Energy
Energy
Uploaded by
anabelled12009Copyright:
Available Formats
Energy
Energy
Uploaded by
anabelled12009Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
Energy
Energy
Uploaded by
anabelled12009Copyright:
Available Formats
Energy
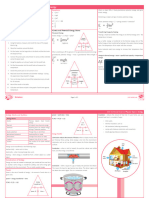
Energy Store Description Changes in stores example
Keyword Definition
Proportion of supplied energy which is Magnetic Energy due to the force of 4
Efficiency transferred usefully (carries out intended attraction (or repulsion)
task) between 2 magnets
3 5
Elastic Energy stored in a stretched
Energy can be transferred usefully, spring or stretched elastic band
Energy
transfer
stored or dissipated but cannot be 2
created or destroyed Nuclear Energy contained within the 6
nucleus of an atom
1
A material with a low thermal Gravitational Energy an object has due to its
Insulator
conductivity potential position from the ground
Power c
Rate at which energy is transferred in Electrostatic Energy due to the force of
attraction (or repulsion) In this case the system is the catapult, the angry bird projectile
unit time
between 2 charged objects and the target blocks. The energy stored in the stretched catapult
is the maximum amount of energy available.
A resource which can be replenished as it Thermal Energy a substance has due to
Renewable
is being used its temperature 1 = Elastic potential energy is stored in the stretched catapult
Chemical Energy found in fuels, foods or 2 = The elastic store (Ee) decreases and is transferred to the
System A group of objects which interact batteries. kinetic store (Ek) in the bird
3 = As the height increases the gravitational potential energy
Thermal A measure of how fast heat can transfer Kinetic Energy an object has because it store (Ep) increases and the kinetic store(Ek) is decreasing
conductivity through a material is moving 4 = At the top of the trajectory the Ep is at a maximum and the Ek
is at a minimum
5 = As the projectile falls the Ep store will decrease and the Ek will
A measure of energy when a force moves Kinetic energy
Work done an object through a distance The kinetic energy (Ek) of an object (also known as
increase again Gravitational potential energy
6 = The bird is back to the original height, so the Ep has reduced The gravitational potential energy (Ep) of an object (also known
its kinetic store) is defined as: to zero and the Ek is back at a maximum as its gravitational store) is defined as:
For calculations we assume perfect energy transfers, however no
The energy an object has due its mass and speed energy transfer is perfect in reality and some energy will be
Energy system The energy an object has due to its height in a gravitational
• Energy will often be described as part of an energy system transferred to the surroundings (dissipated) as thermal energy field
This means that any object in motion has kinetic into the thermal energy store. When producing a physics model
• In physics, a system is defined as: energy
This means:
An object or group of objects for a game such as angry birds only perfect energy transfers will If an object is lifted up it will gain Ep
• When describing the changes within a system, only the be considered. If it falls, it will lose Ep
objects or group of objects and the surroundings need to
be considered
• A system, for example, can be closed or open Thermal conductivity Ep =m x g x h
• An open system allows the exchange of The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability
energy and matter to or from its surroundings Power to conduct heat. The direction of heat transfer is hot to cold
• A closed system can exchange energy but not Power is the rate at which energy is transferred. The higher the thermal conductivity of a material, the higher
matter to or from its surroundings In other words, power is the rate of doing work. the rate of energy transfer by conduction across the material
Energy Energy The unit of power is the watt, W Materials with high thermal conductivity heat up faster than
A power rating of one watt means one joule of materials with low thermal conductivity.
energy is transferred per second, If a house was built of materials with a high thermal conductivity,
or 1 joule of work is done in 1 second. they would be very cold to live in as thermal energy would be
Matter Energy dissipation
1 watt = 1 joule per second 1W = 1 J/s able to leave the house easily.
Dissipation is a term that is often used to describe ways in which
energy is wasted. Any energy that is not transferred to useful
Energy Resources Renewable Transport Electricity Heating Reliable Produces CO2 Environmental impact energy stores is said to be wasted because it is lost to the
generation surroundings
Fossil fuels ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ Greenhouse effect, pollutant gases A mechanical brake applies a friction force to convert the kinetic
Nuclear fuel ✔ ✔ Waste storage, accidents have long lasting effect energy of the vehicle into thermal energy which then dissipates
into the atmosphere.
Biofuel ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ Farmland could be used for food
Wind ✔ ✔ ✔ Noisy. Some think wind farms are ugly
Hydro-electricity ✔ ✔ ✔ Dams flood farmland, loss of habitat Useful YouTube links:
Geothermal ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔ Large ugly buildings, loss of habitat
Tidal ✔ ✔ Can affect life in estuaries, change/affect habitat
Solar ✔ ✔ ✔ Mining of rare metals for solar cells
Wave ✔ ✔ Can affect sea life Energy resources Energy stores Power
You might also like
- 05 MultizoneBuilding PDFDocument230 pages05 MultizoneBuilding PDFGiuseppeNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Pearson Edexcel Physics Unit 4Document11 pagesIGCSE Pearson Edexcel Physics Unit 4Kaung Khant ZawNo ratings yet
- Physics Revision BookletDocument15 pagesPhysics Revision BookletMadalina BotanNo ratings yet
- KS4 Energy Stores Worksheet AnswersDocument1 pageKS4 Energy Stores Worksheet AnswersRamy MohamedNo ratings yet
- Conservation and Dissipation of EnergyDocument2 pagesConservation and Dissipation of EnergyceryssandfordNo ratings yet
- P1 Conservation and Dissipation of EnergyDocument2 pagesP1 Conservation and Dissipation of EnergyArun DonteNo ratings yet
- 1er Devoir Du 2ème Semestre Anglais 2nde 2018-2019 Ceg OuenouDocument3 pages1er Devoir Du 2ème Semestre Anglais 2nde 2018-2019 Ceg OuenouLiza mezariNo ratings yet
- SLA 2 Science 9 Physics 4th QuarterDocument15 pagesSLA 2 Science 9 Physics 4th QuarterNymphaNarvasaDecasaNo ratings yet
- Definitions PhysicsDocument13 pagesDefinitions Physicslidiafnz12No ratings yet
- Aqa Gcse Knowledge Mat Physics p1Document5 pagesAqa Gcse Knowledge Mat Physics p1Clement SundayNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument11 pagesEnergySagar KumarNo ratings yet
- Further Maths - Work, Energy and PowerDocument1 pageFurther Maths - Work, Energy and PowerLola SmithNo ratings yet
- WEP Concept MapDocument1 pageWEP Concept MapsmollilnubNo ratings yet
- Words In Arabic Energy هقاطDocument5 pagesWords In Arabic Energy هقاطapi-498050482No ratings yet
- Notes Chapter 06Document40 pagesNotes Chapter 06Biruk BtNo ratings yet
- Work Power and Energy HandoutDocument3 pagesWork Power and Energy HandoutMica RoscoNo ratings yet
- P2 - Energy Booklet 2022 AnswersDocument20 pagesP2 - Energy Booklet 2022 AnswersTran Anh Quan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Aqa 8464 Collins SampleDocument32 pagesAqa 8464 Collins SampleSrijita RoyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Energy TransformationDocument1 pageLesson 3 - Energy Transformationvictorianomarielle03No ratings yet
- 5 Work Energy PowerDocument11 pages5 Work Energy Powermuhammad abdullah javedNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2-P2.01 Energy Stores, Transfers and ConservationDocument21 pagesChapter-2-P2.01 Energy Stores, Transfers and ConservationMicheal XavierNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Mechanics PDFDocument81 pagesUnit-I Mechanics PDFGundanNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics I CH - 4 - Energy - Transport - by Heat - Work - MassDocument8 pagesThermodynamics I CH - 4 - Energy - Transport - by Heat - Work - MassmathewosNo ratings yet
- Nature of SurroundingsDocument7 pagesNature of SurroundingsJe VisualsNo ratings yet
- Physics A LevelDocument38 pagesPhysics A LevelThoon Nadi NaiNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy & Power..Document39 pagesWork, Energy & Power..Abdul rafay ImranNo ratings yet
- Module 4-Hand OutDocument3 pagesModule 4-Hand Outnoelmarasigan027No ratings yet
- Energies 7th GradeDocument8 pagesEnergies 7th GradeMaria AlejandraNo ratings yet
- Personalised Learning Checklists AQA Physics - Yr 9 2023 Summer ExamDocument2 pagesPersonalised Learning Checklists AQA Physics - Yr 9 2023 Summer ExamVaidile JonikasNo ratings yet
- Re 4.3 (Mio)Document6 pagesRe 4.3 (Mio)Angel PerezNo ratings yet
- P1 - Revision BookletDocument22 pagesP1 - Revision Bookletwarem022.302No ratings yet
- Advanced Mechanism Design (Ue19Me544) : Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Conservation of EnergyDocument1 pageAdvanced Mechanism Design (Ue19Me544) : Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Conservation of EnergySyed Hafeez Peeran QuadriNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS HandoutDocument2 pagesPHYSICS Handoutjeazelmarzo242No ratings yet
- Kinetics - Edexcel A Level ChemistryDocument4 pagesKinetics - Edexcel A Level ChemistryMaddie BaughNo ratings yet
- Physical Dimensions and PropagationDocument9 pagesPhysical Dimensions and Propagationgodsblessings8000No ratings yet
- CHAPTER I - Concept of Work Energy and PowerDocument2 pagesCHAPTER I - Concept of Work Energy and PowerEllaisa Molina Grabanzor0% (1)
- Cascayo, Debelyn S. Beed 3-A (Learning Task 5)Document1 pageCascayo, Debelyn S. Beed 3-A (Learning Task 5)Debelyn CascayoNo ratings yet
- Work and Energy - Mind MapDocument1 pageWork and Energy - Mind Mapyashsn23119No ratings yet
- Transversalidad de Ingles - 20240326 - 122202 - 0000Document2 pagesTransversalidad de Ingles - 20240326 - 122202 - 0000dannaisabellacastroramirezNo ratings yet
- Work Power Energy: Mathematical Expression Forms of EnergyDocument1 pageWork Power Energy: Mathematical Expression Forms of EnergyRavi BNo ratings yet
- Ans-Conservation of EnegyDocument7 pagesAns-Conservation of EnegyBlack arab GaladimaNo ratings yet
- Changing Energy FormsDocument10 pagesChanging Energy FormsZendo KansaNo ratings yet
- Physics Revision Booklet (Higher) PDFDocument30 pagesPhysics Revision Booklet (Higher) PDFChandrasekaran SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- WORK, ENERGY, POWER HandoutDocument1 pageWORK, ENERGY, POWER HandoutrhonNo ratings yet
- Energy Transfers ScienceDocument14 pagesEnergy Transfers Sciencecarrot nuttyNo ratings yet
- Energy GZ 2019Document56 pagesEnergy GZ 2019geetub1No ratings yet
- Edexcel Knowledge Mat Topic 8 Energy Forces Doing Work V1 2Document4 pagesEdexcel Knowledge Mat Topic 8 Energy Forces Doing Work V1 2NetkoNo ratings yet
- Energy, Energy Transfer & General Energy Analysis Energy, Energy Transfer & General Energy AnalysisDocument351 pagesEnergy, Energy Transfer & General Energy Analysis Energy, Energy Transfer & General Energy Analysisrobelassefa708No ratings yet
- Chap 2 ADocument26 pagesChap 2 AamareyeabtsegaNo ratings yet
- AQA Physics Topic 1 Energy Knowledge OrganiserDocument3 pagesAQA Physics Topic 1 Energy Knowledge OrganiserNaveen ChebroluNo ratings yet
- 12A.4 Energy NSDocument2 pages12A.4 Energy NSnishka.sheikNo ratings yet
- EnergyDocument14 pagesEnergyosama100% (1)
- Thermo Chapter - 2 - Lecture PDFDocument30 pagesThermo Chapter - 2 - Lecture PDFFattihiEkhmalNo ratings yet
- Energy TransferDocument7 pagesEnergy Transferlflanagan73No ratings yet
- Aqa 8464 SP 2016.1 PDFDocument22 pagesAqa 8464 SP 2016.1 PDFMatthew KonefalNo ratings yet
- GENERAL CHEMISTRY II 2nd Grading Cycle 1Document23 pagesGENERAL CHEMISTRY II 2nd Grading Cycle 1SEM06-G32-Velasco, Geryne D.No ratings yet
- Experiment 4Document6 pagesExperiment 4Tin-tinNo ratings yet
- Chem2,4-Reaction KineticsDocument3 pagesChem2,4-Reaction KineticsMoeez100% (1)
- Mathematical Solution Unifying the Four Fundamental Forces in NatureFrom EverandMathematical Solution Unifying the Four Fundamental Forces in NatureNo ratings yet
- Simplified Lateral Design of Post-Frame BuildingsDocument77 pagesSimplified Lateral Design of Post-Frame BuildingsRagavanNo ratings yet
- Richard C. Dorf, Robert H. Bishop - Modern Control Systems, 13th Ed.-Pearson (2017) - 397-448Document52 pagesRichard C. Dorf, Robert H. Bishop - Modern Control Systems, 13th Ed.-Pearson (2017) - 397-448Alen Ademar Saavedra VargasNo ratings yet
- Section 9-1 The Constant e and Continuous Compound InterestDocument15 pagesSection 9-1 The Constant e and Continuous Compound InterestArun GhatanNo ratings yet
- Seikoh Giken Seikoh Giken SFP 550CDocument2 pagesSeikoh Giken Seikoh Giken SFP 550Csleh_sbiNo ratings yet
- Boiling ReportDocument5 pagesBoiling ReportVAIBHAV MISHRANo ratings yet
- Grade 6 DLP Q3 W6D2Document13 pagesGrade 6 DLP Q3 W6D2cristineann.arandiaNo ratings yet
- Previews 1554.6 2012 - PreDocument7 pagesPreviews 1554.6 2012 - PreRevan0% (1)
- Manning Coefficient PDFDocument2 pagesManning Coefficient PDFကိုနေဝင်း100% (1)
- 0 8NDocument89 pages0 8NsieNo ratings yet
- Higher Tier: Edexcel GCSEDocument28 pagesHigher Tier: Edexcel GCSEaset999No ratings yet
- Aer - 200kWDocument2 pagesAer - 200kWsergometNo ratings yet
- MATH PETA 4thDocument56 pagesMATH PETA 4thdurpy minshNo ratings yet
- Sap SOLID 2Document13 pagesSap SOLID 2nobodicNo ratings yet
- CL 9 - Phy - Solution WS 5 - 23 24Document5 pagesCL 9 - Phy - Solution WS 5 - 23 24ashishgambhir1986No ratings yet
- ControlExperiments - Precision Modular ServoDocument43 pagesControlExperiments - Precision Modular ServoNachoSainzNo ratings yet
- Succinic Acid Production PlantDocument102 pagesSuccinic Acid Production PlantHafiidz MalekNo ratings yet
- Xxxenglish ConferencesxxxOptimal Capacitor Placement For Loss ReductionDocument5 pagesXxxenglish ConferencesxxxOptimal Capacitor Placement For Loss Reductionapi-26622648No ratings yet
- Lecture Slides On Electrostatic ConductorsDocument61 pagesLecture Slides On Electrostatic ConductorsRitick srivastavaNo ratings yet
- Upqc Block DiagramDocument3 pagesUpqc Block DiagramjpsridharNo ratings yet
- Module Sabah Add Math f5Document296 pagesModule Sabah Add Math f5LIM YAN JOE MoeNo ratings yet
- Spiral CT DR - ShravaniDocument82 pagesSpiral CT DR - ShravaniVajja Swati100% (2)
- Zone 6 Incorporations Genesis of The Individual SimondonDocument21 pagesZone 6 Incorporations Genesis of The Individual SimondonunKnowNNo ratings yet
- SmartCal ShortOperatingInstructionsDocument24 pagesSmartCal ShortOperatingInstructionssaulmamaniNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Introduction To CPM / PERT Techniques: CPM (Critical Path Method)Document32 pages2.1 Introduction To CPM / PERT Techniques: CPM (Critical Path Method)anish.t.pNo ratings yet
- Laboratory TestingDocument423 pagesLaboratory TestingAristidNo ratings yet
- Energy System EngineeringDocument116 pagesEnergy System EngineeringAila DarNo ratings yet
- Cofferdams: "A Cofferdam Is A TemporaryDocument21 pagesCofferdams: "A Cofferdam Is A TemporaryMohamed Amine ZemouriNo ratings yet
- Booklist Iia 5625334acdf5fDocument36 pagesBooklist Iia 5625334acdf5fFeyi AsgillNo ratings yet
- VentSilencerBrochure ImperialDocument9 pagesVentSilencerBrochure ImperialKvvPrasadNo ratings yet