered as the basic unit of heredity.
iii) a regulatory molecule that is transported in an organism to stimulate
specific cells or tissues into action.
b. i) State one main characteristic of bacteria. (1)
ii) Explain why the scientific names of the spindly plant and the bacterium are
written in italics in the text. (2)
c. One of the EU responses to climate change is to limit global warming.
i) Describe how humans have contributed to global warming. (3)
ii) List two other biological impacts of climate change on organisms. (2)
d. Plant hormones provide responses to different plant stimuli. In phototropism the
hormone auxin regulates growth when light is a stimulus.
i) Describe the action of the hormone auxin when unilateral light falls on a
shoot of a plant. (3)
ii) State the direction of movement of the plant when there is unilateral light
on one side of the shoot. (1)
Total: 15 marks
2. Last July two turtles were released back into the Mediterranean Sea after being
treated for sustained injuries. One had fishing hooks and was tangled in a fishing
line while the other had ingested plastic.
a. Turtles are reptiles.
i) Name the phylum of the class reptiles. (1)
ii) State one characteristic of the class reptile. (1)
iii) List two classes of organisms of the same phylum of the reptiles that also
live in the Mediterranean Sea. (2)
b. The Loggerhead turtle is described as both endangered and vulnerable. Explain,
with reference to the first statement, the reasons why such turtles are listed as
endangered. (3)
Biology – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2023 Page 9 of 12
c. Different species of sea turtles feed on animals and plants. The main food
source of Leatherback turtles are jellyfish while that of green turtles are
seagrasses and seaweeds.
i) The teeth of each of the above species have adapted to the diet they eat.
Leatherbacks have pointed teeth while green turtles have teeth that are like
a saw. Explain the importance of such teeth in relation to the type of food
they eat. (4)
ii) Jellyfish are Cnidarians (Coelenterates). State one characteristic of cnidaria.
(1)
iii) One seagrass is the Posidonia oceanica. State the species name of this
seagrass. (1)
iv) Seagrasses are monocots. List two characteristics of monocots. (2)
Total: 15 marks
3. Red blood cell disorders include several types of anaemia including iron-
deficiency anaemia, inherited haemolytic anaemia and aplastic anaemia.
Inherited haemolytic anaemia occurs when red blood cells are broken down more
quickly than they are replaced. Aplastic anaemia occurs when the bone marrow
stops producing red blood cells.
a. Describe the structure of a red blood cell. (2)
b. Why is iron important for red blood cells? (1)
c. Predict one effect/symptom of a person suffering from anaemia. (1)
d. β-Thalassaemia is a type of inherited haemolytic anaemia, prevalent in Malta.
This is an autosomal recessive disease which results in warped haemoglobin.
Most types of β-Thalassaemia are the result of a form of mutation. Humans
having the heterozygous form of the gene are carriers.
i) Why will warped haemoglobin create problems to a human’s health? (2)
ii) Define the term mutation. (1)
iii) Use a genetic diagram to work out the probability of a child being
homozygous recessive to β-Thalassaemia when the parents are both
carriers of the disease. (4)
e. Phagocytes (white blood cells) and platelets are also produced by the bone
marrow.
i) Describe how phagocytes perform their role. (1)
ii) Describe the structure and function of platelets. (3)
Total: 15 marks
Page 10 of 12 Biology – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2023
4. In an investigation on the factors affecting germination, four test tubes at
different conditions were set up as in Figure 6 below.
Figure 6: Investigation on germination
The four test tubes were set with the following conditions:
A Seeds on dry cotton wool at 25˚C
B Seeds submerged in water with a layer of oil on top at 25˚C
C Seeds on moist cotton wool at 25˚C
D Seeds on moist cotton wool at 5˚C
a. i) Define the term germination. (1)
ii) Describe the importance of seeds in the reproductive cycle of plants. (1)
b. Germination occurs in test tube C.
i) Explain why germination occurs in this test tube. (2)
ii) Name the condition that is absent in test tube B. (1)
iii) State one other precaution that must be taken to ensure the lack of
condition of test tube B. (2)
iv) Give two constant variables of this investigation. (2)
c. The seeds used are sunflower seeds. These seeds undergo epigeal germination.
Describe epigeal germination. (2)
d. How does growth of:
i) the embryo take place during germination. (2)
ii) the seedling take place above the ground. (2)
Total: 15 marks
Biology – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2023 Page 11 of 12
5a. Name the process that describes the movement of the following substances into
or out of the cells.
i) glucose moves from the small intestine into the blood. (1)
ii) carbon dioxide passes from the blood into the lungs. (1)
b. Pieces of potato were weighed, placed in salt solutions of different concentrations
for one hour and reweighed. The graph below shows the percentage (%) change
in mass at each concentration.
Figure 7: % change in mass at each concentration
i) Name the substance, the movement of which is responsible for the change
in mass. (1)
ii) Explain why the potato strips are dried before reweighing. (2)
iii) Describe the general trend of the graph. (2)
iv) Give a term to describe the salt concentration in comparison to the
cytoplasm of the potato strips at Point Q. (1)
v) Describe the process responsible for the change in mass at Point R. (4)
c. In an investigation on transpiration, a fan blowing hot air was placed near the
leaves of the plant.
i) Define transpiration. (1)
ii) Describe the effect of the fan blowing hot air on the rate of transpiration. (2)
Total: 15 marks
Page 12 of 12 Biology – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2023
You might also like
- General Biology 1: Quarter 2 - Module 3: When Cells BreatheDocument26 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 2 - Module 3: When Cells BreathePLS help me get 1k subsNo ratings yet
- Section A Answer ALL Question. Write Your Answers in The Spaces Provided in This BookletDocument8 pagesSection A Answer ALL Question. Write Your Answers in The Spaces Provided in This BookletJoy BoehmerNo ratings yet
- Respiration I QuestionsDocument79 pagesRespiration I QuestionsAayma MunirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Cardio and ESD PDFDocument28 pagesChapter 9 - Cardio and ESD PDFDDVNo ratings yet
- Biology Full NotesDocument196 pagesBiology Full NotesNadi Makasaki100% (1)
- Biology (Form 4) - Test 1 (2019)Document12 pagesBiology (Form 4) - Test 1 (2019)Kordell leydNo ratings yet
- Biology Yr10 2024Document12 pagesBiology Yr10 2024ims.muslimacademyNo ratings yet
- Biology P1 PPQ FDocument52 pagesBiology P1 PPQ FJivon MathewNo ratings yet
- Biology Paper 1Document8 pagesBiology Paper 1paqurette3No ratings yet
- ECOLOGY Qus and Mark SchemeDocument62 pagesECOLOGY Qus and Mark Schemetobysmith26922692No ratings yet
- Annual Examinations For Secondary Schools 2016Document11 pagesAnnual Examinations For Secondary Schools 2016mark smithNo ratings yet
- KO2 Transport in Cell HomeworkDocument11 pagesKO2 Transport in Cell Homeworkfahmidaakhi3313No ratings yet
- 4.1 Photosynthesis QPDocument35 pages4.1 Photosynthesis QPZaynab Ameenah KhanNo ratings yet
- Biology 1Document11 pagesBiology 1namelessmsaniiNo ratings yet
- B Yr09 MQF Lev1to3 2023Document12 pagesB Yr09 MQF Lev1to3 2023AdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- Energy and Ecosystems Part 2Document16 pagesEnergy and Ecosystems Part 2dfq67gtkqs100% (1)
- WaterDocument16 pagesWaterdfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- A01 Short Answer QuestionsDocument21 pagesA01 Short Answer Questionsmsuria06No ratings yet
- Biology Mock Paper 02 - CorrectedDocument13 pagesBiology Mock Paper 02 - CorrectedNicketa AndersonNo ratings yet
- B 4 Revision PackDocument64 pagesB 4 Revision PackKrish SharmaNo ratings yet
- BiologyMock 2Document36 pagesBiologyMock 2backup14gNo ratings yet
- Set 5 Bioenergetics Grades 4 6Document17 pagesSet 5 Bioenergetics Grades 4 6Abir OmarNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Assessment Booklet: Marks 1'9 Time Allowed 165 MinutesDocument39 pagesTopic 5 Assessment Booklet: Marks 1'9 Time Allowed 165 MinutesHayley Camenzuli100% (1)
- Organisation Foundation HigherDocument135 pagesOrganisation Foundation HigherSơnSơnNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument12 pagesTransport in PlantsJames FothergillNo ratings yet
- Biology WorksheetDocument44 pagesBiology WorksheetArpita DagliaNo ratings yet
- Ais 2021-2022 Gr-7 Sci MockpaperDocument10 pagesAis 2021-2022 Gr-7 Sci MockpaperMitalNo ratings yet
- E2 Human Impact On The Environment Skill WS 2014, 2015, 2016Document18 pagesE2 Human Impact On The Environment Skill WS 2014, 2015, 2016Ching Man TamNo ratings yet
- B F3 Annual 2023Document18 pagesB F3 Annual 2023AdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- Science Exam QuestionsDocument10 pagesScience Exam QuestionscheetoNo ratings yet
- AnisationDocument28 pagesAnisationStefaniya Dmitrievna “Stef” DeminetsNo ratings yet
- DiseaseDocument5 pagesDiseaseBob yuNo ratings yet
- 3.4.7 Investigating Diversity Pack 2Document81 pages3.4.7 Investigating Diversity Pack 2kyrielyonx100% (1)
- A01 Short Answer QuestionsDocument19 pagesA01 Short Answer Questionsmsuria06No ratings yet
- Section A Answer ALL Question. Write Your Answers in The Spaces Provided in This BookletDocument8 pagesSection A Answer ALL Question. Write Your Answers in The Spaces Provided in This BookletJoy BoehmerNo ratings yet
- Biology Short TestDocument2 pagesBiology Short TestAvantika KumarNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Homework - 231005 - 204804Document36 pagesWeek 4 Homework - 231005 - 204804dongolsaleenNo ratings yet
- National Grade 9 Assessment 2019 Science P2Document14 pagesNational Grade 9 Assessment 2019 Science P2NesiaNo ratings yet
- Plants Homework WorksheetDocument5 pagesPlants Homework WorksheetJiselle ShahNo ratings yet
- Set 1 Bioenergetics Grades 7 9Document22 pagesSet 1 Bioenergetics Grades 7 9Rabia RafiqueNo ratings yet
- SDA End of Year 2023 (AutoRecovered)Document7 pagesSDA End of Year 2023 (AutoRecovered)Nothando PhologotswanaNo ratings yet
- A01 Short Answer QuestionsDocument29 pagesA01 Short Answer Questionsmsuria06No ratings yet
- Set 3 Cell Biology Grades 7 9Document17 pagesSet 3 Cell Biology Grades 7 9Abir OmarNo ratings yet
- St. Joseph's Anglo-Chinese School 2 Term Exam (Sample Paper) F.1 Integrated Science (Paper 1)Document7 pagesSt. Joseph's Anglo-Chinese School 2 Term Exam (Sample Paper) F.1 Integrated Science (Paper 1)LEO NGNo ratings yet
- Troy High School Integrated Science Exam 11-3-4Document6 pagesTroy High School Integrated Science Exam 11-3-4Science,Physical Education And Sports VideosNo ratings yet
- A03 Data AnalysisDocument19 pagesA03 Data Analysisleocarlton0700No ratings yet
- Autumn 1 Biology Y12 TestDocument10 pagesAutumn 1 Biology Y12 TestJivon MathewNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure WorksheetDocument21 pagesCell Structure Worksheethayyannadeem96No ratings yet
- 4.1b Cell Biology Foundation HigherDocument70 pages4.1b Cell Biology Foundation Higherpzulu6774No ratings yet
- Exams 2022 Paper 3 SCDXPKDocument39 pagesExams 2022 Paper 3 SCDXPKQueen Bee (Tt)No ratings yet
- 3.4 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Mass Transport in Animals 2 - QuestionsDocument57 pages3.4 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Mass Transport in Animals 2 - QuestionsMaymunah HussainNo ratings yet
- Bio Unit 4Document38 pagesBio Unit 4Mei NgNo ratings yet
- Extra Cells A and MSDocument29 pagesExtra Cells A and MSKhushi ShahNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Transport Across Cell Membranes 1 E28093 Questions 1Document36 pages2.3 Transport Across Cell Membranes 1 E28093 Questions 1craisha25No ratings yet
- Set 2 Bioenergetics Grades 7 9Document20 pagesSet 2 Bioenergetics Grades 7 9tnishtalaNo ratings yet
- INSTRUCTIONDocument8 pagesINSTRUCTIONkelvinkaykatoyaNo ratings yet
- F4 Bio PT1Document8 pagesF4 Bio PT1msgreenhwangNo ratings yet
- A Level Biology Topic 1 AssessmentDocument15 pagesA Level Biology Topic 1 AssessmentgsapkaiteNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport QPDocument16 pagesCell Transport QPWilliam AcworthNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument103 pagesPhotosynthesisdfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- P5 CT T3 (Science) 2022-2023Document10 pagesP5 CT T3 (Science) 2022-2023Alva SevenNo ratings yet
- Membranes L4 MSDocument19 pagesMembranes L4 MSzaynabaziz52No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Decoded: Master Orgo with Step-by-Step SolutionsFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry Decoded: Master Orgo with Step-by-Step SolutionsNo ratings yet
- CM2024Document2 pagesCM2024AdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Biology TIME: 2 Hours: Annual Examinations For Secondary Schools 2023Document12 pagesYear 10 Biology TIME: 2 Hours: Annual Examinations For Secondary Schools 2023AdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Biology TIME: 2 Hours: Annual Examinations For Secondary Schools 2022Document14 pagesYear 10 Biology TIME: 2 Hours: Annual Examinations For Secondary Schools 2022AdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- B F3 Annual 2023Document18 pagesB F3 Annual 2023AdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen PeroxideDocument32 pagesHydrogen Peroxideskundra100% (1)
- Life Science PPT 1Document41 pagesLife Science PPT 1api-179562730No ratings yet
- 2804 Central Concepts January 2006 Mark SchemeDocument0 pages2804 Central Concepts January 2006 Mark SchemeWK SoohgNo ratings yet
- Topic-2.2-Workbook EssDocument14 pagesTopic-2.2-Workbook EssKonstantinos TsorbatzoglouNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/22Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/22hbasyouny2011No ratings yet
- Lab 6 Damariz CeballosDocument4 pagesLab 6 Damariz CeballosdamarizNo ratings yet
- Microbiology of Meat and PoultryDocument337 pagesMicrobiology of Meat and PoultryFrancylla Milhomens Nogueira92% (12)
- NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 10Document6 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 10SANJEEV KUMARNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis Ch.14Document51 pagesGlycolysis Ch.14Yousef KhallafNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Biology Sample PaperDocument15 pagesClass 11 Biology Sample Papermerebalaji2414No ratings yet
- Ch-6 Plant NutritionDocument32 pagesCh-6 Plant NutritionHaziq KhanNo ratings yet
- Pinya As EthanolDocument28 pagesPinya As EthanolJuliana Elaine MayoNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis HomeworkDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesis Homeworkafmroaceo100% (1)
- Apologia Biology Class Module 6 NotesDocument4 pagesApologia Biology Class Module 6 Noteschickfilamom100% (2)
- Instant Ebooks Textbook (Ebook PDF) Microbiology: An Evolving Science (Fifth Edition) 5th Edition by Joan L. Slonczewski Download All ChaptersDocument51 pagesInstant Ebooks Textbook (Ebook PDF) Microbiology: An Evolving Science (Fifth Edition) 5th Edition by Joan L. Slonczewski Download All Chapterspitefolvik100% (2)
- Critical Power: An Important Fatigue Threshold in Exercise PhysiologyDocument17 pagesCritical Power: An Important Fatigue Threshold in Exercise PhysiologyRonald GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School, Aligarh Biology Notes Chapter: Life Processes Teacher: Tanu Yadav DATE: 24.04.20 Day: FridayDocument29 pagesDelhi Public School, Aligarh Biology Notes Chapter: Life Processes Teacher: Tanu Yadav DATE: 24.04.20 Day: Fridayamrapali singhalNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Biology Term 3 Marks SchemeDocument8 pagesYear 8 Biology Term 3 Marks Schemebfsfhd fdngNo ratings yet
- Aerobic and Anaerobic - RespirationDocument2 pagesAerobic and Anaerobic - RespirationDOMINIO YTNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Cellular RespirationDocument16 pagesLecture Notes On Cellular RespirationBhillee Agas ValdezNo ratings yet
- Final Biochemistry: All The Questions Are in The Form of MC QsDocument4 pagesFinal Biochemistry: All The Questions Are in The Form of MC QsDijattxNo ratings yet
- 23-24 - Bio - Quiz 1Document5 pages23-24 - Bio - Quiz 1PranavNo ratings yet
- BIOL 2P98 D2 2017FW Lab 4Document18 pagesBIOL 2P98 D2 2017FW Lab 4TumuhimbiseMosesNo ratings yet
- Biology - Module 5Document11 pagesBiology - Module 5ASHLEY MONICA PLATANo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Life Sciences Revision Material Term 2 - 2023Document24 pagesGrade 11 Life Sciences Revision Material Term 2 - 2023Junior NgwenyaNo ratings yet
- A2 Student Unit Guide - Edexcel Biology Unit 5Document95 pagesA2 Student Unit Guide - Edexcel Biology Unit 5claimstudent3515100% (12)
- Biochemistry FinalDocument60 pagesBiochemistry FinalAndrassy Twinkle Alinea100% (2)