Phy 3
Phy 3
Uploaded by
Chris BigorniaCopyright:
Available Formats
Phy 3
Phy 3
Uploaded by
Chris BigorniaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Phy 3
Phy 3
Uploaded by
Chris BigorniaCopyright:
Available Formats
What I Know
DIRECTIONS: Read each question carefully. Choose the letter of the best answer.
Write your answer on a separate sheet of paper.
1. Which BEST explains why the Earth is not disk-shaped?
A. Stars are viewed differently when traveling north and south.
B. The shadow cast by Earth during a lunar eclipse is circular.
C. The shadow cast in two different cities during a solstice differed in length.
D. The only shape that cast a circular shadow in whatever direction is a
sphere.
2. Which of the following is an annual motion?
A. Moonrise C. Sunset
B. Eastward rise of stars D. Vernal equinox
3. What astronomical event was NOT known to men before the advent of
telescopes?
A. Solar eclipse C. Retrograde of Mars
B. Summer solstice D. Rotation of the Sun
4. Which aided Eratosthenes in measuring the Earth’s circumference?
A. The appearance of stars differs when travelling from north to south.
B. The shadow cast within the Syene and Alexandria during the solstice.
C. A sphere is the only shape that cast a circular shadow in whatever
direction.
D. The shadow cast by the Earth during a lunar eclipse is circular.
For nos. 5-6, choices are
A. Autumnal equinox C. Summer solstice
B. Eastward rise of stars D. Zodiac cycle
5. What is a diurnal motion?
6. Which does NOT involve the Sun’s ecliptic path?
For nos. 7-10, choices are:
A. All planets revolve around the sun in an elliptical orbit.
B. Any point in the closed curved is equidistant to the two foci.
C. Planets move fastest in the elliptical orbit when nearest to the sun.
D. The length of a planet’s revolution in the Sun is proportional to its orbit’s
size.
7. Which describes the law of ellipse?
8. Which describes the law of harmony?
9. Which describes the law of equal areas?
10. Which explains the difference in the orbital period of Earth and Saturn?
For nos. 11-15, choices are:
A. Copernican C. Ptolemaic
B. Keplerian D. Tychonic
11. Which presents a system with elliptical orbit?
12. Which presents a heliocentric model of the universe?
13. Which presents a geo-heliocentric model of the solar system?
14. Which attributes retrograde motion of the planets to epicycles?
15. Which states that a planet moves fastest when it is nearest to the sun?
1. Law of Harmony: the square of a planet’s orbital period (years) is proportional
to the cube of the semimajor axis of its orbit (in astronomical units or AU) or
𝑃2 = 𝑎3. Thus, the larger the orbit’s size, the longer it takes to orbit the sun.
What’s More
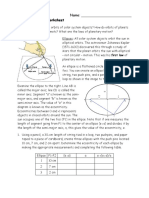
Activity 1.1 Draw it
Draw a model of the solar system based on the Kepler’s Law of Planetary Motions.
Write labels and figures to illustrate the three laws.
Activity 1.2 How far and how many years?
Using the formula given for the Law of Harmony, find the number of years a planet
takes to orbit the Sun and its distance from the Sun (semi-major axis).
Ex. Pluto’s a3 = 64,000. Its distance from the Sun (a) is equal to 40 AU. Likewise,
Pluto’s 𝑃2 64,000. Its orbital period (P) is equal to 252.98 years.
Planet Square of Cube of the Orbital period Distance from
planet’s semi-major (a)in years the sun (P) in
orbital years axis of the AU
(𝑃2) planet’s orbit
(a3) in
astronomical
units (AU)
Mercury 0.058 0.058 (1) (2)
Venus 0.378 0.378 (3) (4)
Earth 1.00 1.00 (5) (6)
Mars 3.54 3.54 (7) (8)
Jupiter 141 141 (9) (10)
Saturn 868 868 (11) (12)
What I Have Learned
Identification
Identify the astronomical events being described in each item. Write your
answer on a separate sheet of paper.
1. It is the daily motion of stars and other celestial bodies across the sky due to
Earth’s rotation.
2. It is a model which deems Earth as the center of the universe.
3. An event in which the sun passes the celestial equator.
4. Occurs when the moon passes between the Earth and sun with the moon
casting a shadow on the Earth’s surface.
5. A model which deems all planets revolve around the sun.
6. Set of thirteen constellations seen along the Sun’s ecliptic path.
7. The astronomical event in which the sun passes the highest or lowest point
from the celestial equator.
8. It is the wobbling of the Earth’s celestial north pole.
9. The apparent yearly motion of stars and other celestial bodies across the sky
due to Earth’s revolution.
10. It occurs when the Earth is directly aligned between the sun and moon with
the Earth casting a shadow on the moon.
What I Can Do
You have learned about the ancient Greek astronomy and the development
of the model of the solar system. Answer the questions in two to three sentences.
1. Using a ball and a Frisbee, how would you explain to a flat-earther friend that
the Earth is round?
2. Why was Tycho Brahe’s work essential in the development of Kepler’s law of
planetary motion?
You might also like
- Rocket Propulsion (Ramamurthi) (2nd Ed.)Document408 pagesRocket Propulsion (Ramamurthi) (2nd Ed.)R9obymn80% (10)
- Satellite Orbital MechanicsDocument29 pagesSatellite Orbital MechanicsmojammeljoyNo ratings yet
- 4 Kepler LabDocument4 pages4 Kepler LabJovie MedsNo ratings yet
- Homework 1 MADocument38 pagesHomework 1 MACarla TolbertNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Week 1 LAS DUE On APRIL 12 2024Document3 pagesPhysical Science Week 1 LAS DUE On APRIL 12 2024Ya NaNo ratings yet
- Physci q2 m1 240114143718 ffc758f0Document85 pagesPhysci q2 m1 240114143718 ffc758f0flordelisaliza18No ratings yet
- 4TH Quarter ModuleDocument6 pages4TH Quarter ModuleJenedil PauloNo ratings yet
- Physical-Science-Quarter 2 Module 1Document15 pagesPhysical-Science-Quarter 2 Module 1Roumarie Ybañez100% (1)
- Cosmic PerspectiveDocument5 pagesCosmic PerspectiveChuah Chong YangNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Social Science Geography Chapter 1 The Earth in The Solar SystemDocument9 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 6 Social Science Geography Chapter 1 The Earth in The Solar SystemRakesh JhunjhunwallaNo ratings yet
- 1 Ncert Ge1Document9 pages1 Ncert Ge1KV MADHUPURNo ratings yet
- Part 2 Questions OnlyDocument42 pagesPart 2 Questions Onlyarmando licanda BSE Math 2ANo ratings yet
- Midterm SolutionsDocument12 pagesMidterm Solutionsozworld3100% (1)
- 1 Eso GeographyDocument3 pages1 Eso GeographyEva Barreiro RománNo ratings yet
- Solar System 2Document2 pagesSolar System 2Koü-ben KhaNo ratings yet
- 6th CBSE Geo Chap 1Document10 pages6th CBSE Geo Chap 1manojboaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science ReviewerDocument23 pagesPhysical Science Revieweradrianhaber321No ratings yet
- 05 EE8086-Paper - 0708S2Document11 pages05 EE8086-Paper - 0708S2Jude WongNo ratings yet
- Astronomy Unit Exam Review Sheet 2017 AnswersDocument7 pagesAstronomy Unit Exam Review Sheet 2017 AnswersKimNo ratings yet
- Term 1 Test Revision Answer KeyDocument7 pagesTerm 1 Test Revision Answer Keymptchxw6rkNo ratings yet
- Selected MCQs On Our Solar SystemDocument12 pagesSelected MCQs On Our Solar SystemexamboonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17Document7 pagesChapter 17keshribhamini1984No ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions For Class 6 Social Science Geography Chapter 1Document3 pagesNcert Solutions For Class 6 Social Science Geography Chapter 1Nitesh Kumar SoniNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Q4Week7Day 4-Period of Revolution of The Inner and Outer PlanetsDocument30 pagesScience 6 Q4Week7Day 4-Period of Revolution of The Inner and Outer PlanetsROCHELLE MATIRANo ratings yet
- SC 5 e 5 3 Solar SystemDocument27 pagesSC 5 e 5 3 Solar Systemapi-263271261No ratings yet
- Q4 Module 1 Physical ScienceDocument10 pagesQ4 Module 1 Physical ScienceMelancholy0% (1)
- Module 1Document7 pagesModule 1Emmarie LlantinoNo ratings yet
- Concept Guide: Science Periodic 2Document7 pagesConcept Guide: Science Periodic 2api-270387817No ratings yet
- Physcie 202405130927 14971Document25 pagesPhyscie 202405130927 14971Faith CalacienNo ratings yet
- Geography Questions: Solar SystemDocument153 pagesGeography Questions: Solar SystemladkibadianjanihaiNo ratings yet
- Class 6 Geography Chapter 1 The Earth in The Solar SystemDocument4 pagesClass 6 Geography Chapter 1 The Earth in The Solar SystemAnas FaisalNo ratings yet
- CLASS VIII QUESTION BANK - 17 Stars and Solar SystemDocument7 pagesCLASS VIII QUESTION BANK - 17 Stars and Solar SystemSurbhi NayarNo ratings yet
- Multiple ChoiceDocument6 pagesMultiple ChoiceShikhar AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Study Guide of Key Ideas For Unit 3 KeyDocument5 pagesStudy Guide of Key Ideas For Unit 3 Keyapi-236114955No ratings yet
- Sitti Rahayu (A1P119093)Document5 pagesSitti Rahayu (A1P119093)Zariana YanaNo ratings yet
- 8th Science July Notes L-18 The Universe 2024-25Document7 pages8th Science July Notes L-18 The Universe 2024-25vijaya103laxmiNo ratings yet
- Physical Science, Q4 - Mod 1 - "Ancient and Modern Astronomy" (Grade 11) What I Need To KnowDocument11 pagesPhysical Science, Q4 - Mod 1 - "Ancient and Modern Astronomy" (Grade 11) What I Need To KnowManuelito Balacuit Pacatang Morre100% (2)
- PHYSICS NOTES For BSC StudentsDocument27 pagesPHYSICS NOTES For BSC Studentskcameppadi123100% (1)
- Practice Questions For Astronomy I - EXAM 1Document8 pagesPractice Questions For Astronomy I - EXAM 1John Paul Sarmiento LatojaNo ratings yet
- Physical-Science q2 Week-1 EditedDocument19 pagesPhysical-Science q2 Week-1 EditedMallari FamNo ratings yet
- Planetary Orbits Worksheet: NameDocument6 pagesPlanetary Orbits Worksheet: NametabilinNo ratings yet
- Class 6 GeographyDocument53 pagesClass 6 GeographyMahendra PandaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Solar System Lesson 1 2Document10 pagesIntroduction To The Solar System Lesson 1 2sangwooeurtNo ratings yet
- Week-1 Q2 Physical-ScienceDocument19 pagesWeek-1 Q2 Physical-Scienceshay.dedoroyNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Astronomy Today 8 e 8th Edition Eric Chaisson Steve McmillanDocument21 pagesTest Bank For Astronomy Today 8 e 8th Edition Eric Chaisson Steve McmillanPaul Fuselier100% (43)
- Class 6 Geog Chap 1 Ques-Ans .Document2 pagesClass 6 Geog Chap 1 Ques-Ans .asNo ratings yet
- AAE 532 - Orbit Mechanics Problem Set 1 Due: 9/2/22Document4 pagesAAE 532 - Orbit Mechanics Problem Set 1 Due: 9/2/22Ali AlmakhmariNo ratings yet
- AST101 Fall2015 Midterm Solutions v5Document6 pagesAST101 Fall2015 Midterm Solutions v5Trash RowzanNo ratings yet
- Social Studies Form 3Document126 pagesSocial Studies Form 3agyapong892No ratings yet
- Quiz AnswersDocument12 pagesQuiz AnswersChuah Chong YangNo ratings yet
- Constellations Stars SummaryDocument67 pagesConstellations Stars SummaryJayru RemillosaNo ratings yet
- chapter 6Document29 pageschapter 6siusinchan26No ratings yet
- Examination 1Document5 pagesExamination 1John Olsen ViloriaNo ratings yet
- 8.5 Cosmic EngineDocument21 pages8.5 Cosmic EngineKevin HuynhNo ratings yet
- 8th Science Lesson 17Document6 pages8th Science Lesson 17sharmaaarti4758No ratings yet
- Worksheet - 7 Class-8Document7 pagesWorksheet - 7 Class-8k l pandeyNo ratings yet
- S116-Maia Toribio - 2023 Solar System Unit Study GuideDocument5 pagesS116-Maia Toribio - 2023 Solar System Unit Study GuideS116-Maia ToribioNo ratings yet
- Class 04Document93 pagesClass 04a00798340No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 19 May 2024Document22 pagesAdobe Scan 19 May 2024aung aungNo ratings yet
- We Live in the Helical Solar System: Our Home in a Helical UniverseFrom EverandWe Live in the Helical Solar System: Our Home in a Helical UniverseNo ratings yet
- Comets and Meteors: Their phenomena in all ages; their mutual relations; and the theory of their originFrom EverandComets and Meteors: Their phenomena in all ages; their mutual relations; and the theory of their originNo ratings yet
- (Notes) The UniverseDocument3 pages(Notes) The UniverseDenver Cho-oyNo ratings yet
- GRAVITATIONDocument30 pagesGRAVITATIONRajendra RathNo ratings yet
- Gmat User GuideDocument77 pagesGmat User GuideAdmin EvanNo ratings yet
- 4 PhyDocument42 pages4 PhyRacoNo ratings yet
- Keplers Law of Planetary MotionDocument3 pagesKeplers Law of Planetary MotionFreddie AbulenciaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science: Quarter 2 - Week 1Document24 pagesPhysical Science: Quarter 2 - Week 1U-one Frago100% (3)
- The Key To Everything - Freeman Dyson PDFDocument9 pagesThe Key To Everything - Freeman Dyson PDFAlexandra TaranuNo ratings yet
- M10 Newtons Law of Universal Gravitation Keplers Laws of Planetary Motion and Simple Harmonic MotionDocument19 pagesM10 Newtons Law of Universal Gravitation Keplers Laws of Planetary Motion and Simple Harmonic MotionLawrence AguilosNo ratings yet
- MathDocument9 pagesMathpingpong playerNo ratings yet
- Fun Dementals of Orbital MotionDocument19 pagesFun Dementals of Orbital MotionEngin TunalıNo ratings yet
- Copernican Theory PDFDocument5 pagesCopernican Theory PDFAdnel Luis Robert GilhangNo ratings yet
- 10 Scientific Laws and Theories You Really Should KnowDocument6 pages10 Scientific Laws and Theories You Really Should KnowShanmukha priyaNo ratings yet
- Geostationary OrbitsDocument6 pagesGeostationary Orbitsandrej rehakNo ratings yet
- Astronomy Research PaperDocument6 pagesAstronomy Research Paperapi-308411782No ratings yet
- Physics Recall Part 1 - LawsDocument3 pagesPhysics Recall Part 1 - LawsXavier100% (1)
- Unesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: A History of Astronomy, Astrophysics and CosmologyDocument21 pagesUnesco - Eolss Sample Chapters: A History of Astronomy, Astrophysics and CosmologycYbernaTIc enHancENo ratings yet
- Satellite Motion NotesDocument23 pagesSatellite Motion NotesVarshLok100% (1)
- History of ScienceDocument103 pagesHistory of Scienceapi-25885481100% (1)
- Phys Int CC CH 6 - Universal Graviation - Answers PDFDocument5 pagesPhys Int CC CH 6 - Universal Graviation - Answers PDFGIDZANIA PLAYSNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 GRAVITATION KSSM Form 4Document32 pagesCHAPTER 3 GRAVITATION KSSM Form 4Azman Selamat100% (1)
- Move PlanDocument2 pagesMove PlanKenjie JaboneroNo ratings yet
- Math Chin CalDocument39 pagesMath Chin CalMonica Beatriz AmatoNo ratings yet
- LP On Kepler's LawDocument11 pagesLP On Kepler's LawJenny May SudayNo ratings yet
- Planets and Electromagnetic Waves First Edition G. Udhaya Sankar & C. Ganesa MoorthyDocument49 pagesPlanets and Electromagnetic Waves First Edition G. Udhaya Sankar & C. Ganesa MoorthybiaramisatoNo ratings yet
- H3 Physics Summary Notes (GCE A-Level Syllabus 9814) (2019 Edition)Document9 pagesH3 Physics Summary Notes (GCE A-Level Syllabus 9814) (2019 Edition)avinash boodhooNo ratings yet
- Physics Dictionary KSSMDocument10 pagesPhysics Dictionary KSSMsueqingNo ratings yet
- Pom9pse SE Section4 5Document10 pagesPom9pse SE Section4 5bugbbtestNo ratings yet