WS Free Fall
Uploaded by
nasrinqblWS Free Fall
Uploaded by
nasrinqbl4
Answer all the questions in the spaces provided.
1 (a) Use the definition of power to show that the SI base units of power are kg m2 s–3.
[2]
(b) Use an expression for electrical power to determine the SI base units of potential difference.
units ...........................................................[2]
© UCLES 2015 9702/21/M/J/15
5
2 (a) Define speed and velocity and use these definitions to explain why one of these quantities is
a scalar and the other is a vector.
speed: ......................................................................................................................................
velocity: .....................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................................................
[2]
(b) A ball is released from rest and falls vertically. The ball hits the ground and rebounds vertically,
as shown in Fig. 2.1.
initial position
ball
rebound
ground
Fig. 2.1
© UCLES 2015 9702/21/M/J/15 [Turn over
6
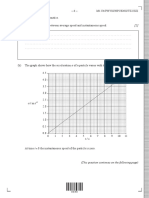
The variation with time t of the velocity v of the ball is shown in Fig. 2.2.
12.0
10.0
8.0
v / m s–1
6.0
4.0
2.0
0
0 1.0 2.0 3.0
t/s
– 2.0
– 4.0
– 6.0
– 8.0
– 10.0
Fig. 2.2
Air resistance is negligible.
(i) Without calculation, use Fig. 2.2 to describe the variation with time t of the velocity of the
ball from t = 0 to t = 2.1 s.
...........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................................
.......................................................................................................................................[3]
(ii) Calculate the acceleration of the ball after it rebounds from the ground. Show your
working.
acceleration = ................................................. m s–2 [3]
© UCLES 2015 9702/21/M/J/15
7
(iii) Calculate, for the ball, from t = 0 to t = 2.1 s,
1. the distance moved,
distance = ...................................................... m [3]
2. the displacement from the initial position.
displacement = ...................................................... m [2]
(iv) On Fig. 2.3, sketch the variation with t of the speed of the ball.
12.0
10.0
8.0
speed / m s–1
6.0
4.0
2.0
0
0 1.0 2.0 3.0
t/s
– 2.0
– 4.0
– 6.0
– 8.0
– 10.0
Fig. 2.3
[2]
© UCLES 2015 9702/21/M/J/15 [Turn over
6
4 A student takes measurements to determine a value for the acceleration of free fall. Some of For
the apparatus used is illustrated in Fig. 4.1. Examiner’s
Use
electromagnet
iron
ball
d
bench
Fig. 4.1
The student measures the vertical distance d between the base of the electromagnet and
the bench. The time t for an iron ball to fall from the electromagnet to the bench is also
measured.
Corresponding values of t 2 and d are shown in Fig. 4.2.
60
50
d /cm
40
30
20
10
0
0 0.02 0.04 0.06 0.08 0.10 0.12 0.14
t 2 / s2
Fig. 4.2
© UCLES 2010 9702/23/O/N/10
7
(a) On Fig. 4.2, draw the line of best fit for the points. [1] For
Examiner’s
(b) State and explain why there is a non-zero intercept on the graph of Fig. 4.2. Use
..........................................................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................... [2]
(c) Determine the student’s value for
(i) the diameter of the ball,
diameter = ........................................ cm [1]
(ii) the acceleration of free fall.
acceleration = ..................................... m s–2 [3]
© UCLES 2010 9702/23/O/N/10 [Turn over
You might also like
- Mazda Protege 2002 Service Manual in English100% (64)Mazda Protege 2002 Service Manual in English20 pages
- 9702 Physics - Definitions and Statements v1.0100% (1)9702 Physics - Definitions and Statements v1.037 pages
- Topic: Kinematics Name: - Date: - Class: - SectionNo ratings yetTopic: Kinematics Name: - Date: - Class: - Section3 pages
- For Examiner's Use: 9702/21/M/J/10 © UCLES 2010No ratings yetFor Examiner's Use: 9702/21/M/J/10 © UCLES 201034 pages
- AS & A Level Physics 9702 - 23 Paper 2 AS Level Structured Questions May - Jun 2022No ratings yetAS & A Level Physics 9702 - 23 Paper 2 AS Level Structured Questions May - Jun 202213 pages
- PHYSICS MEASUREMENT FORCE MOMENT MOMENTUM - DiscussionNo ratings yetPHYSICS MEASUREMENT FORCE MOMENT MOMENTUM - Discussion19 pages
- 09 Physics Year 10 Term 1 Exam Revision Paper 42 FM 0625 - m22 - QP - 42No ratings yet09 Physics Year 10 Term 1 Exam Revision Paper 42 FM 0625 - m22 - QP - 424 pages
- 4 All The Questions in The Spaces Provided.: 9702/21/M/J/14 © UCLES 2014No ratings yet4 All The Questions in The Spaces Provided.: 9702/21/M/J/14 © UCLES 201434 pages
- 3 Mass Weight and Density - 241004 - 194530No ratings yet3 Mass Weight and Density - 241004 - 1945308 pages
- 2 1 Fig. 1.1 Shows The Speed-Time Graph For The Motion of A CarNo ratings yet2 1 Fig. 1.1 Shows The Speed-Time Graph For The Motion of A Car5 pages
- 12.7 Motion Cie Igcse Physics Ext Theory QpNo ratings yet12.7 Motion Cie Igcse Physics Ext Theory Qp10 pages
- Projectile Motion Data Analysis QuestionNo ratings yetProjectile Motion Data Analysis Question3 pages
- Materials Science and Technology of Optical FabricationFrom EverandMaterials Science and Technology of Optical FabricationNo ratings yet
- 8th STD Physical Science Bridge Course PortionNo ratings yet8th STD Physical Science Bridge Course Portion3 pages
- Defining BIM For Project Execution: Sylvia Kendra, GISPNo ratings yetDefining BIM For Project Execution: Sylvia Kendra, GISP40 pages
- Legal Metrology: Rocío M. Marbán Julio A. Pellecer CNo ratings yetLegal Metrology: Rocío M. Marbán Julio A. Pellecer C146 pages
- 01 The Study of Chemistry and MeasurementsNo ratings yet01 The Study of Chemistry and Measurements6 pages
- Newnes - Electrical and Electronic Principles and Technology, 2nd Ed - 2003 - (By Laxxuss)100% (3)Newnes - Electrical and Electronic Principles and Technology, 2nd Ed - 2003 - (By Laxxuss)366 pages
- ANSI ISA 75.19.01hydrostatic Testing of Control Valves (2003)No ratings yetANSI ISA 75.19.01hydrostatic Testing of Control Valves (2003)34 pages
- LP No. 11 (Review and Units of Measurement)No ratings yetLP No. 11 (Review and Units of Measurement)30 pages
- Measuring Electronics and Sensors: Basics of Measurement Technology, Sensors, Analog and Digital Signal Processing Bernstein - The ebook is available for instant download, read anywhere100% (1)Measuring Electronics and Sensors: Basics of Measurement Technology, Sensors, Analog and Digital Signal Processing Bernstein - The ebook is available for instant download, read anywhere73 pages
- Jhango Physics Book3 Corrected - Copy-1No ratings yetJhango Physics Book3 Corrected - Copy-1308 pages
- Shri Gulabrao Deokar Polytechnic: Shri Krishna Educational and Cultural Mandal'sNo ratings yetShri Gulabrao Deokar Polytechnic: Shri Krishna Educational and Cultural Mandal's21 pages
- Immediate download Electrical and Electronic Principles and Technology 2nd Edition John Bird ebooks 2024100% (1)Immediate download Electrical and Electronic Principles and Technology 2nd Edition John Bird ebooks 202477 pages
- CE2215 Fluid Mech & Hydraulics 01 Introduction HONo ratings yetCE2215 Fluid Mech & Hydraulics 01 Introduction HO14 pages
- Beam No - of Length Breadth Height Quantity MRK Beams (M) (M) (M) (M)No ratings yetBeam No - of Length Breadth Height Quantity MRK Beams (M) (M) (M) (M)2 pages
- ISO - TC - 213 - N - 658 - Vocabulario Del VIMNo ratings yetISO - TC - 213 - N - 658 - Vocabulario Del VIM71 pages
- Topic: Kinematics Name: - Date: - Class: - SectionTopic: Kinematics Name: - Date: - Class: - Section
- AS & A Level Physics 9702 - 23 Paper 2 AS Level Structured Questions May - Jun 2022AS & A Level Physics 9702 - 23 Paper 2 AS Level Structured Questions May - Jun 2022
- PHYSICS MEASUREMENT FORCE MOMENT MOMENTUM - DiscussionPHYSICS MEASUREMENT FORCE MOMENT MOMENTUM - Discussion
- 09 Physics Year 10 Term 1 Exam Revision Paper 42 FM 0625 - m22 - QP - 4209 Physics Year 10 Term 1 Exam Revision Paper 42 FM 0625 - m22 - QP - 42
- 4 All The Questions in The Spaces Provided.: 9702/21/M/J/14 © UCLES 20144 All The Questions in The Spaces Provided.: 9702/21/M/J/14 © UCLES 2014
- 2 1 Fig. 1.1 Shows The Speed-Time Graph For The Motion of A Car2 1 Fig. 1.1 Shows The Speed-Time Graph For The Motion of A Car
- Materials Science and Technology of Optical FabricationFrom EverandMaterials Science and Technology of Optical Fabrication
- Defining BIM For Project Execution: Sylvia Kendra, GISPDefining BIM For Project Execution: Sylvia Kendra, GISP
- Legal Metrology: Rocío M. Marbán Julio A. Pellecer CLegal Metrology: Rocío M. Marbán Julio A. Pellecer C
- Newnes - Electrical and Electronic Principles and Technology, 2nd Ed - 2003 - (By Laxxuss)Newnes - Electrical and Electronic Principles and Technology, 2nd Ed - 2003 - (By Laxxuss)
- ANSI ISA 75.19.01hydrostatic Testing of Control Valves (2003)ANSI ISA 75.19.01hydrostatic Testing of Control Valves (2003)
- Measuring Electronics and Sensors: Basics of Measurement Technology, Sensors, Analog and Digital Signal Processing Bernstein - The ebook is available for instant download, read anywhereMeasuring Electronics and Sensors: Basics of Measurement Technology, Sensors, Analog and Digital Signal Processing Bernstein - The ebook is available for instant download, read anywhere
- Shri Gulabrao Deokar Polytechnic: Shri Krishna Educational and Cultural Mandal'sShri Gulabrao Deokar Polytechnic: Shri Krishna Educational and Cultural Mandal's
- Immediate download Electrical and Electronic Principles and Technology 2nd Edition John Bird ebooks 2024Immediate download Electrical and Electronic Principles and Technology 2nd Edition John Bird ebooks 2024
- Beam No - of Length Breadth Height Quantity MRK Beams (M) (M) (M) (M)Beam No - of Length Breadth Height Quantity MRK Beams (M) (M) (M) (M)